Year 12 weak points
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is the differences and similarities between starch, glycogen and cellulose.
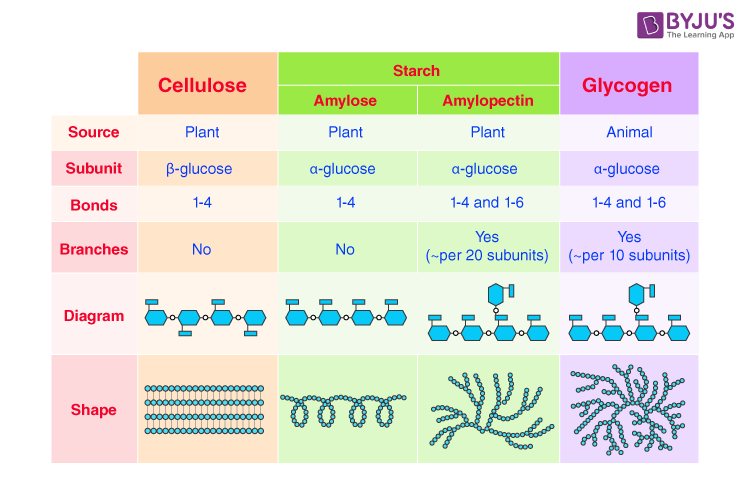
What is a key difference between starch and glycogen?
Starch is found in plants and glycogen is found in animals and glycogen is more highly branched so can be hydrolysed faster and release energy more quickly.
What is the role of hydrogen ions?
Hydrogen ions are used to control the pH in the body as the concentration of hydrogen ions determines the pH. This means that the concentration of hydrogen ions is used to provide optimal conditions for processes such as enzymes.
What are polymers?
A polymer is a large molecule made of many monomers joined by chemical bonds.
What is a monomer?
A monomer is a small molecule that can join with other monomers to form a polymer.
Difference between alpha glucose and beta glucose.
In α-glucose, the OH on carbon 1 is below the plane of the ring; in β-glucose, it is above the plane of the ring
Describe the structure of amylopectin?
Amylopectin is formed from α-glucose, joined by 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds, and is branched
What is the difference between amylose and cellulose?
Amylose is α-glucose, unbranched, forms starch for energy storage.
Cellulose is β-glucose, forms straight chains with hydrogen bonds, provides structural support in cell walls.
Why is heating required for the Benedict’s test?
Heating allows reducing sugars to react with Benedict’s reagent, producing a colour change.
Describe the test for non-reducing sugars?
Firstly carry out a Benedict’s test and if the result is negative then…
Add hydrochloric acid and heat in a water bath for five minutes.
Then neutralize with sodium hydrocarbonate and add benedict’s reagent and heat in a water bath for five minutes.
Blue to brick red shows a positive result.
Describe the process of protein transcription
Firstly RNA polymerase separates the complementary DNA strands breaking hydrogen bonds.
Then complementary RNA nucleotides free floating in the nucleus bind to the bases on the template strand of DNA with uracil replacing thymine.
Then RNA polymerase catalyses the formation of phosphodiester bonds between adjacent nucleotides.
Then the single strand of RNA separates and exits the nucleus through nuclear pores.
How is transcription in prokaryotes different?
There is no cytoplasm so it occurs in the nucleus
There is no splicing
Translation and transcription occur simultaneously
What is the role of ATP in translation?
ATP is used to:
Attach amino acids to tRNA (amino acid activation)
Define a mutation?
A change in the base sequence of DNA.
What is the difference between the genome and the proteome?
The genome is the complete set of genetic material of an organism.
Whereas the proteome is the complete set of proteins expressed by that organism at a given time.
What is a gene?
A gene is a sequence of DNA bases that codes for a polypetide or functional RNA.
Why do cellulose form microfibrils?
Because cellulose is made from beta glucose 1,4 so it forms linear unbranched chains and many hyrdogen bonds form between these leading to cellulose being packed together in microfibrils.
What is immunology?
First, albumin from one species is injected into others, which produces complementary antibodies.
These molecules are then added to test tubes, along with albumin from the other two species.
The albumin and these molecules bind to form a precipitate.
The amount produced indicates how closely related species are.
What do helper T cells do after activation?
Stimulate phagocytosis
Stimulate clonal selection of B cells
Activate cytotoxic T cells through releasing cytokines to kill pathogens by releasing the protein perforin leading to holes in the cell surface membrane
Some convert to memory cells providing long term immunity
What is clonal selection?
Where once B and T cells are activated they undergo rapid mitosis and differentiate to take part in an immune response.
How does a cell presenting antigens on its cell surface membrane lead to an immune response?
Firstly helper T cells bind to the antigens on the antigen presenting cell as they are complementary
Then these helper T cells stimulates B cells to divide through mitosis and differentiate into memory cells and plasma cells
Plasma cells release antibodies complementary to the pathogen’s antigens
Also they differentiate into memory B cells which provide long term immunity.
What molecules have antigens allowing the immune response to recognise them?
Pathogens
Cells from other organisms of the same species
Abnormal body cells
Toxins
Define antibody structure
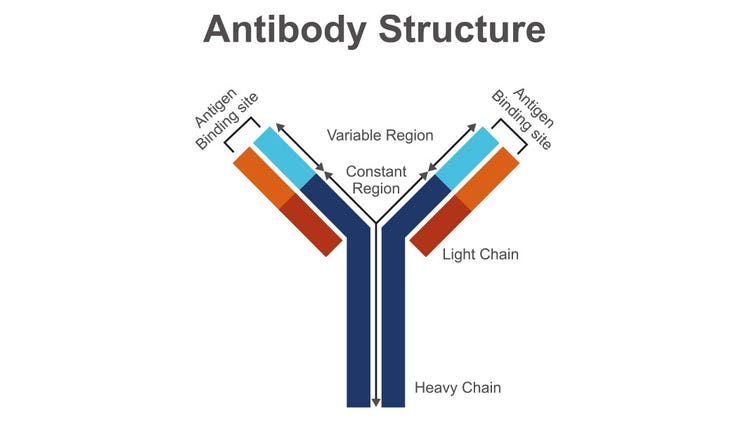
What bonds are between the light and heavy chain of an antibody?
Disulphide bridges