Chapter 1 - Introduction to Software Engineering
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
What is software?
Computer programs and associated documentation. Software products may be developed for a particular customer or may be developed for a general market.
What are the attributes of good software?
Good software should deliver the required functionality and performance to the user and should be maintainable, dependable and usable
What is software engineering?
Software engineering is an engineering discipline that is concerned with all aspects of software production from the early stages of system specification through to maintaining the system after it has gone into use.
What are the fundamental software engineering activities?
Software specification, software development, software validation and software evolution
What is the difference between software engineering and computer science?
Computer science focuses on theory and fundamentals; software engineering is concerned with the practicalities of developing and delivering useful software
What is the difference between software engineering and system engineering?
System engineering is concerned with all aspects of computer-based systems development including hardware, software and process engineering. Software engineering is part of this more general process.
What are the key challenges facing software engineering?
Coping with increasing diversity, demands for reduced delivery times and developing trustworthy software
What are the costs of software engineering?
Roughly 60% of software costs are development costs, 40% are testing costs. For custom software, evolution costs often exceed development costs.
What are the best software engineering techniques and methods?
While all software projects have to be professionally managed and developed, different techniques are appropriate for different types of system. You can't, therefore, say that one method is better than another
What differences has the web made to software engineering?
The web has led to the availability of software services and the possibility of developing highly distributed service-based systems. Web-based systems development has led to important advances in programming languages and software reuse.
Software Products
Tangible output (software) of a software development process
Product Specification
Detailed documents outlining the features, functions, and requirements of a software product. Serves as a blueprint for the development process.
Generic Products
Stand-alone systems that are marketed and sold to any customer who wishes to buy them.
Ex: PC software like graphics programs, project management tools, CAD software, software for specific markets
Generic Product Specification
what the software should do is owned by the software developer and decisions on software change are made by the developer.
Customized Products
Software that is commissioned by a specific customer to meet their own needs.
Ex: embedded control systems, air traffic control software, traffic monitoring systems
Customized Product Specification
what the software should do is owned by the customer for the software and they make decisions on software changes that are required.
Software Engineering Diversity
Many different types of software systems, no universal set of software techniques that are applicable to all of those.
SWE methods and tools depend on type of application being developed, the requirements of the customer, and the background of the development team
Stand-alone Applications
Run on a local computer, such as a PC and do not need to be connected to a network.
Interactive transaction-based applications
Execute on a remote computer and are accessed by users from their own PCs or terminals
Embedded control systems
Control systems that control and manage hardware devices.
Batch Processing Systems
Business systems that are designed to process data in large batches
Entertainment Systems
Systems primarily for personal use and intended to entertain the user.
Systems for Modelling and Simulation
Systems developed by scientists and engineers to model physical processes or situations, which include many, separate, interacting objects
Data Collection Systems
collects data from their environment using sensors and send that data to other systems for processing.
Systems of systems
System composed of several other software systems.
Attributes of Good Software
Maintainability, Dependability and Security, Efficiency, and Acceptability
Maintainability
Software should be written in such a way so that it can evolve to meet the changing needs of customers. This is a critical attribute because software change is an inevitable requirement of a changing business environment.
Dependability and security
includes a range of characteristics including reliability, security and safety. Dependable software should not cause physical or economic damage in the event of system failure. Malicious users should not be able to access or damage the system.
Efficiency
Software should not make wasteful use of system resources such as memory and processor cycles. Efficiency therefore includes responsiveness, processing time, memory utilization, etc.
Acceptability
Software must be acceptable to the type of users for which it is designed. This means that it must be understandable, usable and compatible with other systems that they use
Fundamental Principles
Should be applied to all types of software systems, irrespective of the development techniques used:
1) Develop the system using a managed and understood development process
2) Dependability and performance are important for all types of system
3) Understanding and managing the software specification and requirements are important
4) Reuse software that has already been developed when appropriate instead of writing new code.
Engineering discipline
A mindset for Software Engineering that prioritizes using appropriate theories and methods to solve problems bearing in mind organizational and financial constraints
"All aspects of software production"
Not just technical process of development. Also project management and the development of tools, methods etc. to support software production.
IEEE's Definition of SWE
The application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of software. The application of engineering to software
Bureau of Labor Statistics's Definition of SWE
The systematic application of scientific and technological knowledge, methods, and experience to the design, implementation, testing, and documentation of software
Fritz Bauer's Definition of SWE
The establishment and use of sound engineering principles in order to economically obtain software that is reliable and works efficiently on real machines
Software Specification
Where customers and engineers define the software that is to be produced and the constraints on its operation.
Software Development
Where the software is designed and programmed
Software Validation
Where the software is checked to ensure that it is what the customer requires.
Software Evolution
Where the software is modified to reflect changing customer and market requirements
Categories of Fundamental Activities of SWE
Process Activities and Umbrella Activities
Process Activities
Core development tasks in SWE
Includes: Requirements Gathering & Analysis, Design, Coding, Testing, and Deployment
Umbrella Activities
Support functions in SWE
Includes: Project Management, Configuration Management, Quality Assurance, Documentation, and Software Standards Compliance
Framework Process Activities (FPA)
Communication, Planning, Modeling, Construction, and Deployment
FPA: Communication
Maintain communication channels
FPA: Planning
Defines scope, resources, schedule
FPA: Modeling
Create abstract representation of the system
Analysis of requirements
Design: turn requirements into plans for architecture, components, and interfaces
FPA: Construction
Implement the software design by coding
Code generation: auto code generation from design models
Testing
FPA: Deployment
Delivers software to end user and provide support
Framework Umbrella Activities (FUA)
Software project management
Formal technical reviews
Software quality assurance
Software configuration management
Work product preparation and production
Reusability management
Measurement
Risk management
FUA: Software project management
Planning, organizing, and controlling the software project
FUA: Formal technical reviews
Structured meetings to evaluate software work products
FUA: Software quality assurance
Focuses on establishing and maintaining quality standards throughout the software development process
FUA: Software configuration management
Identifying, controlling, and tracking changes to the software and its associated documentation.
FUA: Work product preparation and production
The activities required to create various work products
FUA: Reusability management
Identifying opportunities to reuse software components
FUA: Measurement
Defining, collecting, and analyzing data about software processes and products
FUA: Risk management
Identifying, assessing, and responding to potential risks that could impact the project's success.
Software Engineering
Focused on building and maintaining software systems.
Applied, practical discipline that emphasizes real-world problem-solving
Delivers functional and efficient software products that meet customer needs
Computer Science
Focused on understanding the theoretical foundation of computation.
Explores computation limits, algorithms and hardware.
Advances computing through research and innovation.
Systems Engineering
Concerned with all components of a system (hardware, software, and user processes)
Key challenges in SWE
Increasing diversity of devices and increasing complexity from new capabilities
Quick responsiveness or delivery of software
Production of trustworthy software
Software Project Failure
When it does not meet defined objectives, within the allocated time and budget.
Can manifest as increasing system complexity and failure to use software engineering methods
General issues that affect software
Heterogeneity, Business and social change, Security and trust, and Scale
Costs of software engineering
Varies, but typically professional software is 60% towards development and 40% towards maintenance
Web's Impact to SWE
Web services, cloud computing, advances to SWE
Advances: programming language, deployment and maintenance techniques, software reuse
Issues of professional responsibility
Confidentiality, Competence, Intellectual property rights, Computer misuse
ACM/IEEE Code of Ethics Principles
Public, Client and Employer, Product, Judgment, Management, Profession, Colleagues, and Self
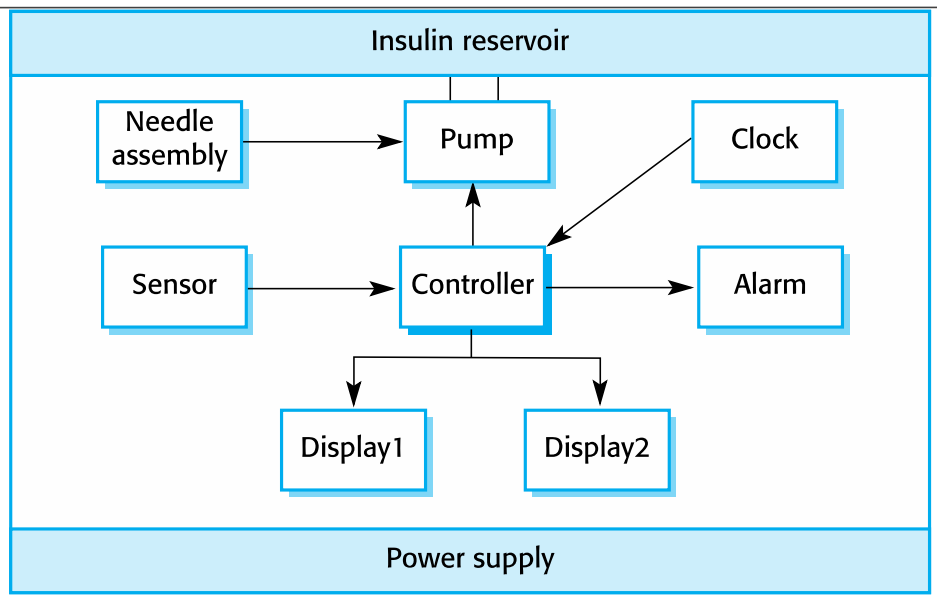
Insulin Pump: Hardware Architecture
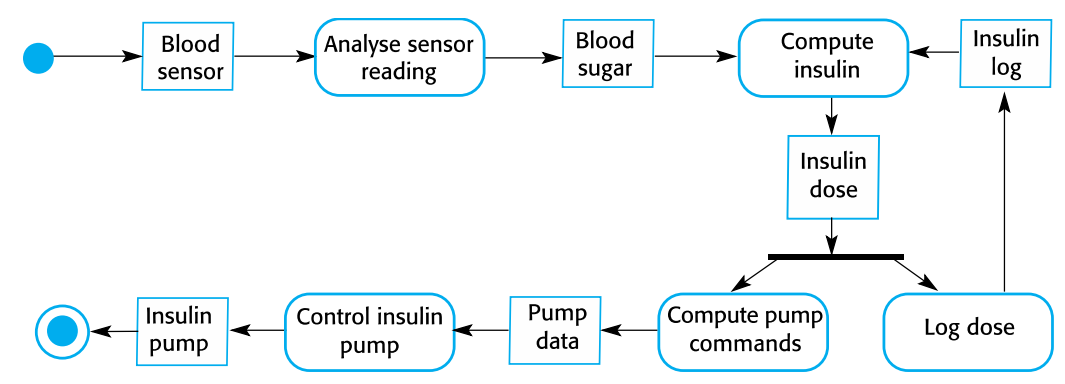
Insulin Pump: Activity Model
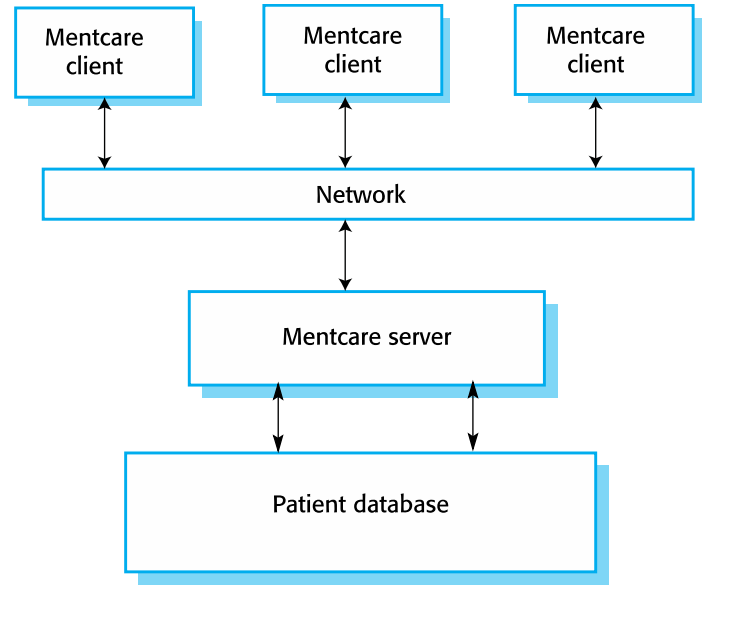
MentCare: Organization
Weather Station: Environment
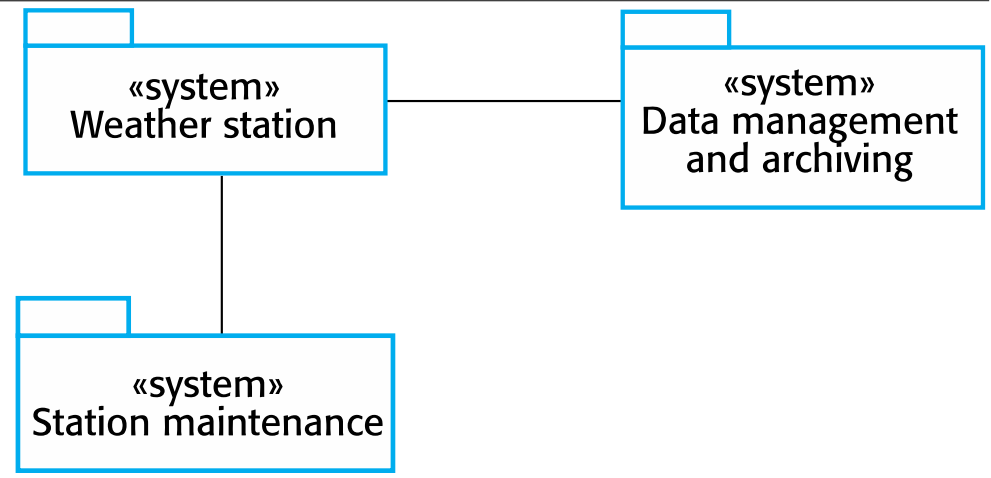
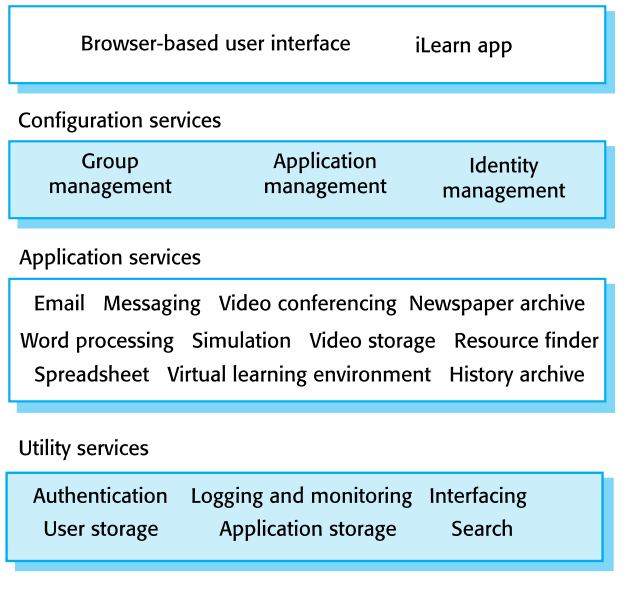
iLearn: Architecture