Pediatric Infectious Disease - Clin Med
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
What does this refer to
A 9-month-old girl presents to the pediatrician for a rash on her trunk.
She had a high-grade fever for 3 days, and she has been receiving ibuprofen for the fever.
She has been more irritable but has been eating and having sufficient diapers.
This morning, she no longer had a fever but developed a pink rash over her chest and back.
On physical exam, there is a blanching, light pink rash with macules and papules on the trunk and back.
She also has erythematous papules on her soft palate.
Her mother is reassured that this disease is self-limited and has no complication
Rosela
What does this refer to
______ Infantum
Viral syndrome due to HHV-6
Roseola
What does this refer to
More than 3 million cases every year
MC in children 5yo and younger
MC 9-12 month old infants
Accounts for up to 45% of febrile illness in infants
Epidemiology of Roseola
What does this refer to
Transmitted by direct contact (saliva)
Primary infection with human herpes virus 6 (HHV-6)
HHV-6A (immunocompromised adults)
HHV-6B (roseola infantum)
Recurrence is uncommon
Etiology of Roseola
What does this refer to
May be asymptomatic
May cause the exanthem subitum/roseola syndrome which consists of
Otitis
Gastroenteritis, Respiratory distress
Seizures
Acute onset of high fever (40C/104F) with non-specific sx for 3 days
+/- febrile seizure
Morbilliform exanthem rash
Diffuse and symmetric erythematous macules or small papules
Conjunctivitis
Acute otitis media
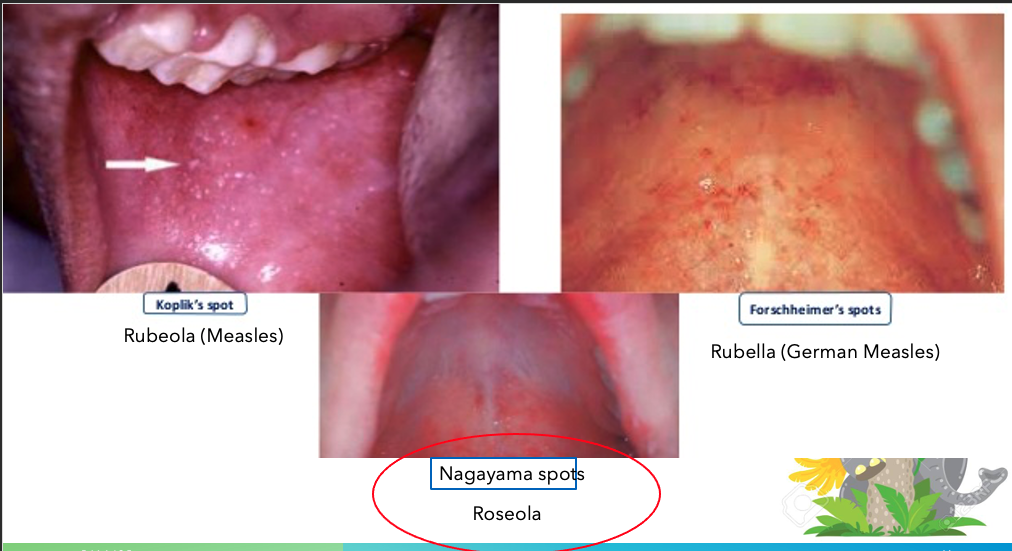
Uvulopalatoglossal junctional macules or ulcers (Nagayama spots)
Rhinorrhea
Cough
Vomiting
Diarrhea (24 to 68 percent)
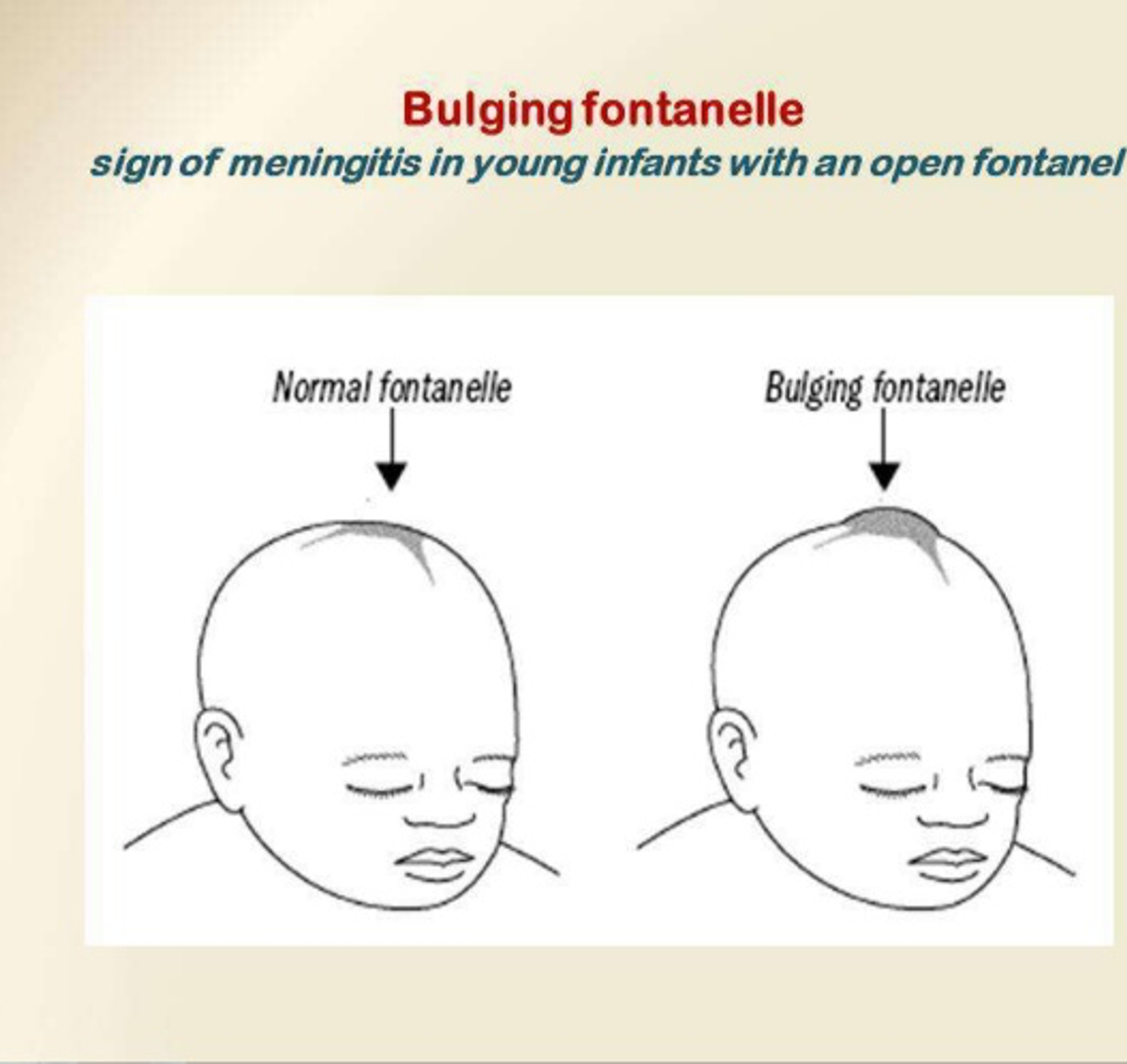
Bulging fontanelle
Clinical history of Roseola
What does this refer to
HHV-6 infection in AIDS patients
Viremia
Lymphadenopathy
Disseminated organ involvement
Active CNS infection
Retinitis
Death
MC in people with AIDS compared to general population
Clinical history in patients with aids Roseola
What does this refer to
After an abrupt loss of fever, the characteristic rash appears
Generalized and subtle eruption of rash
Discrete, small, pale pink papules or a blanchable, maculopapular exanthem that is 1-5 mm in diameter
Starts on neck and trunk
Spreads to face and extremities
May last 2 days
Typically a clinical dx based on hx and physical exam
Physical exam Roseola
What does this refer to
Rubeola (Measles)
Rubella (German measles)
Fever of unknown origin (FUO)
Pneumococcemia
Viral syndromes with fever and exanthem
Differential diagnosis Rosela
What does this refer to
Typically only in ill-appearing children
CBC w/ diff
BMP
UA
Blood cultures
LP (cerebrospinal fluid examination)
CXR
Workup for Roseola
What does this refer to
Supportive care
Alternate Acetaminophen (Tylenol) – Ibuprofen (Motrin) every 4-6 hours for fever
Hydration
Aspirin is contraindicated in viral illnesses
Reye syndrome
Exception to this C/I —> Kawasaki Disease
Clinical Management of Roseola
What does this refer to
Treatment of complications
Gastroenterologic
Respiratory
Hematologic
CNS
When to admit/disposition Roseola
What does this refer to
Recurrence is uncommon
Immunocompetent survive roseola infantum without sequelae
Patients who are immunosuppressed, multisystem complications
No risk appears to be present to pregnant women exposed to roseola
Care must be taken to distinguish this from rubella
Prognosis of Roseola
What does this refer to
A 30-year-old woman presents to the emergency room.
She is a tourist from Southeast Asia and reports having a low-grade fever for several days.
She also reports having arthralgias, especially in her wrists and knees.
Additionally, she has a pink rash on her face and her chest.
The rash appears to be spreading downward.
She does not recall whether or not she had the measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine.
Physical exam – lymphadenopathy in her postauricular and posterior cervical chains.
Petechiae on her soft palate and uvula and a pink maculopapular rash on her face and trunk.
Isolation precautions are indicated.
Rubella
What does this refer to
Contagious disease caused by a virus
Usually have a mild illness, with symptoms that can include a low-grade fever, sore throat, and a rash that starts on the face and spreads to the rest of the body
Rubella
What does this refer to
Last cases (endemic & congenital) reported in 2009 from the Americas region
Fewer than 10 cases of _______ are reported each year in the US
Most due to the arrival of infected persons from other countries
2015 - WHO declared the Americas region free of rubella and congenital rubella syndrome
2016 – added to the national vaccine regimen
Epidemiology for Rubella
What does this refer to
Systemic disease caused by
Togavirus
Natural hosts include humans, mammals, birds, and mosquitoes
Transmitted by inhalation of infective droplets
Through direct contact with the saliva or mucus of an infected person
Through air by respiratory droplets (from coughing or sneezing)
From pregnant woman to unborn baby
Etiology Rubella
What does this refer to
Exposure 14–21 days before onset
No prodrome in children and mild prodrome in adults
(Low grade) fever, malaise, coryza
Onset of rash
With onset of sx OR
5 days prior to other sx
Fine, pink, NON-CONFLUENT maculopapular rash of 3 days’ duration
Starts on face
Spreads to trunk and extremities
Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia
Clinical history of Rubella
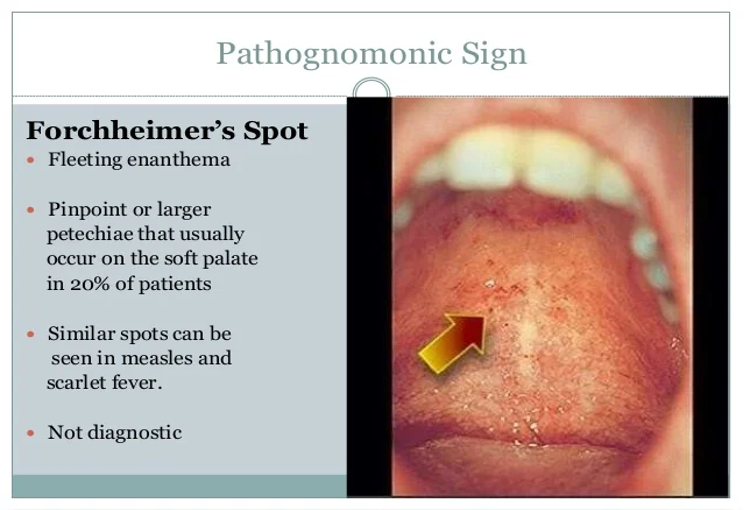
What does this refer to
Fine pink, maculopapular rash
Typically lasts 3 days’ duration
Descending spread
Starts on face then spreads —> trunk —> extremities
Lymphadenopathy
Posterior cervical/suboccipital
Postauricular is classic
Petechial rash on soft palate (Forschheimer spots)
Orchitis may be present in males
Physical exam Rubella
What does this refer to
Roseola
Erythema Infectiosum (5th disease)
Rubella
Meningitis
Differential diagnosis for rubella
What does this refer to
CBC w/ diff
CMP
UA
Serum or saliva
Elevated IgM antibody
At least 4x > rise in IgG antibody titers
Isolation of the virus
RT-PCR from throat swabs, oral/nasopharyngeal secretions
Best if collected within the first 3 days
Within 3 months in case of congenital rubella syndrome.
Work up Rubella
What does this refer to
Clinical diagnosis
Serum or saliva confirms
Elevated IgM antibody
At least 4x > rise in IgG antibody titers
Isolation of the virus
OR
RT-PCR virus detection
How Rubella is diagnosed
What does this refer to
No specific treatment of the disease itself
Treat the symptoms
Antipyretics
Analgesics
Hydration
High dose vitamin A supplement x 2 days for children to reduce morbidity and mortality
Clinical management for Rubella
What does this refer to
Complications are rare
Polyarticular arthritis and arthralgia MC adult women
Involves fingers, wrists, and knees
Usually subside within 7 days
May persist for weeks
Hemorrhagic manifestations MC in children
Hepatitis has been reported
Encephalitis (rare)
More common in adults
High mortality rate
Vertical transmission to fetus —> congenital rubella syndrome
Thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)
Guillain-Barre syndrome
Complications of Rubella
What does this refer to
Vaccination
MMR
1st dose – age 12-15 months
2nd dose – age 4-6 years (prior to starting school)
Check immune status of pregnant women
Antibody titers fall about 10% within 12 years of vaccination
Per UpToDate, the MMRV vaccination is contraindicated in pregnancy
Vaccine C/I in solid organ transplant patients
Prevention for Rubella
What does this refer to
Devastating effects on the fetus in utero
May cause fetal death, preterm delivery, and teratogenic effects
Severity of symptoms is directly related to the gestational age
1st trimester leads to congenital rubella in at least 80% of fetuses
Manifestations of congenital rubella syndrome
Transient
Permanent
Developmental
Congenital rubella syndrome (CRS) Rubella
What does this refer to
Low birth weight, and hepatosplenomegaly
Early-onset cataracts and glaucoma
Microphthalmia
Hearing deficits
Psychomotor retardation
Congenital heart defects
Patent ductus arteriosus
Branch pulmonary artery stenosis
Manifestations of Congential rubella
When do you admit/disposition for Rubella
Complications
Meningitis
Encephalitis
Myelitis
Severe pneumonia
Diarrhea that significantly compromises fluid or electrolyte status
What does this refer to
Pregnancy
Meningitis/encephalitis
Significant vaccination reactions
Suspect cases should be reported to public health authorities
Referral/Consult for Rubella
What does this refer to
Mild illness and rarely lasts more than 3–4 days
Congenital rubella has a high fetal mortality rate
Associated congenital defects are permanent
Infants with CRS can transmit virus for up to 1 year after birth
Prognosis for Rubella
What does this refer to
A 2-year-old child presents to the pediatrician’s office for a rash.
Her mother is against vaccines, so the child had not received any childhood vaccines. Her father, however, is worried about her lack of vaccination and asks the doctor if this is measles or rubella. On physical exam, she has a high fever as well as a confluent maculopapular rash. She also has blue-white spots on her buccal mucosa. The family is instructed to take isolation precautions and to bring in the child’s siblings who are also unvaccinated.
Rubeola
What does this refer to
Paramyxoviral infection that occurs acutely
Serious Infection that has a high incidence of morbidity and death
Rubeola
What does this refer to
______ virus
Highly contagious
Transmission
Inhalation of Respiratory droplets
Etiology of Rubeola
What does this refer to
Pediatric patients infected annually result in almost a million deaths
Very contagious
Especially before the onset of rash and the
Catarrhal stages (until the rash subsides)
Number of cases in the US has been increasing over the past decade
2019 – 1282 cases dx in US
Risk factors
Lack of vaccination
Travel to endemic areas
Epidemiology of Rubeola
What does this refer to
Prodrome Symptoms
(High grade) fever (high Fever 104)
Coryza
Rash –occurs 5 days or less once symptoms occur
Cough
Conjunctivitis
Koplik spots
Clinical history for Rubeola
What does this refer to
Koplik spots are pathognomonic
Tiny bluish-white spots with red background
on buccal mucosa opposite the molars
Palms and soles are spared from rash
Rash blanches in the first few days
Physical exam for Rubeola
What does this refer to
Onset 3-5 days after sx begin
Small papules (pinhead size)
Progresses to brick red, irregular blotchy maculopapular rash
Face and ears downward to (trunk) and outward to (limbs)
RARELY effecting the palms and soles
Coalesces can occur if severe
Other symptoms
Lymphadenopathy
Reddened Pharynx
Yellow colored exudate on the tonsils
Splenomegaly
Physical exam of Rubeola
What does this refer to
These groups developed hypersensitivity rather than protective immunity
Vaccinated with the inactivated measles vaccine from 1963-1968
Received live measles vaccine before 12 months of age
Atypical measles
What does this refer to
More prolonged and severe than regular measles
Marked by
Prolonged high fever
Pneumonitis
(Varying) rash begins peripherally
Urticarial
Maculopapular
Hemorrhagic
and/or vesicular
Physical exam of atypical (wild) measles
What Nagayama spots refer to
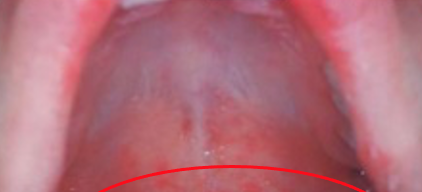
Roseola
What does Koplik’s spot refer to
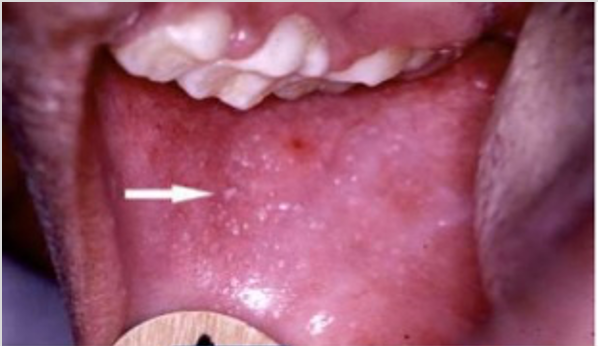
Rubeola (Measles)
What does Forschheimer’s spots refer to
Rubella (German measles)
What does this refer to
CBC w/ diff
CMP
Virus culture can be done thru nasopharyngeal secretions
Measle antibodies (IgM) or IgG or virus detection on RT-PCR
Fluorescent antibody screening
Eval for presence of IgM antibodies in blood
Lymph node bx (rarely needed)
Wartin-Finkeldey giant cells
Fused lymphocytes with paracortical hyperplasia
Workup for Rubeola
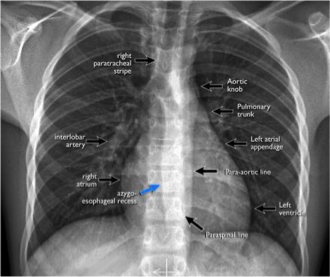
What does this refer to
Contour
Heart
Effusion
Symmetry
Trachea
Reading a chest x-ray
What does this refer to
Pneumonitis of atypical measles
What does this refer to
Drug reactions
Parvovirus B19
Roseola
Rubella
Less likely
Kawasaki Disease
Dermatologic Manifestations of Viral hemorrhagic fever
Epstein Barr Virus (causes Mononucleosis)
Scarlet fever
Differential of Rubeola
What does this refer to
ISOLATION for a week following the onset of rash
Bedrest until afebrile
Antipyretics and fluids
Vitamin A may be used
Treat secondary bacterial infections
Clinical Management of Rubeola
What does this refer to
VACCINATION with MMR, MMRV
Children first vaccinated at 12-15 months and then again at 4-6 years before entering school system
Unvaccinated –outbreak more likely
Prevention for Rubeola
What does this refer to
Pregnancy
Void of fetal abnormalities
Risk to the pregnancy
May result in spontaneous abortion or premature birth
Measles and pregnancy Rubeola
What does this refer to
Encephalitis
Lung infections
Secondary Bacterial Infections
GI Complications
Complications of Rubeola
What does this refer to
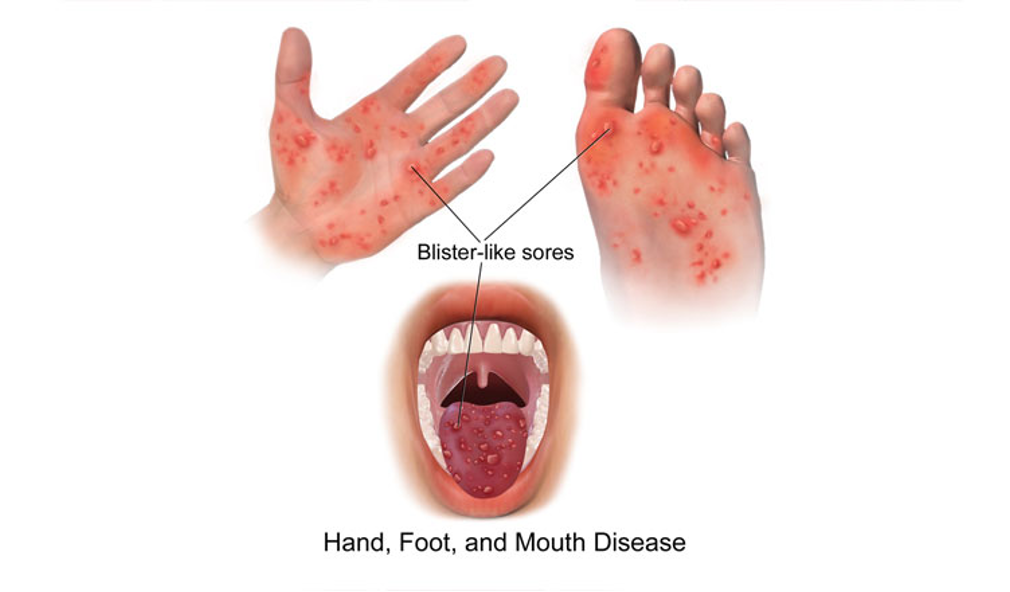
A 2-year-old girl is brought to her pediatrician’s office for a new rash on the palms and soles that developed yesterday.
For the past few days, she has had low-grade fevers and a slight cough, and of note, her 6-year-old sister had similar symptoms.
Upon further questioning, she and her sister have had all routine childhood vaccinations.
Physical exam
Multiple 2-3-mm grey vesicular lesions on the bilateral palms and soles and several vesicles and ulcers on the oral mucosa.
Hand-foot-mouth disease (HFMD)
What does this refer to
Common pediatric viral illness causing sores in/on/around the mouth, and palms and soles
Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease (HFMD)
What does this refer to
MC young children
Risk Factors
Exposure to others
Daycare centers
Poor hygiene
Finger sucking
Epidemiology of Hand-Foot-Mouth-Disease (HFMD)
What does this refer to
Coxsackie virus
Type A*
HFMD
Herpangina
Type B
Nonspecific prodrome
Myocarditis
Pericarditis
Once infected —> lymph nodes >>> prodromal sx
Etiology of Hand-Foot-Mouth-Disease (HFMD)
What does this refer to
Flu-like sx
Low-grade fever
Cough
Malaise
Mouth sores
Rash
Clinical history of Hand-Foot-Mouth-Disease (HFMD)
What does this refer to
Grayish-yellow vesicles or erythematous papules on the palms and soles
Vesicles and ulcers in oral mucosa and around the mouth
Physical exam Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease (HFMD)
What does this refer to
Rickettsia rickettsi
Chickenpox
Diagnosis is often clinical, but can be confirmed with labs
Differential diagnosis of Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease (HFMD)
What does this refer to

Workup for Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease (HFMD)
What does this refer to
Coxsackievirus-specific immunoglobulin A +
Viral culture
How to diagnose Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease (HFMD)
What does this refer to
Supportive care
Antipyretics
Analgesics
Hydration
Clinical Intervention of Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease (HFMD)
What does this refer to
“No specific pharmacologic therapy”
Clinical pharmacotherapeutics Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease (HFMD)
What does this refer to

Prognosis/prevention for Hand-Foot-Mouth-Disease (HFMD)
What does this refer
“Most patients have full, spontaneous recovery”
Prognosis of Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease (HFMD)
What does this refer to
Acute, febrile medium vessel vasculitis
Also known as Acute Systemic Vasculitis
Kawasaki Disease
What does this refer to
A 5-year-old boy presents to the emergency room with 5 days of fevers, ranging from 102-104°F (38.9-40°C).
His mother reports that he also has a bad rash that developed on day 3.
Physical exam
Bilateral conjunctivitis
Extensive morbilliform rash on his trunk with desquamation
Bright red tongue
Swollen hands and feet
Labs
Elevated C-reactive protein, white blood cell count, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Kawasaki Disease
What does this refer to
MC peds < 5yo
MC Asian descent
Risk Factors
Family hx
Asian or Pacific Islander descent
Epidemiology of Kawasaki Disease
What does this refer to
No known specific etiology
Combination infectious, environmental, immunologic, and genetics
Etiology of Kawasaki Disease
What does this refer to
General arthralgias
High fever
Clinical history of Kawasaki Disease
What does this refer to

Physical exam of Kawasaki Disease
What does this refer to
Fever for 5 or more days (burn) PLUS
Must have 4 of 5 CRASH sx
Conjunctival injection
Rash
Adenopathy
Strawberry tongue
Hand and foot rash
Diagnostic Criteria for Kawasaki Disease
What does this refer to
Takayasu arteritis
Scarlet fever
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
Differential diagnosis of Kawasaki Disease
What does this refer to
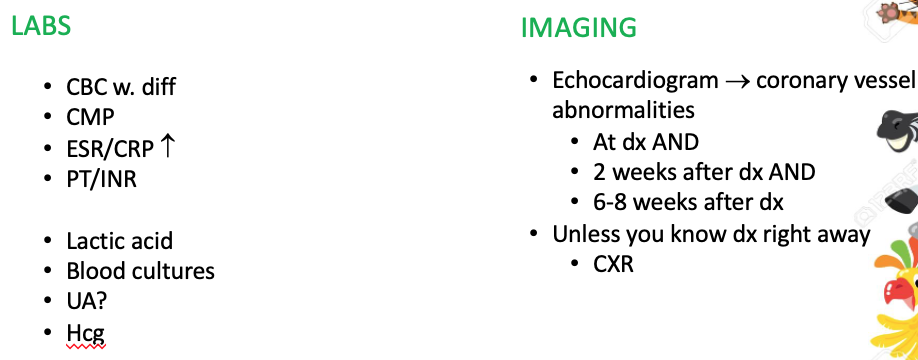
Workup for Kawasaki Disease
What does this refer to
“Vaccinations if not up to date (UTD)”
Clinical intervention Kawasaki Disease
What does this refer to
Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG)
High-dose aspirin (ASA) with taper to lower dose
DC if imaging confirms no coronary vessel abnormalities weeks after onset of disease
Anticoagulation (warfarin (coumadin) often drug of choice)
↓ risk of thrombosis
+ thrombocytosis
Monitor INR if taking warfarin
Clinical pharmacotherapeutics Kawasaki Disease
What does this refer to
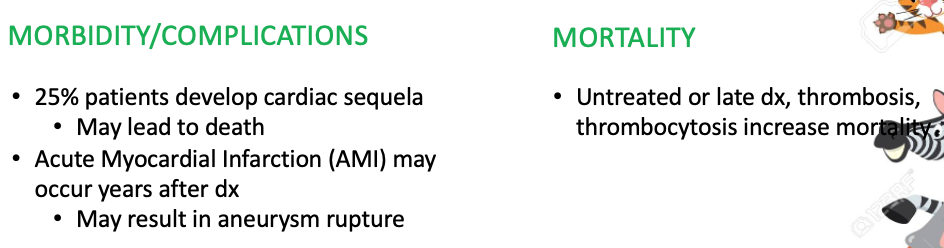
Prognosis/prevention Kawasaki Disease
What does this refer to “Most cases are self-limited and resolve with treatment”
Prognosis for Kawasaki Disease
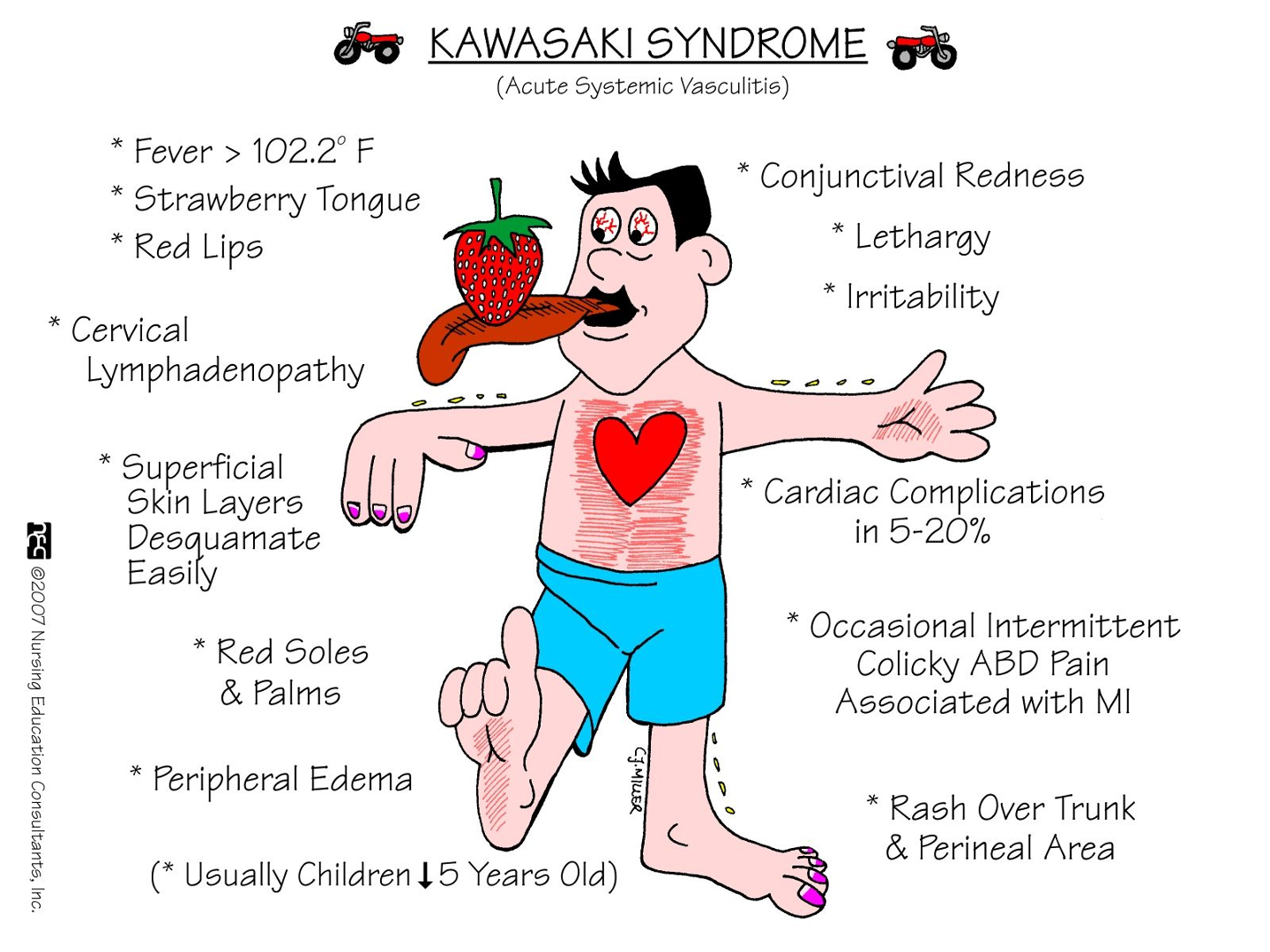
What does this refer to
4-year-old boy presents to the urgent care clinic for a new rash.
His mother reports that the rash started on both his cheeks yesterday, but since then he has developed a rash on his trunk.
On physical exam, he has a slapped cheeks appearance and has a maculopapular rash on his trunk with some areas having a lacy or reticular appearance.
The physician advises him to stay home while he is still contagious and to stay away from pregnant women.
Erythema infectiosum (5th disease)
What does this refer to
Viral illness parvovirus B19
Can cause a variety of illnesses (depending on patient population)
Erythema Infectiosum (5th disease)
What does this refer to
Highest incidence in winter and spring
Children > adults
Risk Factors
Sickle cell disease
Thalassemia
Hereditary spherocytosis
Close proximity to others
Epidemiology of Erythema Infectiosum (5th disease)
What does this refer to
Parvovirus B19
Variety of illnesses
Aplastic crisis – red blood cell disorders
Pure RBC aplasia in adults
Rheumatoid arthritis-like sx in adults
Erythema infectiosum (5th disease) in children
Hydrops fetalis
Maternal exposure
Transmission —> respiratory droplets
Etiology Erythema Infectiosum (5th disease)
What does this refer to
Peds
Prodromal flu-like sx
Fetus
Fetal death in pregnant women
Adults
Polyarthropathy may be only sx
Clinical history of Erythema Infectiosum (5th disease)
What does this refer to
First appears as “slapped cheeks”
Followed by erythematous maculopapular rash on trunk and limbs
Lacy or reticular
Physical exam of Erythema Infectiosum (5th disease)
What does this refer to
Measles (Rubeola)
German Measles (Rubella)
Differential Diagnosis of Erythema Infectiosum (5th disease)
What does this refer to

Workup for Erythema Infectiosum (5th disease)
What does this refer to
History and physical exam
Parvovirus-specific IgM +
PCR + for parvovirus
How Erythema Infectiosum (5th disease) is diagnosed
What does this refer to
Supportive care
Analgesics
Hydration
Clinical intervention Erythema Infectiosum (5th disease)
Only use aspirin for
Kawasaki disease
What does this refer to “No antiviral therapy indicated”
Clinical pharmacotherapeutics Erythema Infectiosum (5th disease)
What does this refer to

Prognosis/prevention Erythema Infectiosum (5th disease)
What is the prognosis of erythema infectiosum (5th disease)
Usually self-limiting
What does this refer to
An 8-year-old boy is brought by his parents to the pediatrician with complaint of a fever and sore throat for the past few days.
He says that he has felt tired and that his "neck is sore."
Physical examination is notable for the finding seen in the image.
Heterophile antibody test is negative
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Peds
What does this refer to
CMV (HHV-5)
Causes CMV mononucleosis
Can cause congenital CMV
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Peds
What does this refer to “Congenital infection 1% of all births”
Epidemiology Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Peds
What does this refer to
CMV (HHV-5) transmission
Sexual
Transplacental —> congenital
Breast milk
Respiratory droplets
Blood transfusions
Etiology Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Peds
What does this refer to

Clinical history of Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Peds
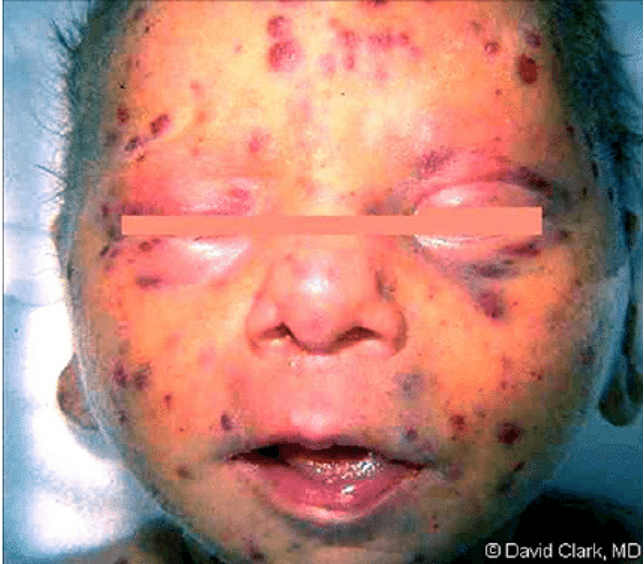
What does this refer to
Cervical lymphadenopathy
Petechial (“blueberry muffin”) rash
Physical exam Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Peds
What does this refer to
Congenital toxoplasmosis
EBV mononucleosis
Differential Diagnosis of Cytomefalovirus (CMV) Peds
What does this refer to
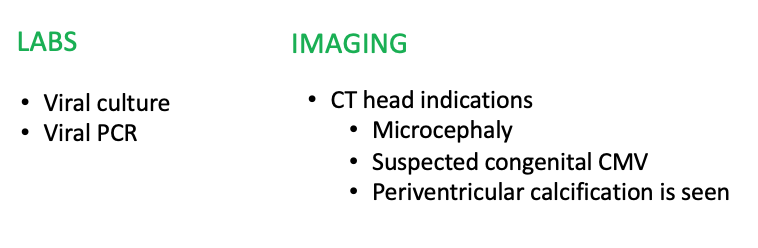
Diagnostics Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Peds
What does this refer to
Supportive care
ID consult
Clinical intervention Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Peds
What does this refer to
1st line therapy
Ganciclovir (Cytovene)
Cidofivir (Vistide)
Foscarnet (Foscavir)
Clinical pharmacotherapeutics Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Peds
What does this refer to

Prognosis Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Peds