Organic molecules
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
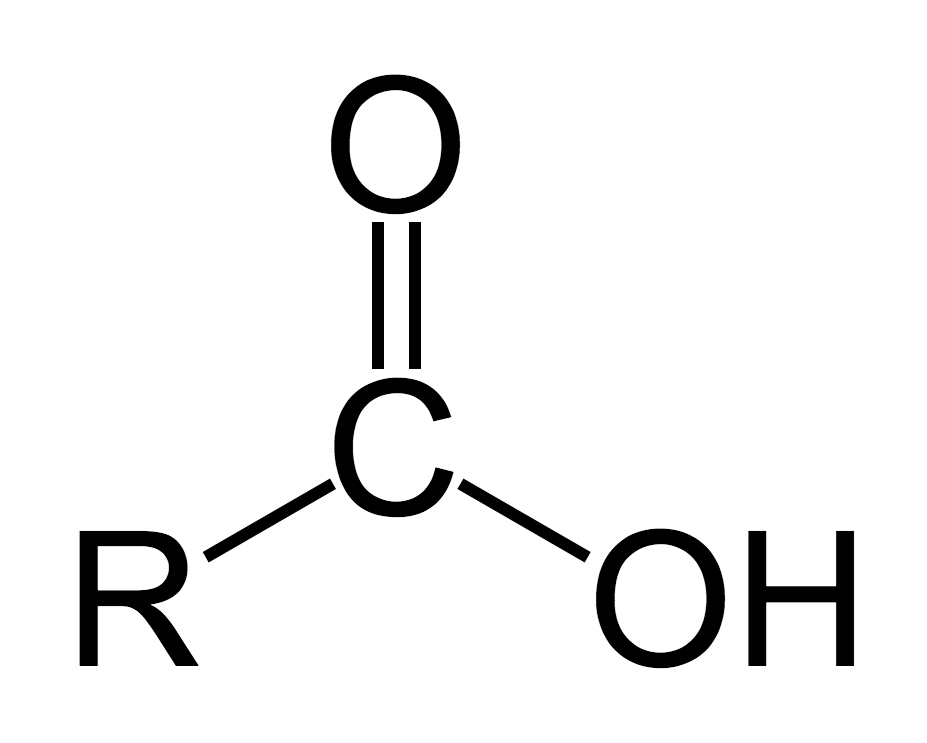
Carboxylic Acid
acts as an acid, releasing H+ ions to become R—COO-
fatty amino acids
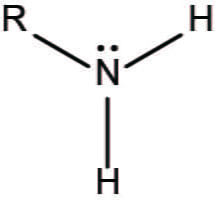
Amino group
Can accept or release H+, depending on pH; can form bonds with other molecules
amino acids
Hydroxyl group
strong bases dissociate to release hydroxide ions [OH-'], may link molecules through dehydration synthesis (condensation)
Carbohydrates, fatty acids, amino acids
![<p>strong bases dissociate to release hydroxide ions [OH-'], may link molecules through dehydration synthesis (condensation) </p><ul><li><p>Carbohydrates, fatty acids, amino acids</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5cc9c20b-198a-4b4d-ad3c-3385329855f7.png)
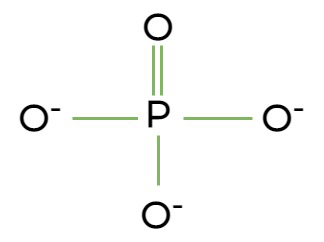
Phosphate group
May link other molecules to form larger structures; may store energy in high-energy bonds
phospholipids, nucleic acids, high energy compounds
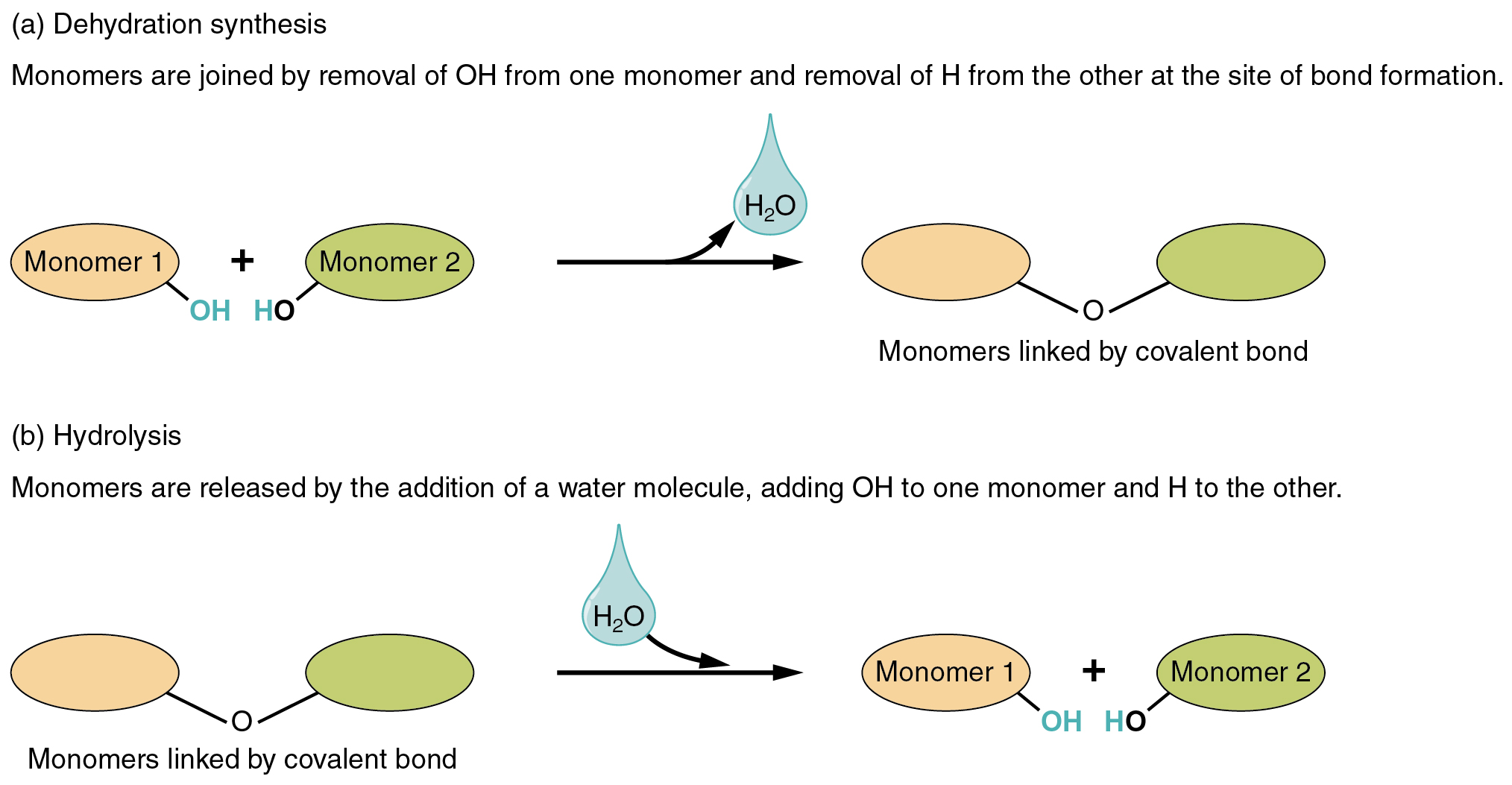
Dehydration synthesis
WATER comes out as PRODUCT
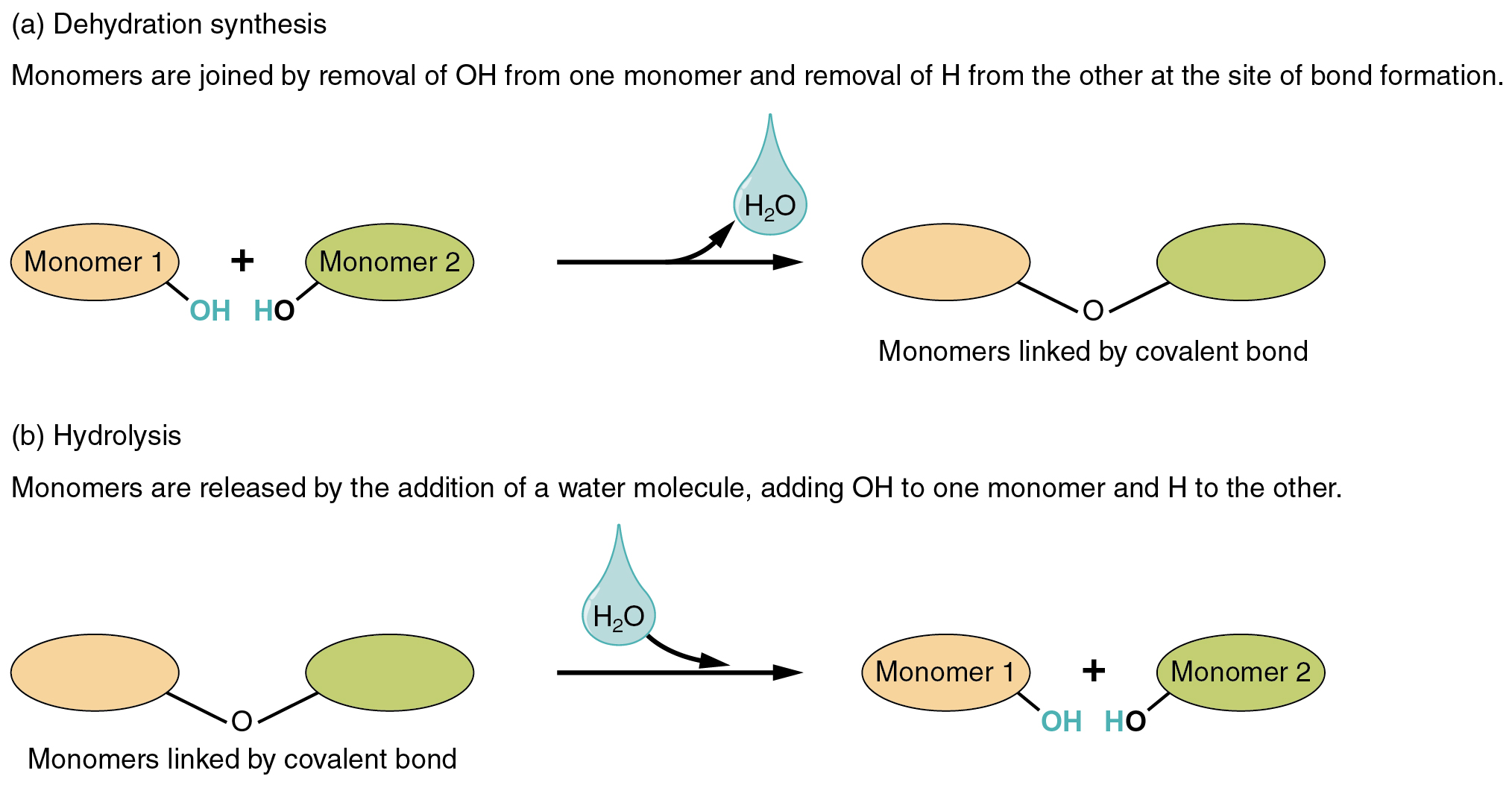
Hydrolysis
WATER is a REACTANT
Carbohydrates
ratio is 1(C):2(H):1(O)
monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides (sugars)
ENERGY SOURCE; SOME STRUCTURAL ROLE WHEN ATTACHED TO LIPIDS OR PROTEINS; ENERGY STORAGE
Monosaccharides
Glucose - blood sugar - energy source for most cells
Galactose - converted to glucose and metabolized
Fructose - fruit sugar - converted to glucose and metabolized
Glucose
blood sugar - energy source for most cells
Galactose
converted to glucose and metabolized
Fructose
fruit sugar - converted to glucose and metabolized
Disaccharides
sucrose - cane sugar - digested to glucose and fructose
lactose - milk sugar - digested to glucose and galactose; important in infant nutrition
maltose - malt sugar - product of starch digestion, further digested to glucose
sucrose
cane sugar - digested to glucose and fructose
lactose
milk sugar - digested to glucose and galactose; important in infant nutrition
maltose
malt sugar - product of starch digestion, further digested to glucose
Polysaccharides
Cellulose - structural polysaccharide of plants; dietary fiber
starch - storage in plant cells
glycogen - energy storage in animal cells (live, muscle, brain, uterus, vagina)
Cellulose
structural polysaccharide of plants; dietary fiber
starch
storage in plant cells
glycogen
energy storage in animal cells (live, muscle, brain, uterus, vagina)
Conjugated carbohydrates
glycoprotein - component of the cell surface coat and mucus, among other role
glycolipid - component of the cell surface coat
proteoglycan - cell adhesion; lubrication; supportive filler of some tissues and organs
glycoprotein
component of the cell surface coat and mucus, among other role
glycolipid
component of the cell surface coat
proteoglycan
cell adhesion; lubrication; supportive filler of some tissues and organs