Erythrocytes lecture
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Function
Transport, O2 nutrients CO2 to and from cells, regulate temperature and tissue fluids, defense, and volume
Regulate
Temperature and tissue fluid fluids allows balance, and pH
Volume
1 kg is about 1 liter, 7% lean body weight per kg
hemostasis
Stop bleeding
Primary hemostasis
platelets plugs carry vesicles that release chemicals that initiate secondary hemostasis after a hole is plugged in capillaries
Secondary hemostasis
Is when we form a fibrin clot through a cascade of 13 different factors
Plasma
45-78% blood volume
The larger the cell volume
the smaller the volume of plasma
How much percent of plasma is water
93%
Primary proteins in plasma
Albumin, globulins, and fibrinogen
Albumin
Primary colloid or protein created by our liver
Globulins
Antibodies created by cells to fight disease
Fibrinogen
One of the clotting factors before blood clots
Electrolytes in plasma
Sodium and potassium and chloride and bicarbonate
Why are sodium and potassium important?
Used for muscle movement and depolarization
Metabolic waste
The metabolism in our cells create waste products such as BUN, creatinine, etc.
Enzymes and plasma
ALT, AST, ALKPHOS, GGT (erase)
Gas is in plasma
O2, CO2
Nutrients in plasma
Nutrients are getting into the plasma after being absorbed from the G.I. tract ex. amino acids and lipids
Erythrocytes function
Gas transport (primary cell)
Leukocytes
White blood cells
What are the two types of leukocytes?
Granulocytes and agranulocytes
Types of granulocytes
Neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
Types of agranulocytes
Monocyte and lymphocytes
What is the plate in birds, reptiles and fish?
Thrombocytes
Hematopoiesis
Blood cell production
Hematopoiesis in the fetus
Occurs in the liver and spleen
Hematopoiesis in neonates
Occurs in bone marrow, red marrow being active, yellow marrow being inactive
Hemopoietic stem cells
Have multiple potentials and need stimulus to become a type of blood cell, but it is a one-way process
Hormone that turns hemopoietic stem cells into RBC
Chemical produced by kidneys called erythropoietin
How hemopoietic stem cells become WBC
Need a specific type of granulous stimuli
Erythron
Includes all the RBC, erythropoietin cells after getting stimulus, and recycling tissues in the spleen
Reason for the kidney cells to create erythropoietin
The lower the O2 levels the kidney cells release erythropoietin into the bone marrow, so it can start to make more RBC
Bone marrow will produce RBC
6 to 8 day maturity cycle
Increased demand for RBC
The bone marrow will release immature RBC (3-5 day prior) and depending on how bad the anemia is, it will tell us what type of immature RBC we will see
How much RBC’s are produced for canine
800,000 RBC/sec also equals removal
Erythrocyte lifespan
About 2 to 5 months
Erythrocyte senescence
After RBC flows for a couple of months the enzyme activity and flexibility decreases
extravascular hemolysis
Breakdown of RBC outside vessels, either recycled through the spleen or eaten by macrophages
RBC recycled back into bone marrow
Recycled globulins are turned into hemoglobin, iron is recycled because it binds to oxygen
HEME
Protein that is not commonly used
heme recycled
Heme is eliminated and made into Bilirubin which is either unconjugated or conjugated (paired with something)
Intravascular hemolysis
RBC breakdown inside blood vessels (bad)
Haptoglobin
Produced by intervascular hemolysis and taken to the liver to be processed creating excess
Hemoglobinemia
Excess haptoglobin, removed by floating in the body creating pink plasma
Hemoglobinuria
Excess hemoglobin that goes to the kidneys is removed through the urine, turning it brown
Erythrocyte morphology
Round, anuclear if mature immature is nuclear, biconcave to increase surface area, central palor will look pale in the middle
Erythrocyte size
Variable; dog > cat> horse/ cow>sheep> goat (1/2 the size of dog)
Erythrocyte membrane
Flexible, deformable, not elastic
Erythrocyte semipermeable
Respond to tonicity, cremation shrivel, hemolysis pop
Erythrocyte O2 transport
Hemoglobin binds to oxygen distributing it depending on the concentration of O2 in an area
Hemoglobin molecule
Four goblin with heme groups, each group requires an iron atom and 102 combined to one iron atom
Types of hemoglobin
Embryo and fetal have O2 affinity adults replace fetal
RBC CO2 direct transport
Directly bind with carbon dioxide
RBC CO2 indirect transport
Combined CO2 with something else
Indirect CO2 transport equation
H2O + CO2 = H2 C03 = H+ + HCO3 -
What helps control pH in the body?
Carbon dioxide
Erythrocyte energy
Do not contain mitochondria, utilize glucose for energy even if they are removed from the body
Hematocrit PCV
Total percent of RBC out of total blood volume plus white blood cells and red blood cells
PCV
Packed cell volume
RBC measurements
Hematocrit PCV, [HB], RBC count
RBC indices
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (mchc), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH)
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV)
Reflect average RBC size
Accuracy of indices
Depend on RBC measurements and the interpretation classifies the types of anemia
MCV calculation
PCV * 10 \ by RBC count (8×10^6/mm3) = MCV in fL
MCV Morphologic description
Normocytic: normal rbc size
Macrocytic: big rbc
Microcytic: small rbc
Mchc calculation
Hb (g/dL) grams per deciliter / PCV * 100
MCHC morphologic description
Normochromic: red
Hypochromic: pale
MCH calculation
Hb (g/dL) 10 \ RBC 8.5 × 10^6/mm3
MCH morphologic description. ( not common)
Normochromic
Hypochromic
Anemia
low O2 carrying capacity because of low RBC, loss, destruction, low hemoglobin production, low MCV (iron)
Polycythemia
High number of RBC relative to fluid loss making plasma low, compensatory (hypoxemia)
Polycythemia Vera
High production of rbc
Erythrocyte structural alterations
Can occur in healthy cells, size, shape, cytoplasm
Potential changes in erythrocytes
Membrane composition, hemoglobin structure
Causes of erythrocyte change
Physical response, chemical/metabolic damage, mechanical damage, parasitic organism
Erythrocyte change evaluation
Blood smear mono layer
Cytoplasmic variations
Depend on the degree of staining a.k.a. hypochromic which could mean low MHCH
Hyperchromic
If it does not have pale area in the middle of the cell
Polychromasia
Meaning, many colors usually macrocyte/immature stains faint blue color, and with an NMB stain you get reticulocyes (bluish dots)
Polychromatiphilia
One cell with different colors, patchy areas in the individual cell
Cytoplasmic inclusions
Nucleated RBC (really immature), reticulocytes,
Cytoplasmic inclusions nucleated RBC
Metarubricyte, regenerative, anemia, bone marrow disease, lead toxicosis
Lead toxicosis
With basophilic stepping
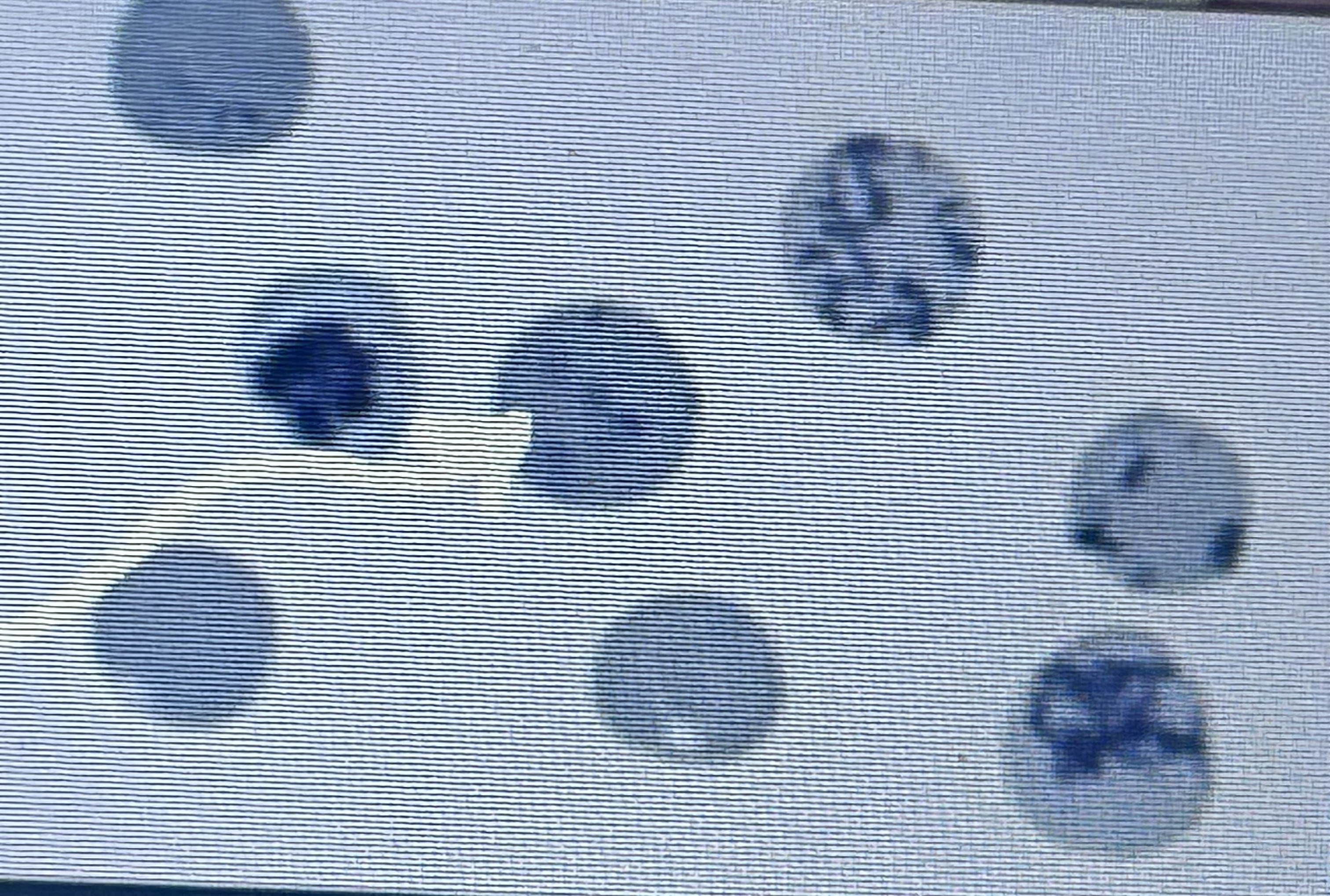
Two types of reticulocytes in cats
Aggregate: clumped spots, Punctate ting spots
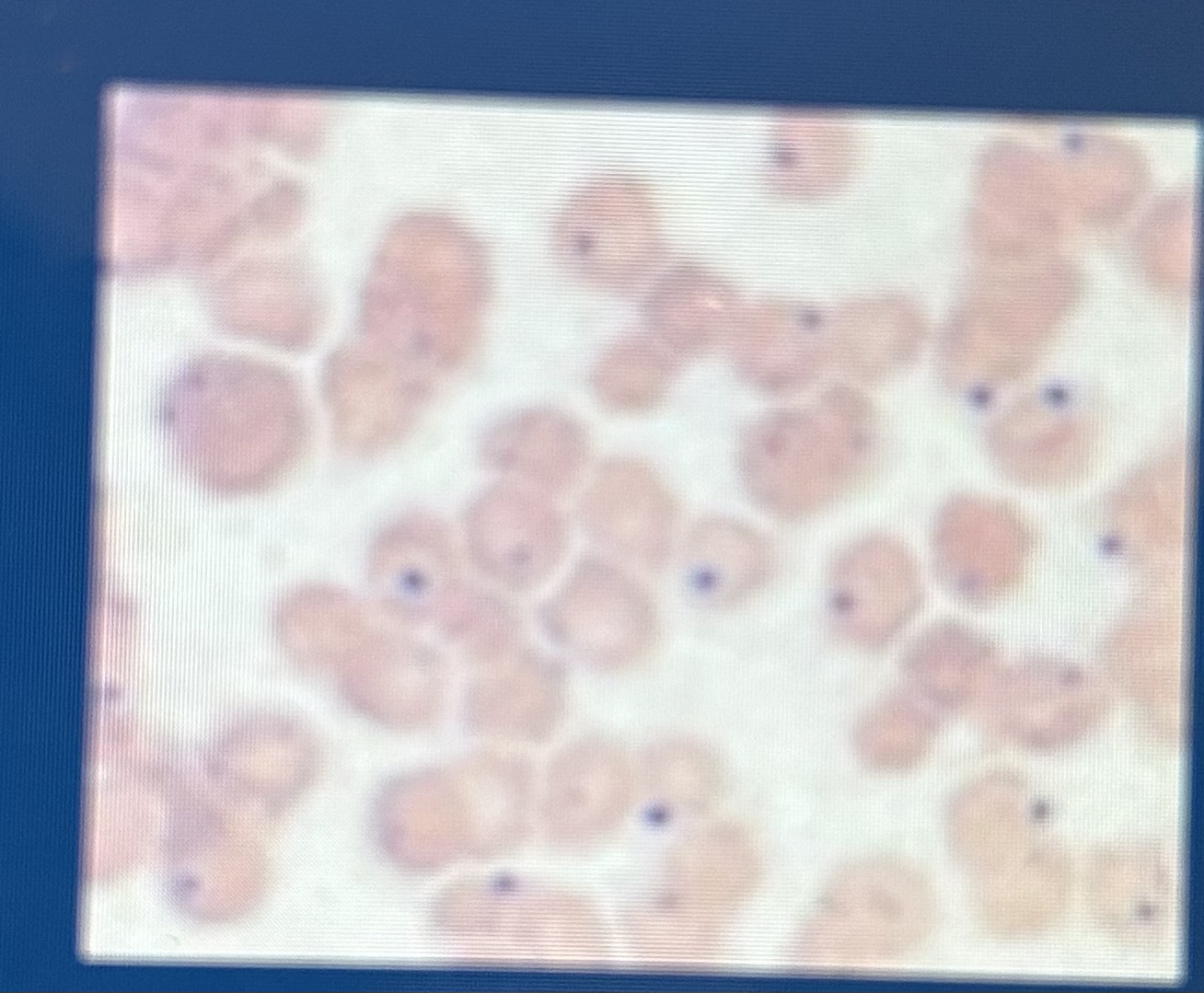
Howell Jolly body
Nuclear remnant single round object, blue stain
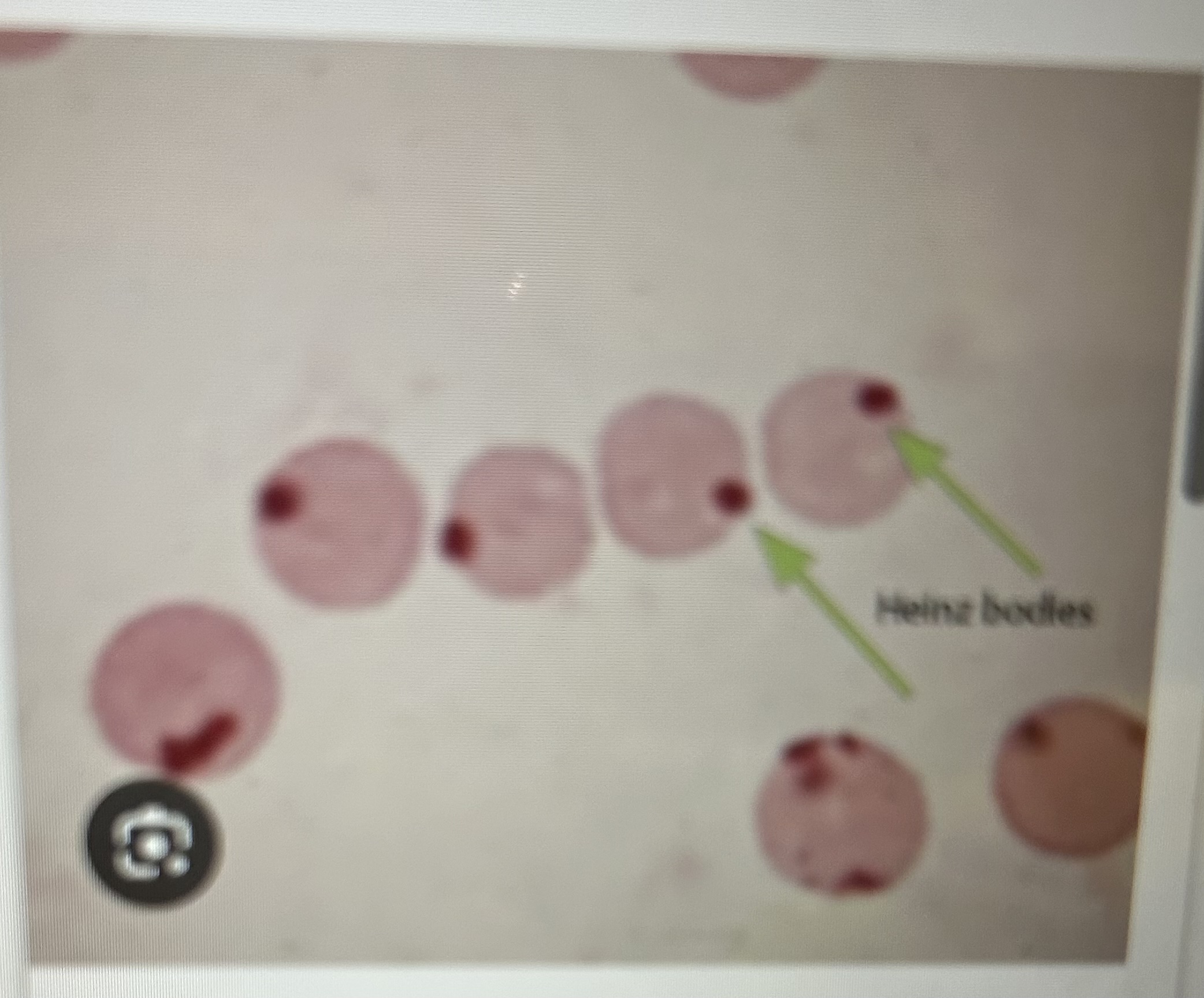
Heinz body
Refractile single to multiple, stain poorly, oxidative damage, can be normal in cats
Pappenheimer bodies
Iron inclusions (too much)
Parasitic inclusions
Small percent of cells have parasites
Comment types of parasitic inclusion
Hemobartonella canis/felis, coccoid or rod shaped, babes is canis, anaplasma marginale
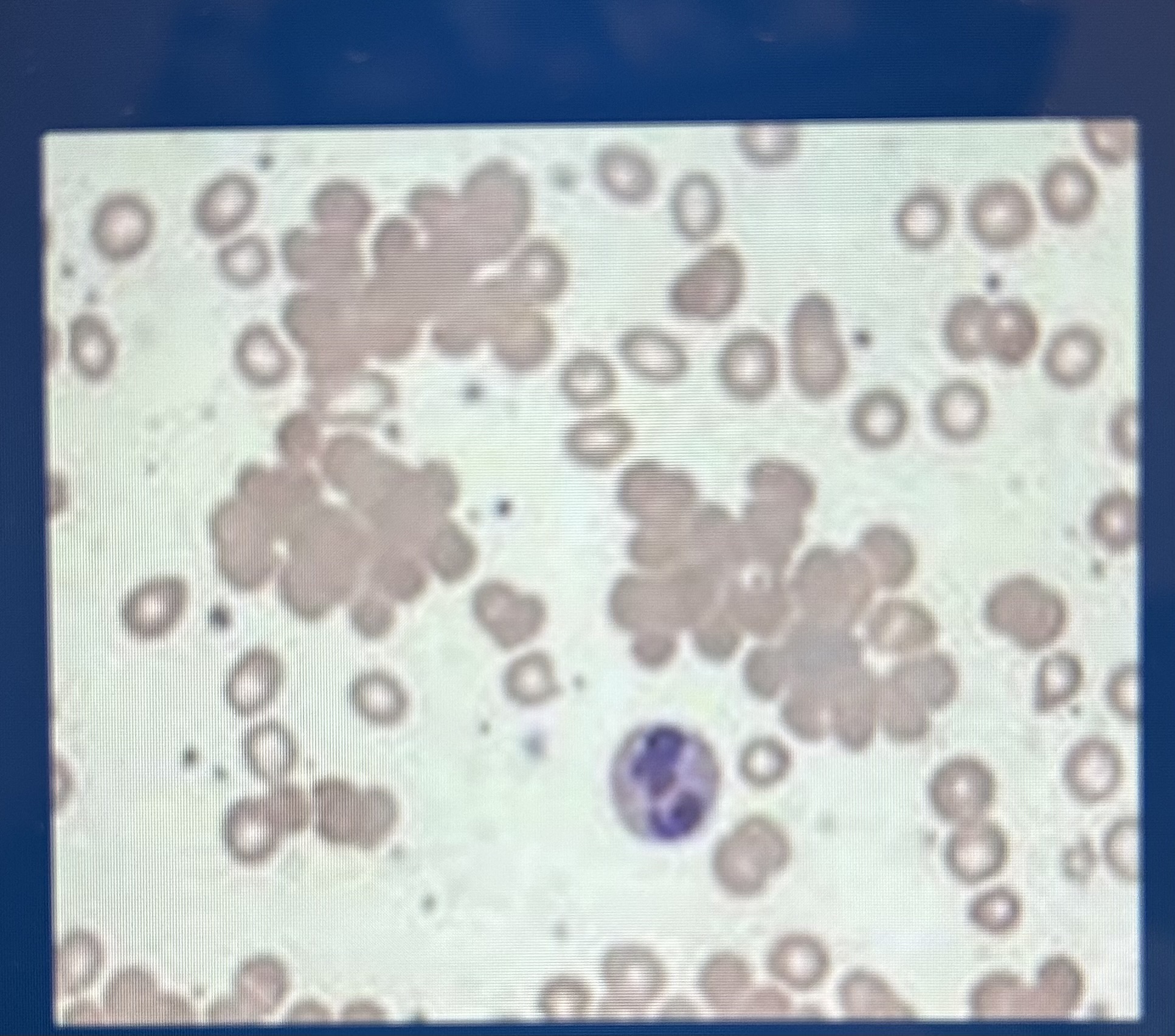
RBC clustering
Agglutination; could mean immune system disorders
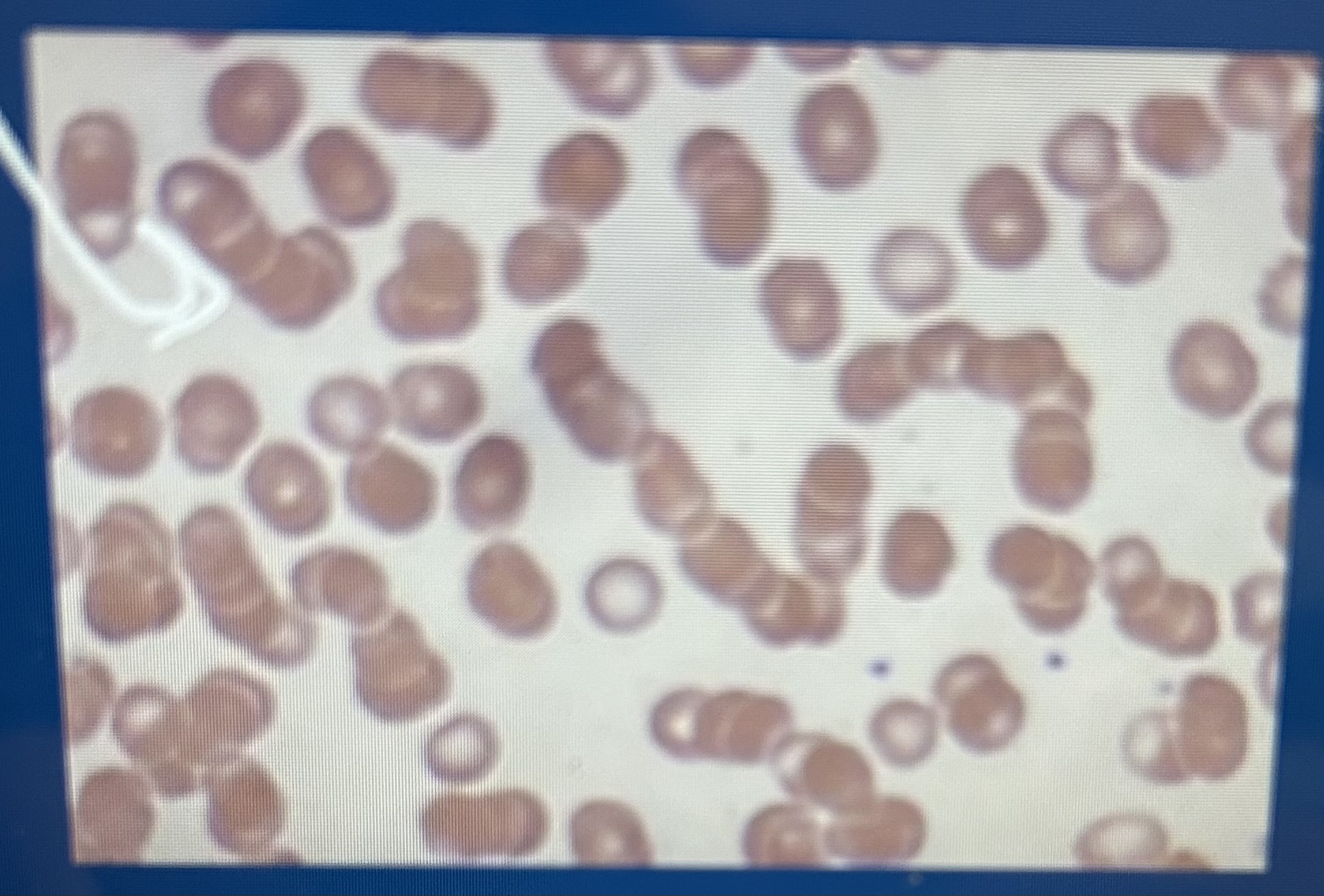
Rouleaux
Rbc stacked, normal equine blood