4.8 Stationary Waves
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Stationary Wave
A wave formed by superposition of waves with the same wavelength moving in opposite directions. They do not transfer energy
Their superposition creates constructive and destructive interference
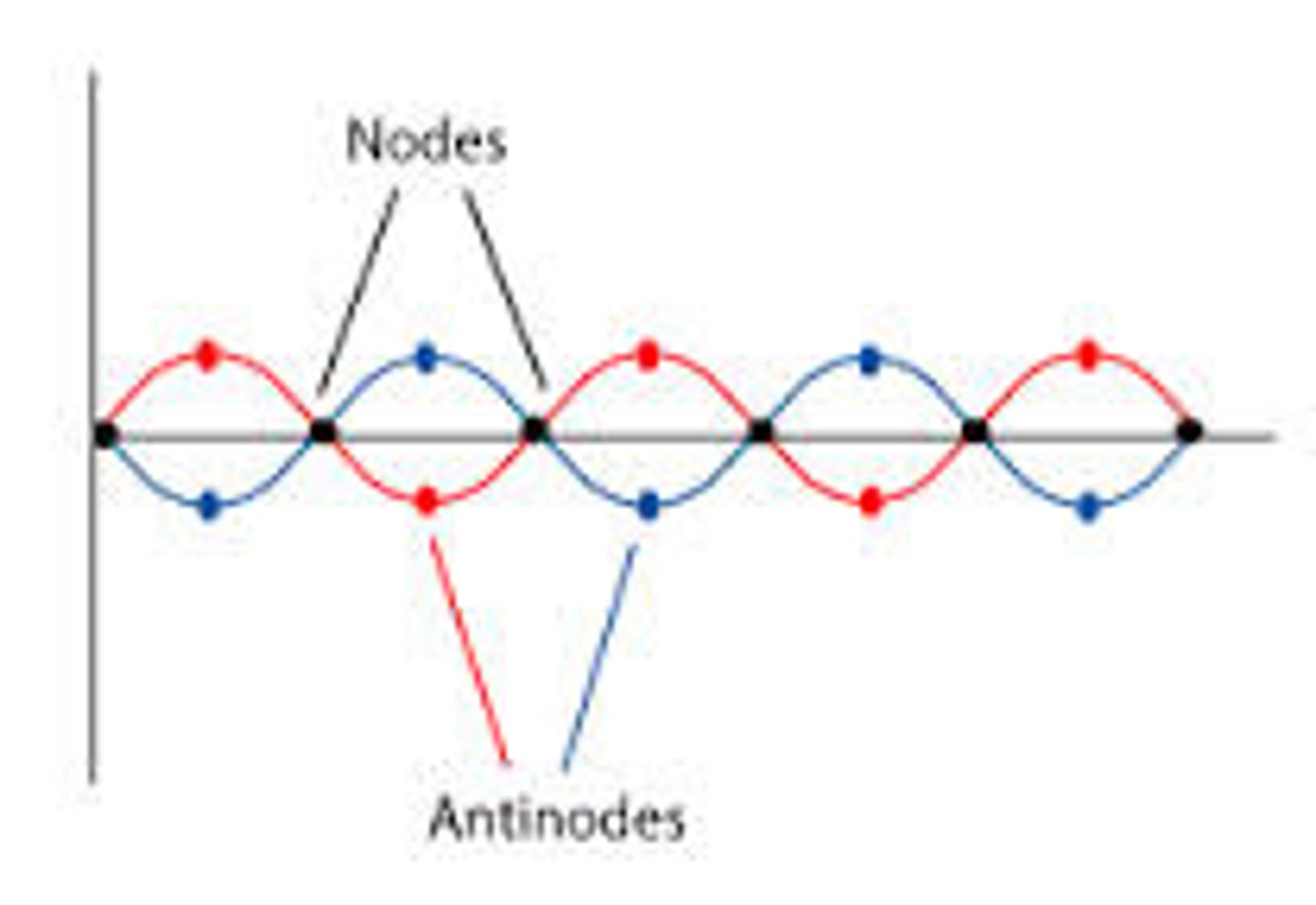
Nodes
Points of destructive interference where the two waves cancel each other out resulting in zero amplitude
Antinode
Points of constructive interference creating points of maximum amplitude
Fundamental mode of vibration (1st harmonic)
The lowest frequency in a harmonic series where a stationary waves forms.
Stationary Wave in Strings
Length of a string on a stationary wave is 1/2λ.
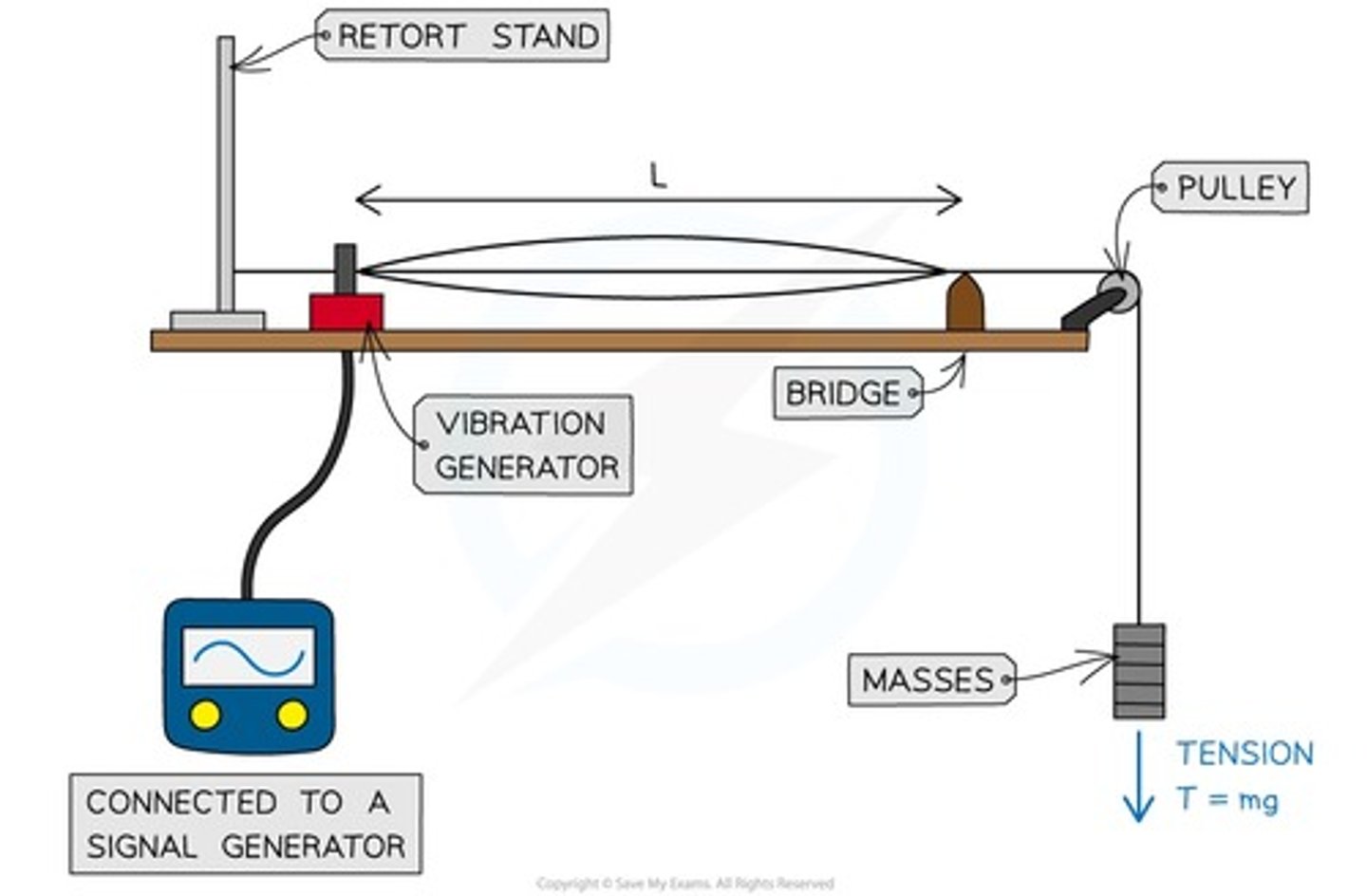
Calculating Wave Speed
v = (T/u)^1/2 (u=mass T= tension)
For the fundamental mode of vibration, the length of the string is equal to 1/2λ
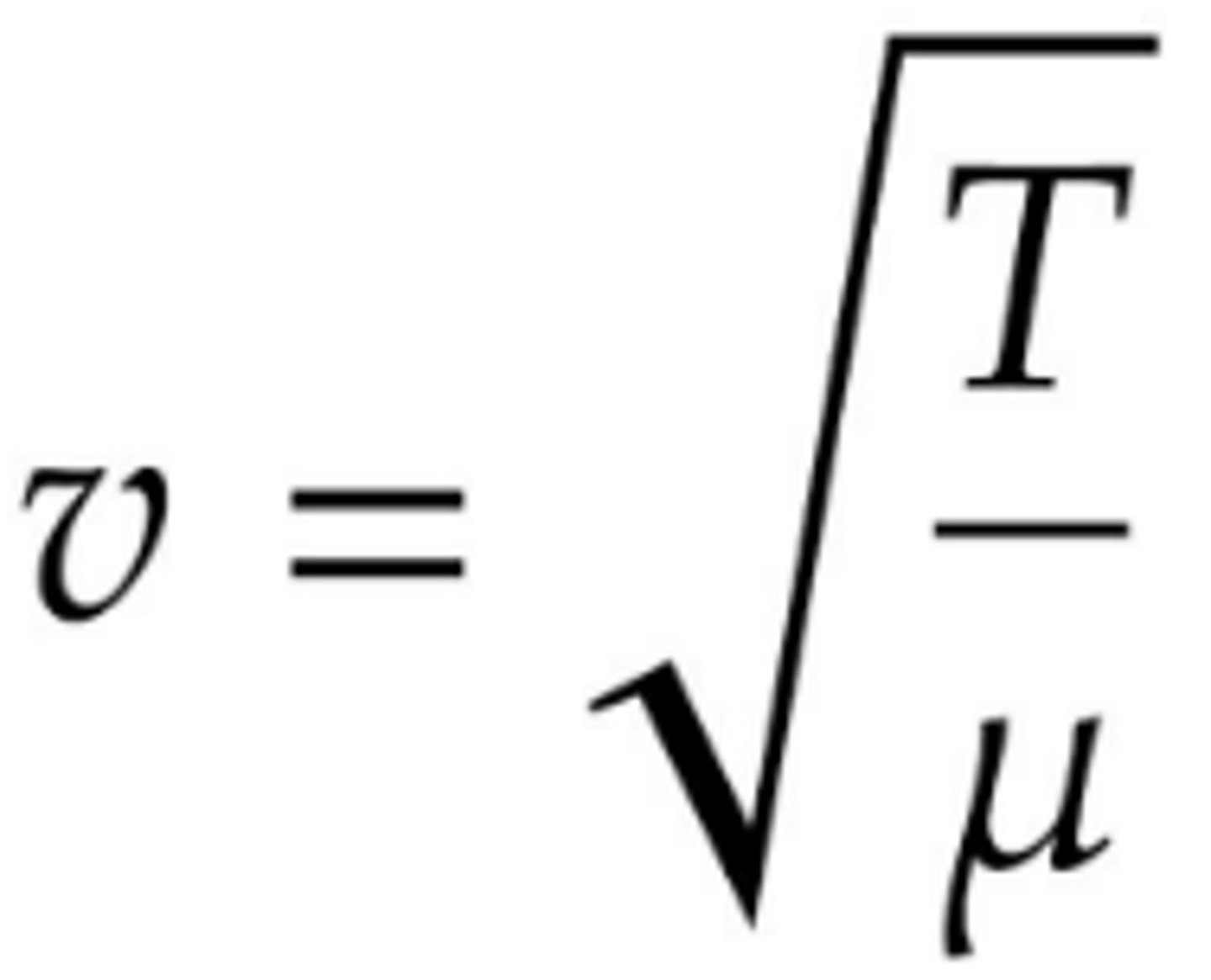
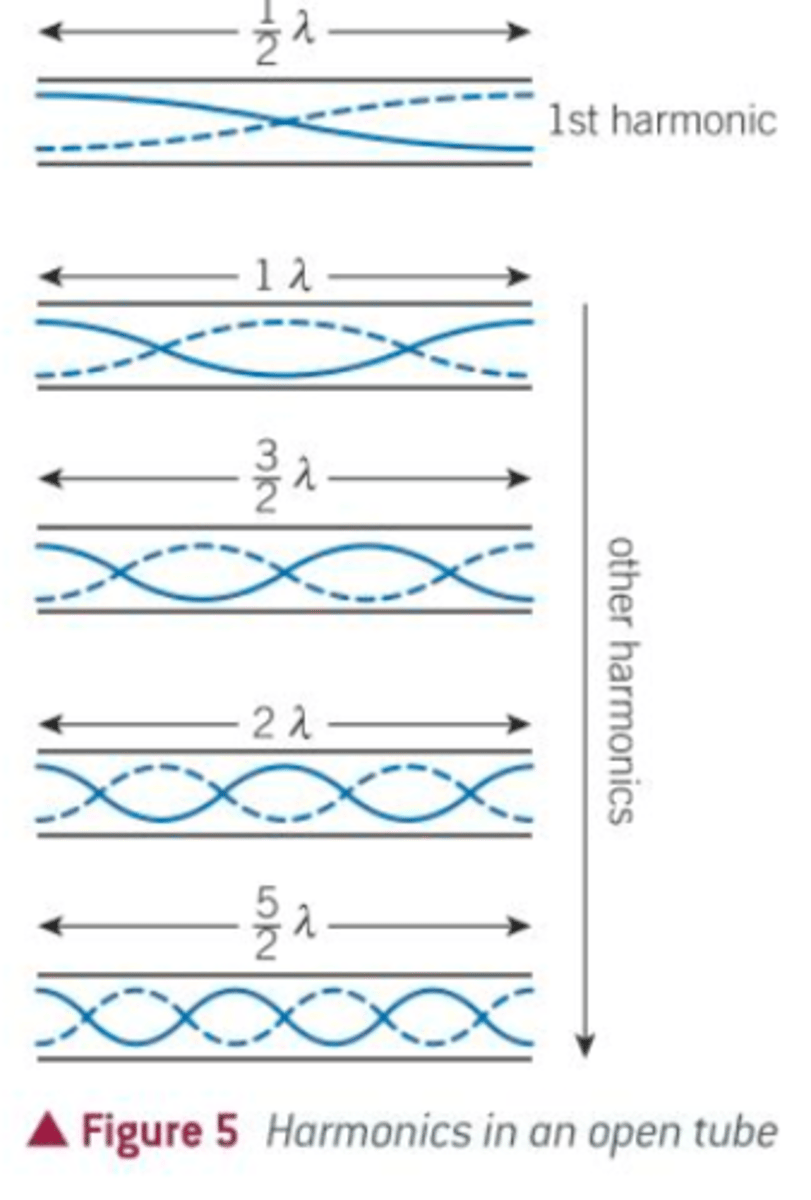
Stationary Waves At an Open Pipe
Antinodes occur at open ends
Lowest frequency is produced when length is 1/2 λ
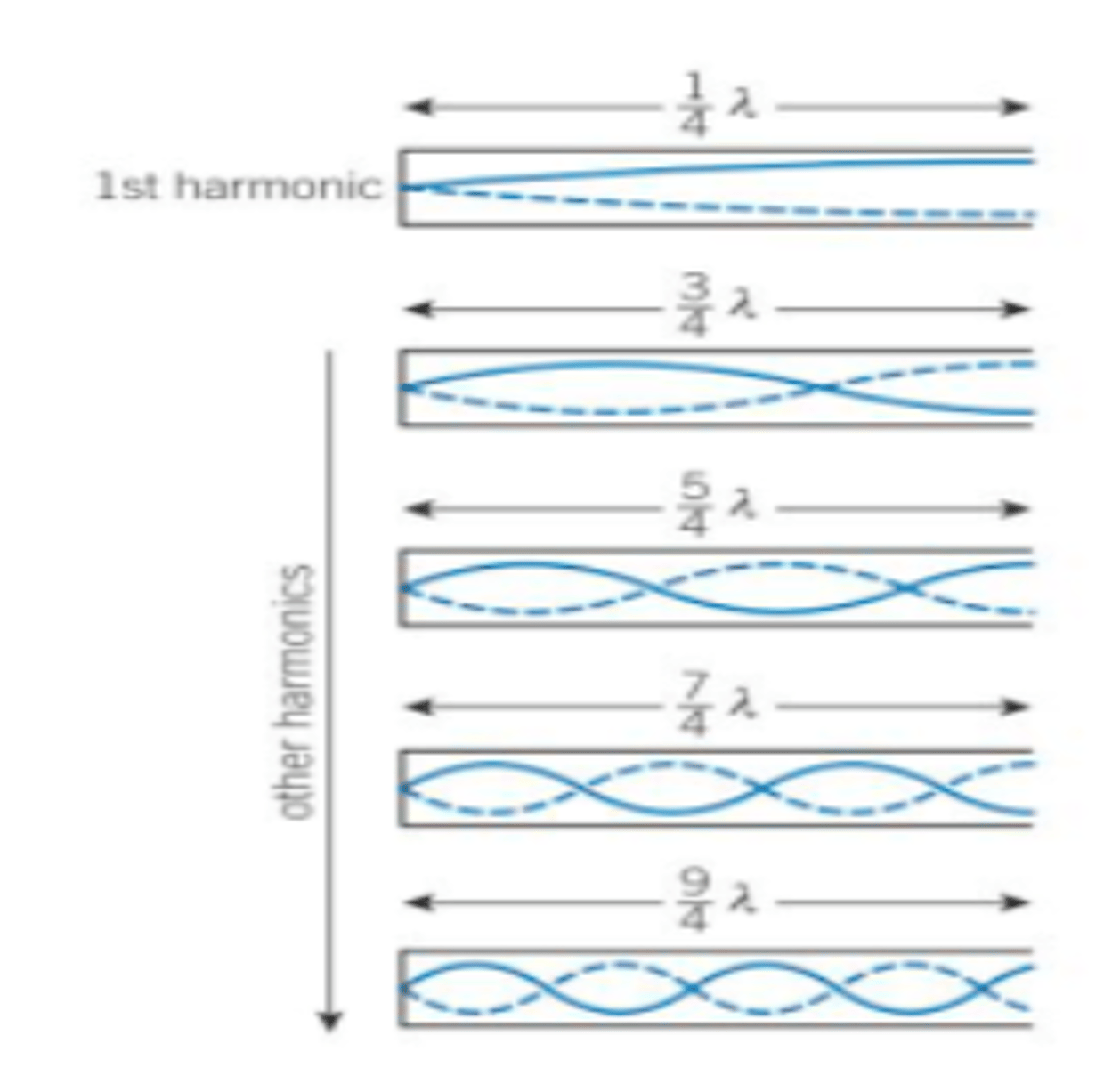
Stationary Waves At an Closed Pipe
Nopdes occur at both ends
Lowest frequency is produced at 1/4 λ
Resonance
Occurs when the frequency of the wave is equal to the natural frequency of air column
Constructive interference produces stationary waves
Dictated by pipe length