Unit 1 Exam: Proteins and DNA
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Proteins and DNA/January 27th, 2026
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
What subatomic particle allows for bonds to occur between atoms? How?
electrons allow for bonds to occur; they are shared (covalent) or transferred (ionic) between atoms to fill outer electron shells
Covalent Bonds
the strongest bond; involves sharing electron pairs between atoms
nonpolar covalent bonds: between two atoms of the same element and electronegativity
polar covalent bonds: between atoms of differing electronegativity
Ionic Bonds
formed by the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions (cations and anions)
Hydrogen Bonds
a weak attraction between a hydrogen atom with a slight positive charge is bonded to another electronegative atom
Van der Waals
weak, short-range attractions between nonpolar molecules due to transient local partial charges
Where do you find the different bonds along a polypeptide?
covalent bonds (peptide bonds): form the backbone
hydrogen, ionic, and Van Der Waals: stabilize the folded shape
What are the building blocks of protiens?
amino acids
What kind of bond links amino acids?
peptide bonds; multiple peptide bonds form a polypeptide chain
What part of an amino acid dictates its behavior?
the R-group (side chain) dictates the specific behavior (polar, nonpolar, acidic, basic)
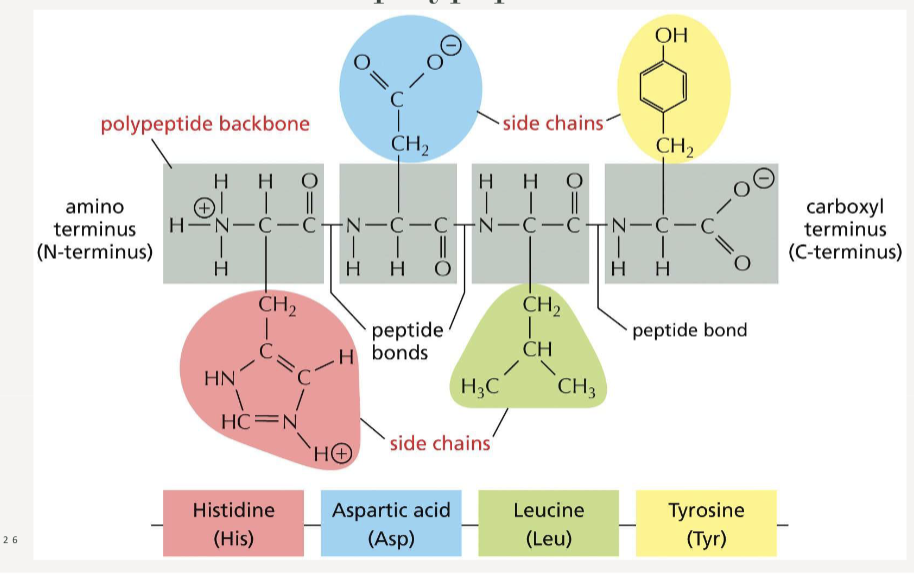
How many amino acids are there?
20, each with unique side chains
Name the polar side chains (Santa’s Team New Quilts Yearly)
Serine (S/Ser)
Threonine (T/Thr)
Asparagine (N/Asn)
Glutamine (Q/Gln)
Tyrosine (Y/Tyr)
Name the non-polar side chains (Grandma Always Visits Lagos In May For Winston’s Cheap Party)
Glycine (G/Gly)
Alanine (A/Ala)
Valine (V/Val)
Leucine (L/Leu)
Isoleucine (I/Ile)
Methionine (M/Met)
Phenylalanine (F/Phe)
Tryptophan (W/Trp)
Cysteine (C/Cys)
Proline (P/Pro)
Name the charged side chains (Dragons Eat Knights Riding Horses)
Aspartate (D/Asp)
Glutamate (E/Glu)
Lysine (K/Lys)
Arginine (R/Arg)
Histidine (H/His)
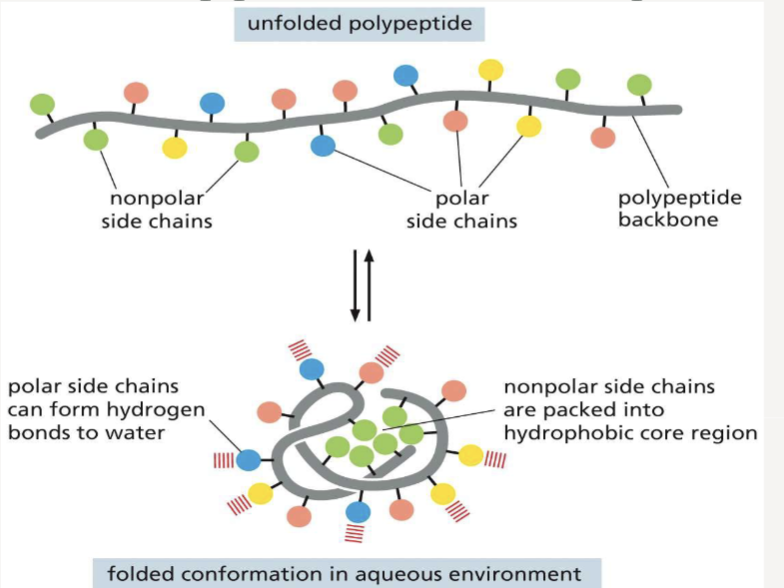
What helps proteins fold?
Non-covalent bonds and hydrophobic forces
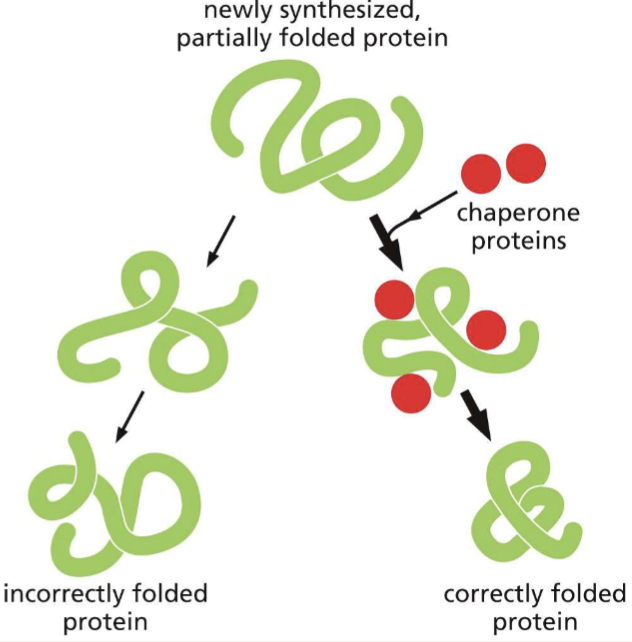
What is the purpose of a chaperone protein? Do proteins need them to fold?
assist with folding a newly synthesized polypeptide chain and act as an isolation chamber to help proteins fold; no
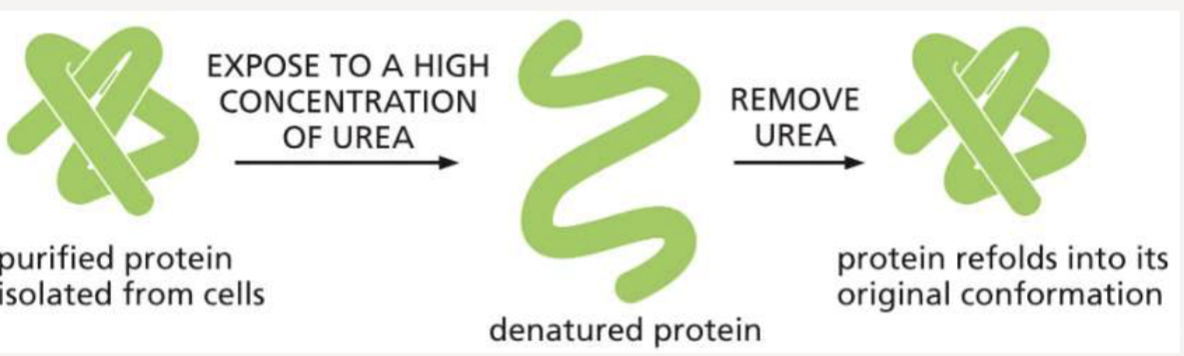
Why do denatured proteins refold?
can return to their natural folded state because the primary sequence contains all the information necessary for folding
What is one adverse effect of mis-folded proteins and why is it bad?
can form amyloid structures, which form prions that can aggregate and are toxic to cells; Alzheimers
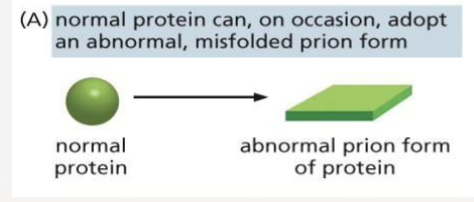
How many structural levels does a protein have?
4; primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary
Primary structure of amino acids
linear, specific sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain

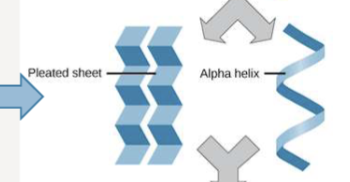
Secondary structure of amino acids
local folding patterns, made up of alpha helices and beta sheets, stabilized by hydrogen bonds in the polypeptide backbone
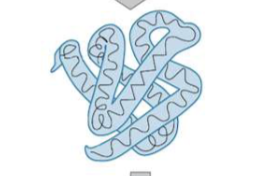
Tertiary structure of amino acids
the full 3D confirmation of a single polypeptide chain
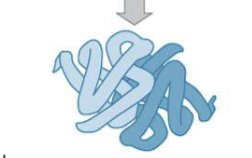
Quaternary structure of amino acids
the arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains into a functional complex
How do alpha helices form?
an amino group is hydrogen bonded to a carboxyl group 4 amino acids away
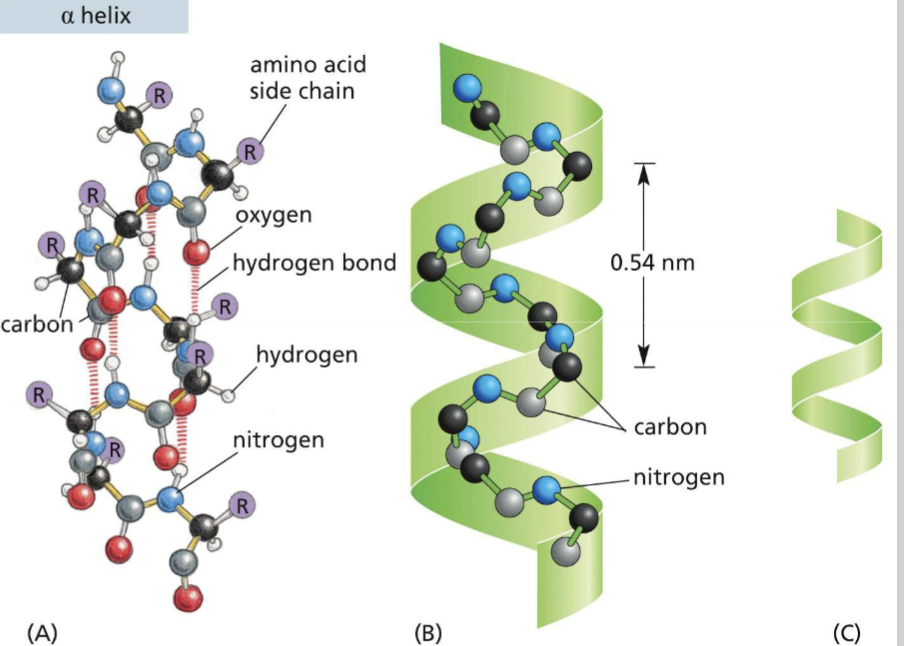
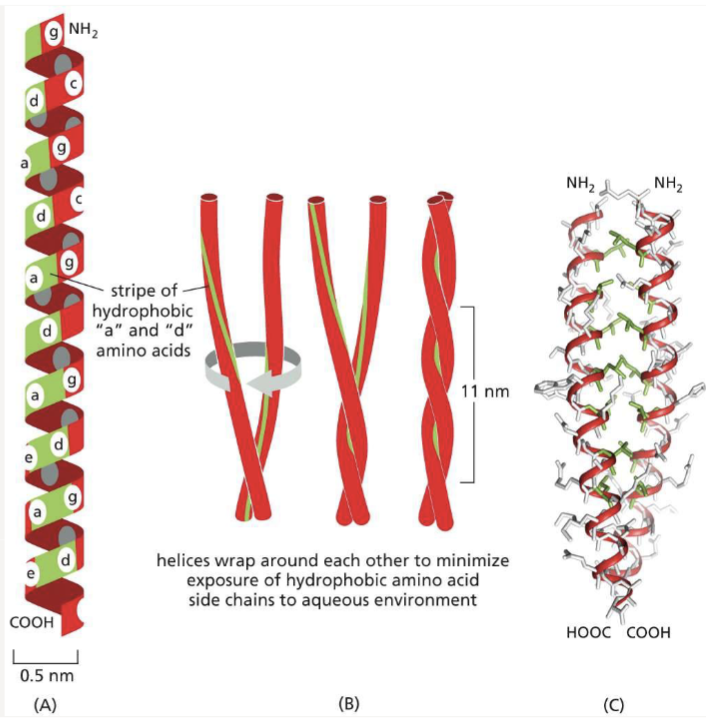
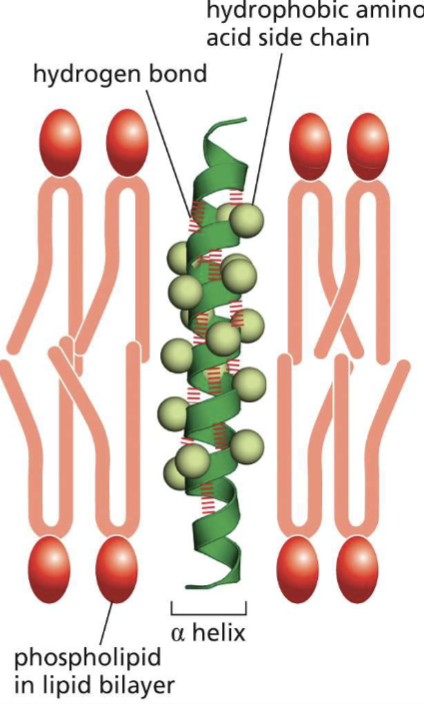
Where would you find nonpolar and polar amino acids along an alpha helix if:
it crosses a phospholipid bilayer?
forms a coiled coil?
the helix buries hydrophilic amino acids in the core and hydrophobic amino acids on the exterior interact with the phospholipid tail
helices wrap around each other to minimize exposure of hydrophobic amino acid side chains to aqueous environment
How do beta-sheets form?
held together by hydrogen bonds between amino acids that project above and below the plane of the sheet; can stack to form amyloid structures
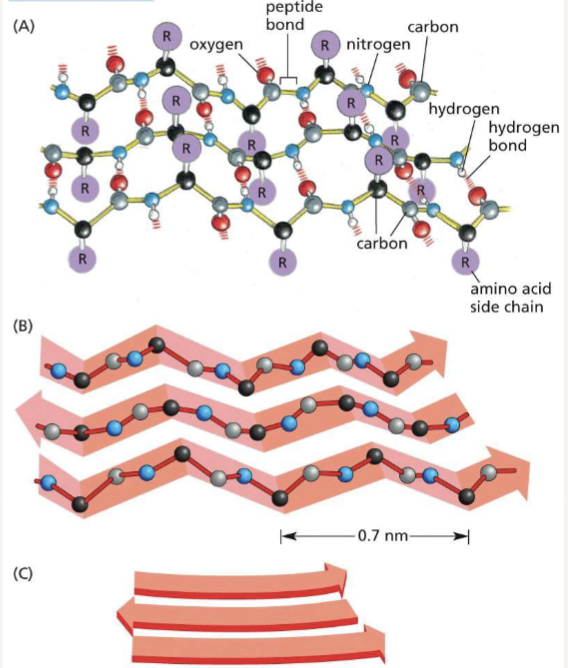
What is the difference between parallel and anti-parallel sheets?
parallel: adjacent strands run in same orientation
anti-parallel: adjacent strands run in opposite directions
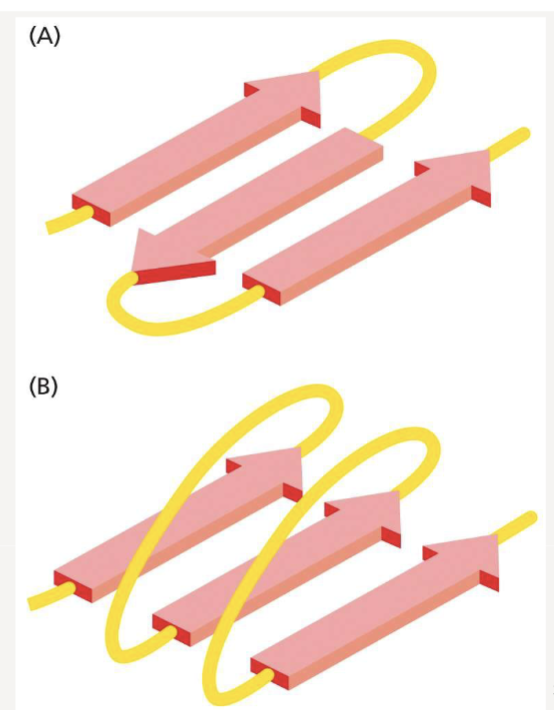
What would cause two proteins to be classified in the same family?
similar amino acid sequences and 3D structures
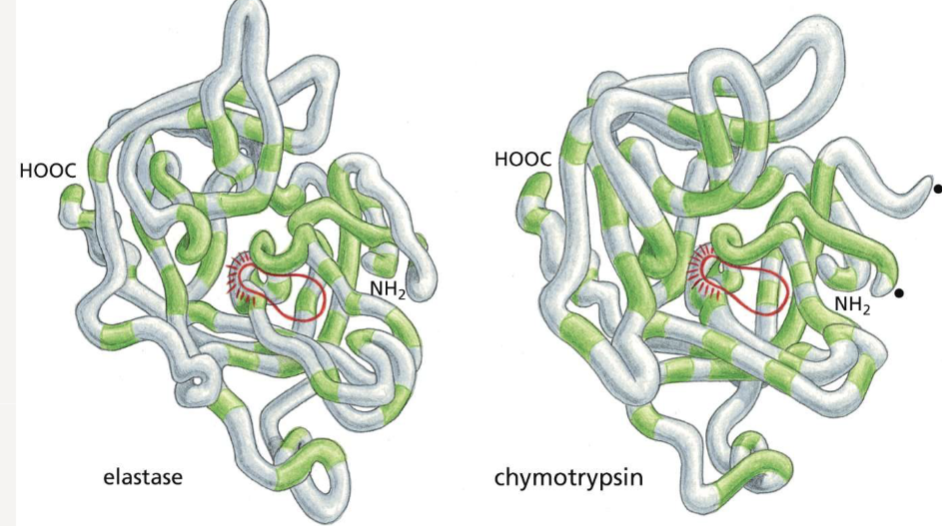
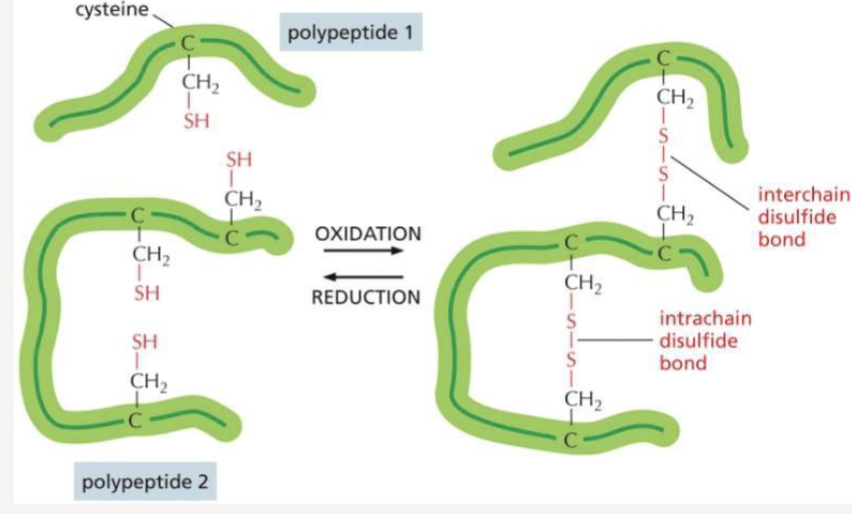
What do covalent crosslinks do to a protein?
stabilize protein structure, especially in harsh extracellular environments
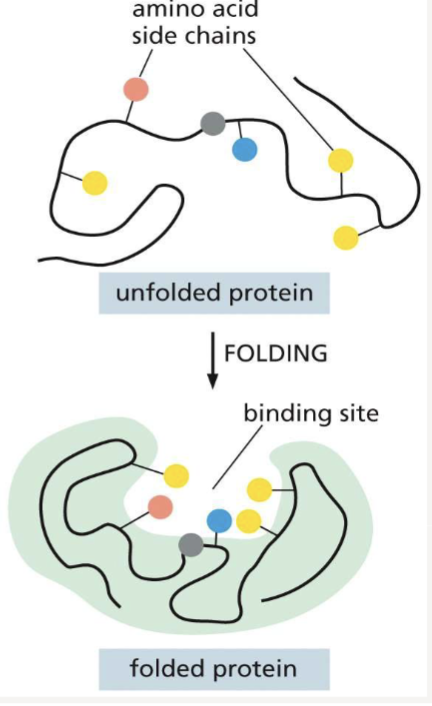
How does protein folding contribute to how a protein binds to ligands?
creates a pocket where other proteins can bind, binding sites allow interactions with specific ligands
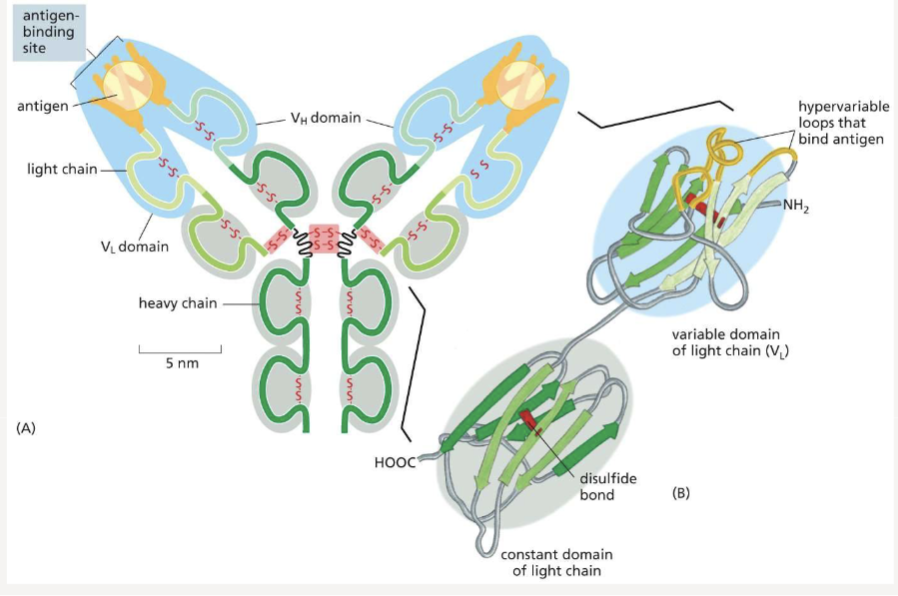
What portion of an antibody gives it specificity for its antigen?
polypeptides on the variable domains
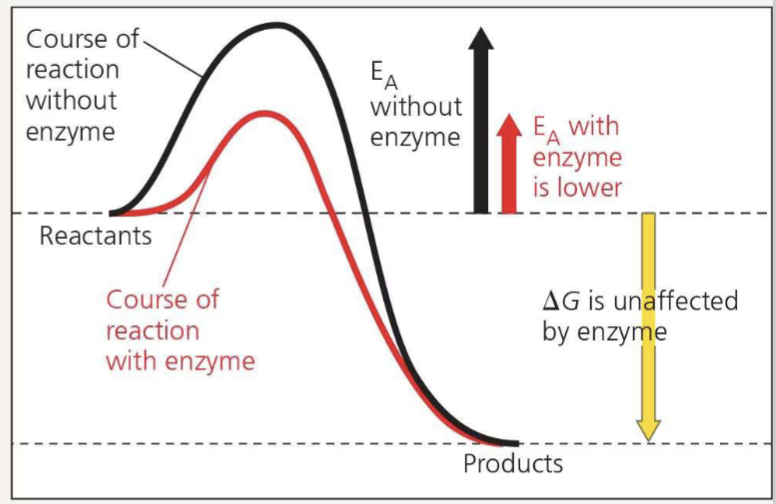
How do enzymes speed up reactions?
by lowering the activation energy
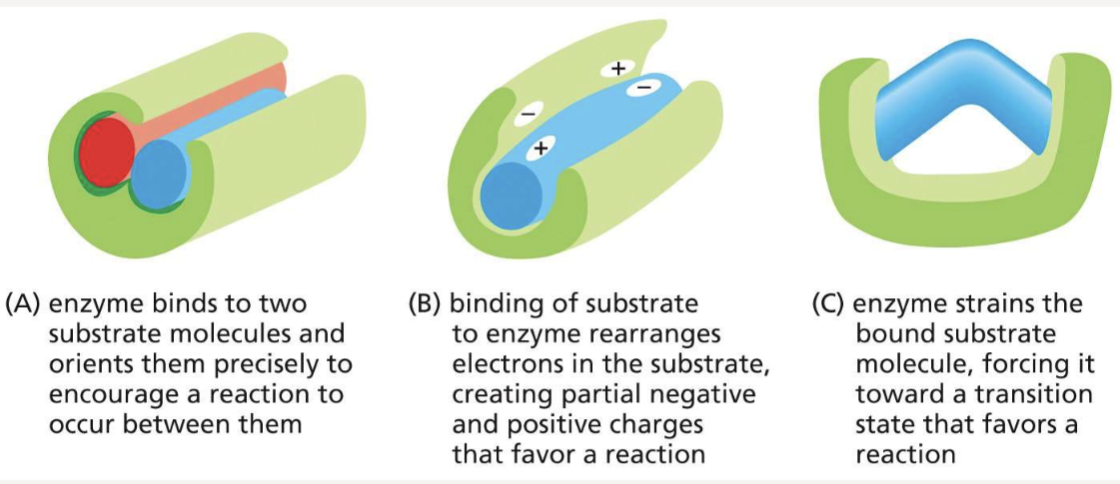
What are 3 ways enzymes can chemically change their substrates?
orient substrates, rearrange electrons, or bend bonds to reach a transition state
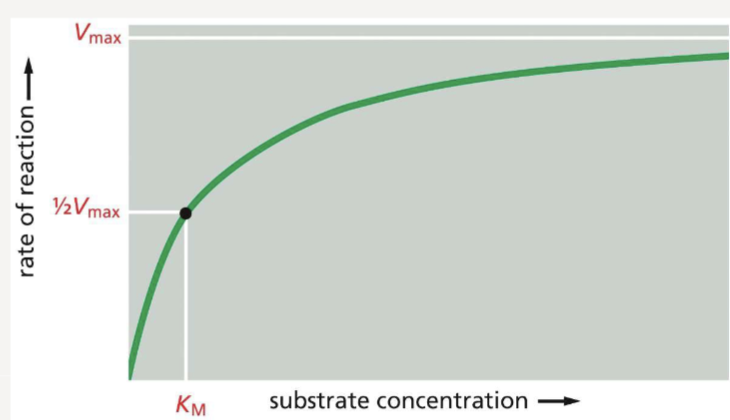
What is Vmax and KM ?
the maximum rate of an enzymatic reaction (reached when all enzymes are occupied by a substrate)
the concentration of substrate at which an enzyme works at half its maximum velocity
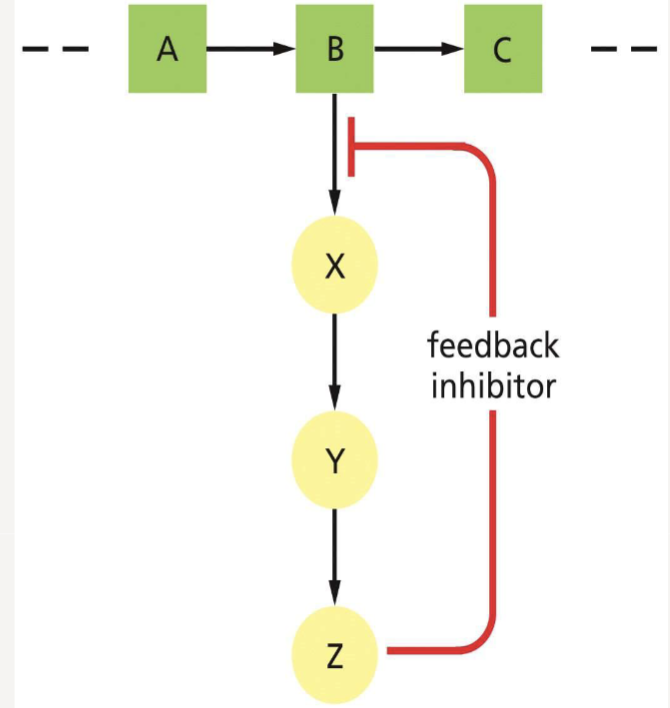
What is feedback inhibition?
regulates metabolic pathways; the end product of a pathway inhibits an upstream enzyme to prevent overproduction
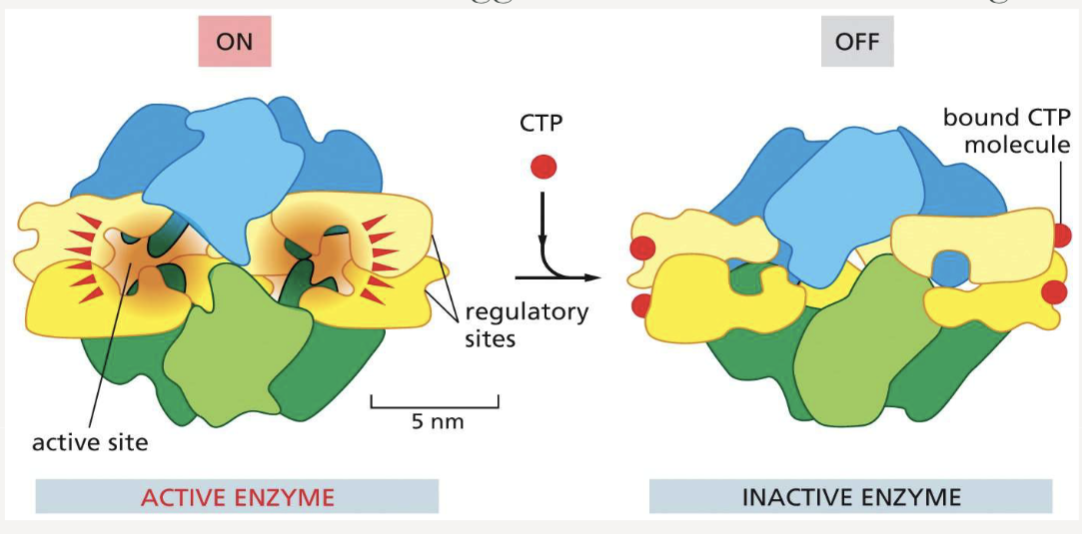
How can regulatory ligands dictate protein confirmation?
by binding to a site other than the active site, inducing a conformational change that turns the protein “on” or “off”
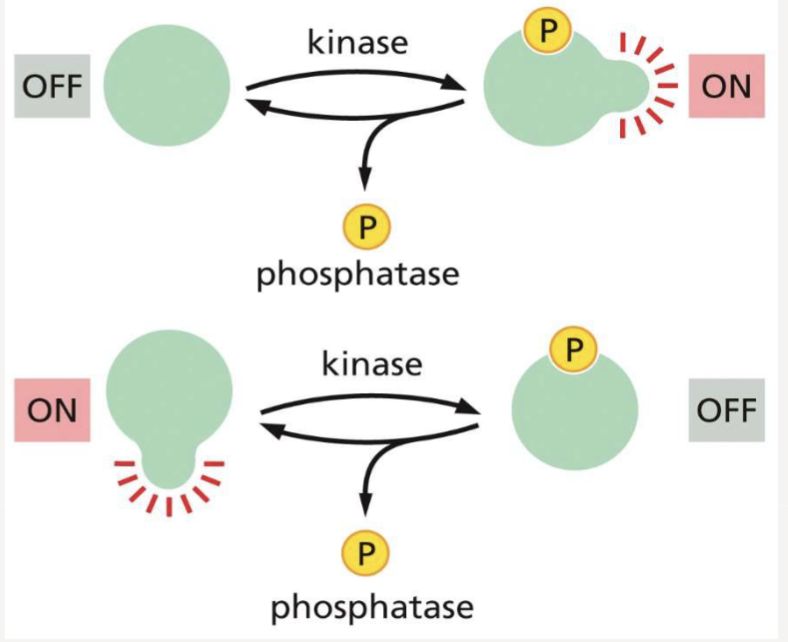
What is protein phosphorylation?
a common mechanism for regulating protein activity; the addition of a phosphate group by a kinase; removed by a phosphatase
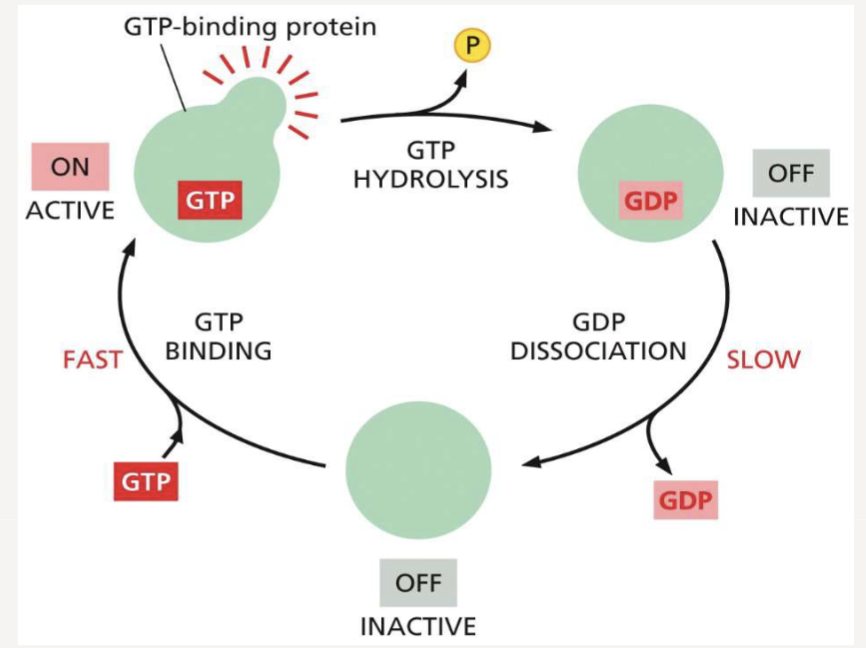
How does GTP act as a molecular switch?
proteins are active when bound to GTP and inactive when they hydrolyze it to GDP
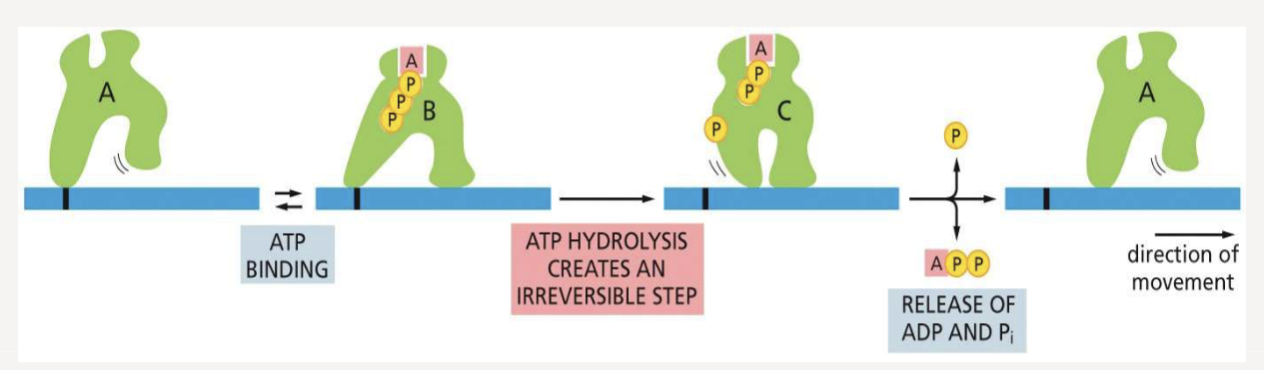
How does ATP hydrolysis help motor proteins move?
provides the energy and directional “step” needed for movement
How can protein modifications control protein behavior?
produce regulatory codes to control protein behavior
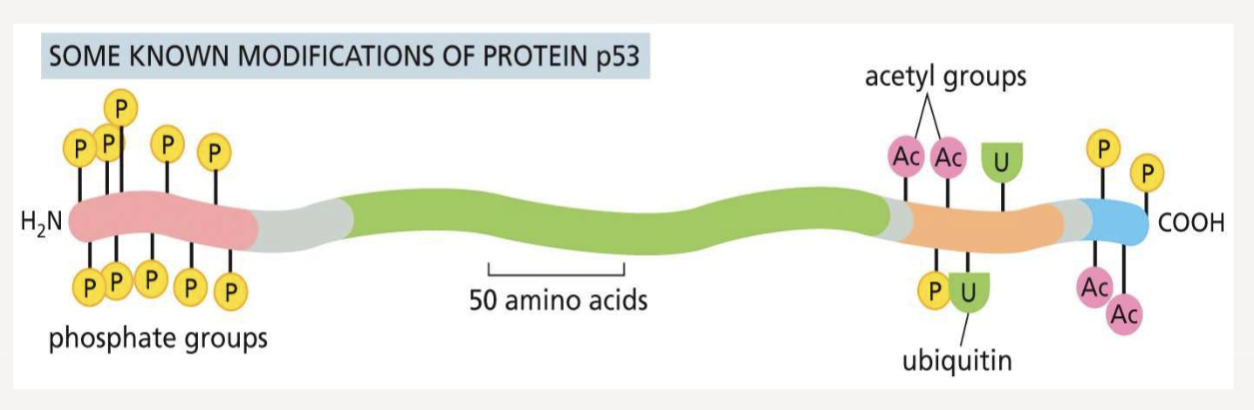
What happens when a protein phosphorylated?
the proteins activity can either increase or decrease
How does the GTP-bound form of a GTP-binding protein switch to a GDP-bound form?
it hydrolyzes GTP, releasing a phosphate
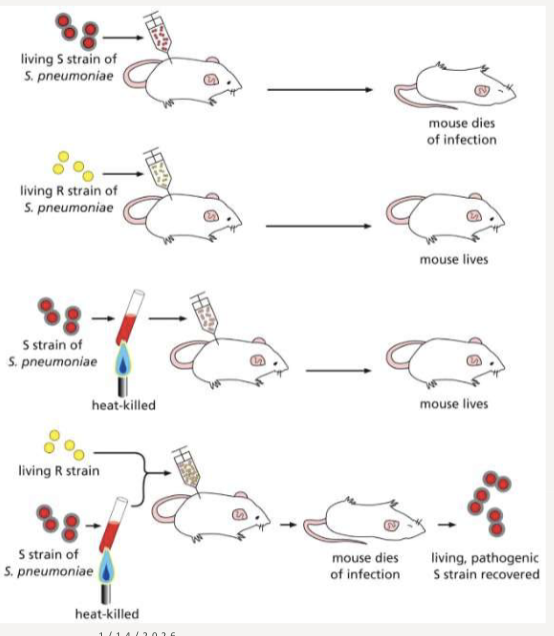
How did Fred Griffith’s heat-killed bacteria contribute to the discovery of DNA?
discovered bacteria could be transformed and made pathogenic; S strain and R strain
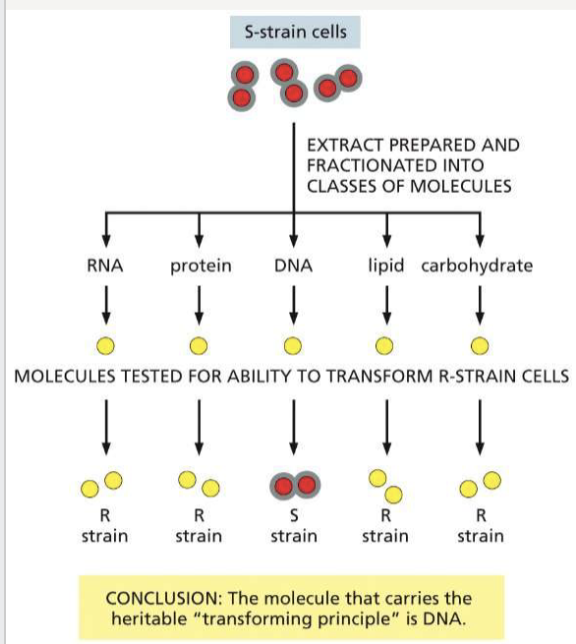
How did Avery, Macleod, and McCarty continue Griffith’s experiment?
separated various components of the cell (proteins, DNA, RNA) to determine what the transforming molecule was; provided first evidence that DNA could be genetic material
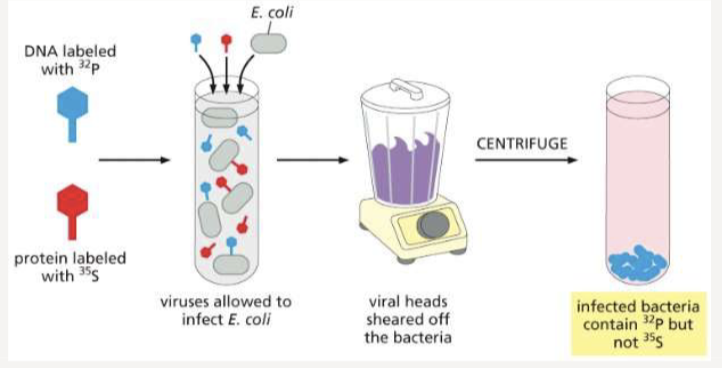
What were Hershey and Chase’s bacteriophages?
used radioactive labeling of bacteriophages to show that DNA enters the cell to direct viral replication
What are the building blocks of DNA?
nucleotides (4 in total)
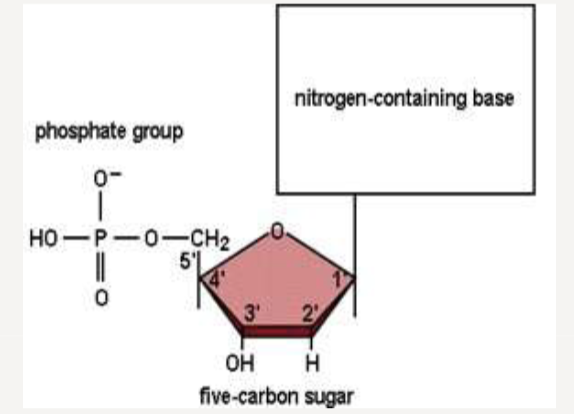
What are the different components of a nucleotide?
a nitrogenous base connected to the sugar phosphate deoxyribose; sugar phosphate backbone covalently links nucleotides
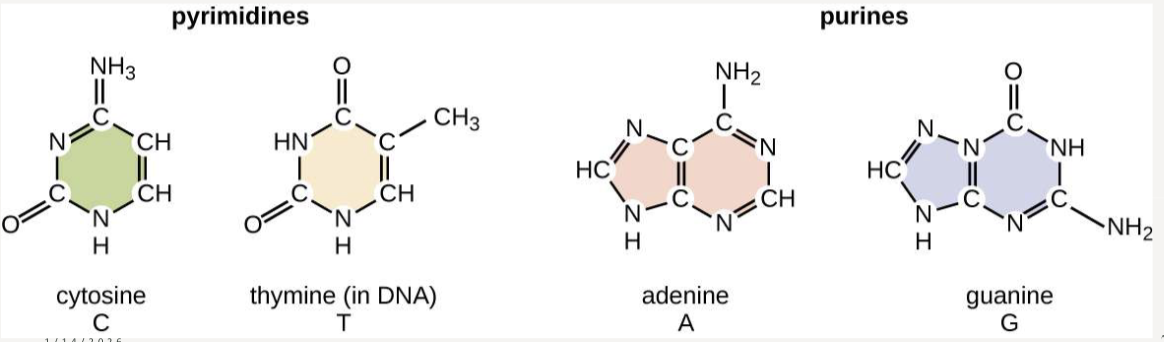
What are the different nucleotide structures?
pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine) and purines (adenine and guanine)
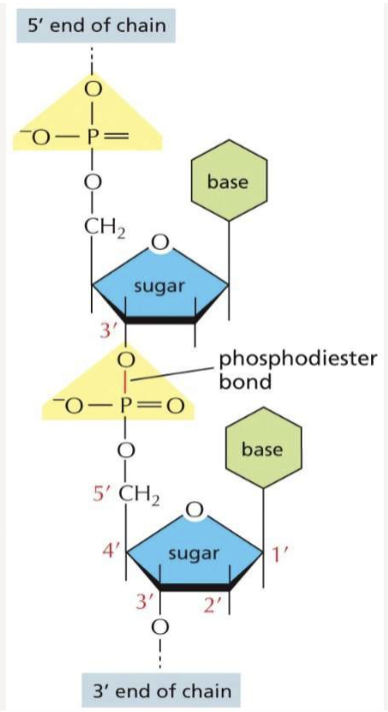
How do nucleotides connect to one another? What is the bond called?
held together by phosphodiester bonds that link 5’ of one sugar to the 3’ end of the next; bonded covalently; two polynucleotide chains are held together by hydrogen bonds and run antiparallel
How do nucleotides base pair? How many hydrogen bonds exist between each pairing?
A (adenine) pairs with T (thymine) to make 2 hydrogen bonds
C (cytosine) pairs with G (guanine) to make 3 hydrogen bonds
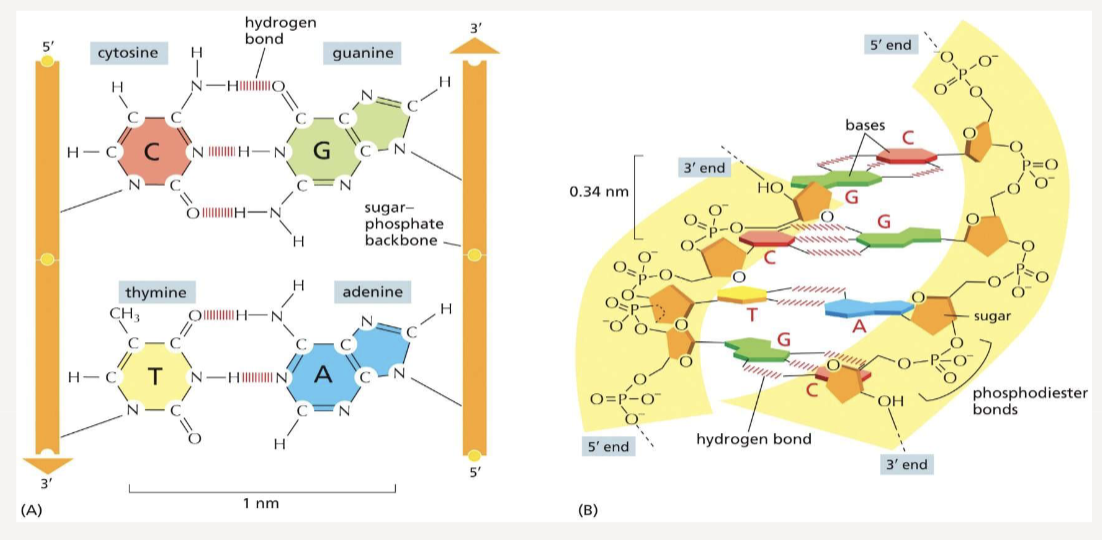
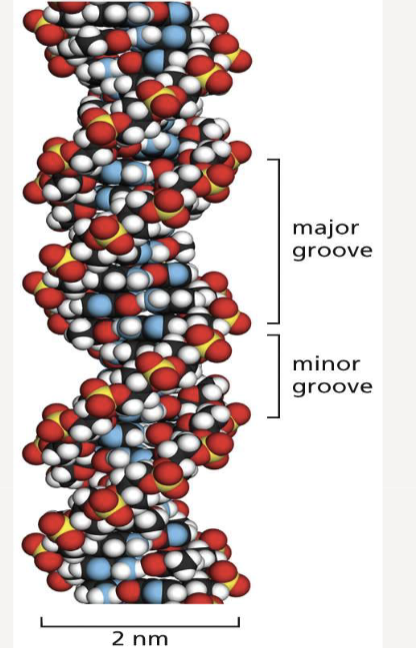
What structure does double-stranded DNA form?
two polynucleotide strands twist around each other to form a right-handed double helix
10 base pairs per helix turn
What proteins help DNA compact into chromosomes?
histone and non-histone proteins
Karyotype
an organism’s full set of chromosomes
22 autosomes that form homologous pairs and 1-2 gender chromosomes
Reciprocal Chromosomal Translocation
occurs when a portion of one chromosome swaps with another; often occurs in cancer cells
Genome
the complete set of an organism’s genes
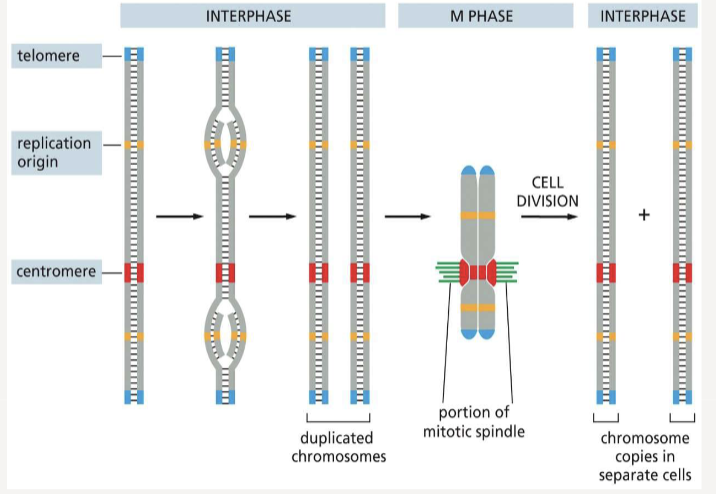
When are chromosomes in their most compact form?
mitosis
Replication Origin
the site where DNA replication begins
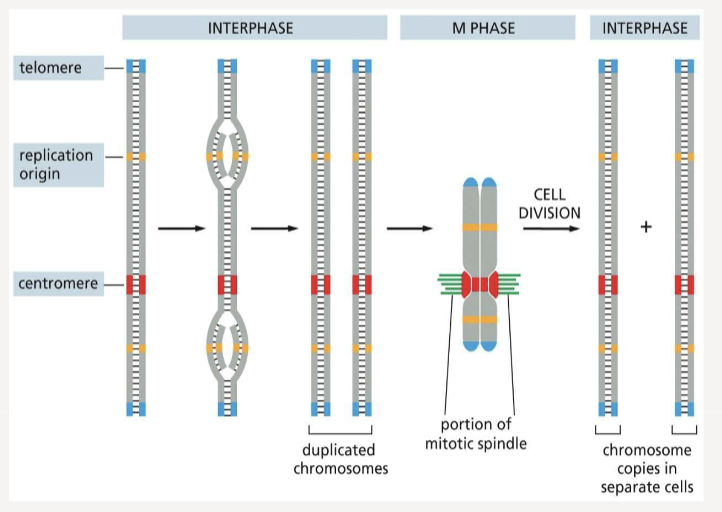
Centromeres
allow duplicated chromosomes to be separated during M phase
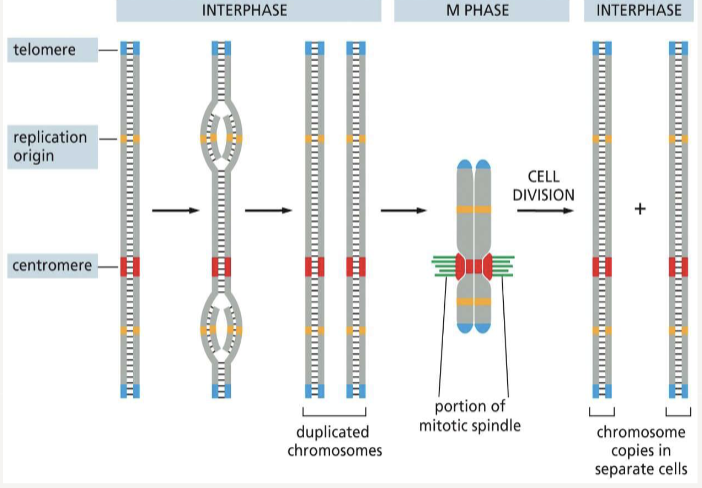
Telomeres
mark the end of each chromosome
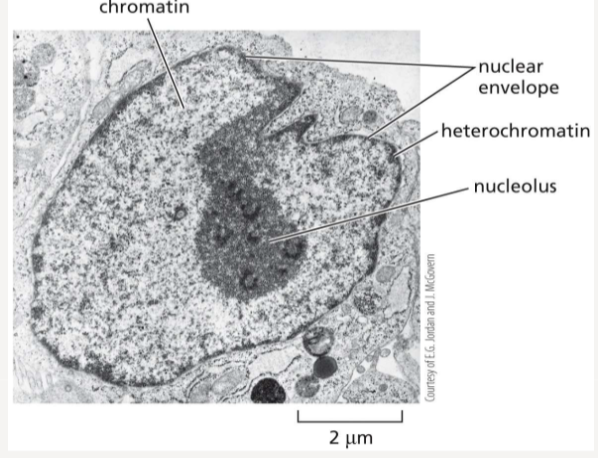
Nucleolus
a large structure within the nucleus where RNA is transcribed
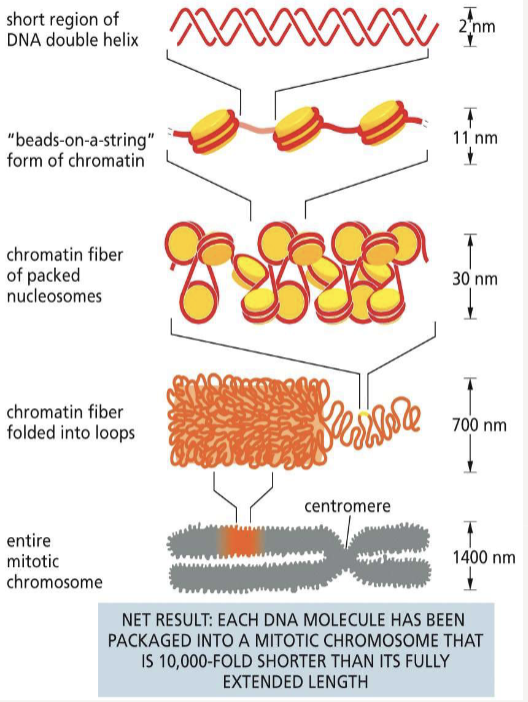
Histones
small proteins that DNA wraps around to form the nucleosome
What makes up of chromatin?
the complex of histones, non-histones, and DNA
Nucleosomes
beadlike structures of DNA wrapped around an octameric core of histone proteins; the basic unit of chromatin
What are the 8 histone proteins that the nucleosome core is made up of?
H2A, H2B, H3, and H4
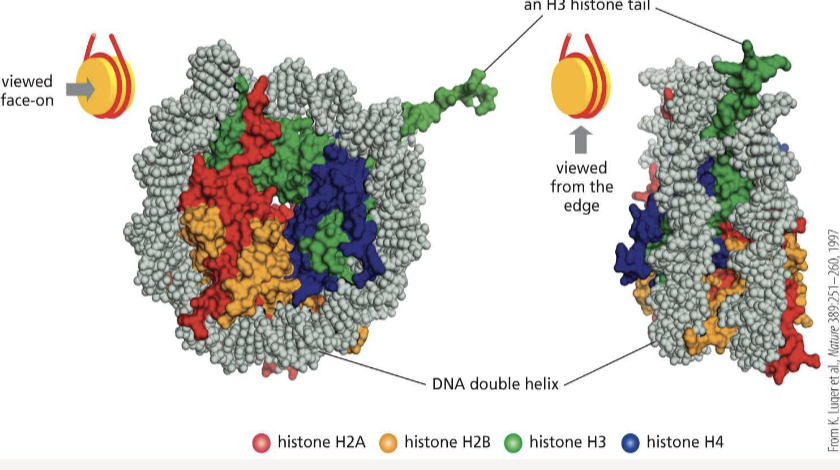
What does histone H1 do?
joins nucleosomes as a linker to pack DNA even tighter and alter the path it takes as it exits the nucleosome core
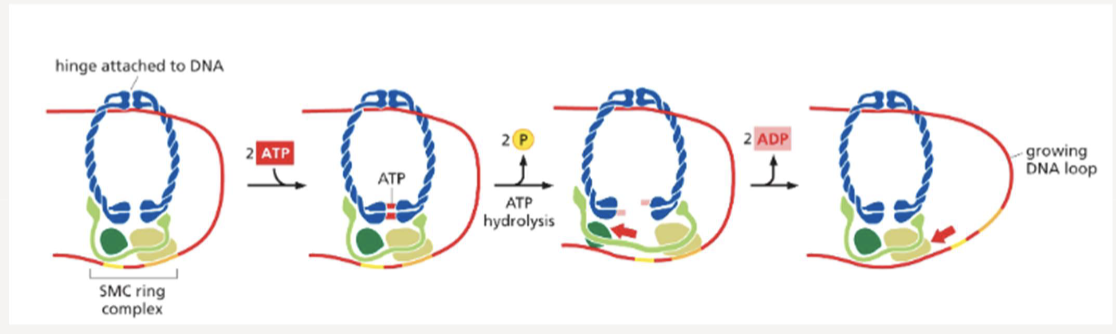
What do SMC proteins do? How do they work?
form a ring with additional proteins that chromatin fibers can pass through; use ATP hydrolysis to form the chromosome loops
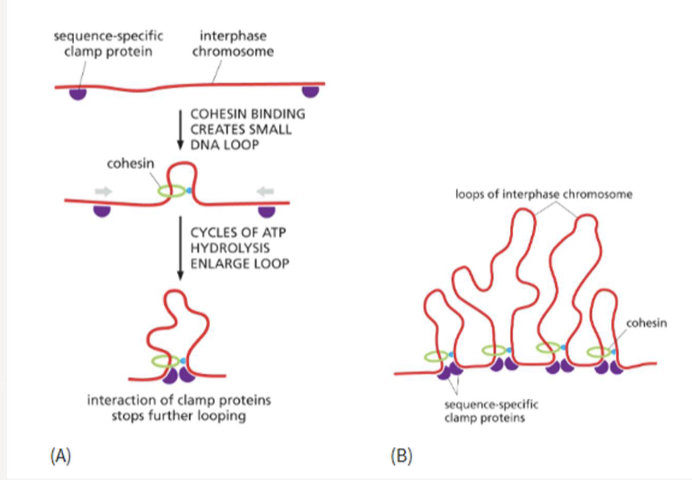
What do cohesion rings do? How are they stopped?
travel along DNA creating loops until they encounter a sequence-specific clamp protein that stops it and bring DNA together at the base of each loop
holds sister chromatids together
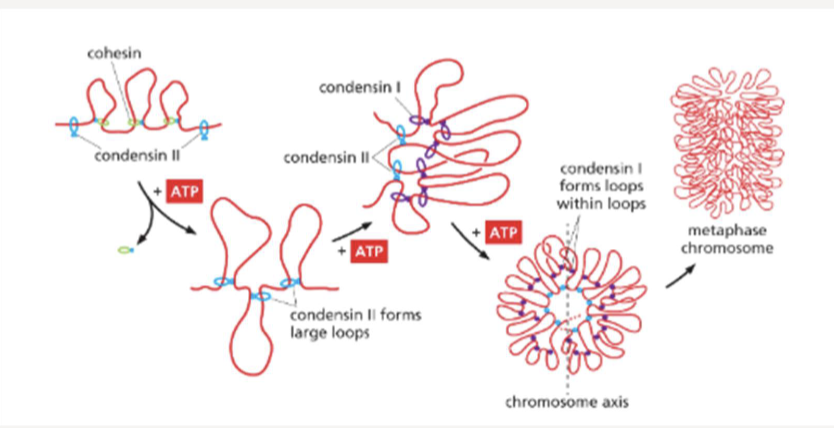
What do condensin rings do? When do they appear?
replaces cohesin and form loops within loops to further pack DNA during mitosis
What is true about the relationship between histones and DNA?
Histones have positively charged amino acids that are attracted to negatively charged DNA
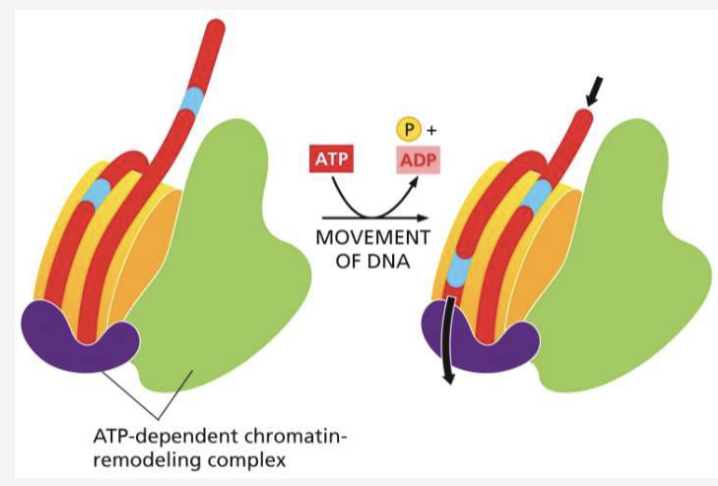
What do chromatin-remodeling complexes do? How do they work?
use ATP hydrolysis to slide DNA onto histones, making it more or less accessible
1 chromatin remodeling complex for every 5 nucleosomes
What do histone-modifying enzymes do? How do they work?
add/remove chemical groups to histone tails to signal expression or silencing
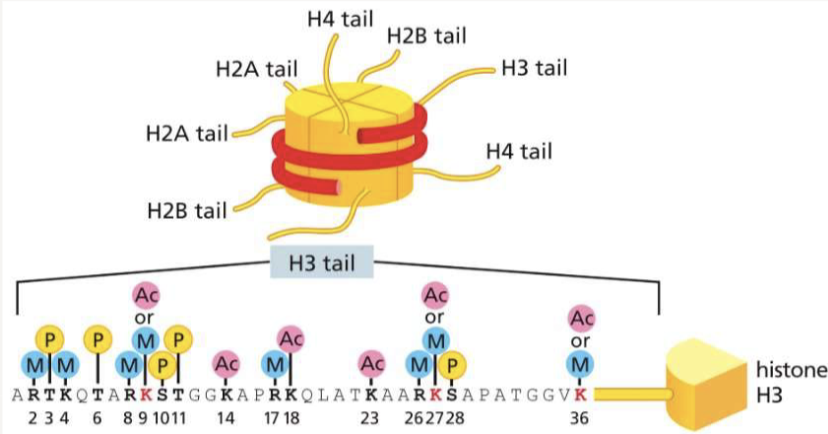
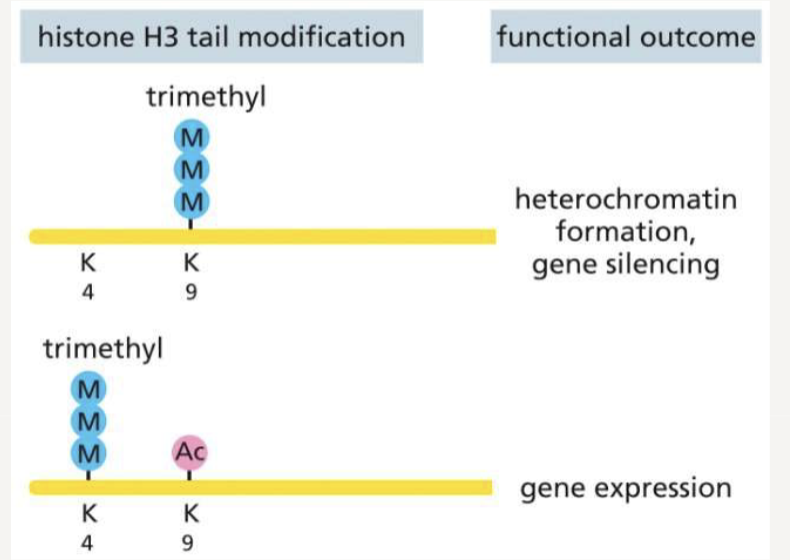
What are the histone H3 tail modifications and their functional outcome?
trimethylation of H3K9 leads to heterochromatin formation and gene silencing
trimethylation and acetylation of H3K4 and H3K9 - leads to gene expression
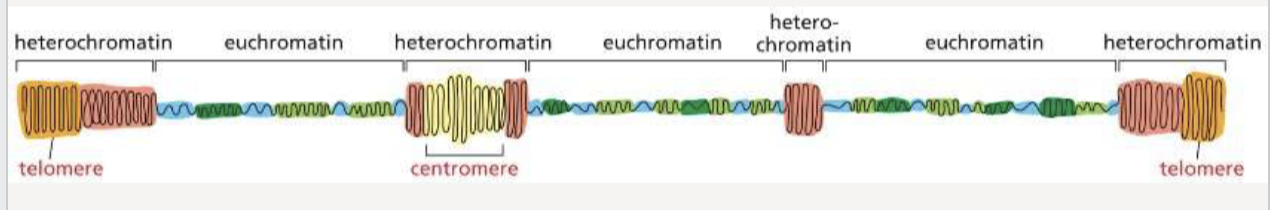
What is the difference between heterochromatin and euchromatin?
the most condensed form of chromatin found in centromeres and telomeres
prevalent in gene-rich areas and is less compact
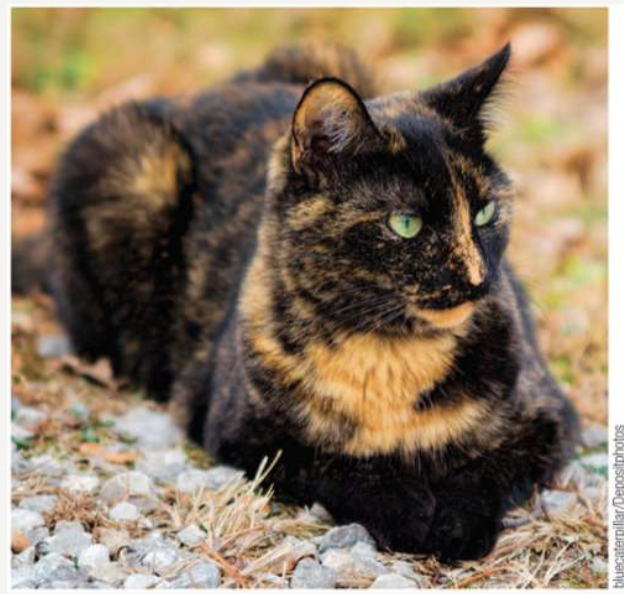
What is X-inactivation?
a process in female mammals where one X chromosome is highly condensed into heterochromatin to balance gene dosage; is inactive and random

What does epigenetic inheritance mean?
the transmission of gene activity from generation to generation
Where would you NOT expect to find heterochromatin?
protein-coding regions of DNA