A Level AQA 4.9 Fundamentals of communication and networking | 4.9.1 Communication and 4.9.2 Networking
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What is serial data transmission
Bits are sent one after another along the same line
Examples of serial data transmission
Mouse joystick
Modem link
What is parallel data transmission
Several bits are sent simultaneously along sperate lines or channels
(Faster but with drawbacks)

Examples of parallel data transmission
Local printer
Scanner
Hard drive
Two problems with parallel data transmission
Skew
Crosstalk
What is skew
As every wire has slightly different properties, hence meaning bits travel at slightly different speeds
What is corsstalk
Refers to electromagnetic interference between two adjacent channels or parallel wires.
It gets more pronounced as the frequency increases
Why do these issues of Skew and Crosstalk’s occur
As data gets sent across multiple lines
Serial VS Parallel transmission
(Parallel Faster but with drawbacks so good for short range serial the opposite)
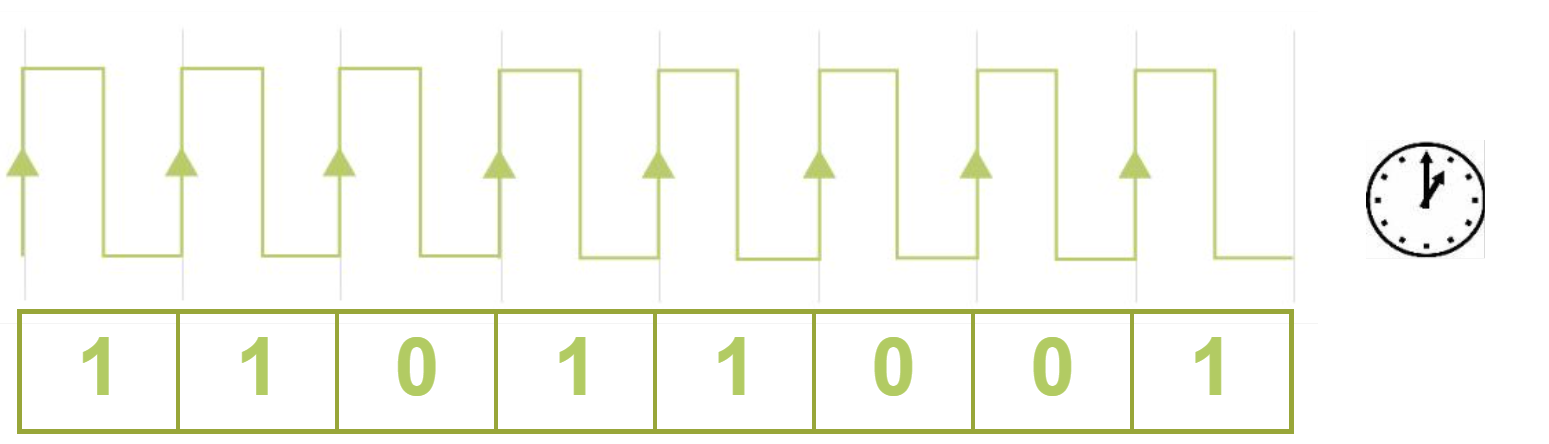
Synchronous transmission
All data transfers are timed to coincide with an internal clock pulse.
(The data is sent as one long stream or block data, with no gaps in the transmission. The receiver counts the bytes to reconstruct the bytes)
Asynchronous transmission
Each byte is sent separately the moment it is available instead of waiting for a clock signal

The parity bit
It is added as the 8th bit as a form of error detection
(Odd ore even parity bits could be used )

Synchronous vs Asynchronous transmission
Image talks about asynchronous
for synchronous just say the opposite of asynchronous

Define Baud rate
Is the number of signal changes per second in a communication channel.
Define Bit rate
Ss calculated as baud rate × number of bits per signal unit.
Define Bandwidth
Is the range of frequencies available for data transmission.
Define Latency
The time delay between the moment the first byte or packet of a communication starts and when it is received at its destination.
Define Protocol
The set of rules relating to communication between devices
List examples of what the protocol needs to define
Standards of physical connections and cabling
The rate of transmission (bit rate or baud rate)
Data format
Whether transmission is synchronous or asynchronous
The differences between Baud rate and Bit rate
Baud rate differs from bit rate, as bit rate considers the number of bits transmitted while baud rate does not.
The relationship between Bit rate and bandwidth
Bit rate is directly proportional to bandwidth in a communication channel.
(So higher bandwidth means more bits are allowed to be transmitted per second, increasing data transfer speed.)
What is a computer network
A system of interconnected devices that share resources and data. Networks can be wired or wireless and vary in scale
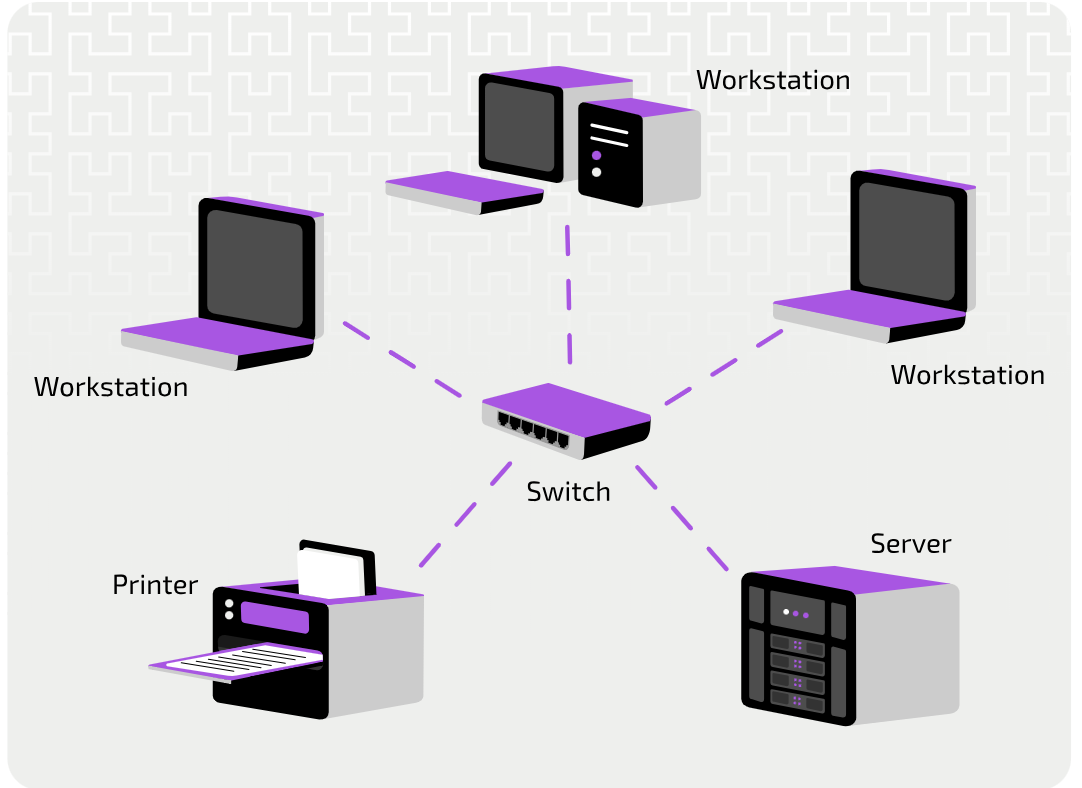
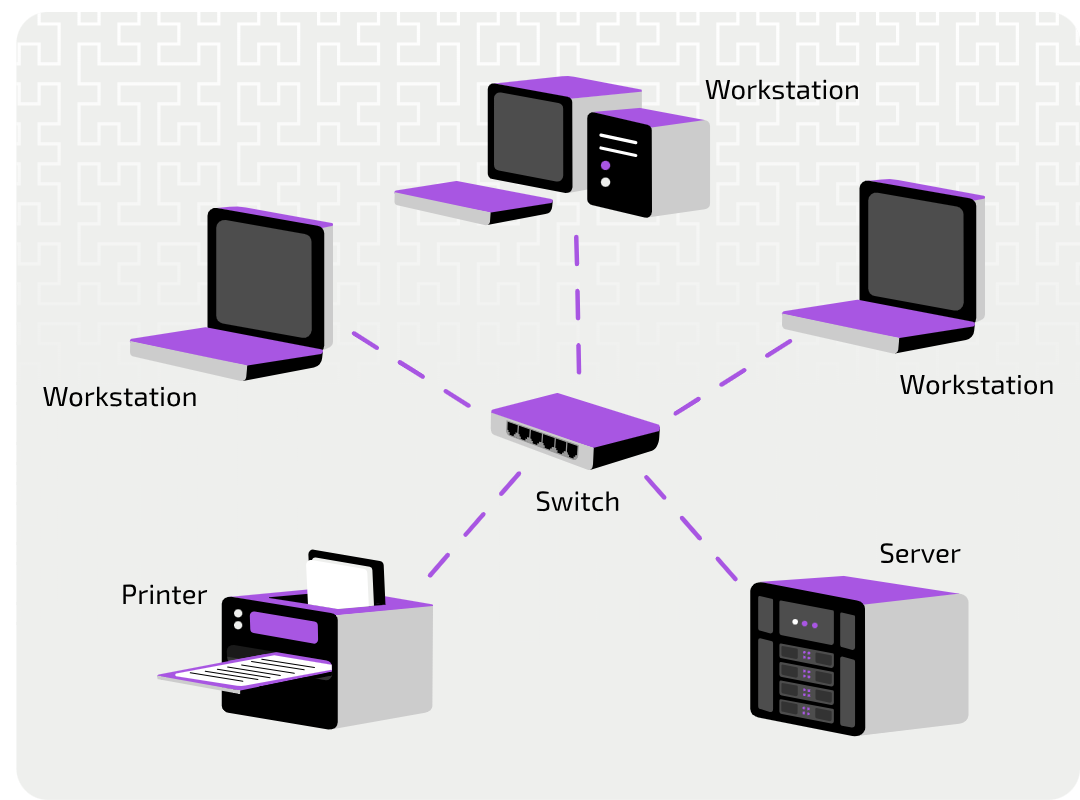
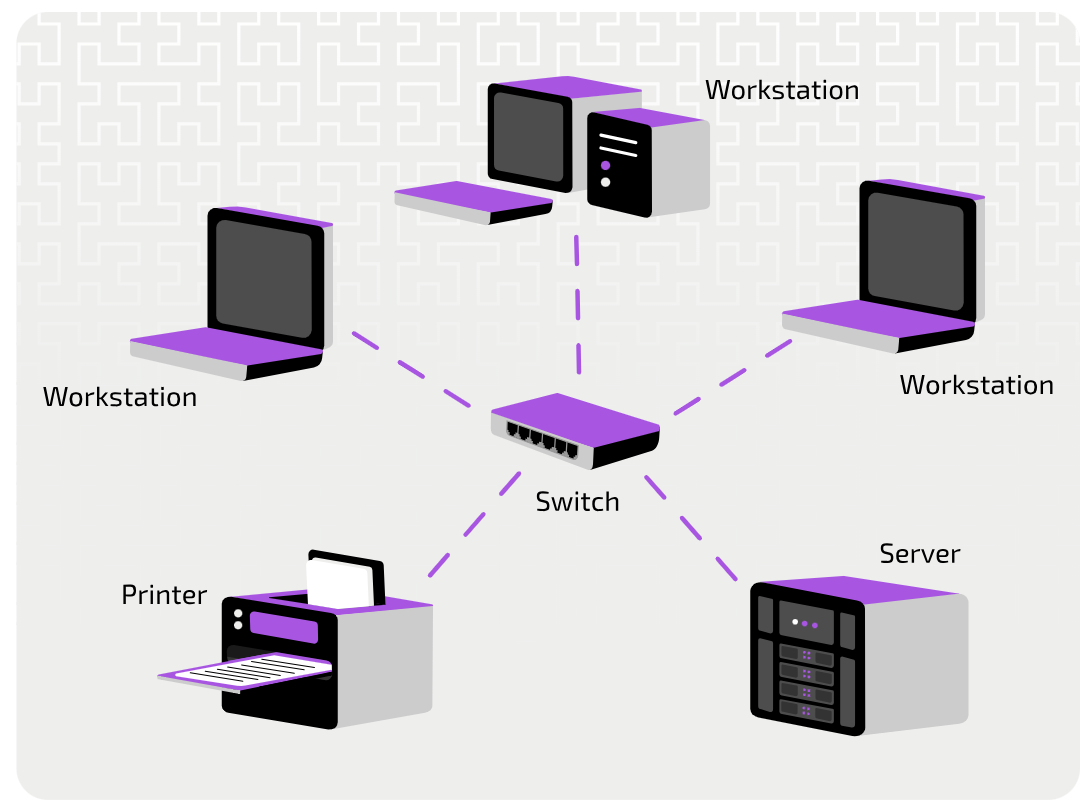
Physical star topology
Each device on the network is connected to a central communication device, such as a Hub or a Switch
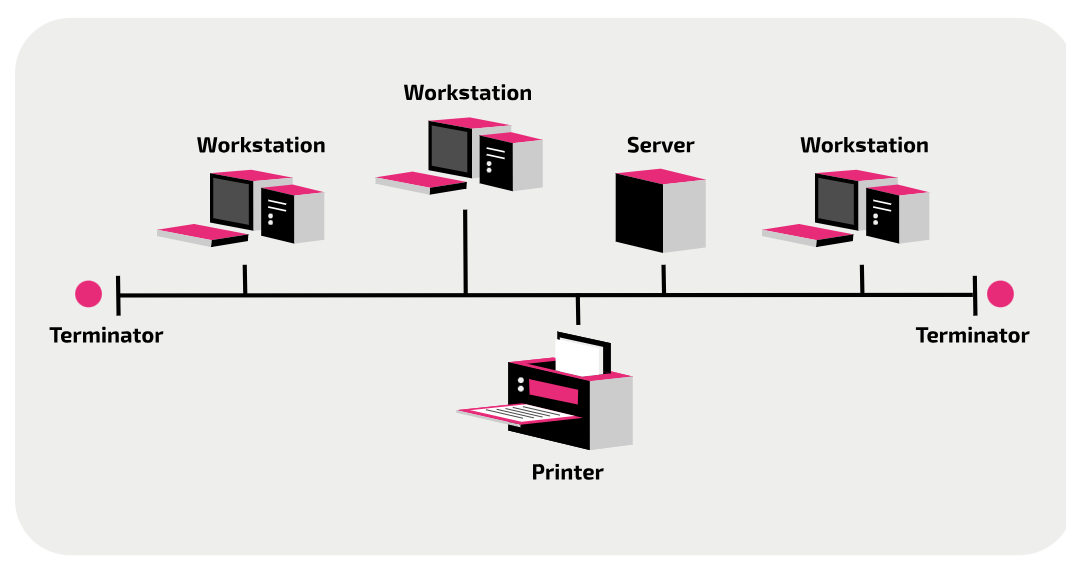
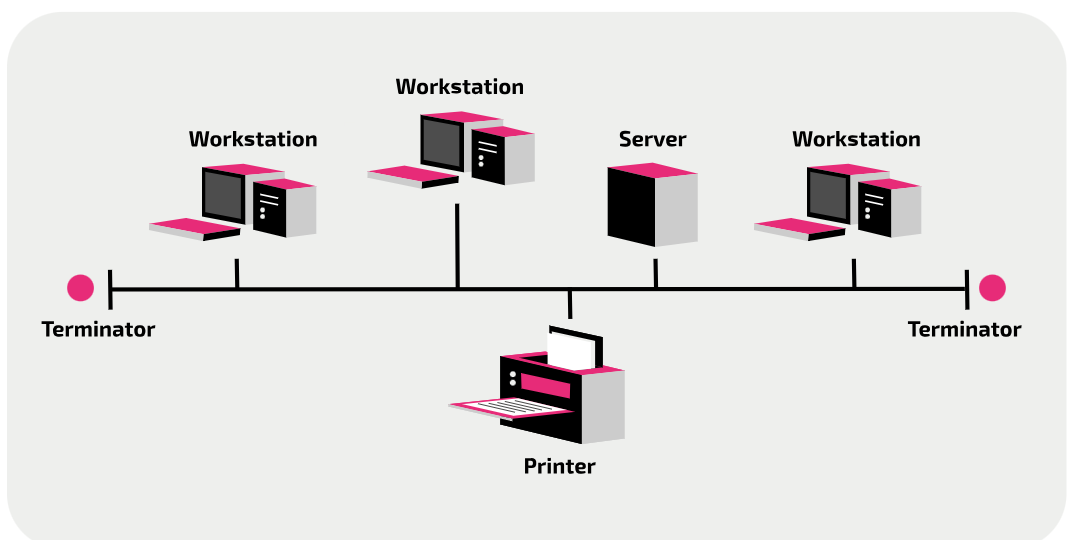
Logical bus network topology
One cable connects every device to the network. This is called the backbone. At each end a device called the terminal is placed at each ends this is done to absorbs the signals when they reach the end, to prevent interference.
Pros of a Physical star topology
Improved security and speed -Use of a switch improves the security and speed of a star network (not every deceive can see or intercept other packets)
Increased reliability -The switch or hub is a central point of failure, so if one workstation fails the entire system wont fail.
It is easy to add and remove clients to and from the network.
Cons of a Physical star topology
Expensive to install thanks to the amount of cable required.
Should the central hub fail, all communication over the network is stopped.
Pros of a Logical bus network topology
There is no central hub, reducing the chances of a network failure
Cheaper to set up due to not having a central hub and less cable is used
Cons of a Logical bus network topology
Should the backbone fail, the entire network becomes unusable.
The backbone is used for communication by multiple clients, introducing the risk of collisions.
Packets are sent through the shared backbone, allowing every client on the network to see packets that aren’t intended for them
How does a Physical star topology operate with a hub
Network signals that reach the hub are sent out to all connected devices. The hub does not process the signals that pass through it, but just repeats them on all of its connections.
How does a Physical star topology operate with a switch
Uses a table that maps each device to the port it is connected to. In this way, the switch is able to direct messages to the correct recipient (receiving device).
How does a Logical bus network topology operate
Network signals travel through a main cable to all connected devices. Each message includes a destination address linked to a device's MAC address. The intended recipient processes the message, while others ignore it.
(Messages travel via a main cable, with the destination's MAC address ensuring only the intended device responds.)
What is peer to peer networking (P2P)
Networks are decentralized but can be less efficient for large-scale use
Allows devices to share resources without a central server
What is client server networking
Centralized control improves security and resource management.
Has dedicated servers providing resources to client devices.
What does LAN stand for
Local Area Network
What is a LAN
Covers a small geographic area, such as a home or office (e.g. Wi-Fi)
What does WAN stand for
Wide area network
What is a WAN
Spans large geographic distances, connecting multiple LANs (e.g the internet)
What does WLAN stand for
Wide Local Area Network
What is WLAN
Uses radio waves instead of physical cables to connect devices. (More convenient but are less secure than wired LANs)
What is WiFi
A wireless local area network that is based on international standards. And connects devices to a network using radio waves
What are the common frequency bands WiFi operates on
It typically operates on 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequency bands.
2.4GHz vs 5GHz
2.4GHz has longer range but lower speed
5GHz offers faster speed with shorter range
Identify the components required for wireless networking.
Wireless network adapter and wireless access point.
What is a Wireless network adapter
A physical device that allows a computer system to connect to a wireless network.
What is a Wireless access point.
Uses a radio transceiver (so radio waves) to allow wireless connections to a network
Describe how wireless networks are secured.
Through strong encryption methods like WPA/WPA2, disabling SSID broadcast, and implementing MAC address filtering.
Explain the wireless protocol Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA) with and without Request to Send/Clear to Send (RTS/CTS).
CSMA/CA is a network protocol that listens to a network channel before transmitting to avoid collisions. With RTS/CTS, a device sends a request to send before transmitting, and waits for a clear to send signal, further reducing collision risk.
Explain the purpose of Service Set Identifier (SSID).
SSID is the name assigned to a WiFi network, allowing devices to distinguish between different networks.