microbiology OSPE (BLOOD)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
there is a small problem here is that there arent enough pictures for all the text that we have so iam gonna separate some texts from their original pictures yk
staphylococci
arrangement ?
gram ?
catalase ?
coagulase ?
dnase ?
aerobes , anaerobes or facultative anaerobes ?
s. aureus selective media properties ?
Staphylococci Gram positive cocci
arranged in clusters
Catalase: positive
Coagulase: S. aureus (positive) & S. epidermidis, S. saprophyticus (negative)
DNase: S. aureus (positive)
Facultative anaerobes
S. aureus grows in presence of 7.5% sodium chloride and ferment mannitol
samples for staphylococci laboratory diagnosis ?
1- Sample:
Pneumonia [sputum]
Abscess [pus / swab]
Food poisoning [Stool/ vomitus] -
Endocarditis - Bacteremia [Blood]
UTI [Urine]
2-direct film from the sample
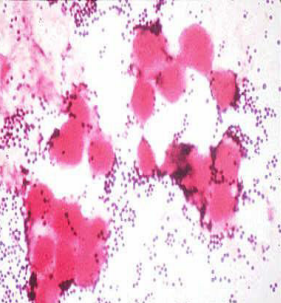
identify the sample
Direct film: from the sample
Gram stain of Staphylococcus aureus in pus
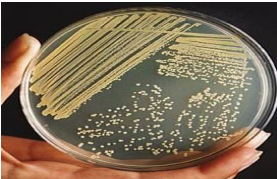
identify ?
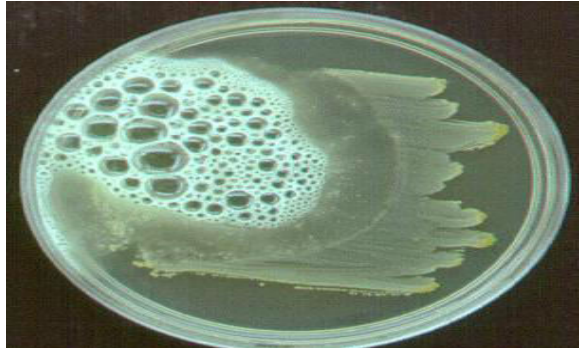
ordinary media for s.aureus —> golden yellow endopigment
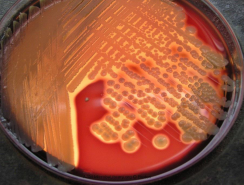
identify ?
enriched media (blood agar)
s. aureus —-> Beta hemolysis
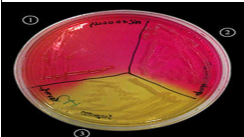
identify ?
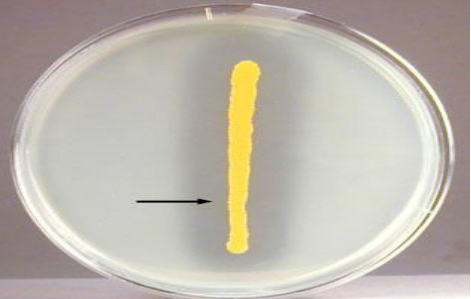
selective media mannitol salt agar
s. aureus —> ferment mannitol —-> yellow
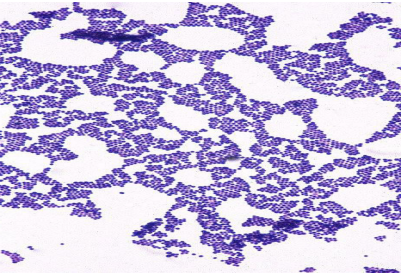
identify ?
gram positive cocci arranged in clusters
identify the test ?
use ?
principle ?
method ?
Catalase test
Use: Differentiate bacteria that produce catalase enzyme, Staphylococci, from non catalase producing bacteria such as Streptococci.
Principle: • some organisms produce catalase enzyme which breakdown the hydrogen peroxide to oxygen and water.
Method: Few drops of 3% hydrogen peroxide solution, are placed on a clean glass slide; coloney of the organism is removed and immersed in the hydrogen peroxide solution. Interpretation: Immediate bubbling indicates positive results.

identify the test ?
use ?
principle ?
method ?
Coagulase test:
Use: differentiate Staphylococcus aureus that produce coagulase enzyme from non coagulase producing Staphylococcus (S. epidermidis and S. saprophyticus).
Principle: Coagulase causes plasma to clot by converting fibrinogen to fibrin.
Method: Slide coagulase test Tube coagulase test • 0.5 ml of the diluted plasma is put into tube. 5 drops of the suspension of test organism is added to the plasma in the tube. The tube is mixed gently, incubated at 35-37˚C, 1 hour Interpretation of test: • positive result :presence of fibrin clot.
identify the test ?
use ?
principle ?
method ?
DNase agar
Use: differentiate S. aureus which produce the DNAase enzyme from other staphylococci.
Principle: • Deoxyribonuclease enzyme hydrolyses DNA
Method: • The test organism is cultured on medium containing DNA. • Incubation at 37˚C for 18-24 hours, then the plate is flooded with a few millimeters of hydrochloric acid to precipitate unhydrolysed DNA. • The plate is examined against a dark background. • Interpretation: positive result: Clear zone around culture is detected.
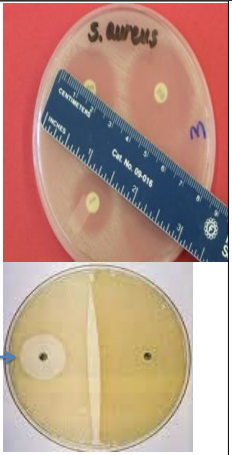
identify the test ?
uses ?
one example ?
Typing:
Antimicrobial susceptibility:
- Selection of effective antibiotic.
- Differentiation between species.
Ex. Novobiocin sensitivity sensitive: S. epidermidis resistance: S. saprophyticus
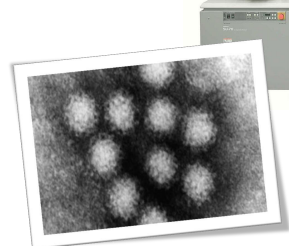
identify
viral particles direct detection by electron microscope
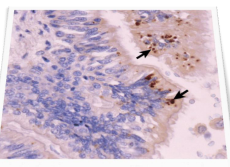
identify ?
virus direct detection through inclusion bodies by inverted microscope

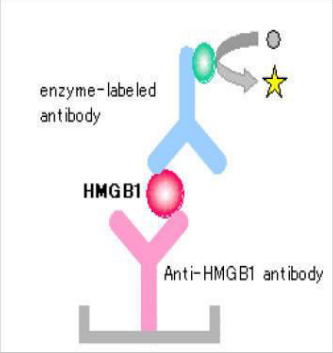
identify ?
mechanism ?
how is HIV detected by this method
direct detection of viral antigen by ELISA
color change is detected by spectrophotometer
Direct detection of P24 antigen

identify ?
direct detection of the viral antigen through immunofluorescence
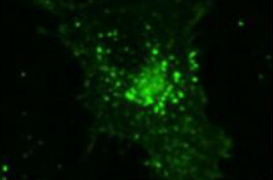
identify ?
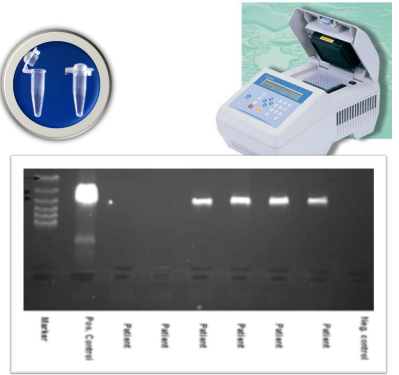
direct detection of the viral nucleic acid through PCR and RT-PCR, probes

identify ?
virus isolation through tissue culture (viruses are obligate inrtra-cellular)
identify and compare between the 3 cell lines of virus cell culture

what virus causes CPE
- Cell death & detachment from surface
- Rounding & grape-like cluster formation
- Syncytium ‘giant cell formation’
(polio v.)
(adeno v.)
(measles, mumps)
what are the 6 other ways to detect virus that doesnt produce CPE and describe each (مستحيل يطلب 6 بس تخيل )
1- Haemadsorption: attachment of erythrocytes to the surface of virus infected cells e.g. in mumps, parainfluenza and influenza viruses
2-Haemagglutination: some viruses (influenza) can agglutinate sheep RBCs.
3- Hemagglutination inhibition: It is a test used for detection of specific antibodies that could prevent haemagglutination by the virus.
4- Detection of the virus antigens or its genome in infected cells.
5- Inclusion bodies in some infected cells.
6- Viral growth can be identified serologically by neutralization test.
identify ?
mention the mechanism
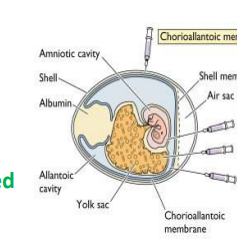
virus isolation in the embryonated egg
• Some viruses will replicate in the living tissues and membranes of embryonated hen’s eggs, such as influenza virus.
• Egg-adapted strains of influenza virus replicate well in eggs and very high virus titers can be obtained.
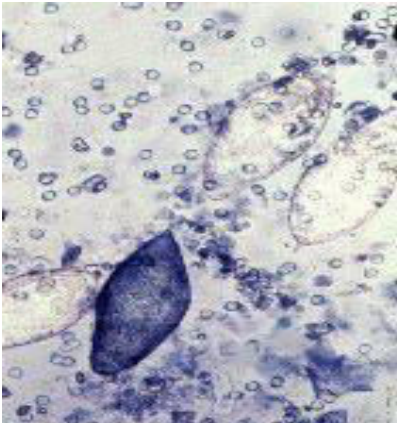
identify ?
egg adapted strain of influenza virus
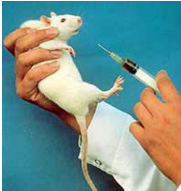
how does this mechanism of virus isolation works
by inoculating a susceptible host (laboratory animal) with infectious material derived from a patient and then observing that animal for signs of disease - suckling mice are used
- limited by virus ‘species specificity’, human viruses may need primates for replication.
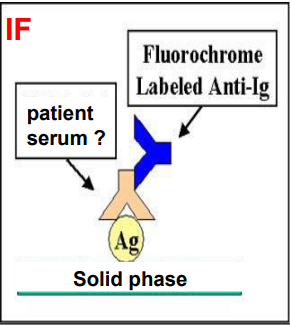
identify ?
indirect serologic detection of antiviral antibodies = hist response
by IF, ELISA, CF, WB
(detection of IgM / or at least 4 fold increase of IgG)
i have no place for the image in the back

how are the antibodies detected in HIV
• Serology: Screening of blood for antibodies to HIV is first done by ELISA which is very sensitive test.
• Positive results should be confirmed using more specific tests like Western Blot (WB) or immunofluorsence (IF)