Year 10 Science Revision
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
what is an element?
a pure substance made from only one atom and cannot be broken down
what is a compound?
two or more atoms/element combined together.
what is a combustion reaction?
a fuel (hydrocarbon) reacts with oxygen to produce energy
what is a decomposition reaction?
a compound breaking down into smaller components
what is a neutralisation reaction!
acid + base —> salt + water
what does acids + metals equal to?
hydrogen + salt
what does acids + metal carbonates/bicarbonates equal to?
salt + carbon dioxide + water
what is a corrosion reaction
when a metal reacts with oxygen and water to create rust.
what does metal + oxygen equal to?
metal oxide.
what is an aqueous (aq)
a solution that has something soluble mixed into water
which of these donate electrons: metals or non-metals?
metals.
why do we have to balance chemical equations?
to follow the law of conservation of mass, which states that matter is neither created nor destroyed.
what is all matter composed of?
atoms
what is a displacement reaction?
where the more reactive element swaps (displaces) with the less reactive element.
what is a precipitation reaction?
when a displacement reaction occurs, the solid ‘falls out’ of the solution due to it’s heavier mass.
what is an exothermic reaction?
a reactions where heat is released (amount of reactants are greater than amount of product)
what is an endothermic reaction?
a reaction where heat is absorbed (amount of reactants are less than amount of product)
what are the factors that affect the rate of reaction?
surface area, temperature, concentration, mixing/stirring, catalyst
what does rate of reaction mean?
how fast the reaction proceeds
what is activation energy? (Ea)
the minimum amount of energy stored for a chemical reaction to occur of for a physical change to happen.
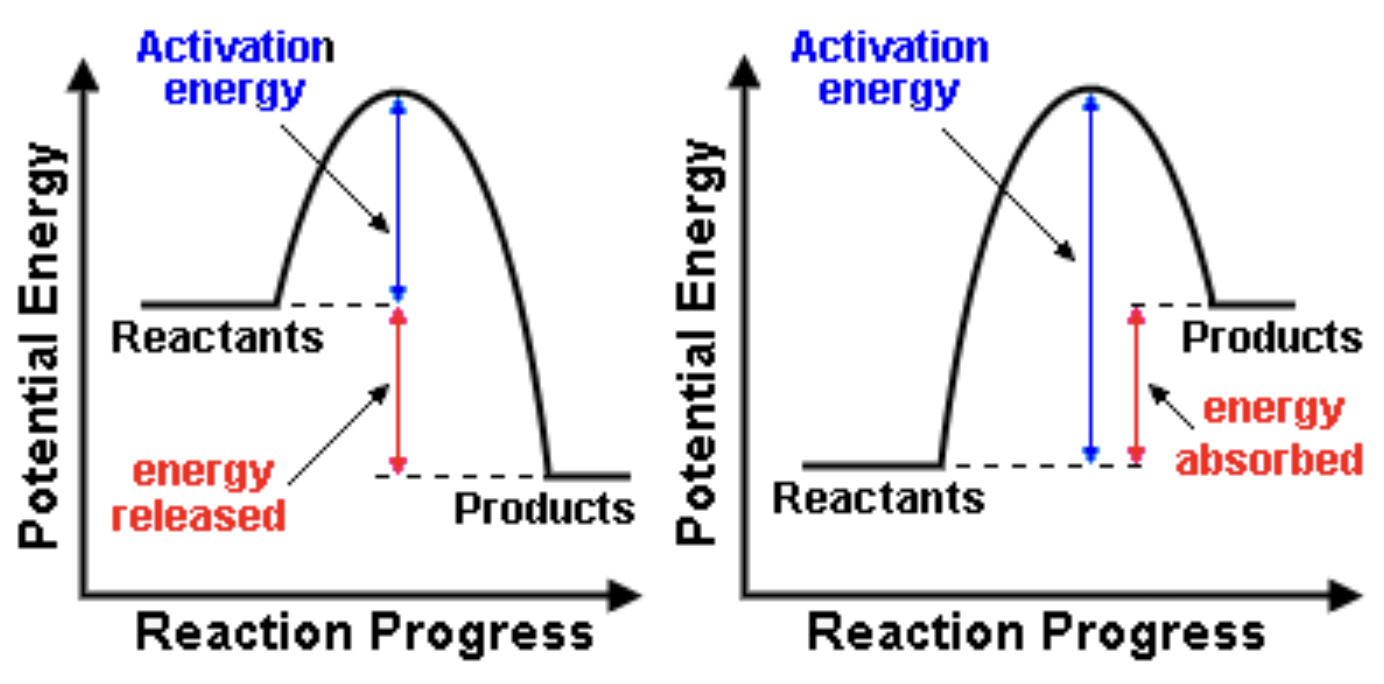
which reaction is which?
exothermic | endothermic
what is newton’s first law?
law of inertia: an object at rest with remain at rest and an object that is in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force
what is newton’s second law?
law of acceleration: the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force applied to it, and inversely proportional to its masses.
what is newton’s second law’s formula?
a = f/m
what is the difference between speed and velocity?
speed is how fast it is going and velocity is how fast plus the direction.
what is the net force and its formula
the overall force of an object | Fnet = F1 + F2
velocity formula —
v = d/t
what are genetics
segment of DNA which codes for a specific effect/feature
what is an allele (both dominant and recessive)
allele: two or more forms of a gene which are matching genes (one from out biological mother, and one from our biological mother)
dominant: when two or more genes (allele) are present, the dominant one will be expressed
recessive: the one that is not being expressed.
what is a genotype
a genetic makeup of an organism, including the specific alleles.
what is a phenotype
the set of observable traits in which is a result from genotypes, the dominant genes are the expressed trait if present.
homozygous meaning
you have inherited the same alleles of a gene from each of your parents.
heterozygous meaning
you have inherited two different alleles from a gene from your parents
what do the A, T, C and G stand for
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine