A level Physics electric and magnetic fields
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:00 AM on 4/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
Force field
A force field is an area in which an object experiences a non-contact force
2
New cards
how to represent force fields
Force fields can be represented as vectors
3
New cards
electric fields
An electric field is a force field in which charged particles experience a force
4
New cards
Electric field strength
Electric field strength (E) is the force per unit charge experienced by an object in an electric field.
E = F/Q
E = F/Q
5
New cards
Coulomb’s law
the magnitude of the force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of their charges
and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
6
New cards
Coulomb’s Law formula
\
Q1 = charge 1
Q2 = charge 2
ε0 = permittivity of free space
r = distance between the particles
Q1 = charge 1
Q2 = charge 2
ε0 = permittivity of free space
r = distance between the particles
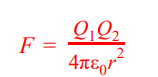
7
New cards
attraction and repulsion
If charges have the same sign the force will be repulsive , and if the charges have different signs the force will be attractive .
8
New cards
Point charges
Point charges form a radial electric field
9
New cards
electric field strength formula
formula:
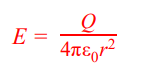
10
New cards
Absolute electric potential
at a point, it is the potential energy per unit charge of a positive point charge at that point in the field
11
New cards
absolute magnitude
greatest at the surface of a charge
as the distance from the charge increases, the potential decreases
so, the electric potential at infinity is zero
as the distance from the charge increases, the potential decreases
so, the electric potential at infinity is zero
12
New cards
potential and charge
potential is positive and the charge is repulsive , when the charge is negative, potential is negative and the force is attractive
13
New cards
attraction and repulsion graphs
graphs :
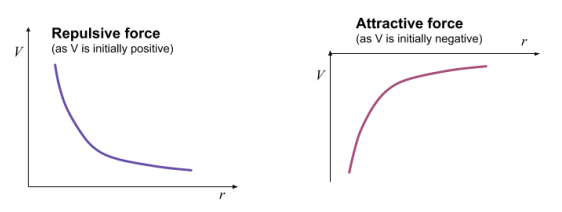
14
New cards
Electric fields between parallel plates
You can form a uniform electric field using a pair of parallel plates with a potential difference across
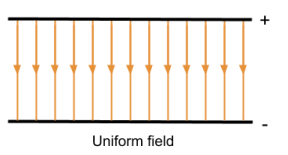
15
New cards
electric field strength formula
formula:
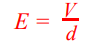
16
New cards
Electric potential difference
is the energy needed to move a unit charge between two points
17
New cards
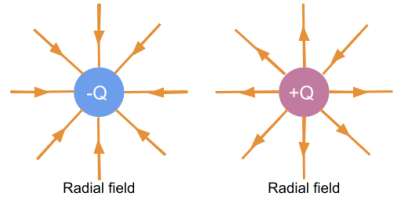
Radial electric fields diagram
18
New cards
Uniform field
A uniform field exerts that same electric force everywhere in the field
19
New cards
radial field
in a radial field the magnitude of electric force depends on the distance between the two charges
20
New cards
equipotential surfaces
The potential on an equipotential surface is the same everywhere, therefore when a charge moves along an equipotential surface, no work is done
21
New cards
Capacitance
Capacitance (C) is the charge stored by a capacitor per unit potential difference .
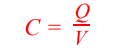
22
New cards
Energy stored by a capacitor
energy stored by a capacitor (W) is given by the area under a graph of charge against potential difference
23
New cards
Capacitor charging
the capacitor is connected to a power supply, current starts to flow and negative charge builds up on the plate connected to the negative terminal.
On the opposite plate, electrons are repelled by the negative charge building up on the initial plate, therefore these electrons move to the positive terminal and an equal but opposite charge is formed on each plate , creating a potential difference.
As the charge across the plates increases, the potential difference increases but the electron flow decreases due to the force of electrostatic repulsion also increasing, therefore current decreases and eventually reaches zero.
On the opposite plate, electrons are repelled by the negative charge building up on the initial plate, therefore these electrons move to the positive terminal and an equal but opposite charge is formed on each plate , creating a potential difference.
As the charge across the plates increases, the potential difference increases but the electron flow decreases due to the force of electrostatic repulsion also increasing, therefore current decreases and eventually reaches zero.
24
New cards
Capacitor discharging
When the capacitor is discharging the current flows in the opposite direction , and the current, charge and potential difference across the capacitor will all fall exponentially , meaning it will take the same amount of time for each of the values to halve.
25
New cards
Magnetic flux density
magnetic flux density (B) of a magnetic field, is a measure of the strength of the field, and it is measured in the unit Tesla
26
New cards
Magnetic flux
Magnetic flux ( ϕ ) is a value which describes the magnetic field or magnetic field lines passing through a given area
\
Φ = BA
\
Φ = BA
27
New cards
Magnetic flux linkage
Magnetic flux linkage (N ϕ ) is the magnetic flux multiplied by the number of turns N , of a coil:
NΦ = BAN
NΦ = BAN
28
New cards
Charged particles moving in a magnetic field
A force acts on charged particles moving in a magnetic field , this is why a force is exerted on a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field, because it contains moving electrons, which are negatively charged particles.
\
F = BQv sin θ
\
F = BQv sin θ
29
New cards
How find the direction of the force
fleming’s left hand rule :
Thumb - represents the direction of the Motion /force
First finger - represents the direction of the Field
Second finger - represents the direction of the Conventional Current (opposite direction to electron flow)
Thumb - represents the direction of the Motion /force
First finger - represents the direction of the Field
Second finger - represents the direction of the Conventional Current (opposite direction to electron flow)
30
New cards
Solenoid
it is a coil of wire carrying an electric current. the chape of the magnetic field around a solenoid is similar to one around a bar magnet
\
the strength increases with:
the electric current
the number of turns in the coil
\
\
the strength increases with:
the electric current
the number of turns in the coil
\
31
New cards
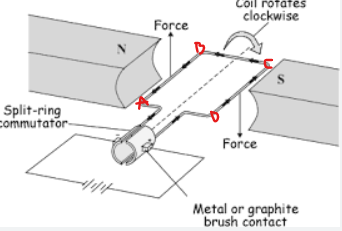
Motor effect
the force on side AB is acting up and the side CD has a force acting downwards. this makes the coil rotate 180 degrees in the clockwise direction. the split ring changes the direction of the current every half cycle. so AB is now acting down and CD is acting up allowing the coil to complete a full cycle.
32
New cards
Moving charged particle in a magnetic field
charged particle in magnetic field will have a circular motion
force is perpendicular to the charge particle
it will accelerate
speed stay the same but the direction changes so velocity changes
force is perpendicular to the charge particle
it will accelerate
speed stay the same but the direction changes so velocity changes
33
New cards
Hall effect
emf is set up across a current carrying conductor when a perpendicular magnet field is applied
\
at the start e- is attracted to 1 side of the conductor.
Eventually enough e- will build up on one side creating a magnetic force that produces an electrostatic force of repulsion
on the remaining free electrons attempting to move on 1 side of the conductor.
\
at the start e- is attracted to 1 side of the conductor.
Eventually enough e- will build up on one side creating a magnetic force that produces an electrostatic force of repulsion
on the remaining free electrons attempting to move on 1 side of the conductor.
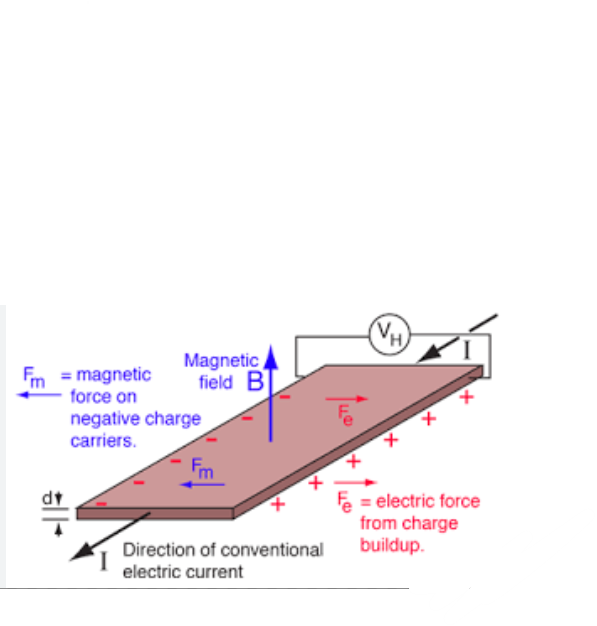
34
New cards
Electromagnetic induction
as the magnet approaches the coil the magnetic flux changes:
the magnetic flux changes and I is induced
\
as the magnet moves away from the coil the magnetic flux changes:
magnetic flux decrease and I is induced
\
\
the magnetic flux changes and I is induced
\
as the magnet moves away from the coil the magnetic flux changes:
magnetic flux decrease and I is induced
\
\
35
New cards
Lenz’s Law
the direction of induced EMF is such that it opposed the change that produces it.
36
New cards
Faradays Law
induced EMF is proportional to the rate of change of flux linking through the coil
37
New cards
Explain why there is an induced EMF in a copper tube as a magnet passes through it
in the copper tube when the magnet is passed through the magnetic flux changes. so there is an induced current the produces an induced EMF . this happens when copper is a conductor
38
New cards
AC generators Vs Motor effect
difference is that AC isn’t connected to a power supply but motor effect is
39
New cards
AC generator
the coil starts in a position of 90 dgrs and the induced EMF is at 0v.
as the coil turns it cuts through the magnetic field change the mg flux inducing an EMF. the induced EMF is at its highest when the coil is at 180 dgrs
as the coil turns it cuts through the magnetic field change the mg flux inducing an EMF. the induced EMF is at its highest when the coil is at 180 dgrs
40
New cards
Transformers
a device that converts AC voltage of one level to AC voltage of another level
\
\
41
New cards
core of transformers
made up of laminated iron sheets. this is a magnetically soft material and magnetises and demagnetises easily
42
New cards
eddy currents
if fulx changes in the core then EMF is produced. so there will be an induced EMF all over the block which is the eddy currents
eddy currents produce heating effect so loss of energy
eddy currents produce heating effect so loss of energy
43
New cards
why is the core made of laminated sheets
the iron sheet are laminated to prevent electrons from moving layers which could cause short circuiting
44
New cards
step up transformer
change in I so a change in magnetic flux in the primary coil. so EMF is induced. the primary coil is linked to the secondary coil by the core. so current is induced in the secondary coil.
45
New cards
primary coil and secondary coil
if number of turn in primary < number of turn in secondary coil:
more change in flux in secondary coil
more induced EMF
more induced current
more change in flux in secondary coil
more induced EMF
more induced current