Psychology Exam 1 2023
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/217
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I'll be updating this as I go so don't be scared if there's only a few cards at first, I assure you there will be more
Last updated 1:24 PM on 6/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
218 Terms
1
New cards
Nature (Heredity)
the transmission of characteristics from biological parents to their offspring via genes at the time of conception
2
New cards
Nurture (Environment)
all the experiences, objects and events, which we are exposed to throughout our entire lifetime
3
New cards
‘Biological’ perspective - Nature vs Nurture argument
heredity primarily determines our psychological development
4
New cards
‘Behaviorist’ perspective - Nature vs Nurture argument
environment is responsible for determining what anyone could become, believes heredity has little to do with the development of psychological characteristics
5
New cards
Deprivation
the loss or withholding of normal stimulation, nutrition, comfort, love, etc.
6
New cards
Enrichment
the attempt to ensure that an environment (particularly that of a child) has intellectual, perceptual stimulation and that it is complex and original; allows for investigation
7
New cards
4 types of unresponsive care
1. occasional inattention
2. chronic under-stimulation
3. severe neglect in a family context
4. severe neglect in an institutional setting
8
New cards
occasional inattention
Children receive attention most of the time, but occasionally adults don’t respond. No harm to the child, and perhaps even some benefit; child can learn to self-sooth and explore their environment.
9
New cards
chronic under-stimulation
on a regular basis, children have less interaction with adults around them than is needed for healthy development. can show ‘catch-up’ when provided with an enrich
10
New cards
severe neglect in a family context
prolonged period of inattention and lack of responsiveness. often associated with not being taken care of properly (i.e. feeding, bathing, etc). Children at risk for significant developmental deficits that aren’t easily fixed.
11
New cards
severe neglect in an institutional setting
children living in poor institutional settings e.g. orphanages, ‘transitional care’
12
New cards
Serve
The child ‘serves’ by reaching out for interaction - with eye contact, facial expressions, gestures, babbling, or touch.
13
New cards
Return
A responsive caregiver will ‘return the serve’ by speaking back, playing peekaboo, or sharing a toy or a laugh.
14
New cards
Sensitive period
a period of time during development when a person (or animal) is more responsive (‘sensitive’) to certain types of environmental experiences or learning
within this period of time, we can most rapidly acquire a particular skill or characteristic
within this period of time, we can most rapidly acquire a particular skill or characteristic
15
New cards
Learning after the sensitive period
we can still learn after the sensitive period has closed, but the learning process is less efficient
16
New cards
Critical period
A period in time in which a person (or animal) has heightened sensitivity to external stimuli that is compulsory for the development of a particular skill
17
New cards
Critical period example
Certain areas of the visual cortex are only capable of synapse formation during the early stages of development. Once the critical period has elapsed, the individual will have some visual impairment
18
New cards
Critical period vs sensitive period
If the appropriate experience does not occur during its critical period, then it can permanently and irreversibly affect development.
Critical periods have identifiable start and end times, thereby tending to start and end suddenly, rather than gradually (if at all) as do sensitive periods
Critical periods have identifiable start and end times, thereby tending to start and end suddenly, rather than gradually (if at all) as do sensitive periods
19
New cards
Strengths of the Iowa Orphans study
* Reliable tests - IQ test (qualitative results)
* distinctive experimental and control groups
* provides evidence for the need of interventions
* Cause and effect
* distinctive experimental and control groups
* provides evidence for the need of interventions
* Cause and effect
20
New cards
Limitations of the Iowa Orphans study
* Unethical
* Small sample size - generalizable
* Not able to replicate
* Cross-cultural
* Not necessarily a very rigorous design
* Small sample size - generalizable
* Not able to replicate
* Cross-cultural
* Not necessarily a very rigorous design
21
New cards
Epigenetics
the study of factors other than genetics ones that control how and when each gene is expressed
22
New cards
Neutral Stimulus (NS)
A stimulus that does not evoke a response
23
New cards
Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS)
A stimulus innately capable of eliciting a response
24
New cards
Conditioned Stimulus (CS)
A stimulus that evokes a response because it has been repeatedly paired with an unconditioned stimulus
25
New cards
Unconditioned Response (UCR)
An innate reflex response elicited by an unconditioned stimulus
26
New cards
Conditioned Response (CR)
A learned response elicited by a conditioned stimulus
27
New cards
Example of Classical Conditioning
Pavlov’s Dog Experiment
28
New cards
Neutral Stimulus (NS) in Pavlov’s Dog Experiment
Bell - before conditioning
29
New cards
Unconditioned Response (UCR) in Pavlov’s Dog Experiement
Salivating - before conditioning
30
New cards
Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS) in Pavlov’s Dog Experiment
Meat
31
New cards
Conditioned Stimulus (CS) in Pavlov’s Dog Experiment
Bell - after conditioning
32
New cards
Conditioned Response (CR)
salivating - after conditioning
33
New cards
Positive Punishment
adding something to decrease behavior
34
New cards
Negative Punishment
subtracting something to decrease behavior
35
New cards
Positive Reinforcement
adding something to increase behavior
36
New cards
Negative Reinforcement
subtracting something to incr
37
New cards
three-phase (ABC) model of operant conditioning
Antecedent, Behavior, Consequence
38
New cards
Antecedent in three-phase model of operant conditioning
the environmental stimulus that precedes the relevant behavior and indicates the consequence; ‘What happened before’
39
New cards
Behavior in three-phase model of operant conditioning
voluntary activity that has an effect on the environment; ‘What happens’
40
New cards
Consequence in three-phase model of operant conditioning
the environmental event that follows the behavior; ‘What happens after’
41
New cards
Behaviorism
the theory that psychology can be objectively studied through observable action
42
New cards
Operant conditioning
subject learns behavior by associating it with consequences
43
New cards
Classical conditioning
Subject learns to associate two unrelated stimuli with each other
44
New cards
operant conditioning theorist
B.F. Skinner
45
New cards
Classical conditioning theorist
Ivan Pavlov
46
New cards
Bandura’s Social Learning Theory steps
Attention, Retention, Reproduction, Motivation Reinforcement
47
New cards
Bandura’s Social Learning Theory explained
learning occurs through observation, imitation and modelling and is influenced by factors such as attention, motivation, attitudes and emotions.
48
New cards
Attention in Bandura’s Social Learning Theory
Learner pays attention in order to observed the modelled behaviour
49
New cards
Retention in Bandura’s Social Learning Theory
Learner mentally represents and retains what has been observed
50
New cards
Reproduction in Bandura’s Social Learning Theory
Depending on their physical capabilities, learner converts the mental representation into action
51
New cards
Motivation Reinforcement in Bandura’s Social Learning Theory
Learner must be motivated to reproduce. Reinforcement influences motivation to perform the observed behaviour
52
New cards
Examples of Attention influencers (Bandura’s Social Learning Theory)
* perceptual capabilities of the observer
* motivation and interest level of the observer
* the situation in which the behaviour is being observed
* the kinds of distractors that are present
* the characteristics of the model, such as attractiveness
* motivation and interest level of the observer
* the situation in which the behaviour is being observed
* the kinds of distractors that are present
* the characteristics of the model, such as attractiveness
53
New cards
Model attractiveness explained (Bandura’s Social Learning Theory)
In general, the greater similarity between the model and the observer, the higher status the model, and the more attractive and successful the model, the more likely we are to follow their example
54
New cards
Example of retention (Bandura’s Social Learning Theory)
Linking a visual image with a verbal description of the model’s actions
55
New cards
Types of reinforcement (Bandura’s Social Learning Theory)
External Reinforcement
Vicarious Reinforcement
Self-Reinforcement
Vicarious Reinforcement
Self-Reinforcement
56
New cards
External Reinforcement
comparable to learning by consequences
57
New cards
Vicarious Reinforcement
occurs indirectly by observing the modelled behaviour being reinforced without personally experiencing the reinforcement
58
New cards
Self-Reinforcement
occurs when we are reinforced by meeting certain standards of performance we set for ourselves
59
New cards
Self Efficacy
our belief in our ability to accomplish tasks and succeed in particular situations
60
New cards
4 main sources of self efficacy information
Performance Accomplishments (i.e. past experiences)
Vicarious Experience (i.e. modelling by others)
Social Persuasion (i.e. coaching and evaluative feedback)
Physiological and Emotional States
Vicarious Experience (i.e. modelling by others)
Social Persuasion (i.e. coaching and evaluative feedback)
Physiological and Emotional States
61
New cards
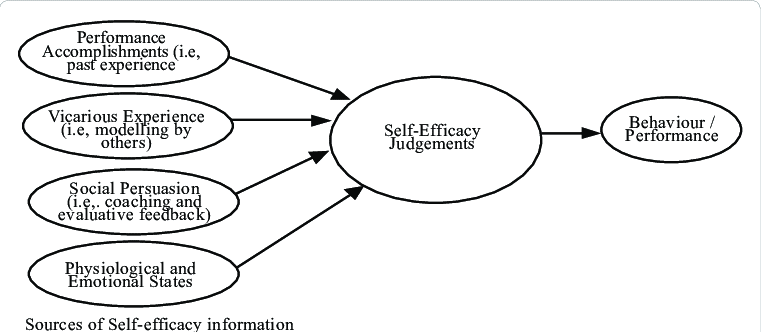
Bandura’s Social Cognitive Theory
62
New cards
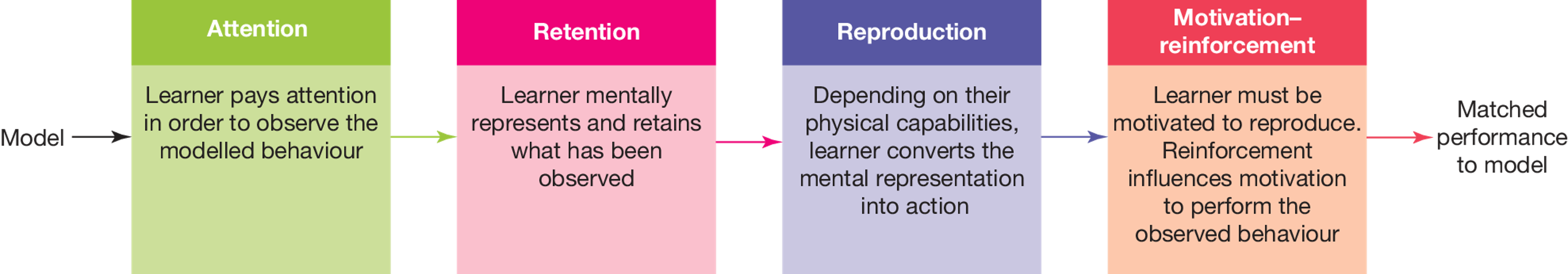
Bandura’s Social Learning Theory
63
New cards

Three Phase model of operant conditioning
64
New cards
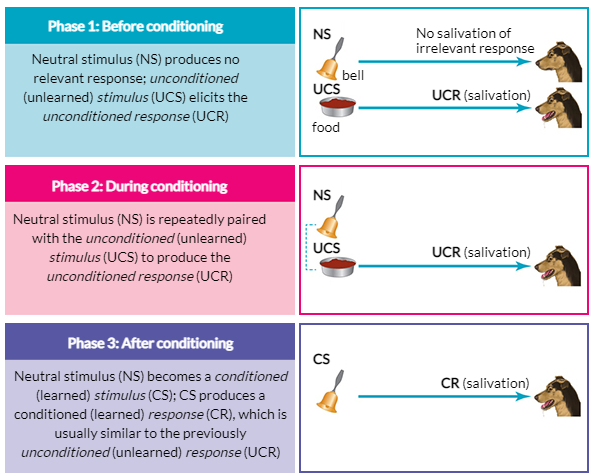
Pavlov Dog experiment - Classical Conditioning
65
New cards
Associative Learning
when a subject links certain events, behaviours, or stimuli together in the process of conditioning
66
New cards
Cognition
our thoughts, perspectives, and expectations
67
New cards
4 attachment types
secure, insecure-avoidant, insecure-ambivalent, insecure-disorganised
68
New cards
secure attachment caregiver behaviours
* react quickly and positively to child’s needs
* responsive to child’s needs
* responsive to child’s needs
69
New cards
secure attachment child behaviours
* distressed when caregiver leaves
* happy when caregiver returns
* seek comfort from caregiver when scared or sad
* happy when caregiver returns
* seek comfort from caregiver when scared or sad
70
New cards
insecure avoidant attachment caregiver behaviours
unresponsive, uncaring, dismissive
71
New cards
insecure avoidant attachment child behaviours
* no distress when caregiver leaves
* does not acknowledge return of caregiver
* does not seek or make contact with caregiver
* does not acknowledge return of caregiver
* does not seek or make contact with caregiver
72
New cards
insecure ambivalent attachment caregiver behaviours
responds to child inconsistently
73
New cards
insecure ambivalent attachment child behaviours
distress when caregiver leaves, not comforted by return of caregiver
74
New cards
insecure disorganized attachment caregiver behaviours
abusive or neglectful, responds in frightened or frightening ways
75
New cards
insecure disorganized attachment child behaviours
no attaching behaviours. often appear dazed, confused or apprehensive in presence of caregiver
76
New cards
Attachment
the emotional bond which forms between an infant and another person
77
New cards
Surrogate
anyone or anything that ‘substitutes for’ or ‘plays the part’ of something else
78
New cards
Learning
the process of acquiring, through experience, new and relatively enduring information or behaviours
79
New cards
Modelling
the process of observing and imitating a specific behaviour
80
New cards
Bobo doll experiment creator
Bandura
81
New cards
Harlow’s monkey experiment proved…
contact and touch are vital to attachment, learning, emotional well-being and psychological development
82
New cards
Harlow’s monkeys post experiment
They showed many signs of atypical behaviour - they were withdrawn and did not want to mate. When forced to mate, these ‘motherless monkeys’ were abusive to their offspring, sometimes killing them.
83
New cards
Harlow hypothesis monkey experiment
the monkey would be drawn to whichever surrogate mother had the bottle
84
New cards
Was Harlow’s hypothesis true? Justify your answer.
Proved false, the monkeys were drawn to the ‘cloth mother’
85
New cards
independent variable in Harlow’s monkey experiment
provision of food by either a cloth or wire surrogate mother
86
New cards
dependent variable in Harlow’s monkey experiment
amount of contact time spent with cloth and wire surrogate mothers
87
New cards
aim of Harlow’s monkey experiment
to find out whether provision of food or contact comfort is more important in the format
88
New cards
impact of Harlow’s research
helped influence key changes in how orphanages, adoption agencies, social services groups, and child care providers approach the care of children.
89
New cards
Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development stage 1
Trust vs Mistrust, birth to 18 months, Hope
90
New cards
Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development stage 2
Autonomy vs Shame and Doubt, 18 months to 3 years, will
91
New cards
Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development stage 3
Initiative vs Guilt, 3 to 5 years, purpose
92
New cards
Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development stage 4
Industry vs Inferiority, 5 to 12 years, confidence
93
New cards
Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development stage 5
Identity vs Role Confusion, 12 to 18 years, fidelity
94
New cards
Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development stage 6
Intimacy vs Isolation, 18 to 40 years, love
95
New cards
Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development stage 7
Generativity vs Stagnation, 40 to 65 years, care
96
New cards
Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development stage 8
Integrity vs Despair, 65 years-death, wisdom
97
New cards
Autonomy
the ability to do things independently and the feelings of self-control, self-confidence, competence which accompanies this.
98
New cards
Wild child
A child raised in the wild or neglected and grossly underdeveloped
99
New cards
wild child example
genie
100
New cards
John Bowlby
Attachment theory. Identified the characteristics of a child's attachment to his/her caregiver and the phases that a child experiences when separated from the caregiver.