21 buffer solutions
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
what is a buffer solution
a system that minimises pH changes when small amounts of an acid or a base are added
what do you need to prepare a buffer solution
a weak acid and its conjugate base
2 different methods for preparing a buffer
a weak acid and a solution of one of its salts
partial neutralisation of the weak acid
what happens when you add an acid to a buffer
concentration of H+ increases
the H+ ions react with the conjugate base, A-
the equilibrium position shifts to the left, leaving most of the H+ ions
what happens when you add a weak acid to a molecule
[OH-] increases
the small concentration of H+ ions react with the OH- ions
HA dissociates, moving the equilibrium position to the right to restore most of the H+ ions
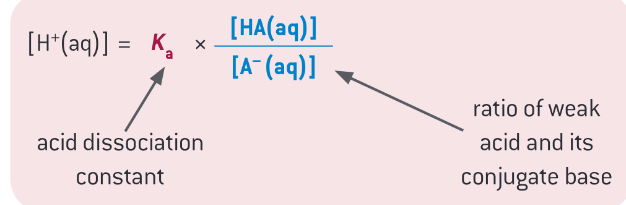
equation for working out [H+] in buffers
how does the carbonic acid-hydrogencarbonate buffer system work to control blood pH
when an acid is added:
concentration of H+ increases and the H+ ions react with the conjugate base HCO3-
the equalibirum shifts to the left, removing most of the H+ ions
when OH- is added
[OH-] increases and reacts with the H+
H2CO3 dissociates, shifting equalibirum position to the right to restore most of the H+ ions
pH titration curve of adding an alkali to an aicd
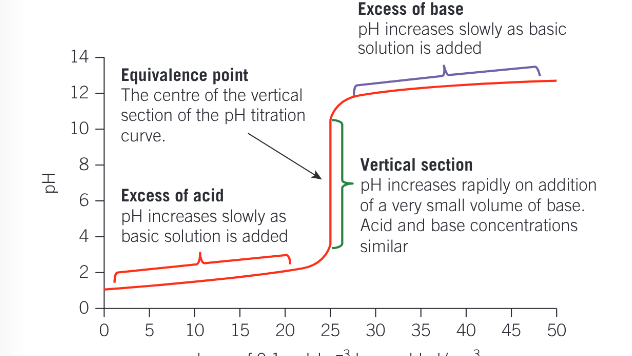
pH titration curve for additions of an acid to a base
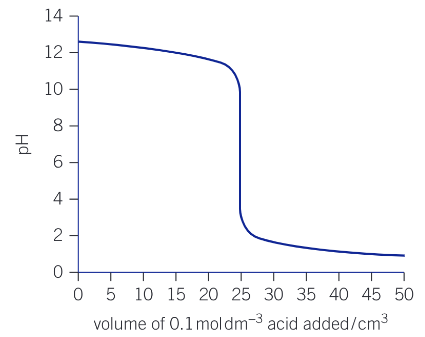
equivalence point
the volume of one solution that exactly reacts with another solution
indicator at the end point of a titration
the indicator contains equal concentrations of HA and A-
the colour will be in between the two extreme colours
what is an indicator
a weak acid that has a distinctly different colour from its conjugate base
what happens when a basic solution is added to an indicator
OH- ions react with H+ in the indicator
the weak acid, HA, dissociated, shifting the equilibrium position to the right
this causes a colour change
what happens to the indicator if there is an initially basic solution and an acid is added
H+ ions react with the conjugate base, A-
the equilibrium position shifts to the left
How sensitive is the end point
most indicators change colour over a range of about 2pH units
how to choose an indicator
use pH titration curve graph and pick an indicator which changes colour in the range of the vertical line. No indicator is sutable for a weak acid and weak alkali