Concept 13.4: Genetic variation produced in sexual life cycles contributes to evolution
1/7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Mutations
Changes in an organism’s DNA that are the original source of genetic diversity
Creates different versions of genes called alleles
Alleles
Different versions of genes created by mutations
Reshuffling these during sexual reproduction produces genetic variation
Chromosomal behavior
What is responsible for most of the variation that arises in each generation during meiosis and fertilization, including:
Independent assortment of chromosomes
Crossing over
Random fertilization

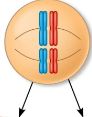
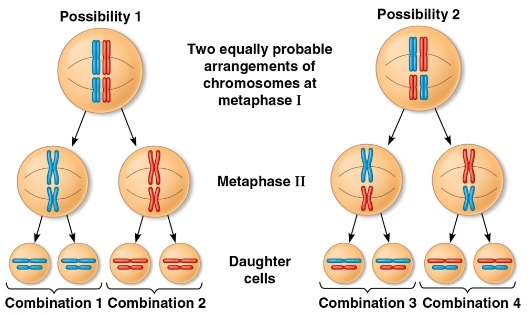
Independent assortment
The sorting of maternal and paternal homologs into daughter cells independently of the other pairs with random orientations
n
The haploid number
2 to the power of this represents the number of combinations possible when they assort independently into gametes
This is 23 in humans, leading to 223 (over 8 million) possible combinations
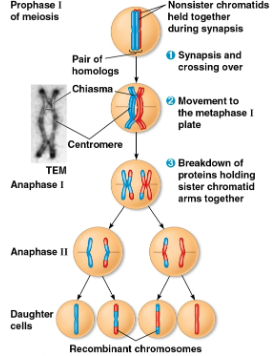
Recombinant chromosomes
Chromosomes that combine DNA inherited from each parent during crossing over, allowing for variation within a single chromosome
1 to 3 crossover events occur per chromosome in humans
Random fertilization
The fact that any sperm can fuse with any ovum (unfertilized egg)
The fusion of two gametes (8.4 million possible combinations) produces a zygote with any of about 70 trillion diploid combinations, adding a unique genetic identity
Genetic variation
Created through natural selection, mutations, and meiosis
Asexually reproducing organisms increase this by incorporating foreign DNA from the environment