4.2 absolute and comparative advantage theories; parallel PPC curve
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
absolute advantage
country’s ability to produce a good using fewer resources than another country
theory of absolute advantage
focus on who can produce more given the same resources
the products can make all countries better off, when a country specialises in the one it has an absolute advantage in and trade it
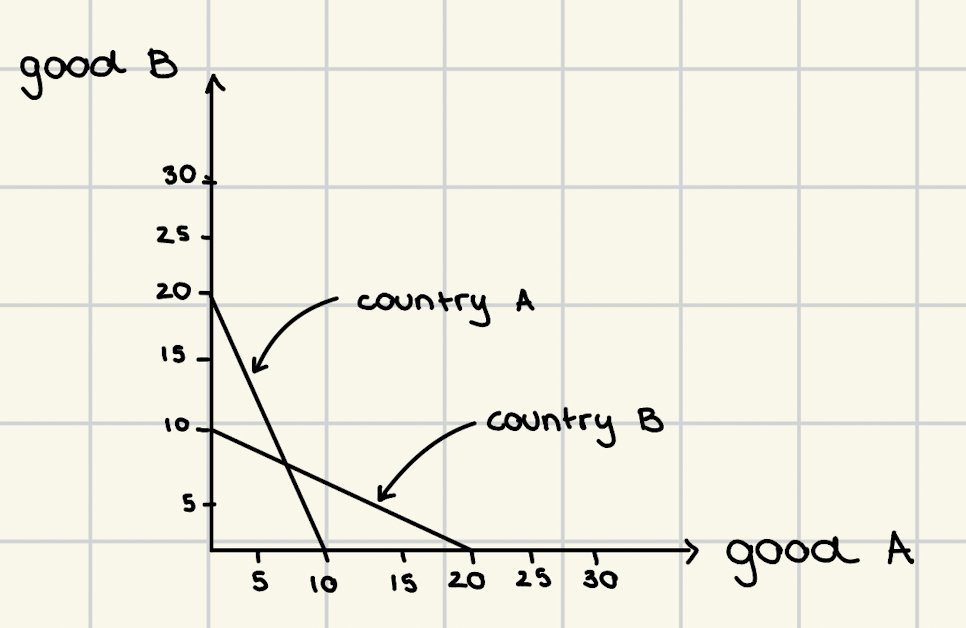
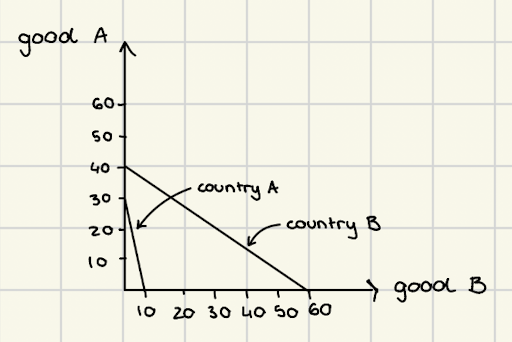
comparative advantage
the ability of an economy to produce a given product at a lower opportunity cost than its trading partners
comparative advantage theory
focus on calculation what is better to be given to us to produce something else
nations will export the good they have a comparative advantage in (can produce more efficiently) and import those that it cannot produce efficiently
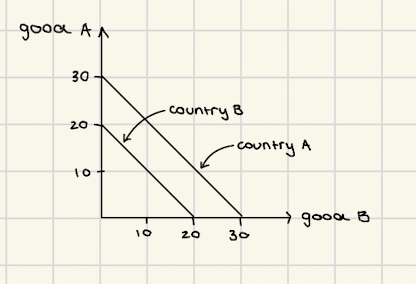
parallel PPC curve case
parallel curves = identical opportunity cost = no comparative advantage in 1 or other good
limitations of theory of comparative advantage
depends on many assumptions
graphs only 2 countries
trade on basis of comparative advantage may lead to excessive specialisation
assumptions of comparative advantage theory
FOPs are fixed
technology is fixed
perfect mobility of FOPs within the country
full employment of resources
free trade
homogenous products
ignored transportation costs