Hereditary Basics and Patterns of Inheritance
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Gene
A basic unit or sequence of genetic material that encodes a trait
Homozygous
Carrying the same alleles on each homologous chromosome
Hemizygous
Having only one copy of a gene instead of two (e.g., sex chromosomes of males are XY)
Locus
A gene's location within a genome
Phenotype
The set of observable characteristics in an individual resulting from the expression of genotype (e.g., Genotype Aa can produce a brown eye phenotype while genotype aa can produce a blue eye phenotype)
Homozygous Dominant
Carries two copies of the dominant allele (e.g., BB)
Homozygous Recessive
Carries two copies of the recessive allele (e.g., bb)
Allele
A variant form of a gene
Wild type
Normal version of an allele
Mutant
An allele with an altered DNA sequence affecting a gene's phenotype
Heterozygous
Carrying a copy of the recessive allele on one of the homologous chromosomes and a copy of the dominant allele on the other chromosome (e.g., Aa)
Homologous chromosomes
A pair of chromosomes (1 maternal, 1 paternal) that contain the same genes in the same locations
Genotype
The alleles an individual carries (e.g., Aa)
Test Cross
A genetic cross between a homozygous recessive individual and an individual in question to determine the latter's genotype for a given trait
Monohybrid cross
Tests a single gene
Punnett squares
Show all possible allelic combinations of gametes in a cross between two individuals with known genotypes
The Law of Segregation
Pairs of alleles are separated when gametes are formed
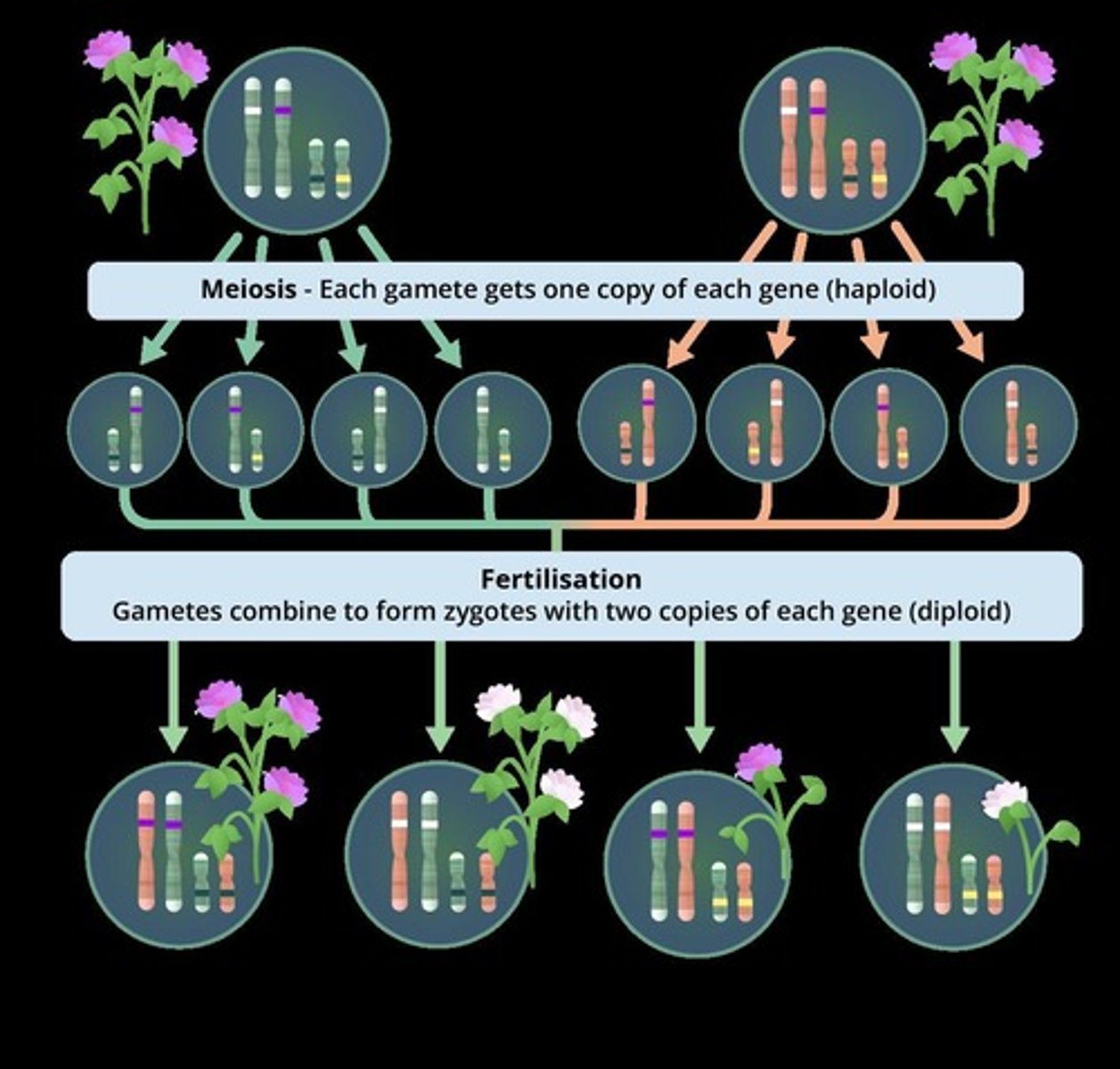
The Law of Independent Assortment
Pairs of alleles will be sorted independently of one another when gametes are formed
Principle of Dominance
One dominant allele masks the effect of recessive allele
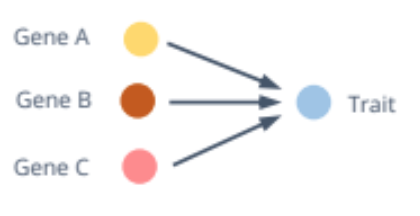
Pleiotropy
Single gene controls for the expression of multiple phenotypic traits
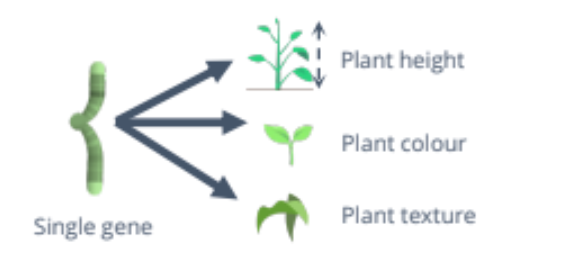
Polygenic Inheritance
Many genes interact to shape a single phenotype, often with continuous variation (e.g., height)
Incomplete Dominance
There is a blending of alleles, producing a unique heterozygous phenotype [e.g., (R red) x (W White) = (RW pink)]
![<p>There is a blending of alleles, producing a unique heterozygous phenotype [e.g., (R red) x (W White) = (RW pink)]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/105f6417-68dd-4f7b-8dbc-ae9dfb174ff4.png)
Multiple Alleles
More than two typical alleles exist for a gene (e.g., A, B, O alleles in the ABO human blood type system)
Epistasis
One gene affects the phenotypic expression of an independently inherited gene (e.g., baldness: 1st gene controls whether one is bald or not, and the 2nd controls the hair color)
Codominance
Both alleles are completely expressed [e.g., (R Red) x (W White) = (RW Red & White speckled)]
![<p>Both alleles are completely expressed [e.g., (R Red) x (W White) = (RW Red & White speckled)]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d1beec92-3d6b-40cd-b24a-c918718c9404.png)
Dihybrid cross
Tests two different genes simultaneously.
Law of Segregation
Pairs of alleles are separated when gametes are formed.
Law of Independent Assortment
Pairs of alleles will be sorted independently of one another when gametes are formed.
Aneuploidy
The occurrence of an abnormal number (extra/missing) of chromosomes that is often caused by nondisjunction.
Nondisjunction
The failure of chromosomes or chromatids to separate during Mitosis/Meiosis; can result in gametes with too many or too few chromosomes.
Sex-linked genes
Genes that reside on a sex chromosome.
Sex-influenced genes
Genes that can be affected by the sex of the individual carrying the trait.
Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome)
Having three copies of chromosome 21 instead of the normal two copies.
X-inactivation
During embryonic development in female mammals, one of the two X chromosomes is inactivated, forming a highly condensed chromosome (Barr body).
Linkage map
Uses recombination frequency to show the relative positions of genes on a chromosome.
Penetrance
The proportion of individuals with a specific genotype that will express the corresponding phenotype.
Expressivity
The variation of a phenotype for a specific genotype.
Autosomal dominant
A single copy of the mutated gene is enough to express the condition.
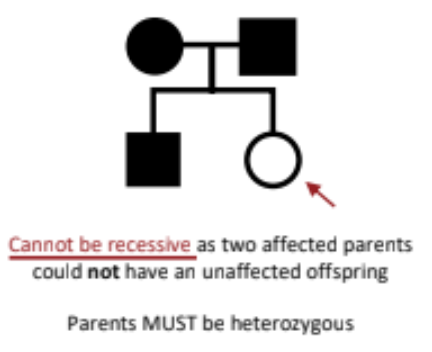
Autosomal recessive
Two copies of the mutated gene must be present to express the condition.
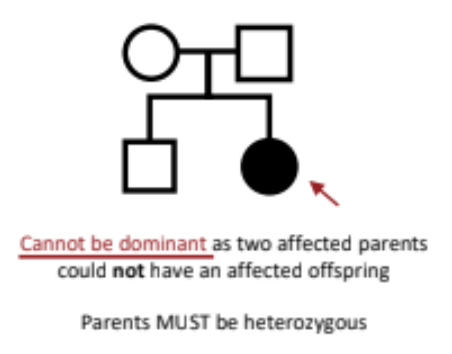
Colchicine
Arrests mitosis by interfering with mitotic spindle formation; it can prevent cells from replicating and has anticancer effects.
Proto-oncogenes
Stimulate normal growth; if mutated, they become oncogenes (cancer-causing genes).
Tumor suppressor genes
Make proteins that help control cell growth; if mutated, may lead to cancer.
X-linked dominant
A single copy of the mutation of a gene on the X chromosome is enough to cause the condition in both males & females.
X-linked recessive
Two copies of the mutated gene on the X chromosomes causes the condition in females; one copy will cause the condition in males.
Chromosomal aberrations
Changes in chromosome number or structure.
Inversions
A chromosome segment is rearranged in the reverse of its original orientation.
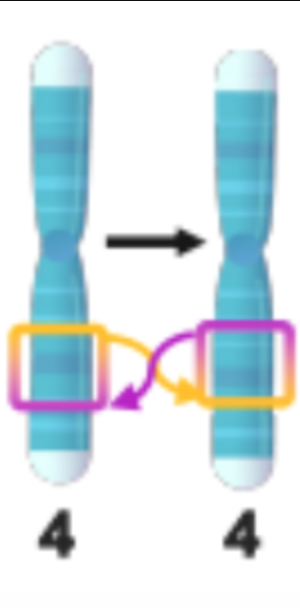
Deletions
A chromosome segment is missing or deleted.
Translocation
A chromosome segment is moved to another; it can be reciprocal or nonreciprocal (substitution).
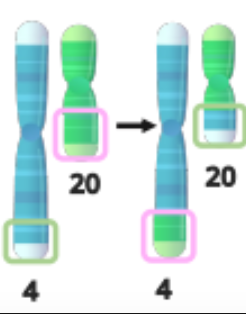
Duplication
A chromosome segment is repeated on the same chromosome.
Y-linked
Genes located on the Y chromosome cause the condition/trait.