Physics particles
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Atomic radius
1x10-10m
Nuclear radius
1x10-15m
Nucleon number
number of protons plus the number of neutrons in an atom
Always a whole number
Isotopes
elements with the same number of protons and electrons, but a different number
of neutrons.
Same charge as each other
Radioisotope
radioactive isotope of an element
Ions
different charges to their equivalent atom (electron gained or lost)
Four fundamental forces
Strong nuclear
Weak nuclear
Electromagnetic
Gravity
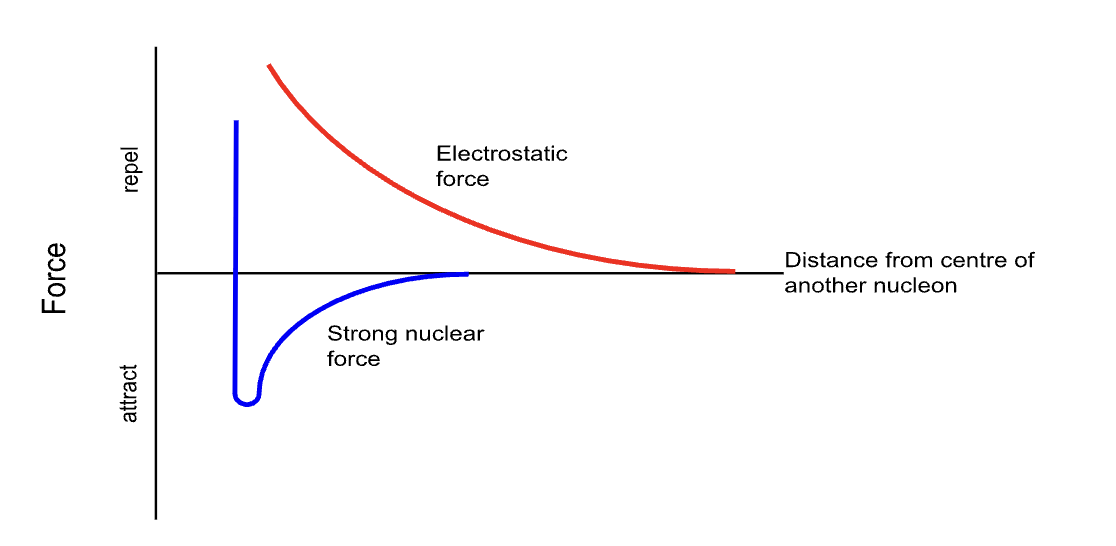
Strong Nuclear force
Both attractive and repulsive
Attractive over short-range (up to 3 fm)
Repulsive over very short range (under 0.5 fm)
Prevents electromagnetic repulsive forces between protons causing nucleus to fly apart
Unstable nucleus
nucleus that will change (by undergoing fission, fusion or emitting radiation)
electron anti-neutrino
by product of beta decay
fundamental, nearly massless particles
Second most common particle in the universe
Specific charge [C]
the relative charge of a particle divided by its mass (the ratio of its total charge to its mass)
Antiparticles
subatomic particles that have the same mass as their corresponding matter particle but with the opposite electric charge
An antiparticle has the exact same mass as its corresponding particle.
The electric charge is opposite to the particle
Have opposite spin and colour (for quarks)
often denoted with a bar over their symbol or a different symbol
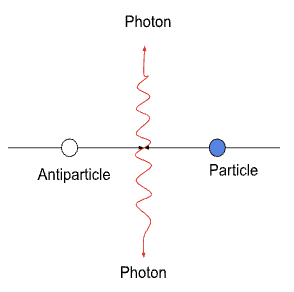
Annihilation
when a particle and the corresponding antiparticle meet and their mass is converted into radiation energy.
This process releases 2 photons (a single photon cannot ensure a total momentum of 0 after the collision)
The minimum energy of each photon, hfmin ,is given by equating the energy of the two photons, 2hfmin, to the rest energy of the particle and antiparticle
I.e. 2hfmin = 2E0, where E0 is the rest energy of the particle
Minimum energy of each photon produced hfmin = E0
Usually gamma-ray photon produced
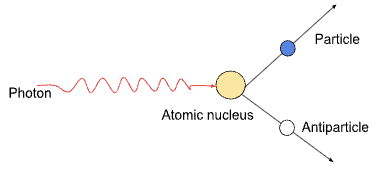
Pair production
when a photon creates a particle and the corresponding antiparticle, and vanishes in the process
For a particle and antiparticle, with both rest energy E0, you can calculate the minimum energy hfmin and minimum frequency Fmin that the photon must have to produce the particle-antiparticle pair
Minimum energy of photon needed = hfmin = 2E0
Starts with a gamma photon, and branches out to produce a particle and anti-particle, nearly always a electron and a positron
Nucleon
a proton or neutron in the nucleus
Nuclide
each type of nucleus
Labelled using isotope notation
Strong nuclear force
a force that holds a nucleus together and overcomes the electrostatic force of repulsion between the protons in the nucleus, keeping the protons and neutrons together
Same effect between two protons as it does between two neutrons or a proton and a neutron
Strong nuclear force effect
Attraction from around 3fm to 0.5 fm, less than 0.5 fm it is a repulsive force
Beta decay
when a neutron in the nucleus changes into a proton
Neutrinos
subatomic particles which carries some energy away from the nucleus during beta decay
Antimatter
the counterpart to ordinary matter, consisting of particles with the same mass but opposite charge
When antimatter and matter particles meet they destroy each other and radiation is released
Can make use of this in a positron emitting tomography (PET) hospital scanner
positron
antiparticle of the electron

Positron emission
takes place when a proton changes to a neutron in an unstable nucleus with too many protons
PET Scanner used for brain scan
Positron emitting isotope administered to patient and some reaches brain via blood
Each positron emitted travels no further than a few millimeters before it meets electron and annihilate each other, causing two gamma photons to be produced and are sensed by detectors
This builds up an image in a computer and an image is built up from the detector signal of where the positron emitting nuclei are inside the brain
Rest energy
mass of a particle when it is stationary
Dirac’s theory of antiparticles
Annihilates the particle and itself if they meet, converting total mass into photons
Has exactly the same rest mass as particle
Has exactly opposite charge to particle if particle has a charge
Millions of electron volts [MeV]
Energy of a particle / Antiparticle unit
1MeV = 1.6 x10-13J
Defined as the energy transferred when an electron is moved through a potential difference of 1 volt
Can be calculated using E=mc2
Minimum energy of each photon produced equation
hƒmin = E0
hƒmin being minimum energy of each photon produced
E0 being rest energy
Minimum energy of each photon needed equation
hƒmin = 2E0
hƒmin being minimum energy of each photon needed
E0 being rest energy
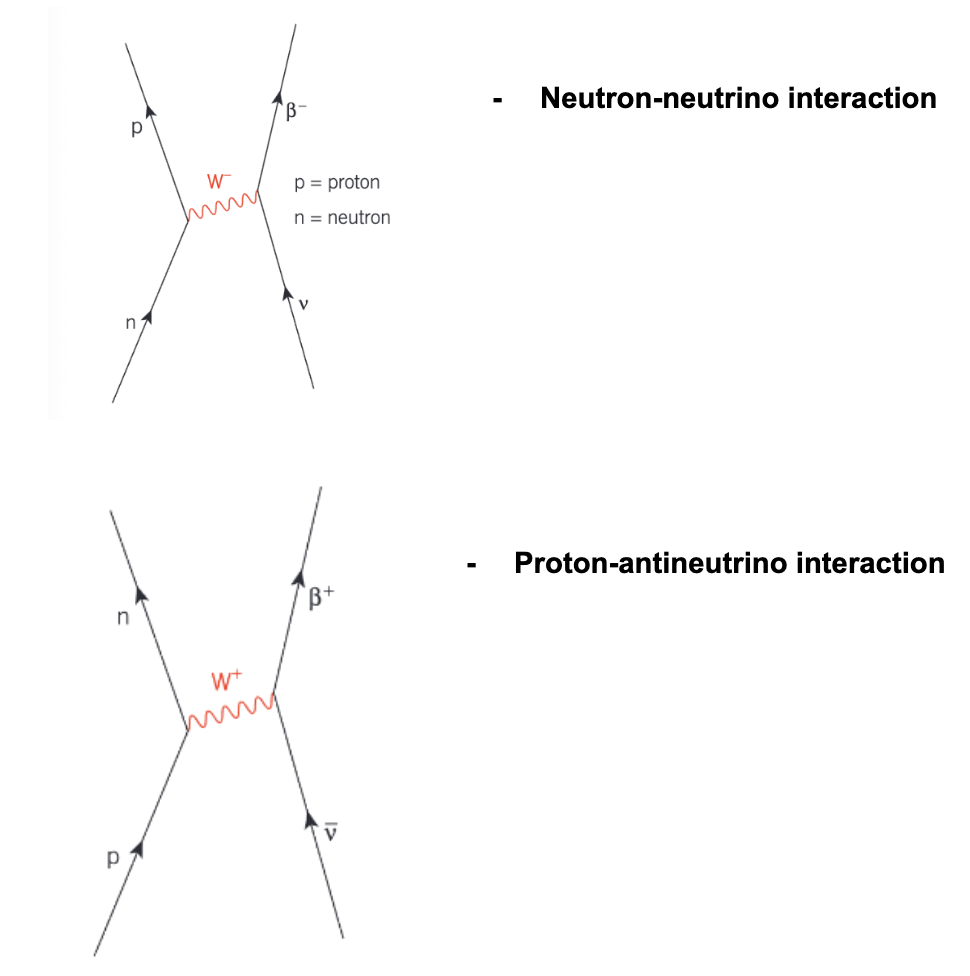
Exchange particles
particles that exist temporarily to cause ‘particle interactions’
e.g.
electrostatic attraction/repulstion
ß- decay
Electromagnetic force: exchange particles = photon
Weak nuclear force exchange: exchange particles = W+, W-, Z+
Feynman diagram
represents particle interactions
Charge must be conserved at each vertex
W bosons and Z bosons
name of the exchange particle for a weak nuclear force
Non-zero rest mass
Very short range (no more than 0.001 fm)
Positively or negatively charged (W+ or W-)
Quarks
make up particles like protons and neutrons
Twelve quarks
6 particles, 6 anti-partiles
Negative name particles are negatively charged
Does interact via / experience a strong nuclear force
Fractional charged
Fundamental particles
particles which cannot be broken down into smaller particles
E.g. neutrinos, anti-neutrino, electrons, positrons, leptons, tau, quarks
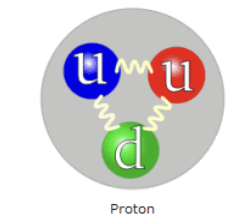
Protons quark structure
made up from 3 quarks (2 up quarks and 1 down quark )
p = u + u + d
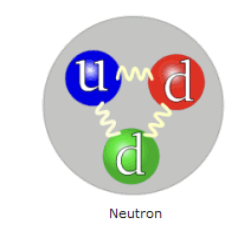
Neutron quark structure
made up from 3 quarks (2 down quarks and 1 up quark)
n = u + d + d
Leptons
Twelve leptons
Six particles, six antiparticles
Don’t interact via / experience a strong nuclear force
Have integer charge
Lighter than hadrons
List of particle Leptons
Electron
Electron Neutrino
Muon
Muon Neutrino
Tau
Tau Neutrino
List of antiparticle Leptons
Positron
Electron anti-neutrino
Anti-muon
Muon anti-neutrino
Anti-tau
Tau anti-neutrino
List of particle Quarks
Up
Down
Top
Bottom
Strange
Charm
List of particle anti-quarks
Anti- Up
Anti - Down
Anti - Top
Anti - Bottom
Anti - Strange
Anti - Charm
Hadrons
Heavy
Not fundamental particles
Subject to the strong interaction
Two types:
Baryons
Mesons
Baryons
made of 3 quarks
Protons are the only stable baryon which other baryons eventually decay to
E.g protons and neutrons
Mesons
made of 1 quark and 1 anti-quark
E.g pions and kaons
Kaons - have to have a strange or anti-strange quark
Quantum numbers
numbers that must be conserved in particle interactions (value before an interaction = value after interaction)
Charge
Mass-energy
Hadron number
Baryon number
Strangeness
Baryon number
Baryon Number = 1 (e.g. proton)
Anti-Baryon = -1 (e.g. anti-proton)
Baryon number of quark = ⅓
Baryon number of anti-quark = -⅓
Non-baryon = 0 (e.g. electron)
Lepton number
Lepton number = 1
Anti-lepton number = -1
Lepton number of quark and anti-quark = 0
Non-lepton = 0 (anything else)
Strangeness
Strange quark = -1
Anti-strange quark = 1
Hadrons
Pion - another exchange particle of the strong nuclear force, between proton (p+) and neutron (n0)
Kaons can decay to pions
Gluons - holds together the quarks within hadrons such as protons and neutrons
General information about particles
Particles beginning with ‘p’ are the most stable
Many exist for very short periods of time due to being unstable
Decay is a weak interaction
Strange quarks
Strange quarks produce via strong nuclear interactions
Created in pairs
Strangeness conserved in the strong interactions
Can change by 0, +1, -1 in weak interactions
Lepton decay
Taus decay into muons
Muons decay into electrons
Electromagnetic waves
consists of an electric wave and a magnetic wave, which travel together and vibrate
Travel and vibrate at right angles to each other and to the direction in which they are travelling
Travel and vibrate in phase with each other
Emitted as short bursts of waves, with each burst leaving the source in a different direction
Photons
a packet of electromagnetic waves that are emitted by a charged particle when it loses energy
Happens when a fast moving electron is stopped, slows down or changes direction
Happens when an electron in a shell of an atoms moves to a different shell of lower energy
Established by Einstein when he used his ideas to explain the photoelectric effect
Photon energy equation
E = hf
h as plancks constant
Laser beams
consists of photons of the same frequency
Power of laser beam is the energy pers second transferred by photons
Laser beam power equation: power of beam = nhf
n = number of photons in beam passing a fixed point per second
hf = energy in each photon
Nature of light
Light sometimes behaves like a particle
Particles of light are called photons and have zero rest mass
Can be:
reflected
refracted
diffracted
Interference
Planck’s constant
6.63 x 10-34 Js
Electron volt (eV)
the amount of energy gained by an electron as it accelerates through a potential difference of 1 volt
an alternative unit to the joule for energy
1eV = 1.6 x 10-19J
1eV has the same magnitude as the charge of single electron
Photon emissions
Emitted when an electron (in an atom) moves from a high energy level to a low energy level
Energy it loses is emitted as a photon
Can also be atoms in a sample going from high energy level to a low energy level
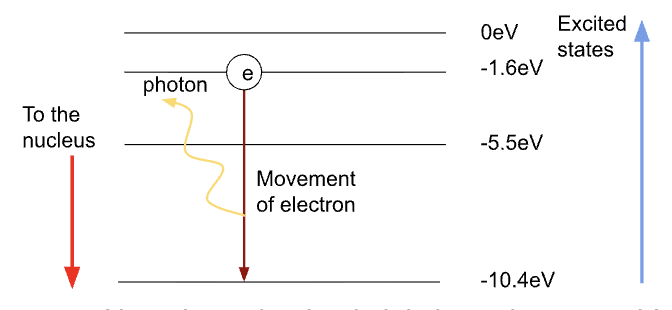
Energy levels diagram
Negative value imply it is bound to something
Photons lose energy to move to a lower energy level (if the levels were given positive values, they would be gaining energy)
Must have 0 energy when they are far away from the nucleus (no longer bound to the atom at this highest 0eV energy level)
Range of wavelength for visible light
400nm to 700nm
Photon emission
Electrons becom excited (gain energy when the gas is heated to a high temperature)
emitted when an electron (in an atom) moves from a higher energy level to a lower energy level.
The energy that it loses is emitted as a photon
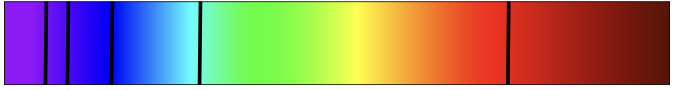
Two types of atomic line spectra
Emission spectra
Absorption spectra
Emission spectra
certain wavelengths / colours of light are given out / emitted
Appears as bright coloured lines on a dark background
Can be produced by heating a gas
Certain wavelengths (colours) of light will be emitted

Absorption spectra
certain wavelength / colours of light are taken in / absorbed.
Will appear as dark lines on a spectrum when viewed with a spectrometer
Can be produced by shining light through a sample of an element (normally as a gas) and observing the wavelengths that have been absorbed
Energy levels
quantised places for electrons(electron shells)
Ionisation
when the electron moves to 0eV energy level , the electron is no longer bound to the atom (leaving the atom)
Photoelectric effect
process of electrons being emitted from a material
When a photon is absorbed by an electron it will excite the electron to a higher energy level
If the energy of an incoming photon is big enough, then the electron will escape the atom and the atom is now ionised
It is evidence of the particle theory of light
Photoelectric effect Process
Ultraviolet light photons excite electrons in the zinc / ionise the zinc
Electrons leave the zinc plate making it positively charged
Electrons from the bass rod are attracted towards the zinc
Leaves brass rod with a positive charge at the bottom
Which attracts the negatively charged gold leaf
Work function
the minimum energy needed to ionise a material
Usually defined from the ground state
Threshold frequency
the minimum frequency associated with the work function energy, if a photon has a lower frequency than the threshold frequency then it cannot ionise the atom
When over threshold frequency, the extra energy becomes kinetic energy of the photoelectron
Photoelectric effect equations
ɸ = hft
h - planck’s constant [Js]
ft - the threshold frequency [Hz]
ɸ (phi) - the work function [J]
Conservation of energy equation
hf = ɸ + Ek max
hf - the energy of an incident photon [J]
ɸ (phi) - the work function [J]
Ek max - the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electron
higher intensity light on photoelectric effect
More intense light hitting a metal, more photons per second hit the metal
More photoelectrons emitted per second
No change to velocity or kinetic energy of electrons
Higher frequency light on hitting a metal (shorter wavelength)
Each photon has more energy (coming in)
Each emitted photoelectron has greater kinetic energy
No effect on number of electron emitted per second
Stopping potential
the minimum potential required to stop photoelectric emission
Depends on the metal, intensity and frequency of incident light
Kinetic energy of electrons is zero because extra work needs to be done against the potential difference
Kinetic energy maximum of emitted electrons = electronic charge x velocity
Wave-particle duality
light sometimes behaves as a wave and sometimes as a particle
Particles only display wave properties only when they are small and relatilistic (moving at a significant proportion to speed of light)
Particle properties of light
Photoelectric effect
Line spectra
Louis de Broglie discovery
said that when a particle has momentum it has a corresponding wavelength
Formula for de Broglie wavelength
λdb = h / p or λdb = h / mv
λdb - de Broglie wavelength (of a particle)
h - planck’s constant
p or mv - the momentum
Wave properties of light
Reflection
Refraction
Diffraction
Interference