Review of the Normal Cell and Causes of Cell Injury
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Define a cell.
a membrane bound structure which can be divided into functional units which is interconnected by a fluidic system of fusing and blebbing of these membrane bound structures
What is the cytocavitary network?
fluidic system of fusing and blebbing of membrane bound structures in a cell
The cell is enclosed by a phospholipid bilayer which forms what?
a selective barrier
What helps determine the cell function?
the selective barrier formed by the phospholipid bilayer
Define selective barrier
keep certain items in selective spaces
Membrane bound vesicles are shuttled in which direction?
from the ER to Golgi apparatus to other organelles or the plasma membrane
Organelles and membrane bound vesicles are embedded within what?
the cytosol
What is the cytosol?
cytoplasmic matrix containing water, dissolved ions, and macromolecules like proteins
Membrane bound structures interact with what?
the cytoskeleton
What is the cytoskeleton?
the structural network of the cell which helps in movement, cell division, and many biochemical pathways
What are the three types of filaments within a cell?
microfilaments
intermediate filaments
microtubules
What is the purpose of microfilaments?
facilitate cell motility
What is the purpose of intermediate filaments?
provide physical strength to the cells, often via junctional complexes
What is the purpose of microtubules?
move organelles and vesicles within the cytosol, and chromosomes via the mitotic spindle
The nucelus is composed of what?
chromatin surrounded by a bilayered nuclear membrane with pores
What is chromatin?
DNA coiled around histones
What are the two types of chromatin?
euchromatic nuclei
heterochromatic nuclei
Which type of chromatin is loosely coiled and involved in active transcription to mRNA?
Euchromatic
Which type of chromatin is tightly coiled and is inactive?
heterochromatic
Is the nucleus membrane bound?
Yes
Which non membrane bound structure is found within the nuclei?
nucleoli
What is the function of nucleoli?
synthesis of ribosomal RNA
The prominence of nucleoli measures what?
the cells synthetic activity
What are the two types of endoplasmic reticulum?
rough
smooth
Which type of endoplasmic reticulum is continuous with the nuclear membrane and is lined by ribosomes?
rough
Which type of endoplasmic reticulum lacks ribosomes?
smooth
What is the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
protein syntehsis
basophilia (staining with H&E) of a cell’s cytoplasm
What is the function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
metabolizing drugs, lipids, steroid, carbohydrates, glycogen
Cells with adbundant smooth endoplasmic reticulum will have what appearance of cytoplasm?
pink, finely vacuolated
Give an example of cells that have adbundant smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
endocrine cells
What is the function of the golgi apparatus?
synthesizes and packaging center for proteins to be exported out of the cell
The Golgi apparatus is not always visible by light microscopy within a cell. When it is viible, it is often due to what?
a large production of proteins such as immunoglobulins (plasma cells)
What are the functions of the mitochondria?
produce ATP through oxidative phosphorylation
involved in apoptosis
cell signaling
cell differentiation
cell growth
Are lysosomes membrane bound?
Yes
Lysosomes contain what type of enzymes?
hydrolytic
The enzymes found in lysosomes digest what?
most chemical compounds taken up through endocytosis or phagocytosis
What is the function of lysosomes?
aid in intracellular digestion
Enzymes in lysosomes are synthesized by what?
rough endoplasmic reticulum
Enzymes in lysosomes are process and packaged where?
in Golgi
Enzyme in lysosomes are released in vesicles from the golgi into where?
cytosol
What are the different types of junctional complexes?
tight junction
gap junction
adherens junction
desmosome junction
hemidesmosome junction
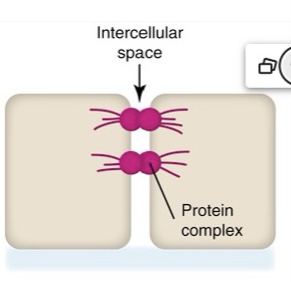
What type of junctional complex is this?
tight junction
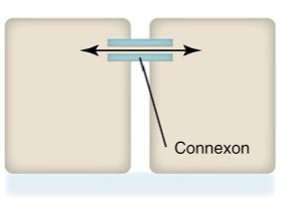
What type of junctional complex is this?
gap junction
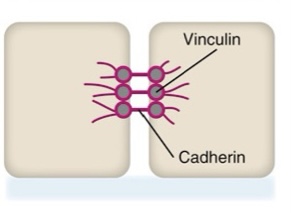
What type of junctional complex is this?
adherens junction
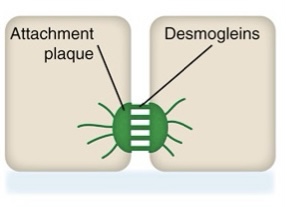
What type of junctional complex is this?
desmosome junction
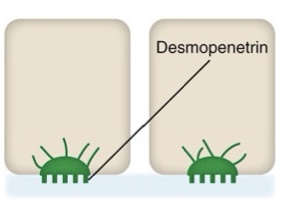
What type of junctional complex is this?
hemidesmosome junction
Can a cell be damaged functionally with no apparent morphologic alterations?
Yes
What are the four major mechanisms of cellular injury?
depletion of ATP
permeabilization of cell membranes
disruption of biochemical pathways, especially protein synthesis pathways
DNA damage
There are too many causes of cell injury to count, what list can be used to make sure you cover all bases? (Hint: DAMNITV)
degenerative
anomalous/aging
metabolic
nutritional/neoplastic
infectious/inflammatory
trauma/toxic
vascular
What is the most common and important cause of cell injury?
hypoxia
Explain the pathway for cell damage caused by hypoxia.
no oxygen —> no oxidative phosphorylation —> anaerobic glycolysis (long term) or reversible injury or no ATP production —> no ATP production causes no ATPase pump function —> no ion stabilization in cell / no homeostasis / cells fill with water and burst —>reversible injury or point of no return (death)
What are the four causes of hypoxia?
cardiac or respiratory failure
reduced vascular perfusion (ischemia)
reduced oxygen transport by erythrocytes
inhibition of respiratory enzymes within the cell
What can cause reduced oxygen transport by erythrocytes?
anemia
carbon monoxide poisoning
What can cause inhibition of respiratory enzymes within the cell?
cyanide toxicosis
Ischemia can result in what?
reperfusion injury
What is reperfusion?
the restoration of blood flow to a site
Reperfusion injury can result in what?
Formation of free radicals (reactive oxygen species)
What are the reactive oxygen species (free radicals)?
superoxide anion (O2-)
hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
hydroxyl radical (HO-)
Free radicals are commonly formed during what?
oxidative phosphorylation
Free radicals function as what?
cell signaling molecules which affect cell proliferation and survival
Where are reactive oxygen species generated?
nucleus
mitochondria
peroxisomes
endoplasmic reticulum
other organelles
Imbalances in reactive oxygen species (increased numbers) causes what?
counteracts antioxidants resulting in oxidative stress and damage to DNA, RNA, cell membranes, proteins, and deactivation of specific enzymes
What is the main enzyme responsible for catalyzing free radicals?
superoxide dismutase
Other than superoxide dismutase, what other components can help catalyze free radicals?
glutathione peroxidase
vitamin E/selenium
vitamin C
When cell injury in irreversible, what will happen?
death
If a cell responds to reversible cell injury, what occurs?
adaptation
What is the response to both reversible and irreversible cell injury, making it difficult to distinguish cells that will recover or die?
acute cell swelling
What is the most common cause of acute cell swelling?
hypoxia
Other than hypoxia, what else can cause acute cell swelling?
direct injury to cell membrane
What can cause direct injury to cell membrane?
lipid peroxidation from reactice oxygen species
binding of toxins
damage to ion channels
transmembrane pores
What do we term cell swelling in hepatocytes and renal epithelial cells?
hydropic degeneration
What do we term cell swelling in keratinocytes?
ballooning degeneration
What do we term cell swelling in astrocytes?
cytotoxic edema
Grossly, cell swelling can appear as what?
increased volume and weight of an organ (increased organ/tissue size)
increased pallor (pale appearance)