bi 114 - class disease presentations
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What causes malaria?
Plasmodium parasites, transmitted to humans through the bites of infected female anopheles mosquitoes.
How is malaria diagnosed?
blood smear, PCR, rapid diagnostic tests, spleen enlargement
How is malaria treated.
Because there is NO MALARIA VACCINE available in the US…
Medications (Artemisinin-based combination therapies)
Is there a malaria vaccine
Yes but they are only used in malaria endemic countries.
Is malaria a pandemic?
Nope! It's endemic.
It's not endemic in Massachusetts but it is in 83 countries, and 1/2 of the world's population lives in areas at risk of malaria transmission.
What kind of disease is rabies?
zoonotic, viral disease that affects the CNS of mammals, including humans.
How is rabies transmitted?
saliva/animal bite
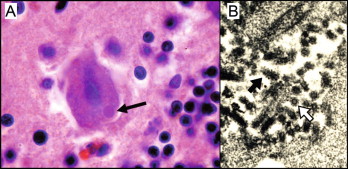
Negri bodies under a microscope are indicative of what disease?
Rabies!
What does the rabies virus look like?
Rod, enveloped virus (lowkey like a bullet).
How is rabies diagnosed?
Direct fluorescent antibody test, reverse transcriptase PCR, direct Immunohistochemistry test.
Is there a vaccine for rabies?
yes, theres one for pre-exposure and post-exposure
additionally, all domestic animals should be vaccinated!
What should you do if you get rabies?
Get a fast acting rabies immunoglobulin shot. It contains antibodies that neutralize the virus.
then, wash bite with soap and water.
talk to a healthcare provider ASAP cus the infection is 100% preventable.
What kind of disease is hepatitis b?
rCDNA virus that causes acute/chronic liver inflammation.
What does hepatitis b lead to?
Cirrhosis (liver scarring, liver cancer, and liver failure).
True or false: hepatitis b is often asymptomatic
Trey, it's usually an asymptomatic disease.
How does one get hepatitis b?
Through contact with blood, semen, or other bodily fluids of an infected person (sex, sharing needles, mother to child transmission during childbirth).
How is hepatitis b diagnosed?
liver imaging/biopsy
serological test (blood test looking for antibodies)
How is hepatitis b treated?
antiviral medication (usually in chronic cases only, acute cases just require rest, good nutrition and water intake).
What kind of virus is hantavirus?
It's a zoonotic disease contracted by contact with rats and other rodents.
True or false: hantavirus is a pandemic
FALSE. Hantavirus is not a pandemic, but it has caused localized public health crises.
Main risk factor for hantavirus
Exposure to rodents or their pee/feces/saliva (particularly through inhalation of airborne particles containing the virus).
How is hantavirus diagnosed?
Hantavirus is diagnosed with serological methods or molecular laboratory testing.
Willy Burgdorfer
Discovered pathogen that causes Lyme disease.
What causes Lyme disease
Borrelia burgdorferi (spirochete)
Vectors of Lyme disease
infected blacklegged (deer) ticks (Ixodes scapularis)
Erythema chronicum migrans
bull's-eye rash characteristically seen in Lyme disease
Lyme disease prevention
Avoid waking in tall grass, light colored clothing to see ticks easily, bug spray, be cautious during warm weather