Test 4: Dynamic Earth
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/142
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
1
New cards
Difference between tide and eustatic sea level change
tides: daily changes in elevation of ocean surface
eustatic sea level change: global sea level changes in volume of water in the ocean
eustatic sea level change: global sea level changes in volume of water in the ocean
2
New cards
Factors causing astronomical tides
earth and sun (based on their relative movement) which makes those tides predictable
3
New cards
Movement of water in tidal currents
A horizontal movement of water often accompanies the rising and falling of the tide.
4
New cards
Causes of spring and neap tides and their relationship to the phases of the moon
spring: when there is the greatest difference between high and low water. (new or full moon)
neap tide: least difference between high and low water. (1st and 3rd quarter moon)
neap tide: least difference between high and low water. (1st and 3rd quarter moon)
5
New cards
Parts of a tidal curve
Taking the appropriate published time and height of high water (or time of low water for a low water curve) and the height of low water you are able to fill in you curve for the day.
6
New cards
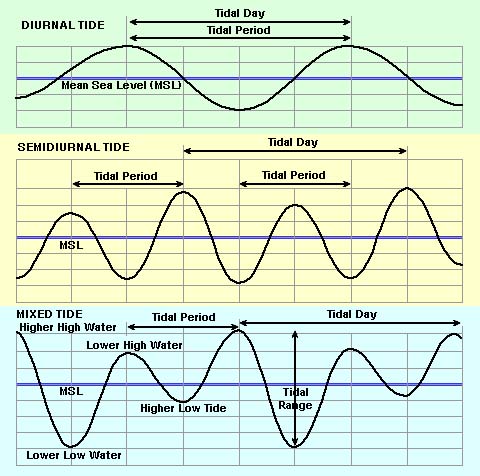
Different types of tidal curves and what produces different tidal curves
\-diurnal, semidiurnal, and mixed
\-produced through high and low tides and the position of the sun and moon
\-produced through high and low tides and the position of the sun and moon
7
New cards
Causes for variation in tidal time, height and ranges
the shape of the shoreline, the alignment of the sun, moon, and earth
8
New cards
Operation of an oceanic amphidromic tide
Amphidromic points occur because interference within oceanic basins, seas and bays, combined with the Coriolis effect, creates a wave pattern — called an amphidromic system — which rotates around the amphidromic point.
9
New cards
Future and past tides
can find out a rough prediction always based on the predictability of the position of the sun, moon, and the earth
10
New cards
Difference between deep-water and shallow-water waves
deep water: depth of the water is greater than 1/2 the wavelength
shallow water: occurs at depth shallower than the wavelength divided by 20
shallow water: occurs at depth shallower than the wavelength divided by 20
11
New cards
Changes in wave as approaches shore and breaking
as waves approach shore they "touch bottom" when the depth equals half of the wavelength, and the wave begins to slow down. As is slows, the wavelength decreases and the wave height increases, until the wave breaks
12
New cards
Development of wind-formed waves
wind-driven waves, or surface waves, are created by the friction between wind and surface water. As wind blows across the surface of the ocean or a lake, the continual disturbance creates a wave crest
13
New cards
Water velocity in standing waves
A standing wave has no water velocity
14
New cards
Movement of water in a rotary seiche
strong winds and rapid changes in atmospheric pressure push water from one end of a body of water to the other. When the wind stops, the water rebounds to the other side of the enclosed area. The water then continues to oscillate back and forth for hours or even days.
15
New cards
Factors controlling the period of a seiche
dependent on the bathymetry of the lake basin and on the effects of gravity and Coriolis forces
16
New cards
Development of cliffed coast and features that develop
A cliffed coast is a section of coast that has been cliffed by marine erosion or drowning.
Small bays, narrow inlets, caves, arches, and stacks
Small bays, narrow inlets, caves, arches, and stacks
17
New cards
Parts of a beach and how they form
berms: relatively flat platforms often composed of sand that are adjacent to coastal dunes or cliffs and marked by a change in slope at the seaward edge.
beach face: wet sloping surface that extends from the berm to the shoreline
foreshore and backshore: look at defintions
beach face: wet sloping surface that extends from the berm to the shoreline
foreshore and backshore: look at defintions
18
New cards
Development of fair-weather and foul-weather beaches
fall in pressure is an indicator of foul weather
19
New cards
Coastal features that can develop from beach migration
barrier islands from as well as a change in shoreline
20
New cards
Cliffed coastal features
Small bays, narrow inlets, caves, arches, and stacks are usually the result of erosion along structural weaknesses, particularly bedding, joint, and fault planes, and in the fractured and crushed rock produced by faulting.
21
New cards
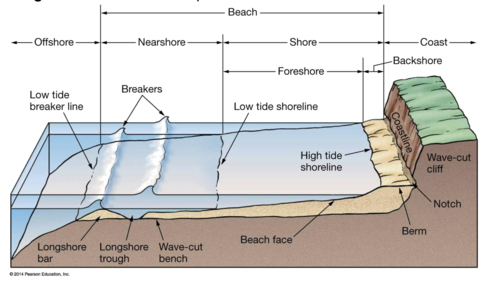
Parts of a beach
shoreline, foreshore, nearshore, offshore, beach face, berm, notch, etc.
22
New cards
Beach migration features
As the sea level rises, the barrier beach migrates landward, rolling landward over itself. The initial beach migrates landward over its own marsh into its second position. (lagoon, shoreface, barrier island, elevation)
23
New cards
Tides
Daily changes in the elevation of the ocean surface, the easiest ocean movements to observe
24
New cards
Eustatic sea level change
global sea level change related to changes in the volume of water in the ocean
25
New cards
astronomical tides
tides caused by inertia and the gravitational force of the sun and moon, predictable
26
New cards
meterological tide
a tide influenced by the weather, atmospheric pressure and wind, only as predictable as the weather
27
New cards
mean sea level
average of the highest and lowest tide levels of the ocean measured over a period of time
28
New cards
gravity
one of the major forces that controls tides, moons gravity causes oceans to bulge on both sides closest to the moon
29
New cards
centrifugal effect
Outward "force" directed away from center of rotation
30
New cards
bary center
point inside the earth, where the earth and moon orbit around
31
New cards
high tide
when water advances to its furthest extent onto the shoreline
32
New cards
low tide
when water recedes to its furthest extent
33
New cards
tidal current
alternating horizontal movement of water associated with the rise and fall of the tide
34
New cards
ebb tide
tidal phase during which water level is falling
35
New cards
flood tide
the tidal phase which the tidal current is flowing inland
36
New cards
slack water
a time of no current, occurs at high and low tides when current change direction, separates ebb and flood tides
37
New cards
tidal range
The difference in levels of ocean water at high tide and low tide, depends on time and location
38
New cards
spring tide
a tide just after a new or full moon, when there is the greatest difference between high and low water.
39
New cards
neap tide
a tide just after the first or third quarters of the moon when there is the least difference between high and low water.
40
New cards
syzygy
lining up of the moon, sun, and the earth (this is when tides are the most exaggerated)
41
New cards
new moon
A moon that is completely dark because it's unlit side is facing Earth
42
New cards
Half Moon
the Moon with half of its disk illuminated
43
New cards
full moon
moon phase when the entire side facing Earth is illuminated.
44
New cards
1st quarter moon
half of the moon near the sun is illuminated. moon is pulling on earth's water at right angle
45
New cards
3rd quarter moon
halfway between a full moon and the next new moon
46
New cards
tidal curve
height of water/time; most tidal curves two high/low tides per tidal day (24 hr. 50 m)
47
New cards
semidiurnal curve
two high tides and two low tides each tidal day with 2 high and 2 low at about the same height
48
New cards
diurnal curve
one low and one high tide for a daily tide
49
New cards
mixed tide
The tidal pattern of two unequal high and low tides daily
50
New cards
solar day
Earth's rotation period as defined by the position of the Sun in the sky; the time between successive passages of the Sun through the meridian
51
New cards
lunar day
Time between two successive overhead moons
24 hours, 50 minutes
24 hours, 50 minutes
52
New cards
solar declination
The latitude of overhead Sun; the place where one would go to find the Sun directly overhead at noon.
53
New cards
lunar declination
\-The moon's angular distance north or south of the equator
\-Creates diurnal and semidiurnal tides
\-Creates diurnal and semidiurnal tides
54
New cards
apogee
(away) centrifugal bulge and gravitational bulge is shorter
55
New cards
perigee
(around) earth is moving fastest in its orbit so centrifugal effect is greatest and tidal bulge is moving its fastest
56
New cards
corange circles
Lines in an amphidromic system connecting all points experiencing the same tidal range.
57
New cards
amphidromic point
A nodal or no-tide point in the ocean or sea around which the crest of the tide wave rotates during one tidal period.
58
New cards
amphidromic system
A depiction of the large-scale rotary motion of the tides in ocean basins and seas that results from the Coriolis deflection of the tides.
59
New cards
windset
Temporary change in sea level associated with the wind-generated build-up of water against the shore.
60
New cards
barometric tide
Term for temporary changes in sea level associated with changes in atmospheric pressure, not caused by wind. (meteorological tide)
61
New cards
Progressive wave tides
the tide wave moving across the sea surface like a shallow water wave, wind generated waves
62
New cards
standing wave tide
when 2 equal waves are going in opposite direction and there's up and down motion on the surface but waves don't progress
63
New cards
Crest
Highest point of a wave
64
New cards
Trough
Lowest point of a wave
65
New cards
wave front
distance measured parallel to crest or trough
66
New cards
wave height
vertical distance between crest and trough
67
New cards
wave period
the time interval between the passage of successive crests at a stationary point
68
New cards
wave length
the horizontal distance between adjacent crests or troughs
69
New cards
wave frequency
The number of waves that pass a fixed point in a given amount of time
70
New cards
wave speed
distance that a wave travels, wavelength and frequency
71
New cards
wave stability
(progressive) wave steepness
72
New cards
wave celerity
speed of the wave
73
New cards
deep water waves
waves moving through water deeper than half their wavelength
74
New cards
shallow water waves
are waves in water shallower than 1/20 their original wavelength.
75
New cards
wave base
The depth below the surface where the circular orbits become so small that movement is negligible. It is equal to one-half the wavelength
76
New cards
mass transport
slow, onshore movement of water
77
New cards
Orbits
circular current in water created by passing waves
78
New cards
wave energy
form of renewable energy that can be harnessed from the motion of the wave, 1/2 potential and 1/2 kinetic
79
New cards
old seas
term for all the waves passing through an area which are not related to the current wave-generating conditions
80
New cards
potential energy
stored energy, stored by the position of water above or below the mean level of the water surface if no wave existed
81
New cards
kinetic energy
energy of motion, moving water, has momentum
82
New cards
fetch
The area over which the wind blows, as fetch increase so does height of the wave
83
New cards
capillary waves
The slowest moving waves, when wind blows across still water, creates irregular surface for wind to transfer energy
84
New cards
chop
when wind speed is greater than celerity (V shaped crests and land troughs)
85
New cards
white cap
A white, foaming wave with a very steep crest that breaks in the open ocean before the wave gets close to the shore
86
New cards
fully developed sea
the maximum wave size possible for a wind of a specific strength, duration, and fetch
87
New cards
swell
long wave of water that moves continuously without breaking; very fast low crested wave
88
New cards
wave dispersion
The separation of waves as they leave the sea area by wave size. Larger waves travel faster than smaller waves and thus leave the sea area first, to be followed by progressively smaller waves
89
New cards
wave reflection
when a wave bounces off of a hard surface that changes the direction of the wave
90
New cards
wave refraction
Slowing and bending of progressive waves in shallow water, affects the shoreline
91
New cards
wave interference
the phenomenon that occurs when two waves meet and produce sea surface distortion and then continue with no alteration
92
New cards
seas
complex sea surface distortion produced by wave interference
93
New cards
headland
a narrow piece of land that projects from a coastline into the sea.
94
New cards
breaking wave
The result of waves dragging on the ocean bottom causing the water in the waves to fall forward as the waves bunch together, rise up, and break against the shore.
95
New cards
undertow
strong seaward bottom current returning the water of broken waves back out to sea
96
New cards
surf
turbulent water created by breaking waves
97
New cards
wave setup
increase in mean of water level above still water level
98
New cards
longshore current
a near-shore current that flows parallel to the shore
99
New cards
rip current
a relatively strong, narrow current flowing outward from the beach through the surf zone and presenting a hazard to swimmers. (swim parallel to get out of it)
100
New cards
tsunami
A giant progressive waves usually caused by an earthquake beneath the ocean floor, not formed by constructive interference, not a tidal wave, japanese for harbor wave