Biology 1.5 Photosynthesis
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is photosynthesis?
A chemical reaction that takes place inside photosynthetic organisms (e.g., plants, algae) converting light energy into chemical energy.
Write the word equation for photosynthesis.
Carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen.
Why is photosynthesis important?
Produces glucose, which is used in respiration to release energy.
Glucose is used to make complex organic molecules required for plant growth.
Animals rely on these organic molecules, which are transferred through food chains.
Produces oxygen, which is required by organisms for respiration.
Where does photosynthesis take place?
Within chloroplasts.
What is required for photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide.
Water.
Light.
Chlorophyll.
What is the role of carbon dioxide (CO2) in photosynthesis?
Provides the carbon (C) and oxygen (O) found in glucose.
What is the role of water (H2O) in photosynthesis?
Provides the hydrogen (H) found in glucose.
Oxygen (O2) is released as a by-product.
Why is light required for photosynthesis?
Provides the energy required for chemical reactions in photosynthesis.
What is chlorophyll?
A pigment found in chloroplasts that absorbs light.
Describe the two main stages of photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll absorbs light energy, which is used to split water into oxygen gas (waste product) and hydrogen ions.
Carbon dioxide combines with hydrogen ions to form glucose.
What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Temperature.
Light intensity.
Carbon dioxide concentration.
What is a limiting factor? (higher)
A variable that limits the rate of a particular reaction.
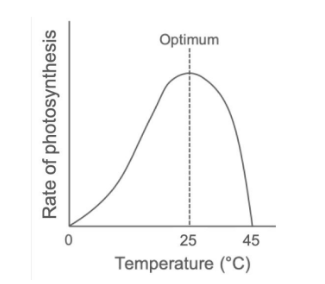
Explain how temperature affects the rate of photosynthesis.
Higher temperatures provide more kinetic energy for enzymes involved in photosynthesis, so the rate increases as temperature rises.
The optimum temperature is usually 25°C. If the temperature becomes too high (around 45°C), enzymes become denatured, and the rate of photosynthesis decreases.
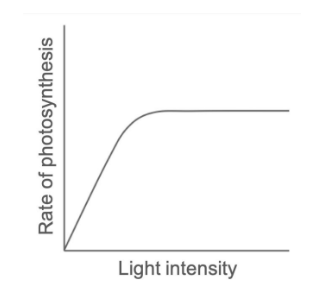
Explain how light intensity affects the rate of photosynthesis.
Rate of photosynthesis is directly proportional to light intensity.
As light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis increases.
Why does the rate of photosynthesis eventually plateau even if light intensity continues to increase? (higher)
Another factor (temperature or CO2 concentration) becomes limiting.
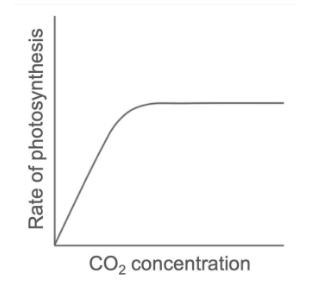
Explain how carbon dioxide concentration affects the rate of photosynthesis.
As carbon dioxide concentration increases, the rate of photosynthesis increases.
Why does the rate of photosynthesis eventually plateau even if CO2 concentration continues to increase? (higher)
Another factor (temperature or light intensity) becomes limiting.
When does temperature become a limiting factor? (higher)
When temperature drops too low on cold winter days.
When does light intensity become a limiting factor? (higher)
At night.
When does carbon dioxide concentration become a limiting factor? (higher)
Atmospheric CO2 concentrations generally remain constant.
CO2 only becomes limiting when light intensity and temperature are not limiting factors.
How is glucose used by the plant?
Used in respiration to release energy.
Converted to starch or oils and stored.
Converted to sucrose and transported to other plant areas.
Converted to cellulose, which is used in cell walls.
Formation of proteins, which requires nitrates from the soil.
Draw a graph to show the effect of increasing temperature on the rate of photosynthesis
Draw a graph to show the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis
Draw a graph to show the effect of carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis