Biology C3 VOCAB
1/37
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
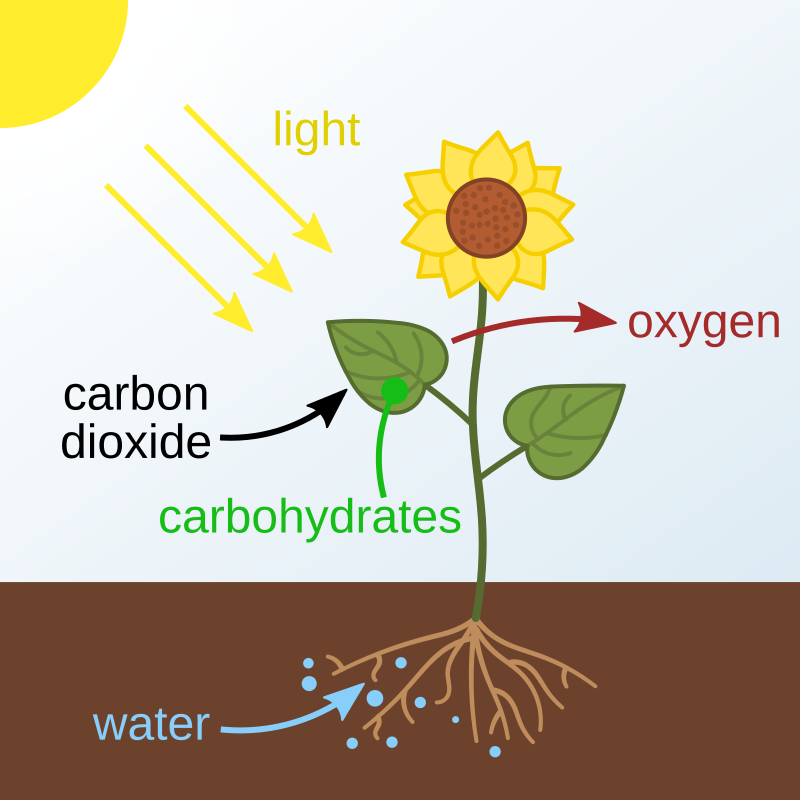
Photosynthesis
The process where plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose and oxygen.
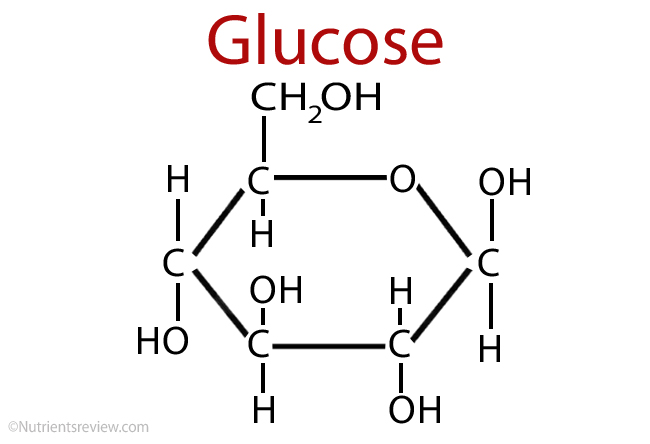
Glucose
A simple sugar produced during photosynthesis; the main source of energy for plant cells.
Chlorophyll
A green pigment found in plants that captures sunlight for photosynthesis.
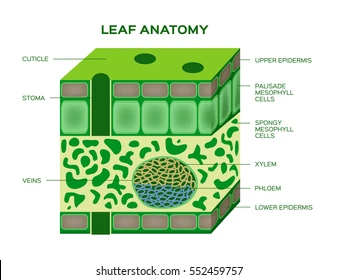
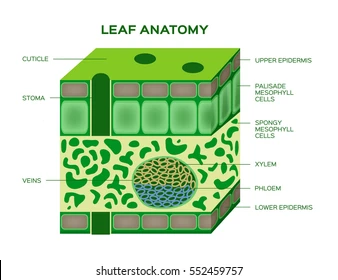
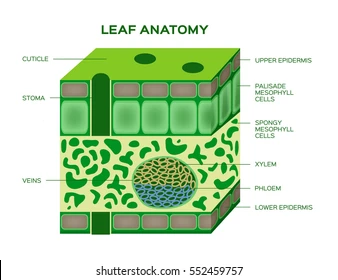
Epidermis
The outer layer of cells covering leaves, stems, and roots that protects the plant
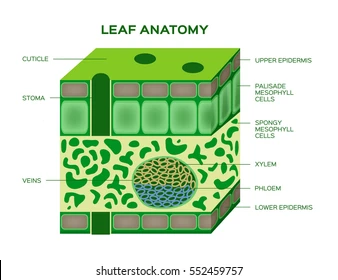
Cuticle
A waxy layer on leaf surfaces that prevent water loss.
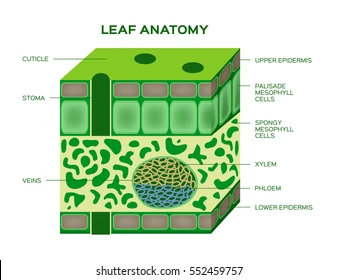
Palisade Tissue Cell
Long, column-shaped cells under the leaf’s upper surface where most photosynthesis occurs.
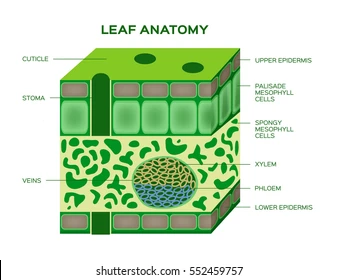
Spongy Tissue Cell
Loosely packed cells in the leaf with air spaces for gas exchange
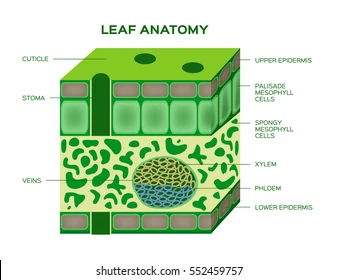
Stomata
Small openings on the leaf underside that allow gas exchange (CO₂ in, O₂ out).
Guard Cell
Cells that surround and control the opening and closing of stomata.
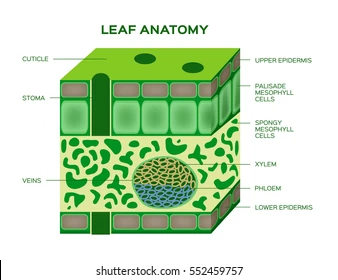
Xylem
Vascular tissue that transports water and minerals from roots to leaves.
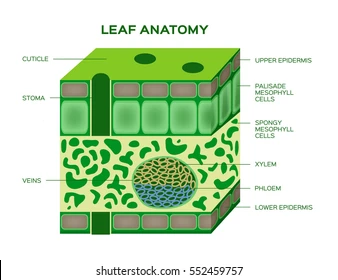
Phloem
Vascular tissue that transports sugars and nutrients throughout the plant.
Vascular Bundles
Groups of xylem and phloem tissues that transport substances in stems and leaves

Tissue
A group of similar cells working together to perform a function.

Organ
A structure made of different tissues working together to perform a complex function
System
A group of organs that work together to carry out a life function (e.g., transport system in plants)

Lenticel
A small pore in a plant's stem or root that allows gas exchange.
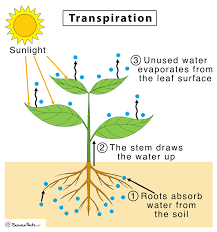
Transpiration
The loss of water vapour from leaves through stomata.

Turgor Pressure
The pressure inside plant cells caused by water pushing against the cell wall, keeping the plant firm.
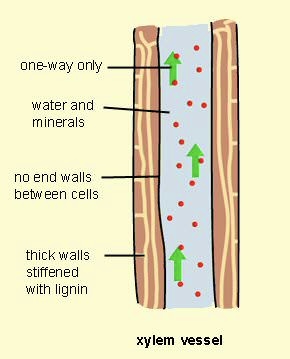
Xylem Vessel
A tube-like structure in xylem made of vessel elements for transporting water.
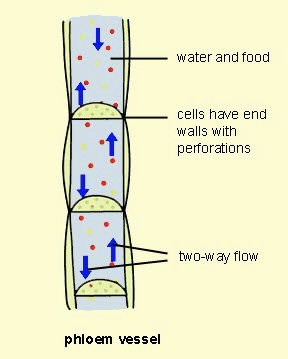
Phloem Vessel
A part of the phloem made up of sieve tubes and companion cells for transporting sugars.
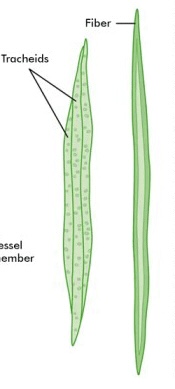
Tracheids
Long, tapered cells in xylem that help transport water and support the plant.
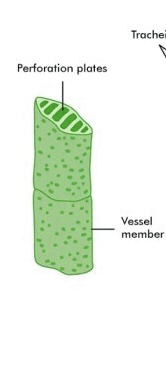
Vessel Elements
Short, wide xylem cells that form tubes for water transport.
Sieve Tubes
Phloem cells with pores that transport sugars; lack a nucleus.
Companion Cells
Phloem cells that support sieve tubes and help with sugar transport.
Sieve Plates
End walls of sieve tubes with holes allowing fluid flow between cells.
Root Hair
Extensions of root cells that increase surface area for water and nutrient absorption.
Xylem Sap
Water and dissolved minerals moving up through the xylem.
Cohesion
Water molecules sticking to each other; helps pull water up the plant.
Adhesion
Water molecules sticking to surfaces (like xylem walls); aids water movement.
Root Pressure
Pressure in roots that pushes water upward through xylem vessels.
Phloem Sap
A sugary fluid that moves through the phloem.
Stimuli
Environmental factors (light, gravity, touch) that plants respond to.
Tropism
A plant’s growth response toward or away from a stimulus.
Phototropism
A plant’s growth response toward light.
Sleep Movements
Daily movements of leaves or flowers in response to light/dark (e.g., folding at night).
Auxin
A plant hormone that controls growth, especially in response to light and gravity.
Nastic Response
A non-directional movement in plants in response to stimuli (e.g., Venus flytrap closing).
Gravitropism (Geotropism)
A plant’s growth response to gravity (roots grow down, shoots grow up).