Animal Ecology Slides Exam 1 Study Guide (2/13/25)
1/300
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
301 Terms
Ecology
the scientific study of the abundance and distribution of organisms in relation to other organisms and environmental conditions
Biotic environment
includes other living things
Abiotic environment
includes nonliving components (temperature, precipitation, pressure, chemical, etc.)
Types of field Ecologists/ Research Ecologists
Basic Research
Agricultural Research
Types Agriculture and Food Production
Crop rotation
Nutrient management
Cover Cropping
Pest management through natural predators
Forestry
Range Management
Pest management through predator
Beer
Cheers
Explain Crop rotation

Explain Nutrient management

Explain Cover Cropping

Explain Pest management through natural predators

Explain Foresty

Explain Range Management

Explain Pest management through predator

Explain Food production: Beer
Explain Food production: Cheese
Types of Natural Resource Management
Water Resource Management
Wetland Regulation and Mitigation
Habitat management
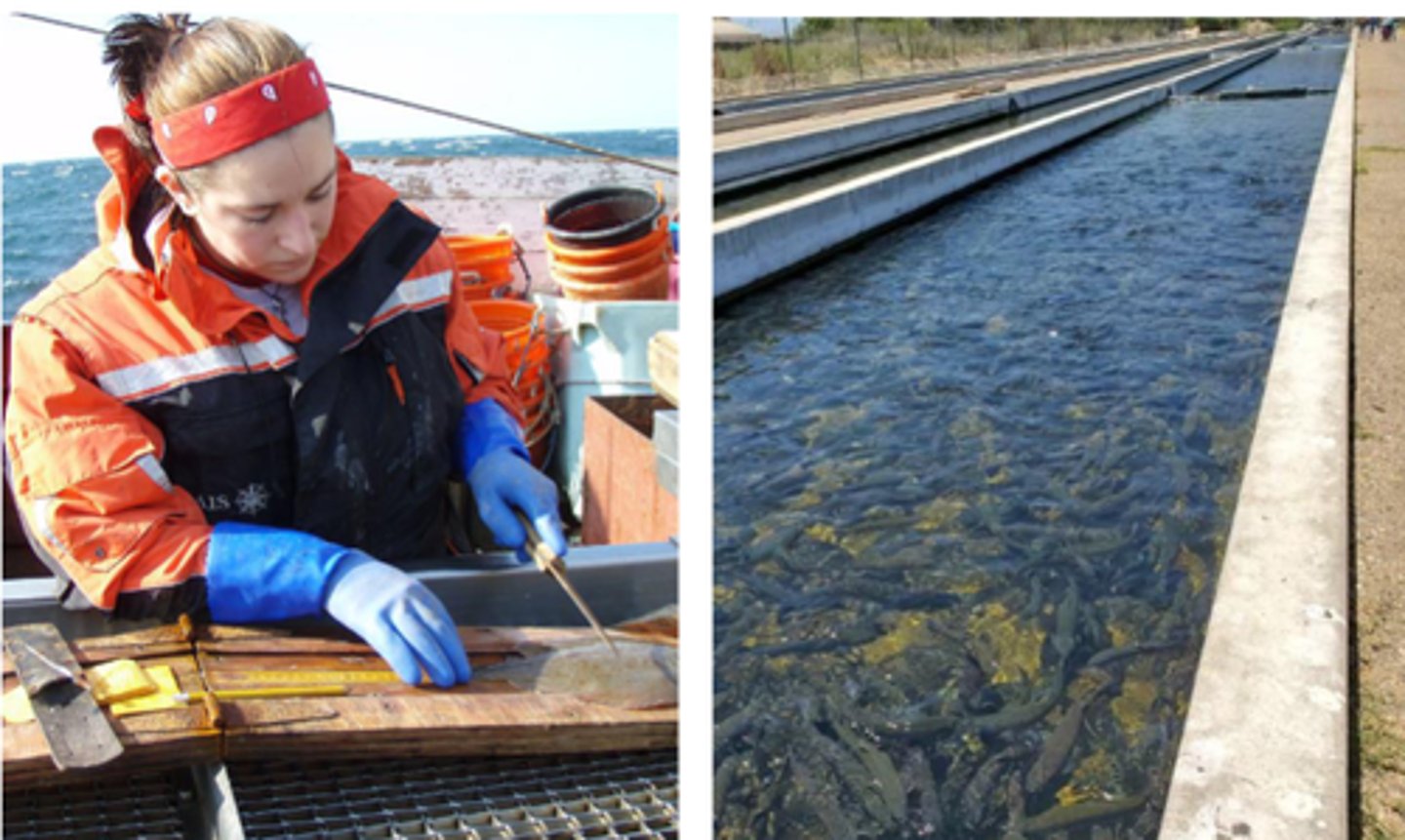
Fisheries biology and aquaculture
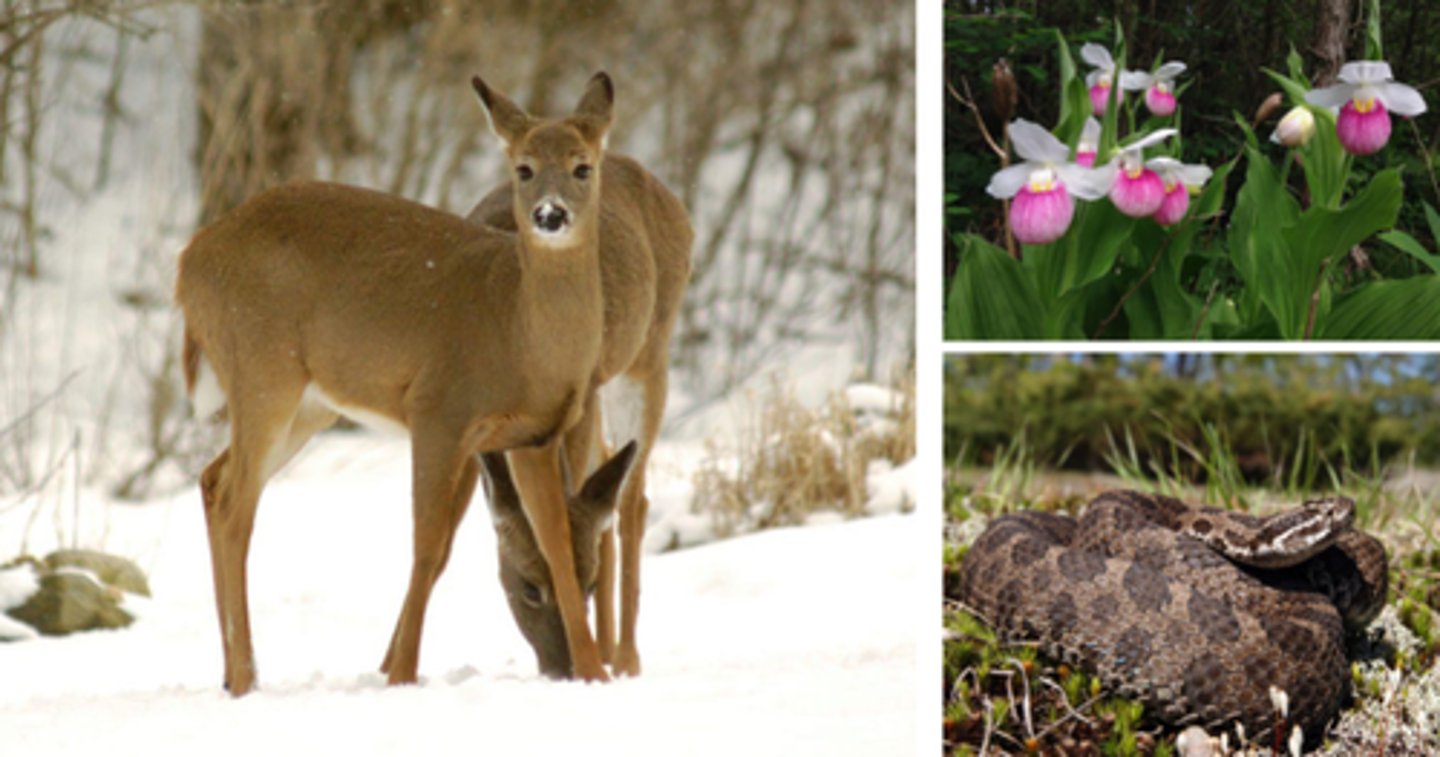
Wildlife Management
Landscape architecture
Explain Resource Management

Explain Wetland Regulation and Mitigation

Explain Habitat management
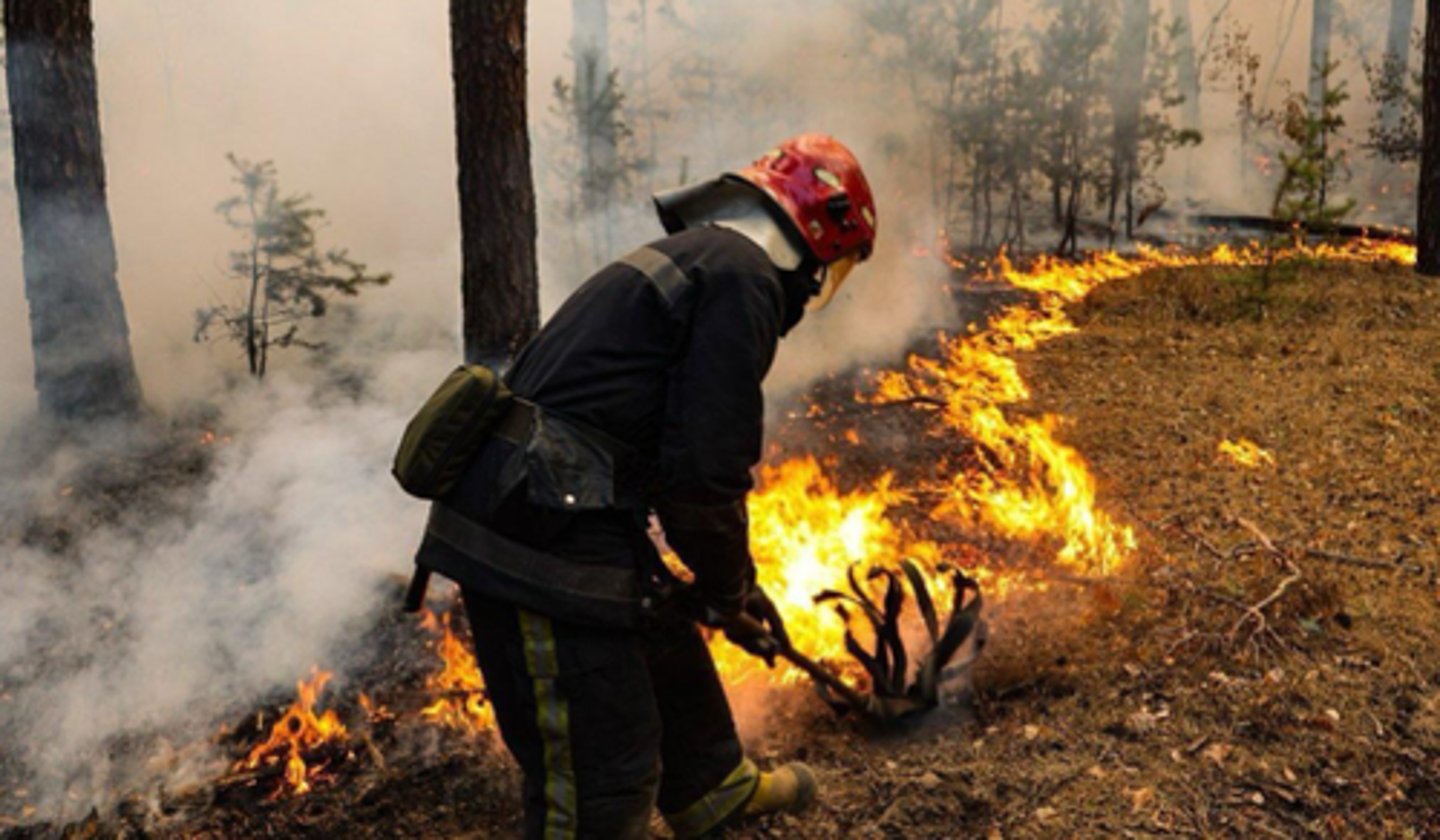

Explain Fisheries biology and aquaculture

Explain Wildlife Management

Explain Landscape architecture

Does Epidemic management have anything to with ecology?
Yes:
In terms of disease ecology explain enzoonotic disease prediction
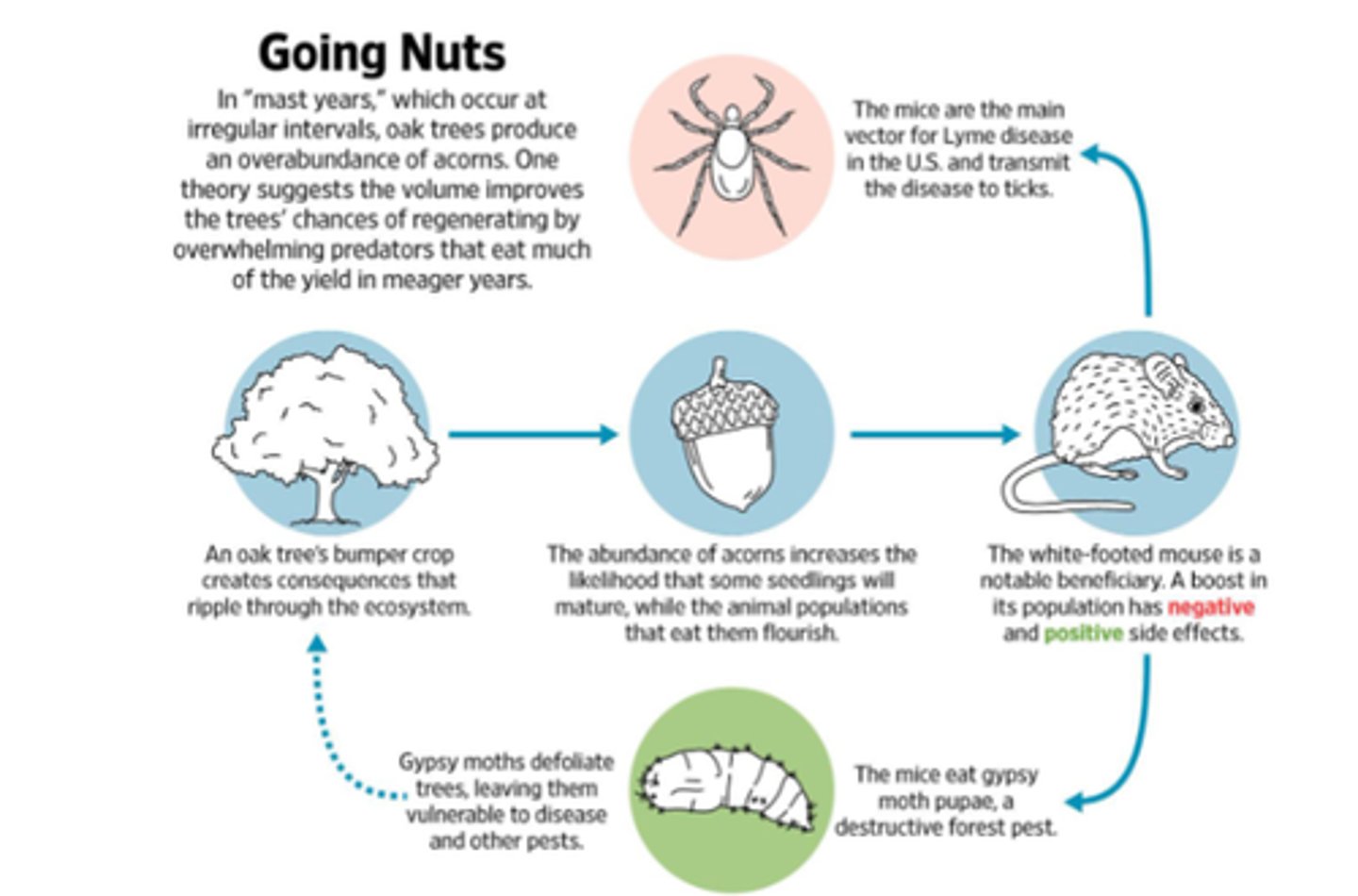
How does human health relate to ecology
microbiome
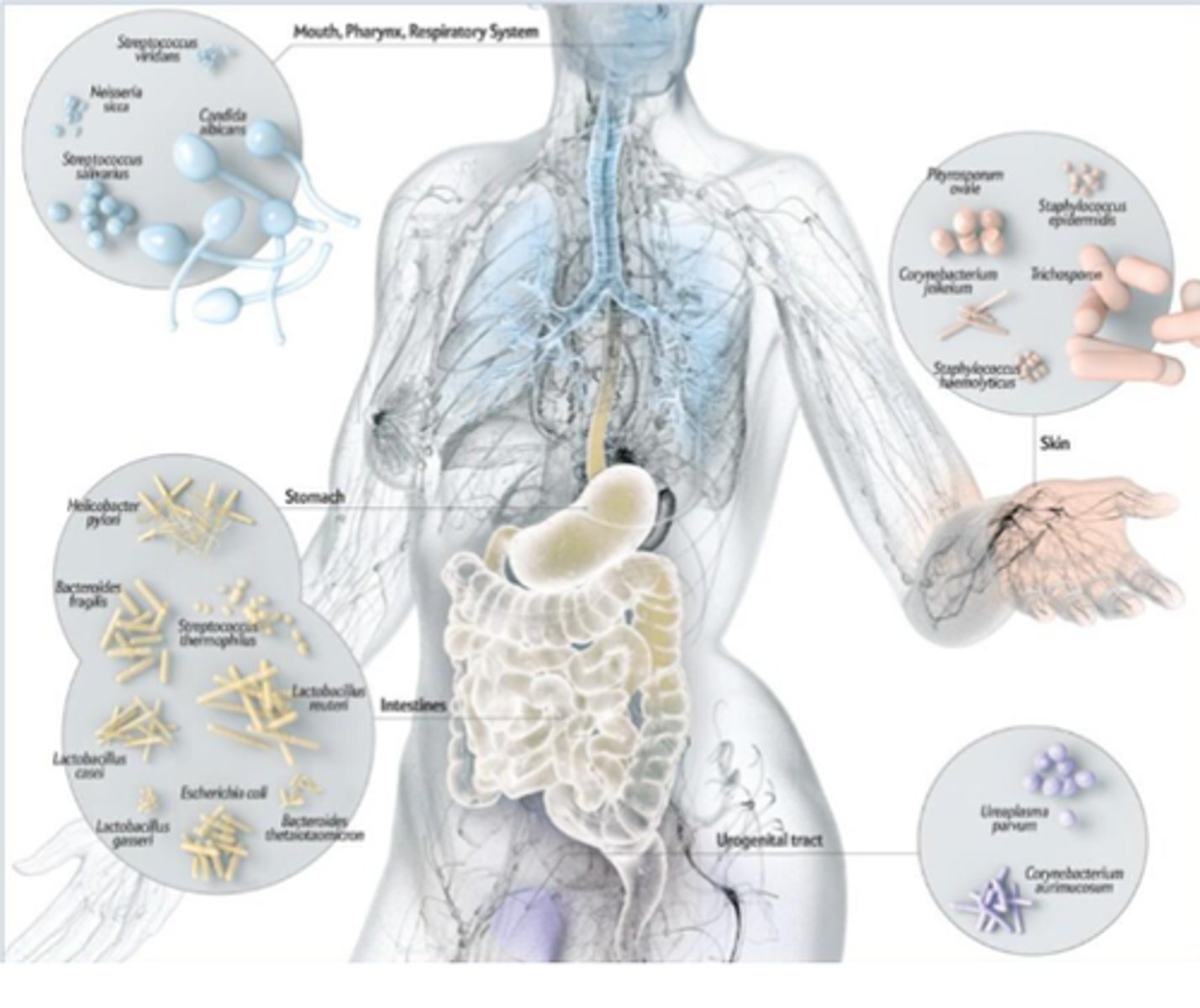
Organizational Schemes for Ecology do what?
1. Outline a hierarchical organization of ecological systems
2. Describe how organisms vary in energy acquisition relationships with other organisms
Examples of hierarchical organization
Individual -> Ecosystems -> Biosphere
Describe how organisms vary in energy acquisition relationships with others organisms
1. Autotrophic, Mixotrophic, Heterotrophic
2. Predation, Parasitism, etc.
What is the most fundamental unit of ecology?
The individual
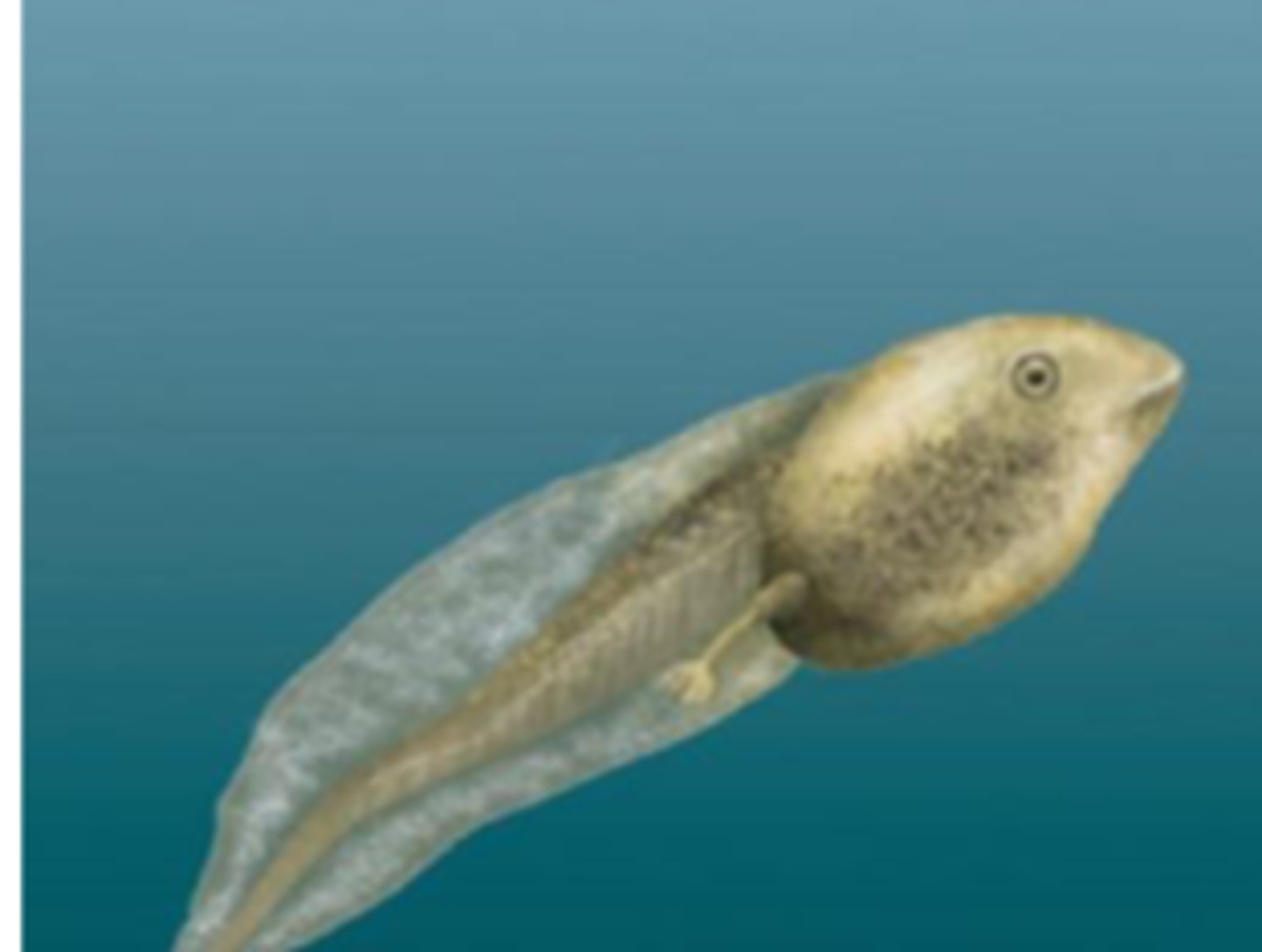

population
Individuals of the same species living in a particular area.
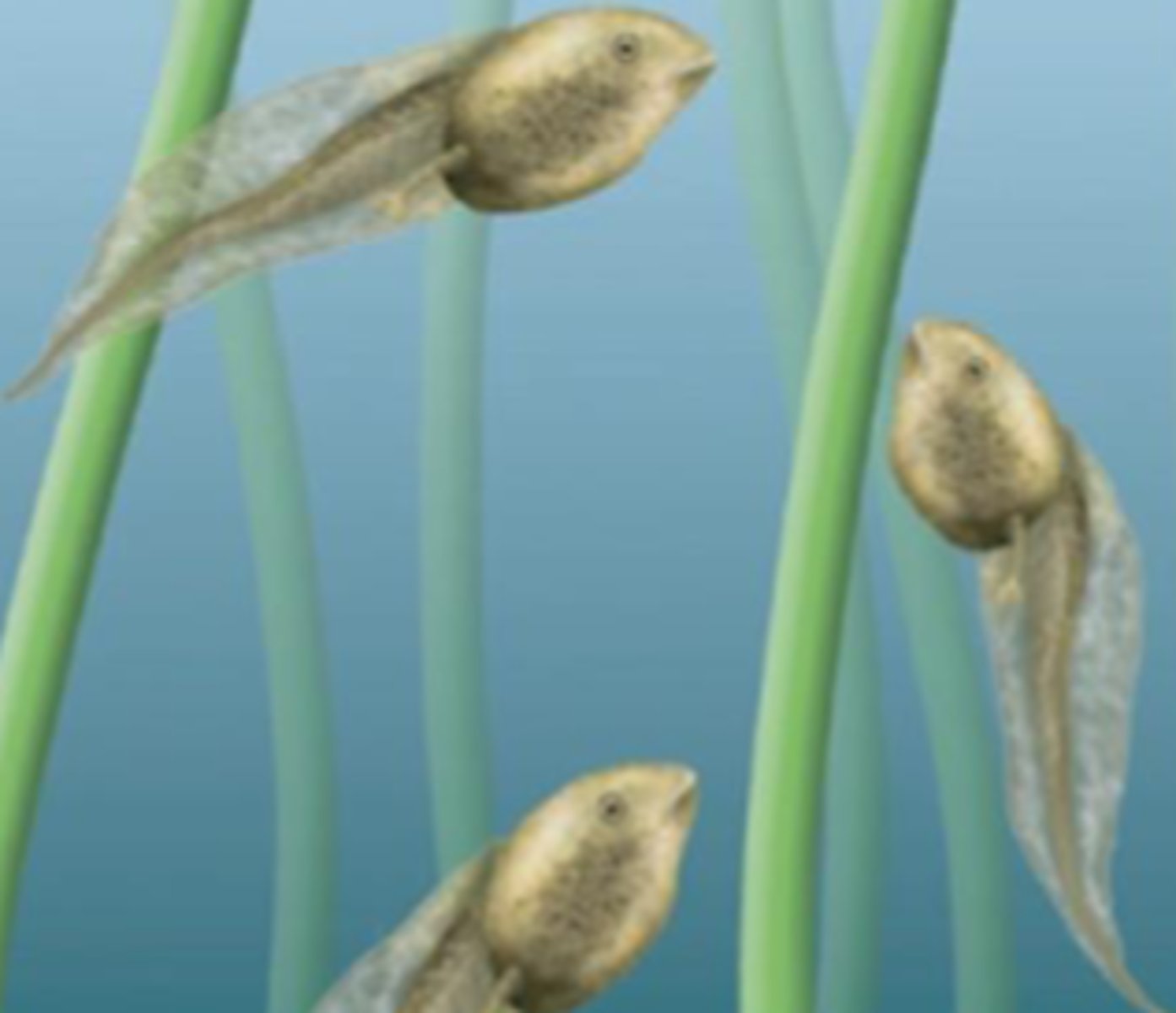

Community
All populations of species living together in a particular area
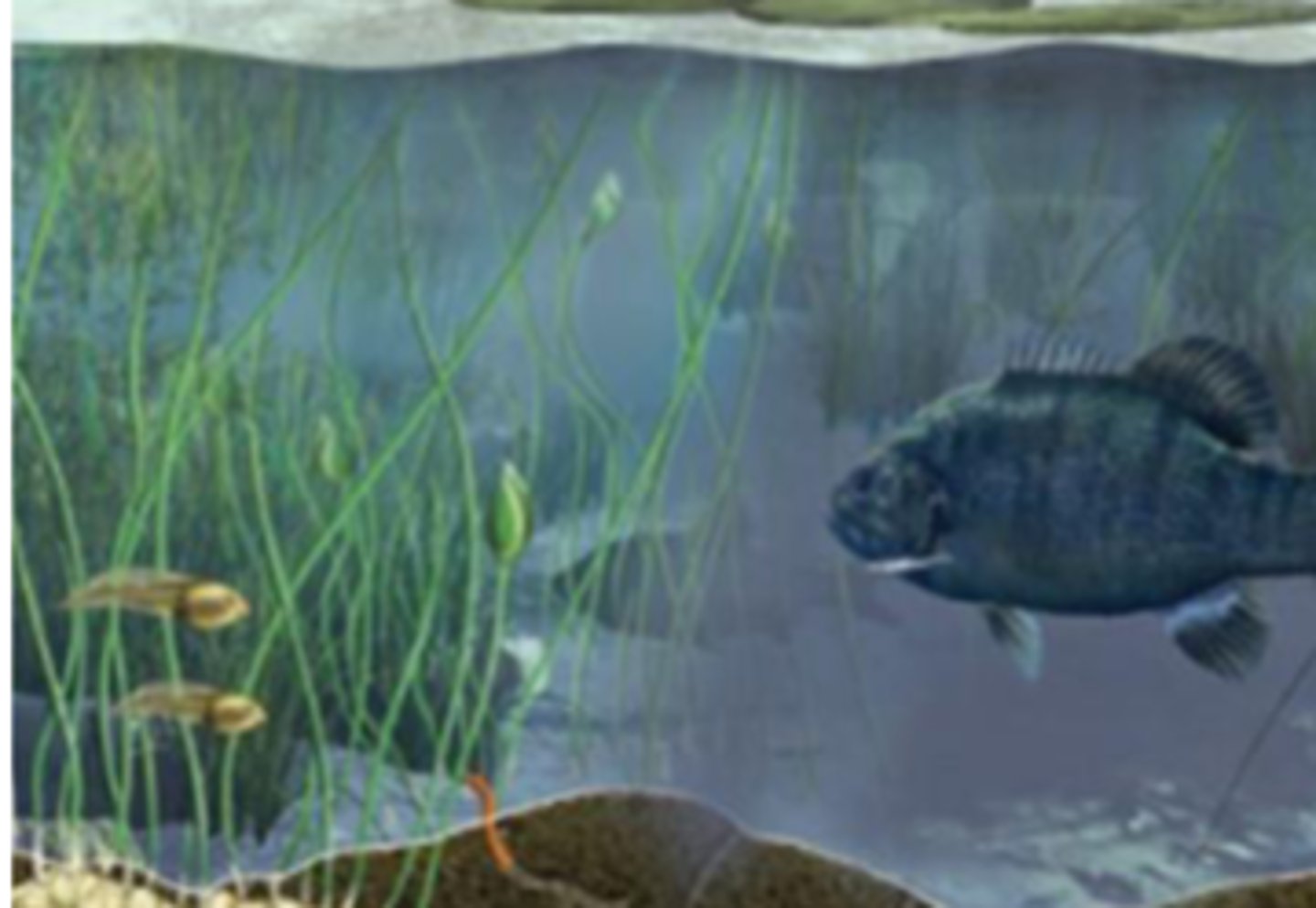

Ecosystem
One or more communities of living organisms interacting with their nonliving physical and chemical environments.

Landscape
Multiple ecosystems that are connected by the movement of individuals, populations, matter, and energy
The Biosphere
All the ecosystems on Earth.
Organisms can be classified based on their sources of _____________.
Organisms can be classified based on their sources of energy
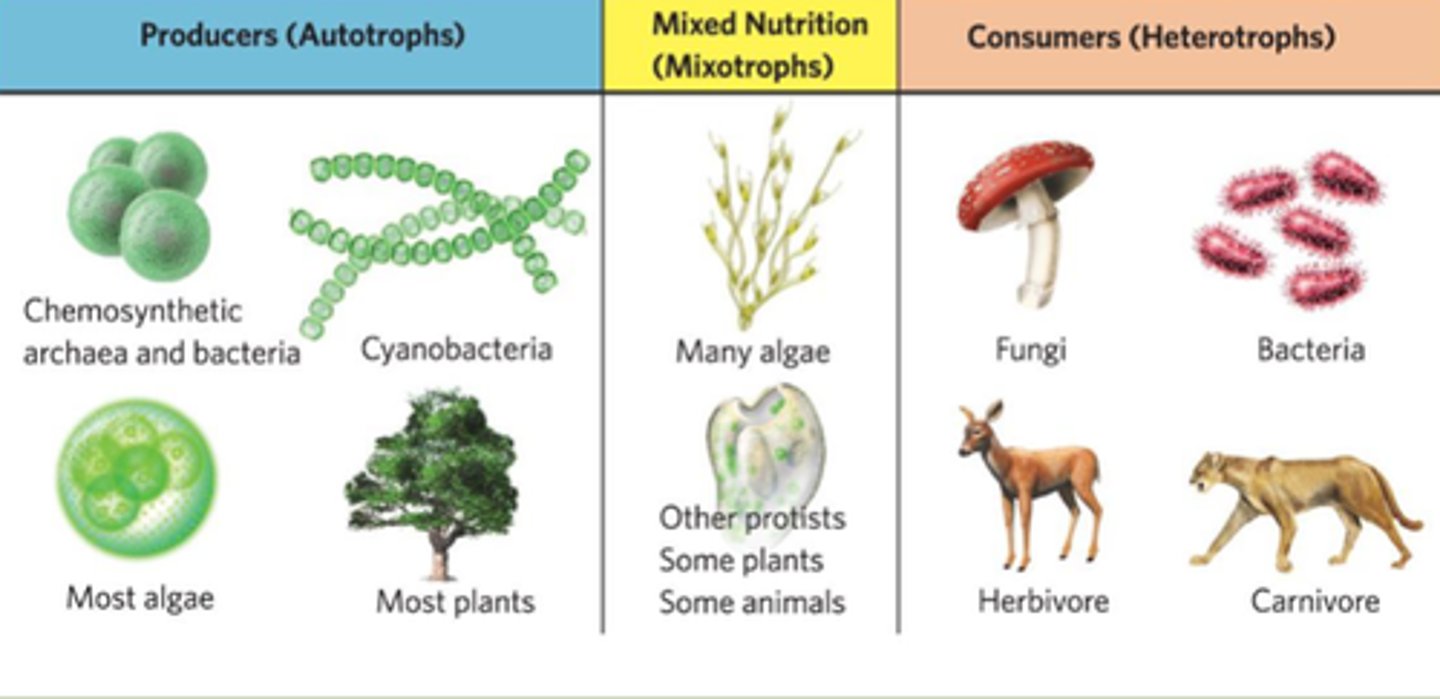
Producers (autotrophs)
an organism that uses photosynthesis to convert solar energy into organic compounds or uses chemosynthesis to convert chemical energy into organic compounds

Mixotrophs
an organism that obtains its energy from more than one source

Consumers (heterotrophs)
an organism that obtains its energy from other organisms; also known as a heterotroph

Organisms can also be classified based on how they interact with other _________________in addition to energy source
Organisms can be classified based on how they interact with other organisms.
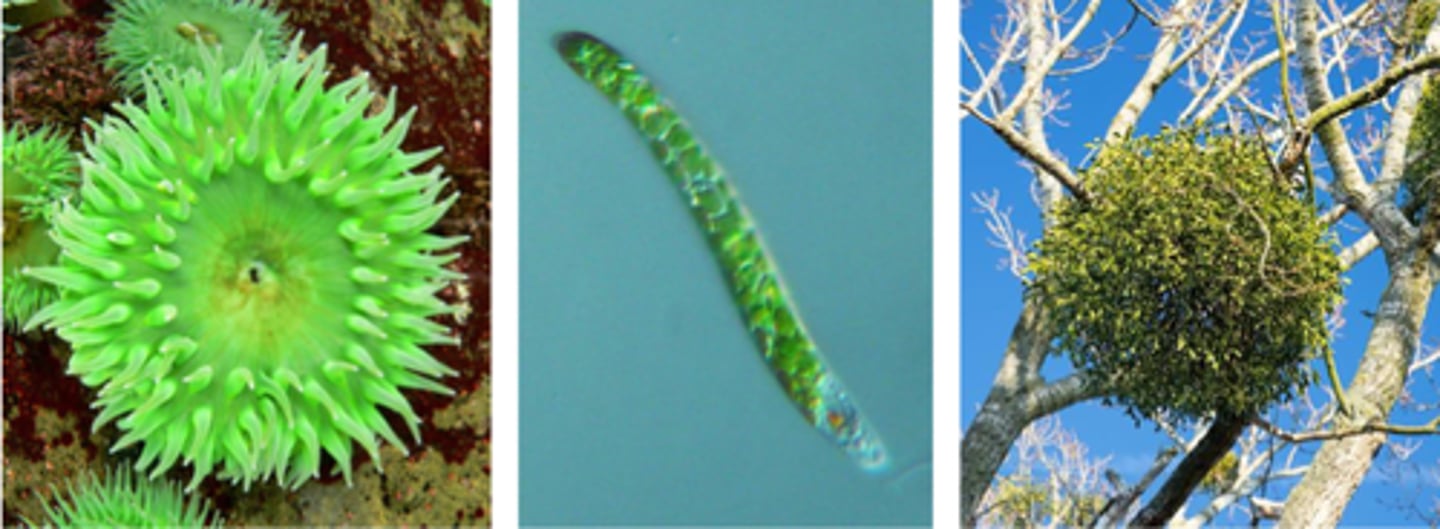
Predator
an organism that kills and partially or entirely consumes another individual

Herbivore
an organism that consumes producers such as plants and algae

Parasites
organisms that live and feed in or on another organism, while rarely killing their hosts
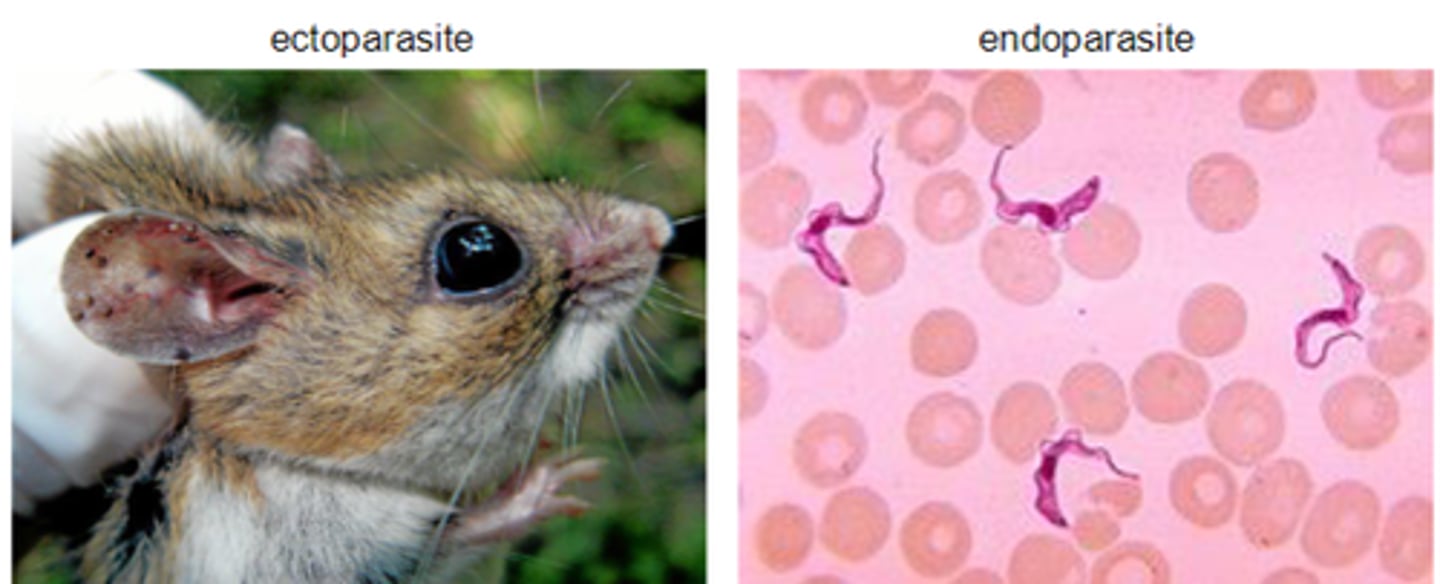
Parasitoid
an organism that lives within and consumes the tissues of a living host, eventually killing it

Scavenger
an organism that consumes dead animals
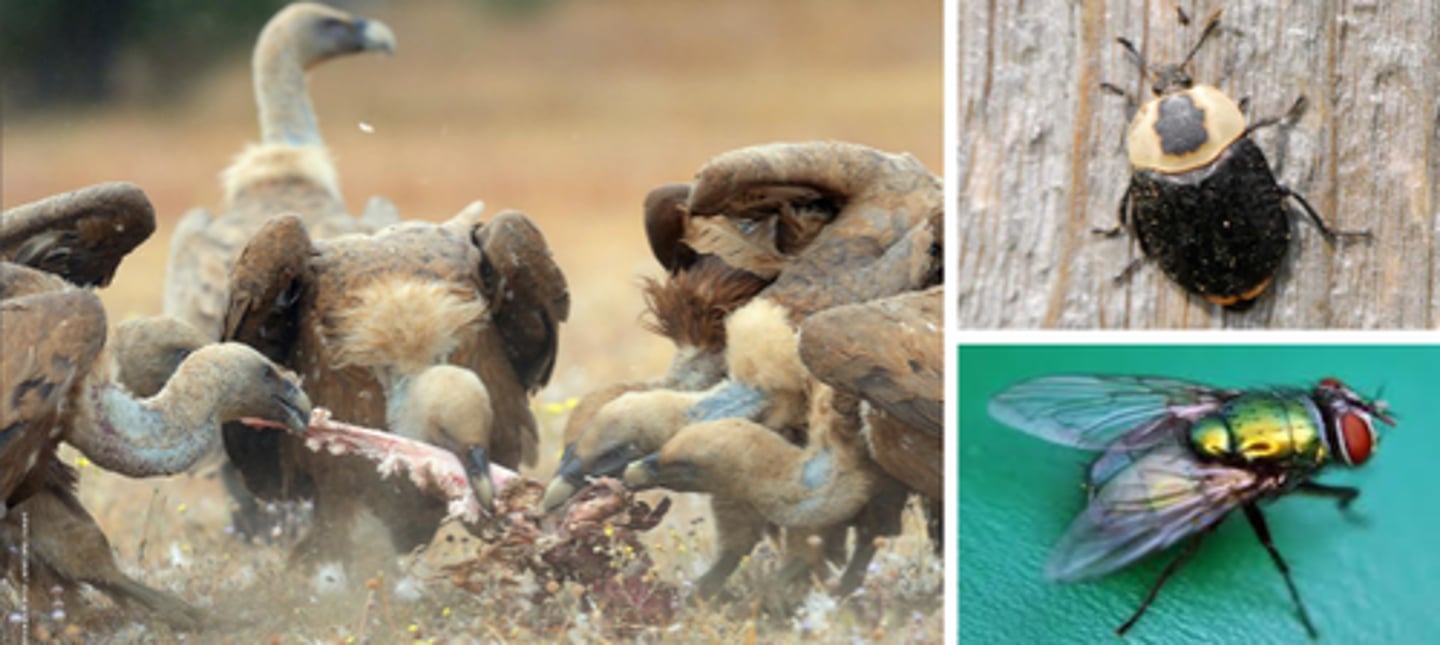

Detritivore
an organism that feeds on dead organic matter and waste products that are collectively known as detritus
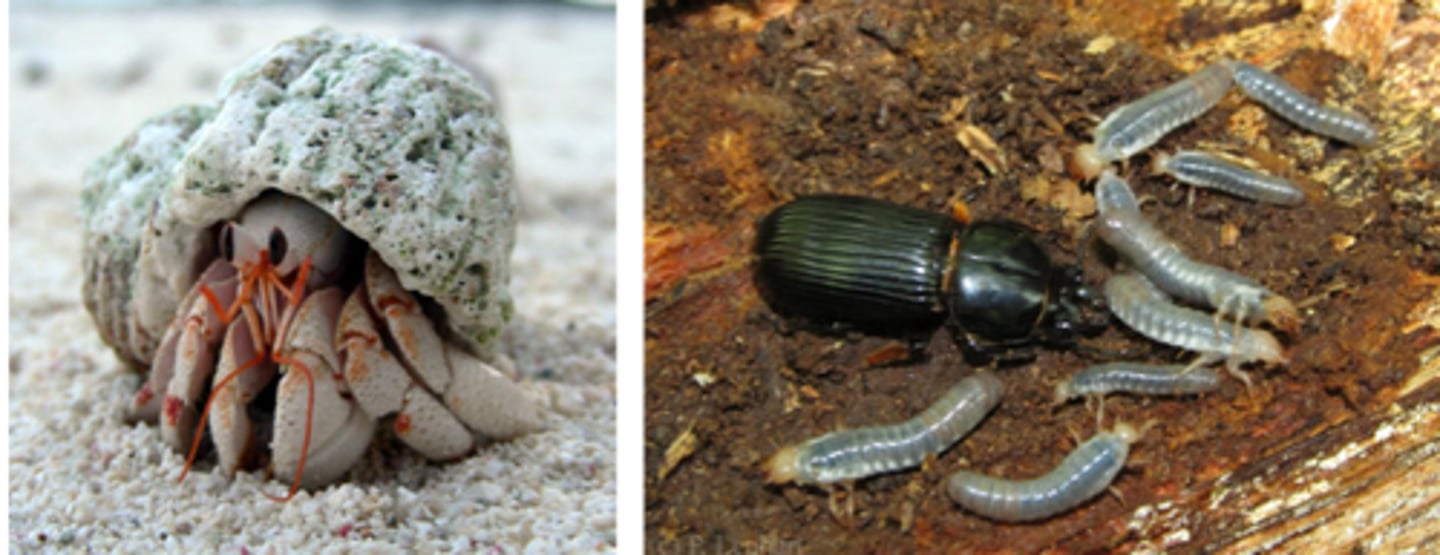

Decomposer
organisms that break down dead organic material into simpler elements and compounds that can be recycled through the ecosystem
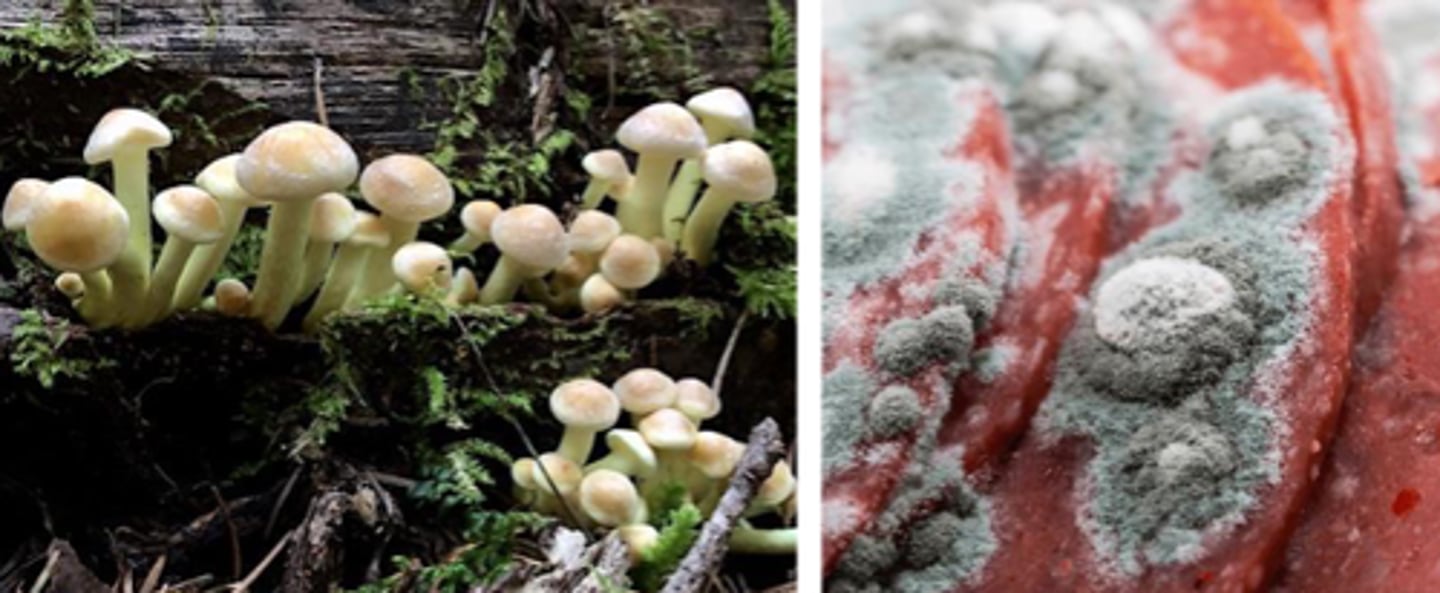

Competition
an interaction resulting in negative effects between two species that depend on the same limiting resource to survive, grow, and reproduce
Commensalism
an interaction in which two species live in close association and one species receives a benefit, while the other experiences neither a benefit nor a cost
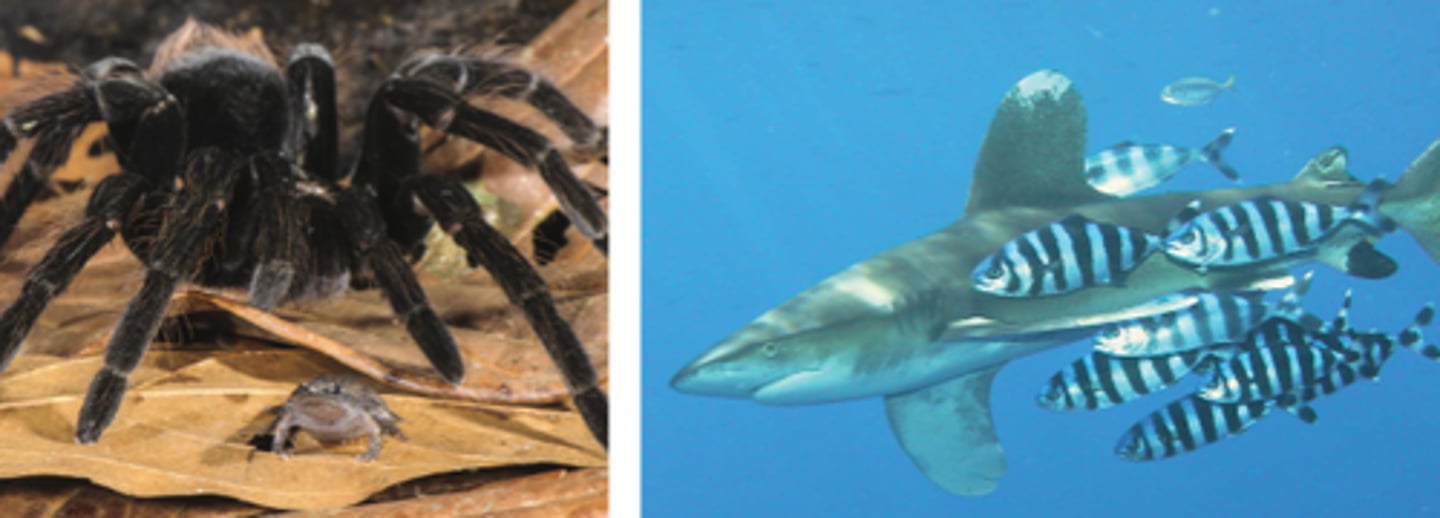

Mutualism
an interaction between two species in which each species receives benefits from the other
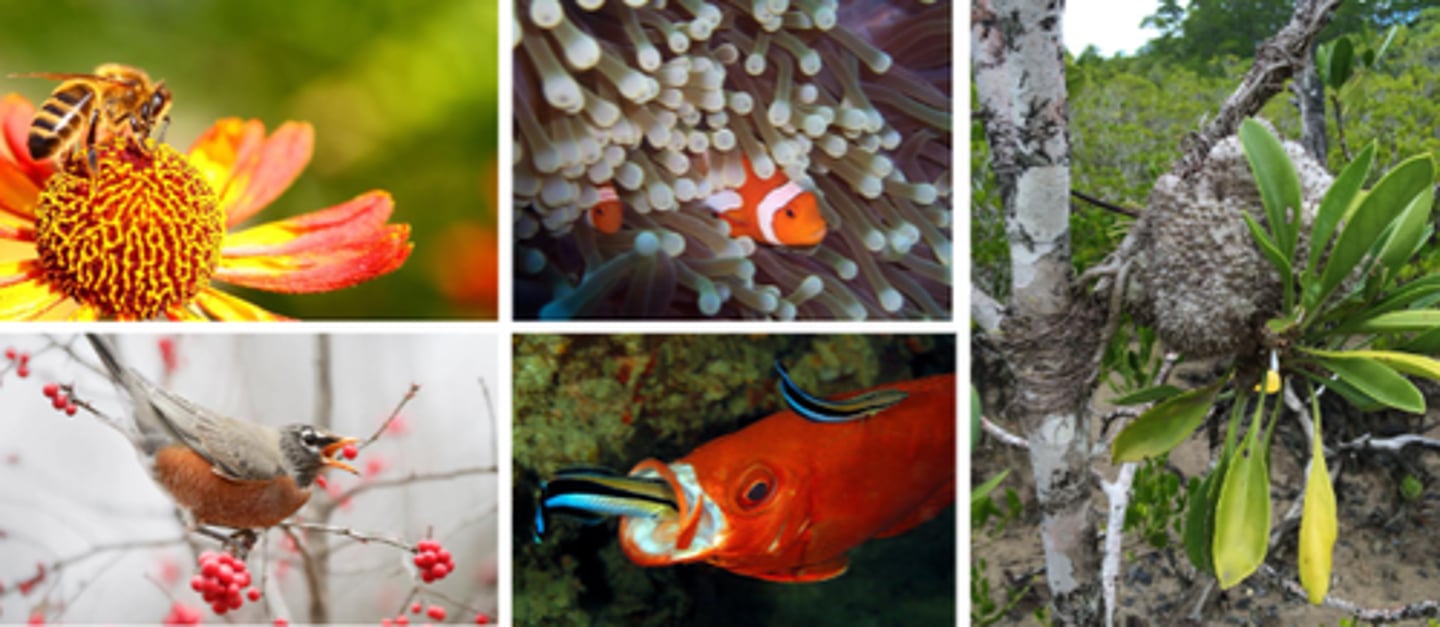

Symbiotic relationship
when two different types of organisms live in a close physical relationship
+ and - interactions for Predation/parasitoids
+ / -

+ and - interactions for
Parasitism
+ / -

+ and - interactions for
Herbivory
+ / -
+ and - interactions for
Competition
- / -

+ and - interactions for
Mutualism
+ / +

+ and - interactions for
Commensalism
+ / 0

Are symbiotic relationships static?
No

Can species manage costs from some symbiotic relationships?
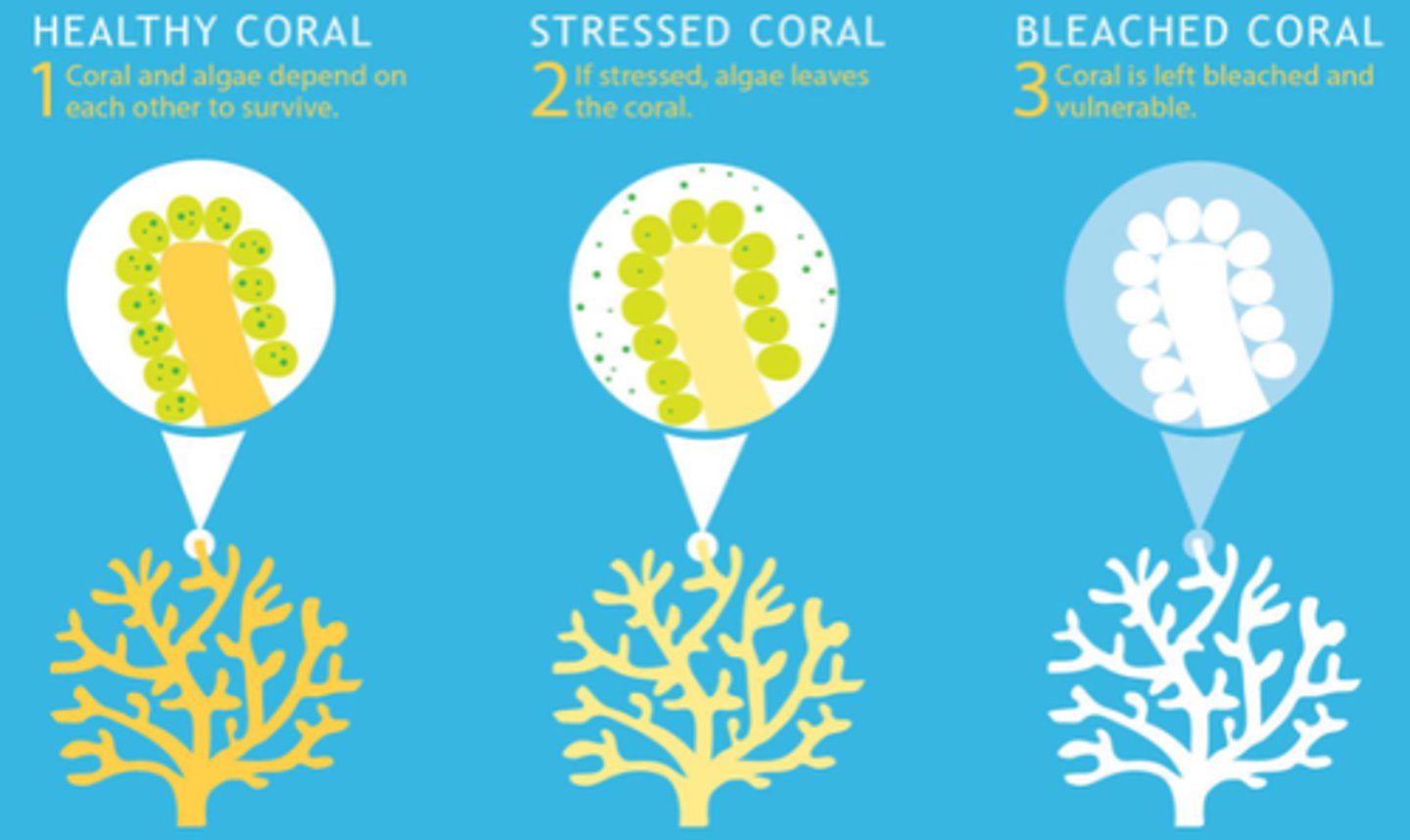
when you heat up the ocean around coral reefs, something happens.
These dinoflagellates start to. I think it's like free radicals or something. They start to give off this stress response that's actually injurious to the body of the coral.
And so, the coral manages this cost and will eject the dinoflagellates from its tissue, resulting in coral bleaching.
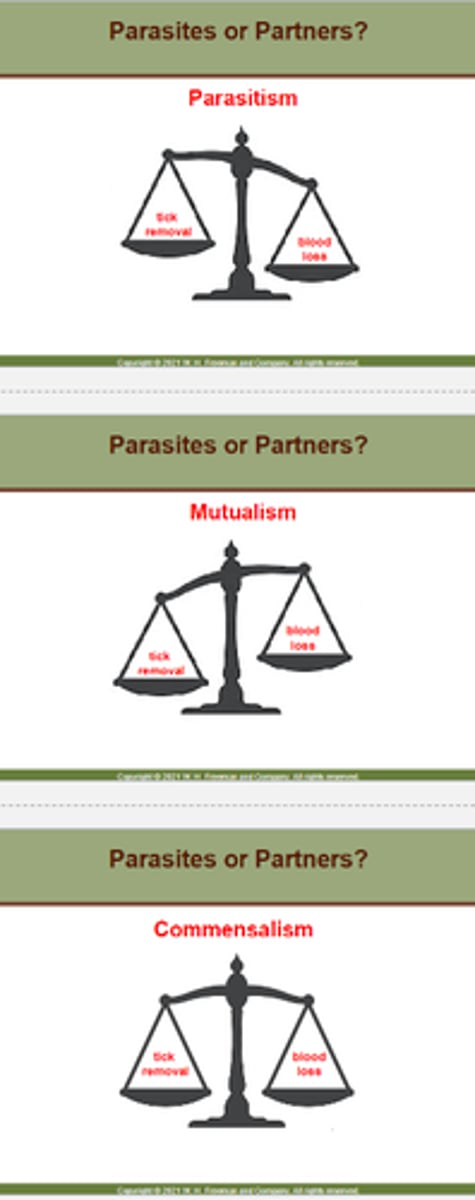
Explain the studies on Red-billed oxpeckers.
A classic mutualism: Feeding on ticks benefits the mammal "host".
However, they also feed on blood and open wounds...
At the end of this chapter do you know all these terms?
• Ecology• Biotic• Abiotic• Individual• Population• Community• Ecosystem• Landscape• Biosphere• Autotroph• Heterotroph• Mixotroph• Mutualism• Commensalism• Detritivore• Competition• Predation• Parasitism
Understand this summary from chapter 1
Ecological concepts and insights are widely applied from endangered species management to cheese production. Ecological systems are organized hierarchically, from individuals to the biosphere.
Organisms gain energy in diverse ways. Biotic interactions range from mutually antagonistic to mutually beneficial. Biotic interactions are not fixed
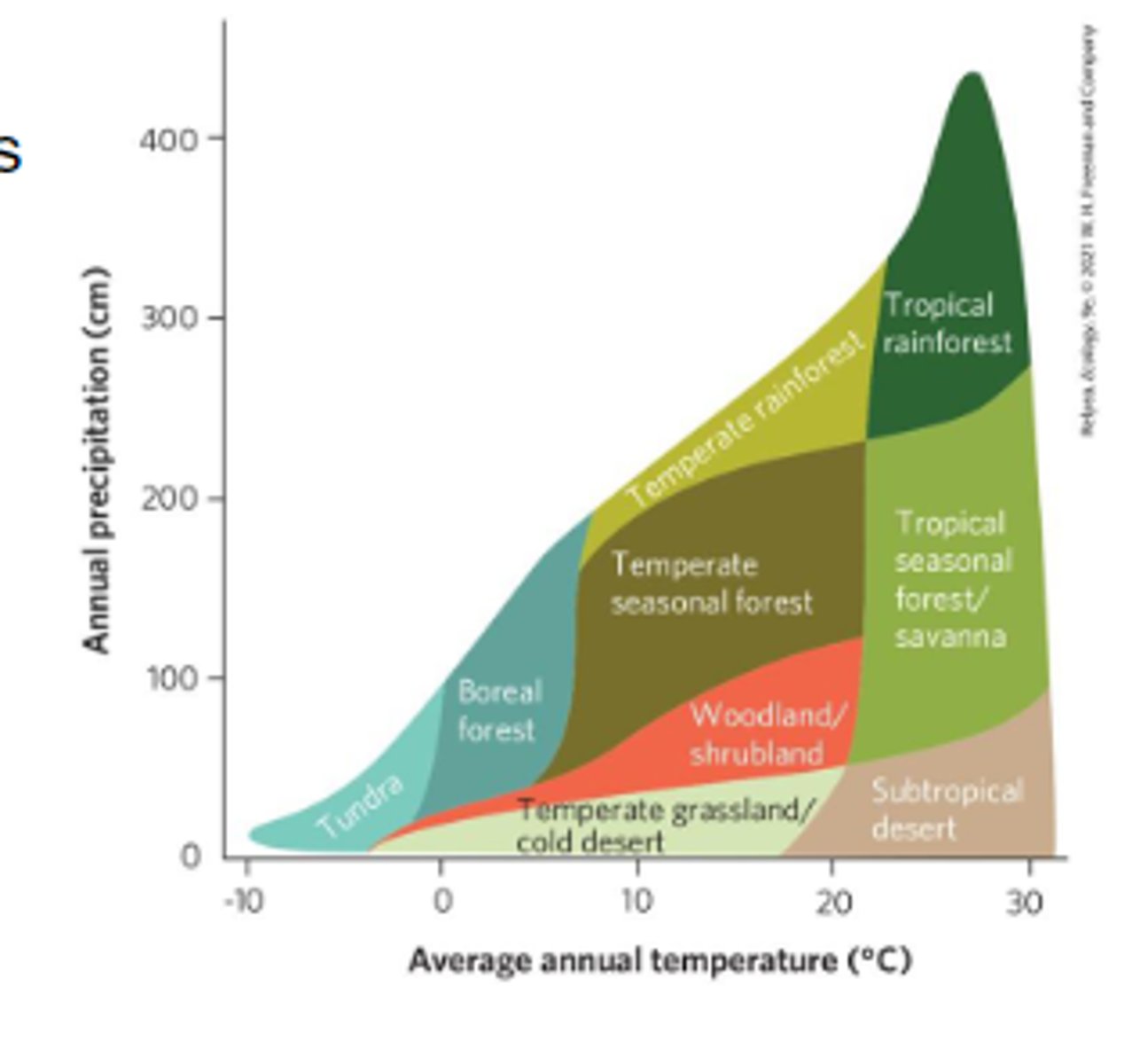
What are terrestrial biomes categorized by?
Terrestrial biomes are categorized by major plant growth forms
Biome
a geographic region containing communities composed of organisms with similar adaptations
Tundra
the coldest biome characterized by a tree less expanse above permanently frozen soil
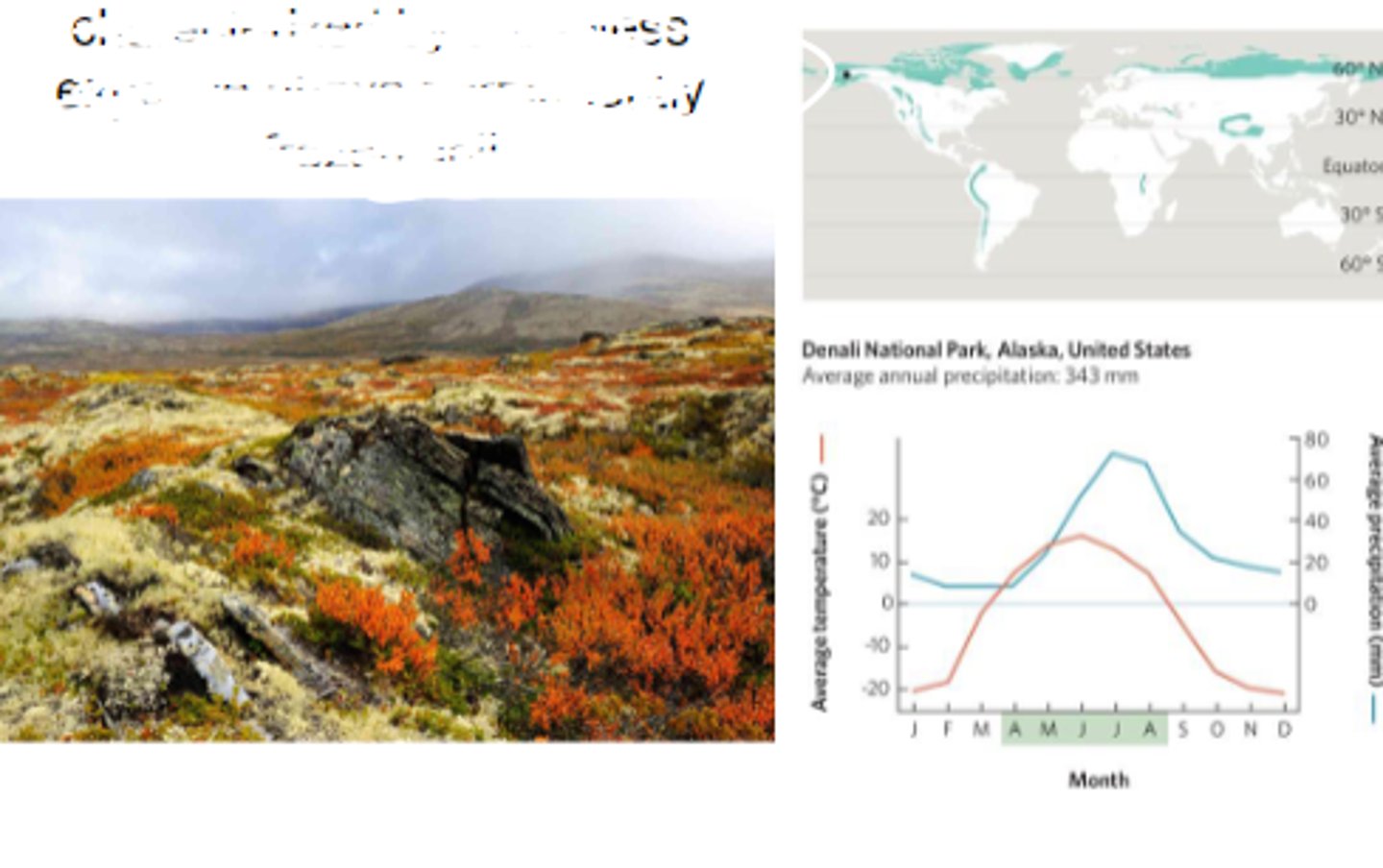
Boreal forest
densely populated by ever green needle-leaved trees, with a short growing season and severe winters.
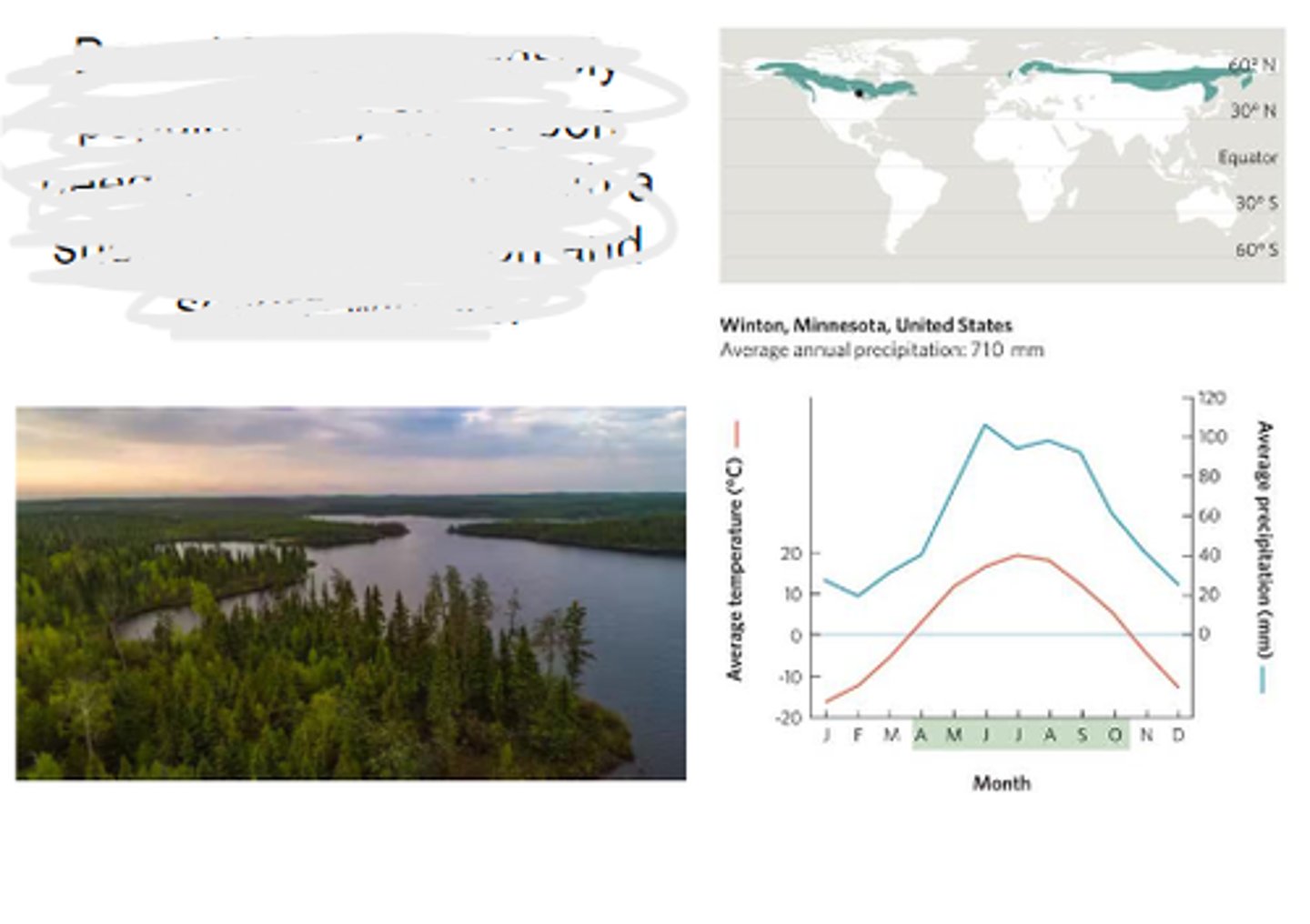
Temperate rainforest
known for mild temperatures and abundant precipitation, dominated by evergreen forests.
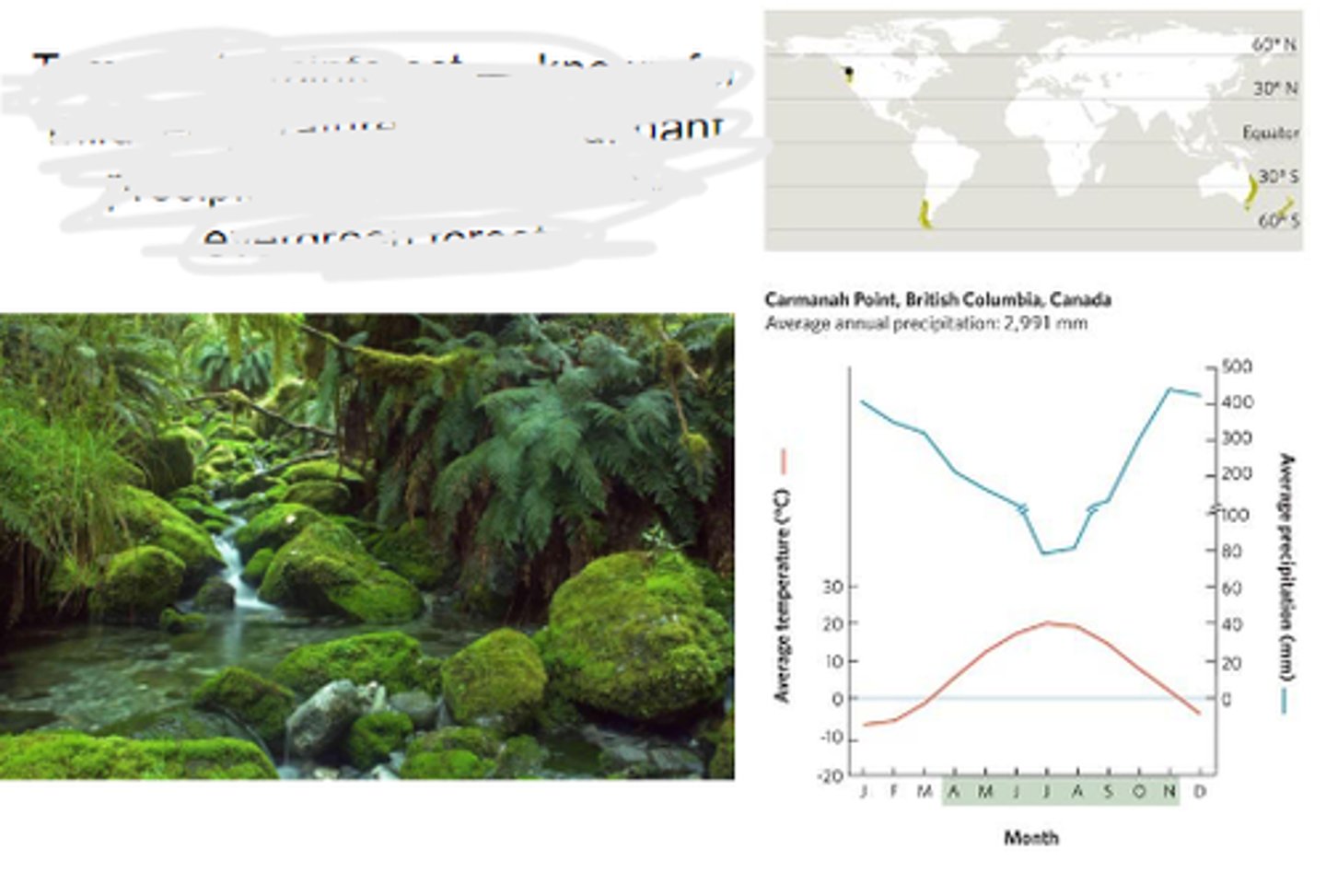
Temperate seasonal forest
a biome with moderate temperature and precipitation conditions, dominated by deciduous trees
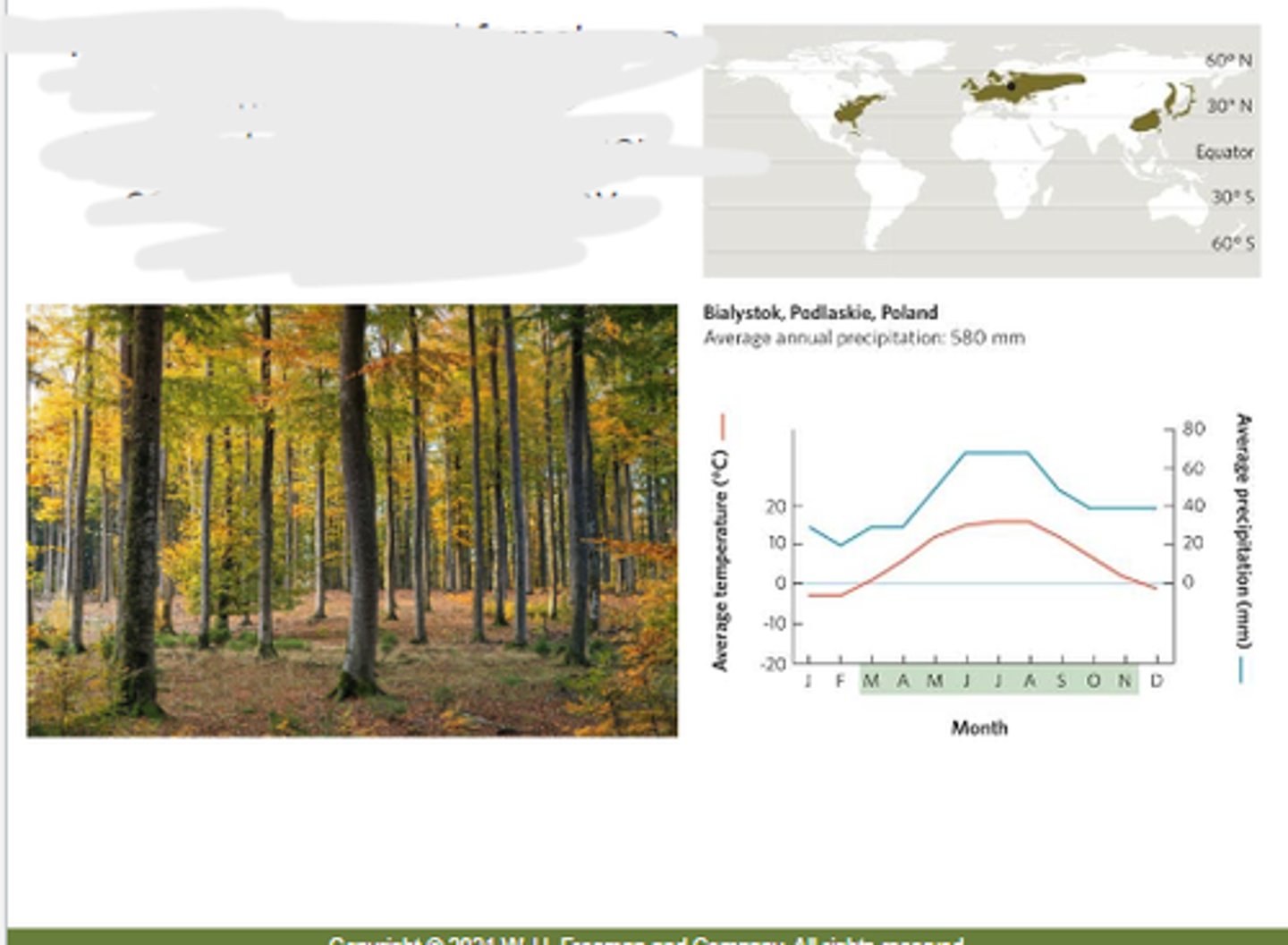
Woodland/shrubland
characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters, a combination that favors the growth of drought-tolerant grasses and shrubs
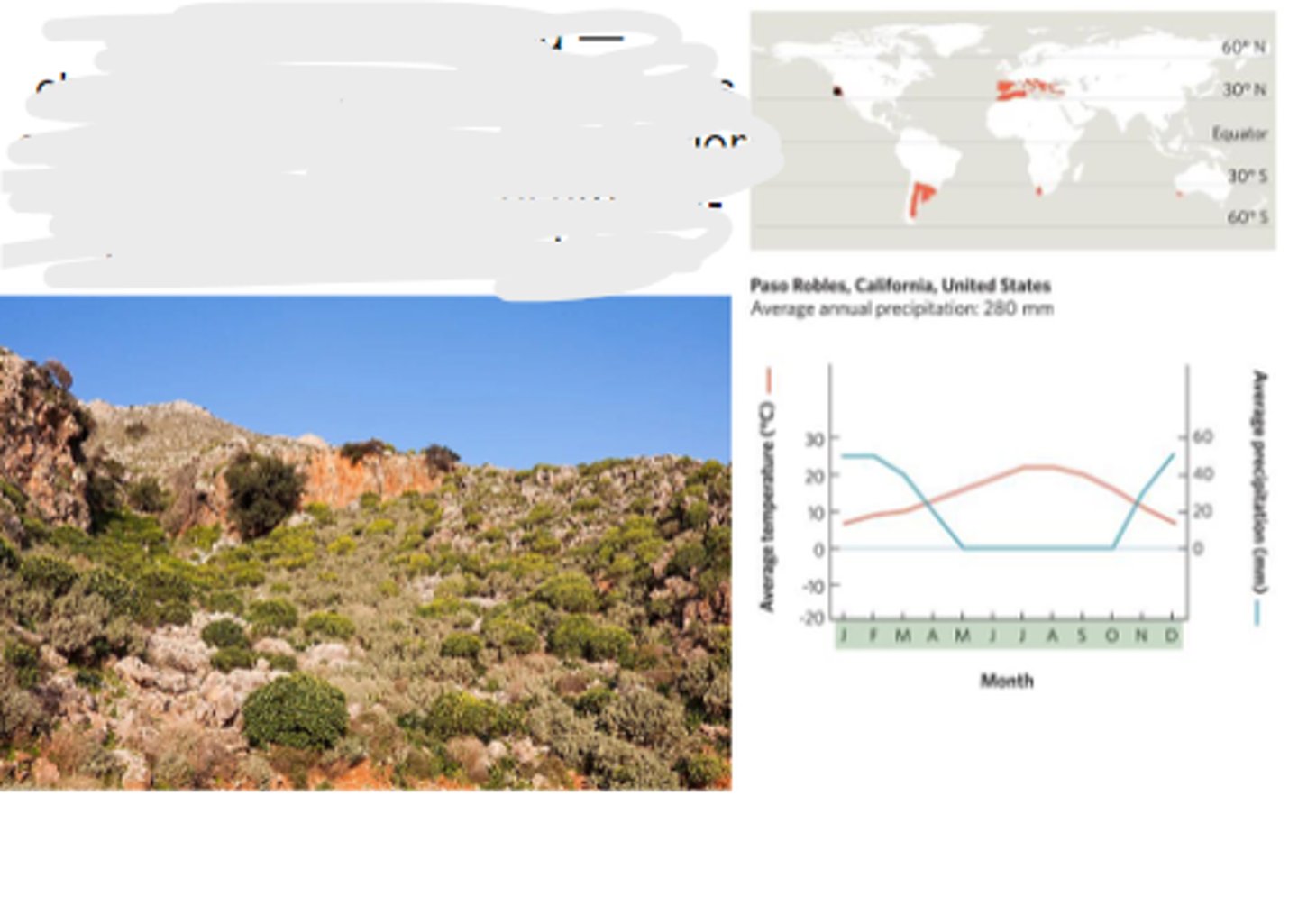
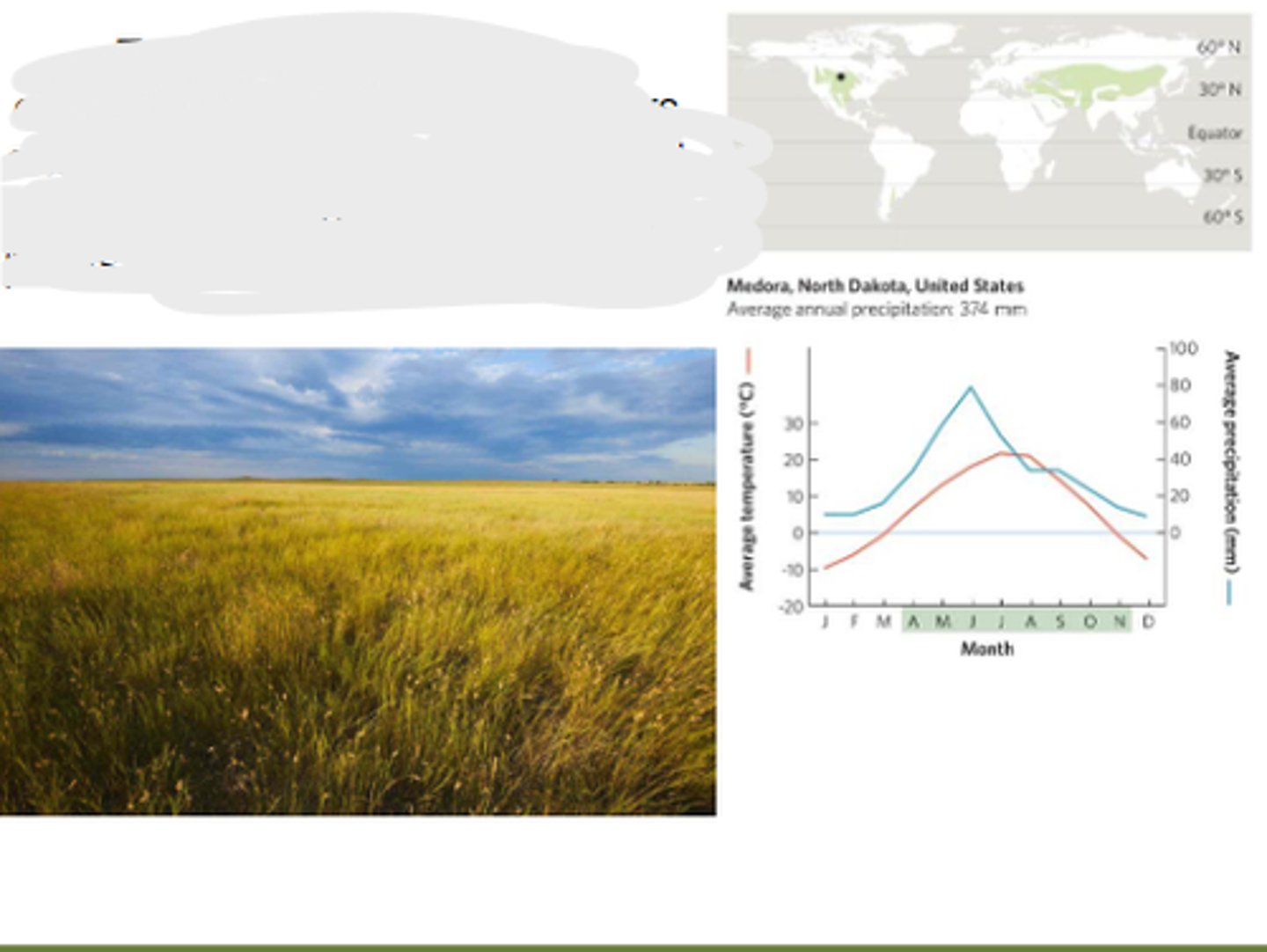
Temperate grassland
characterized by hot, dry summers and cold, harsh winters. Dominated by grasses, nonwoody flowering plants, and drought-adapted shrubs
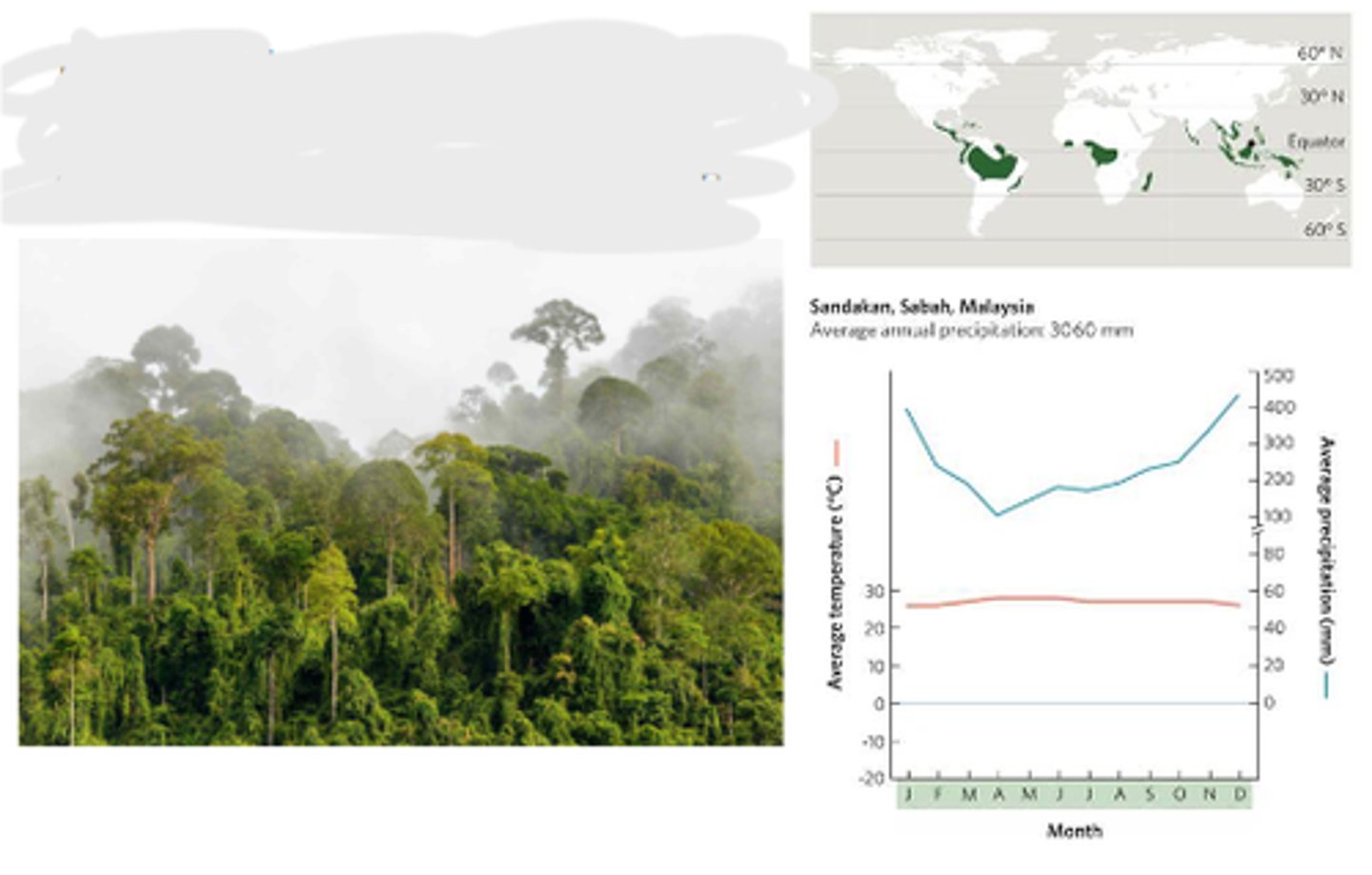
Tropical rainforest
a warm and rainy biome characterized by multiple layers of lush vegetation
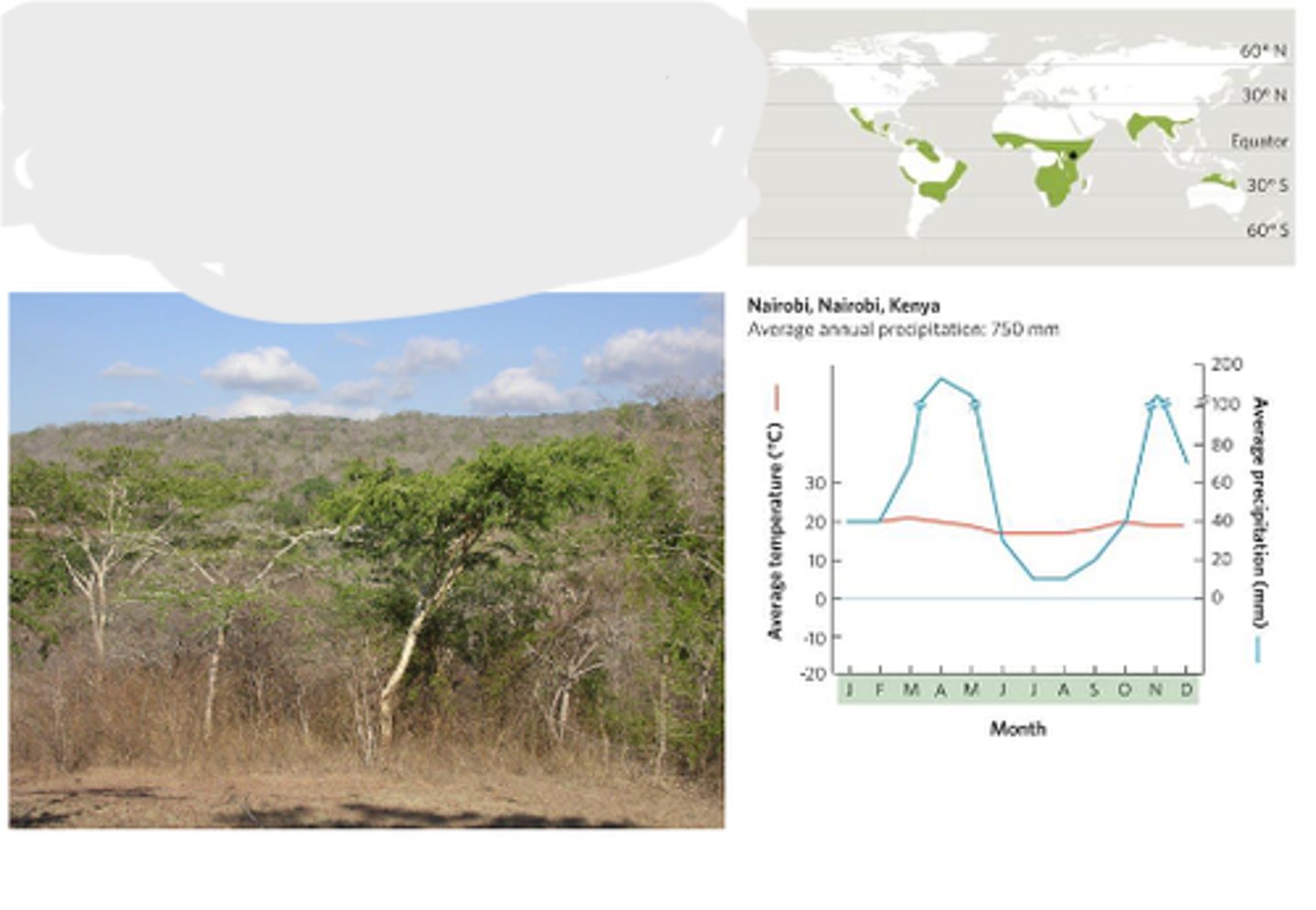
Tropical seasonal forest
warm temperatures and pronounced wet and dry seasons dominated by trees that shed their leaves during the dry season
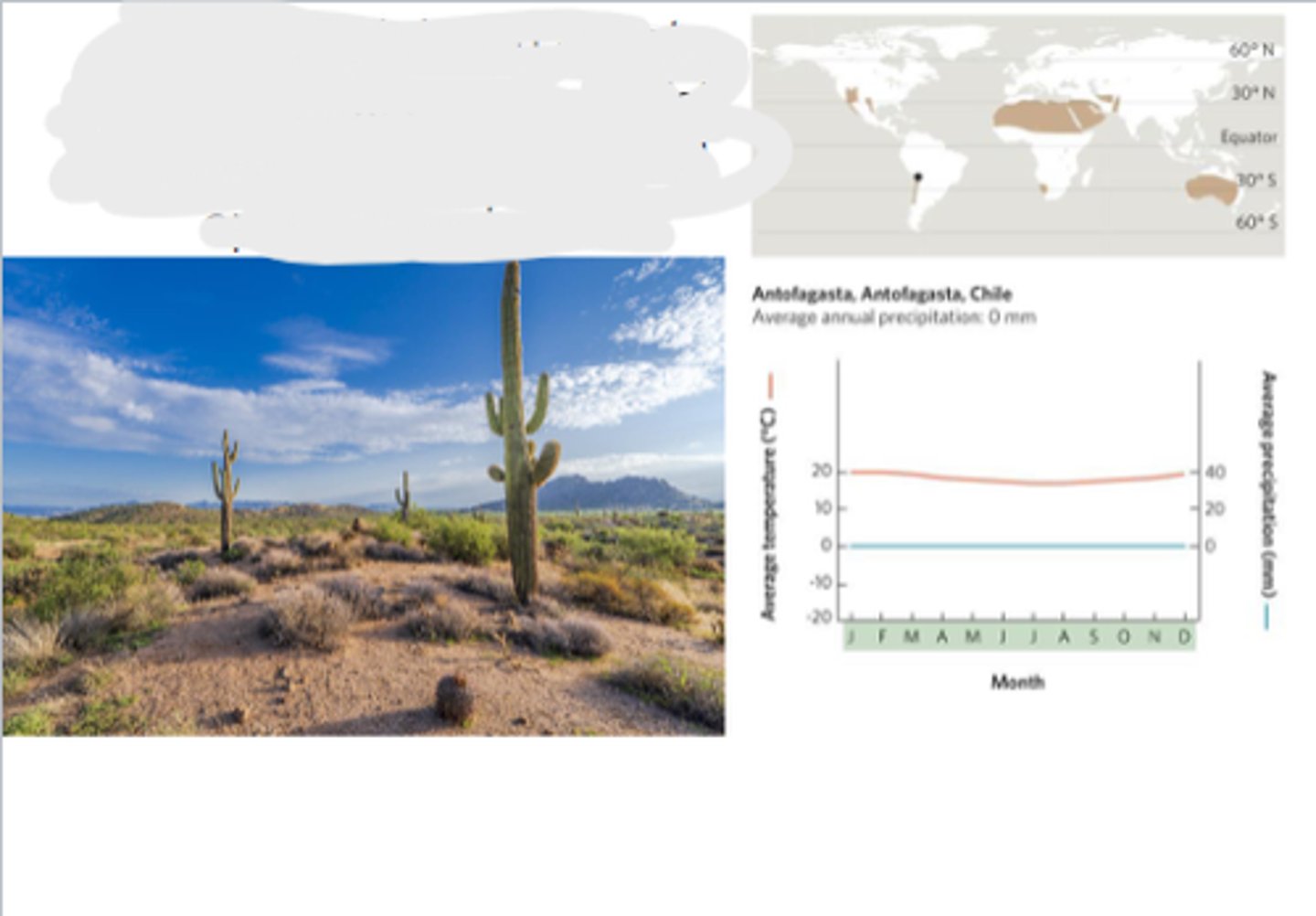
Subtropical desert
hot temperatures, scarce rainfall, long growing seasons, and sparse vegetation
Climate
the typical atmospheric conditions that occur through out the year, measured over many years
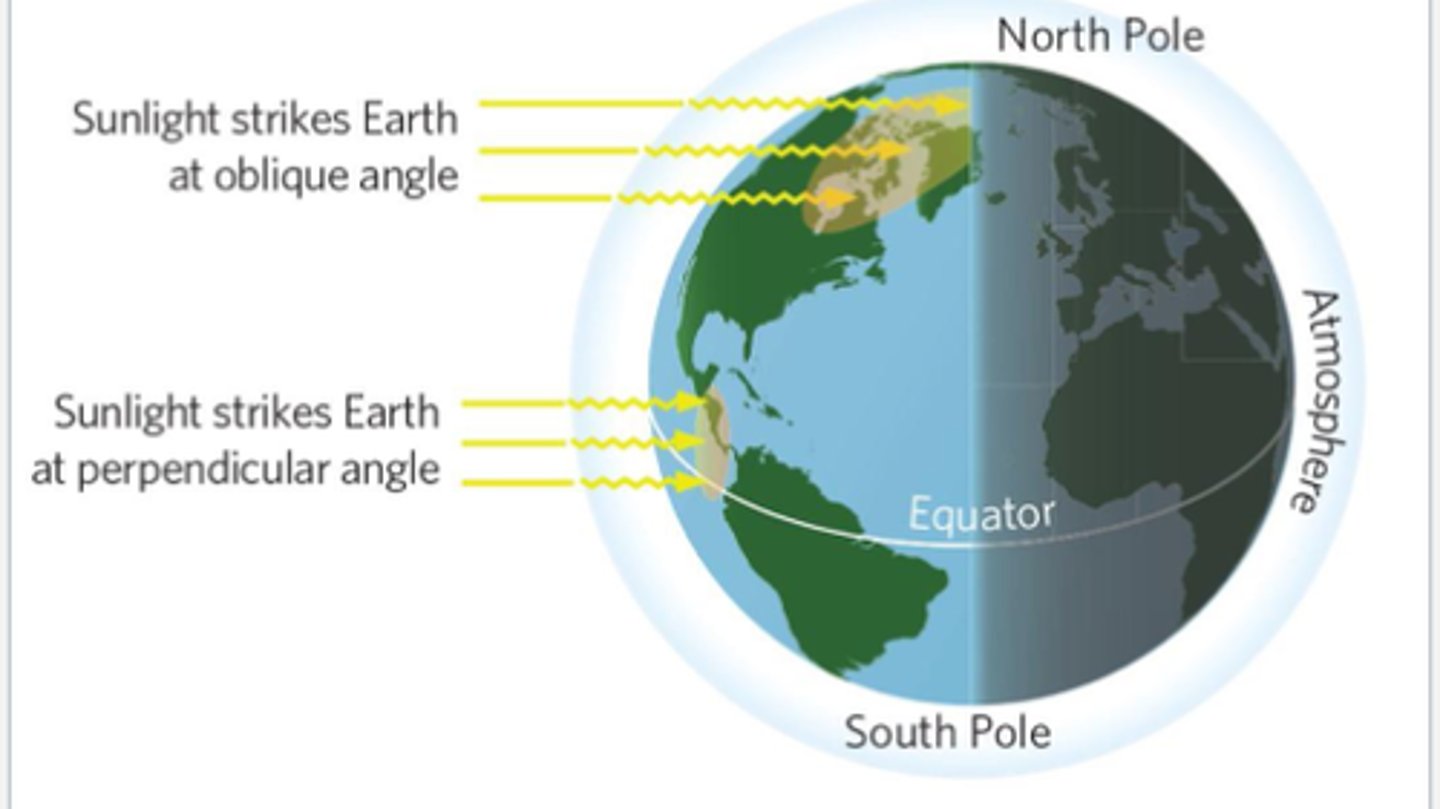
True or False: There is an unequal heating of Earth by the Sun.
True
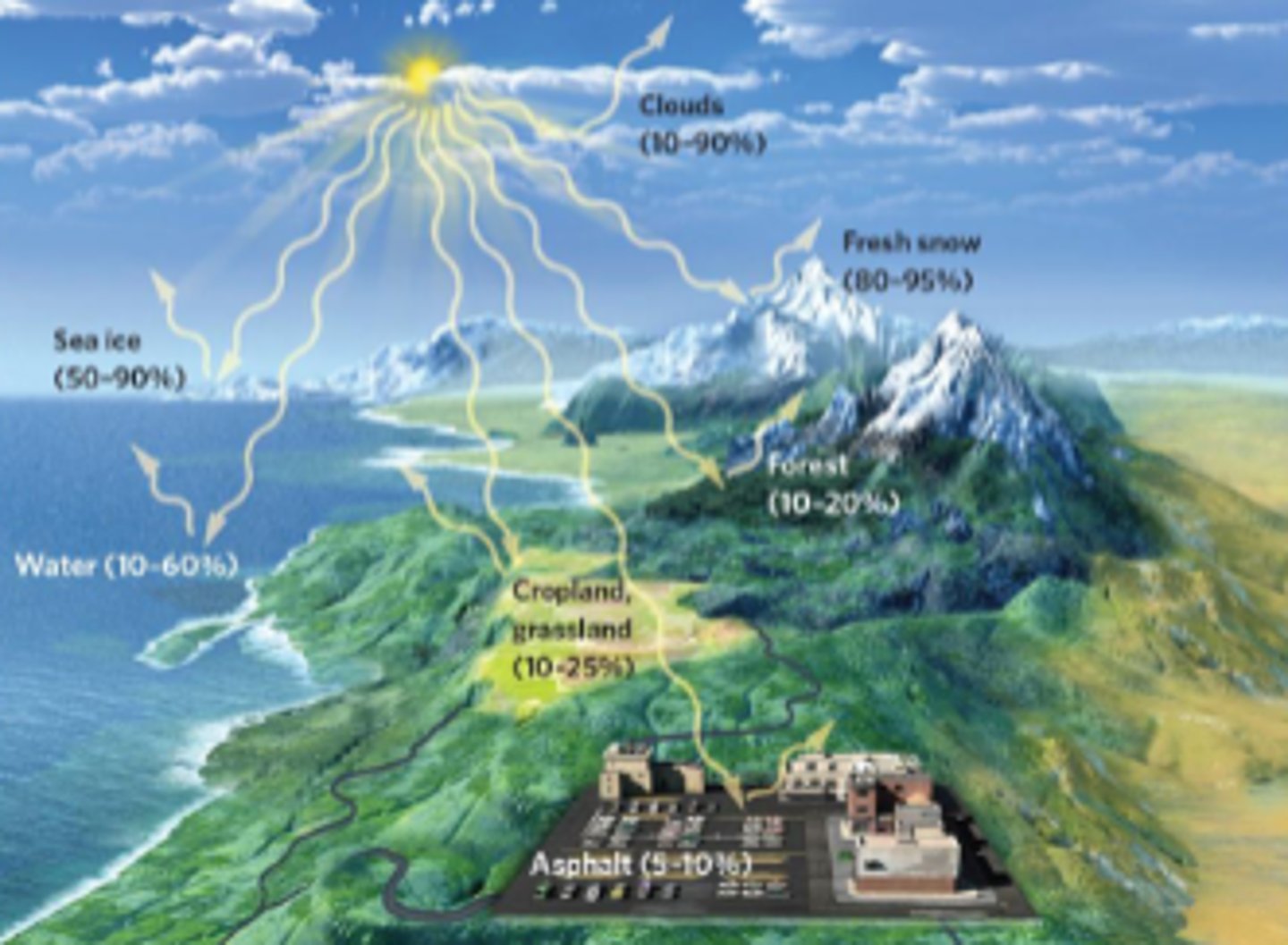
Albedo
the fraction of solar energy reflected by an object
Explain seasonal heating of Earth
tilt generates seasonal variation in that solar radiation flows.
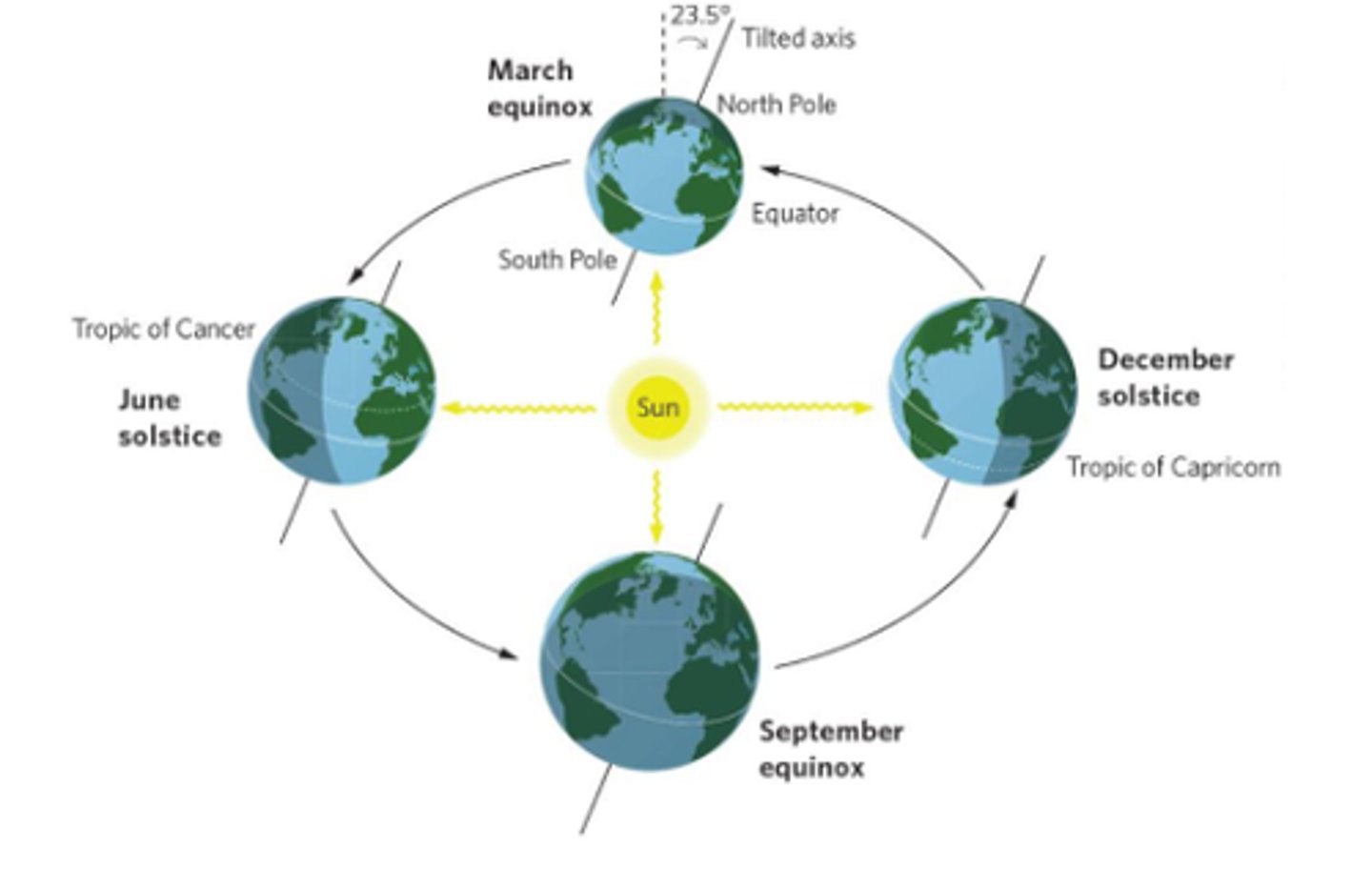
Solar Equator
The latitude receiving the most direct rays of the Sun
equator is a fixed latitude. But in terms of the area where the Earth's light density is the most intense, that area is shifting north and south over the years depending upon the tilt of the Earth's relative to the Sun.
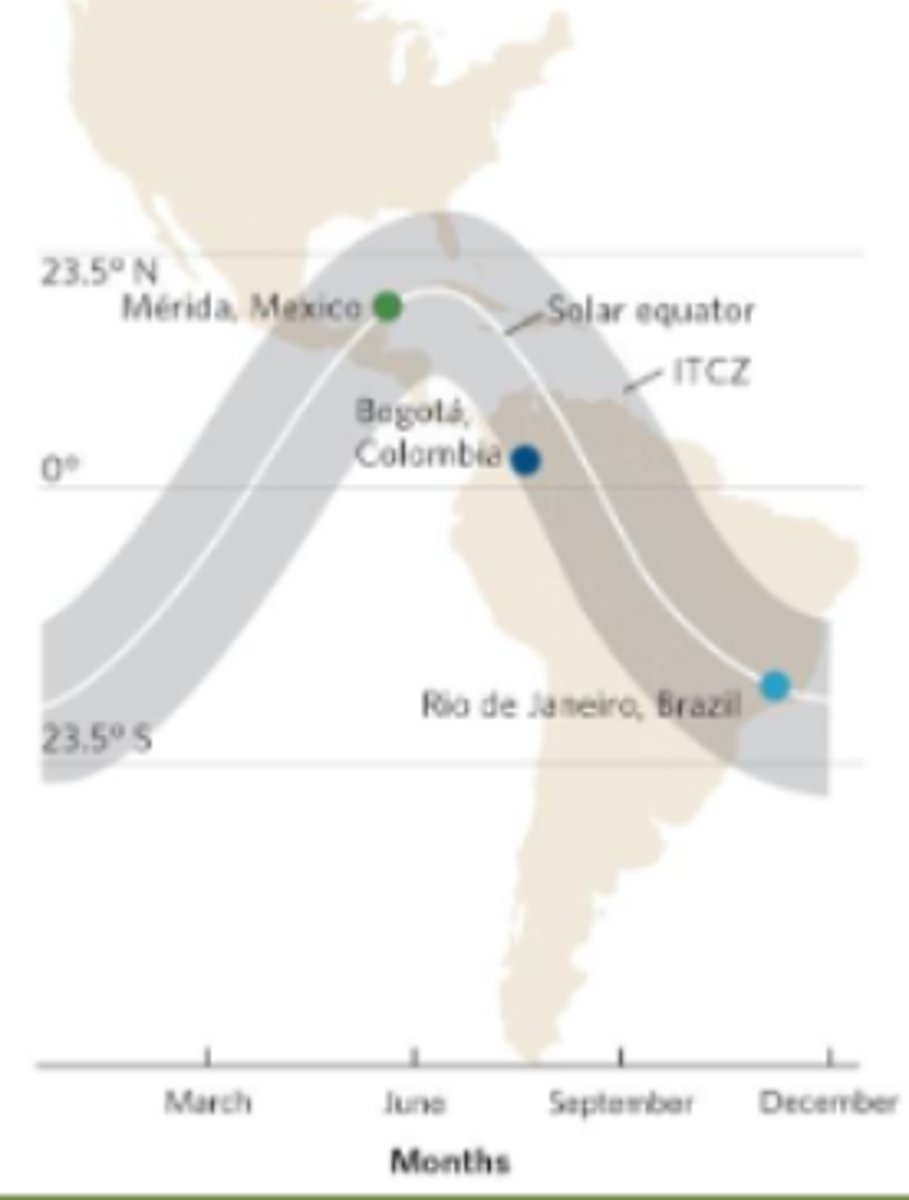
True or False: Uneven heating of Earth fully explains biome diversity and distribution.
False: Alone, uneven heating fails to explain biome diversity and distribution.
Does Earths uneven heating relate to air currents at all?
Yes, the unequal heating of Earth drives air currents in the atmosphere.
What are two important atmospheric currents?
Polar cells
Hadley cells
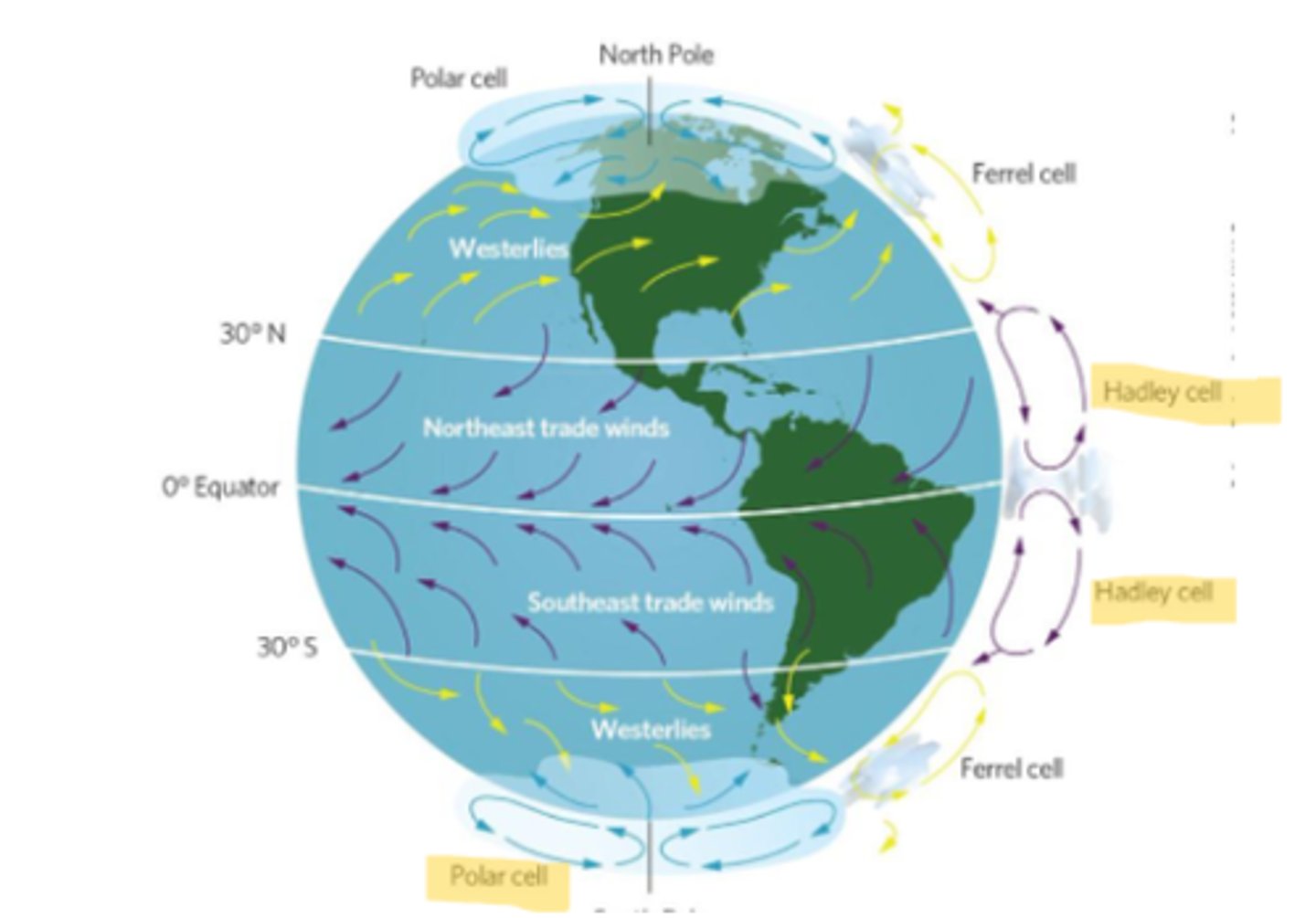
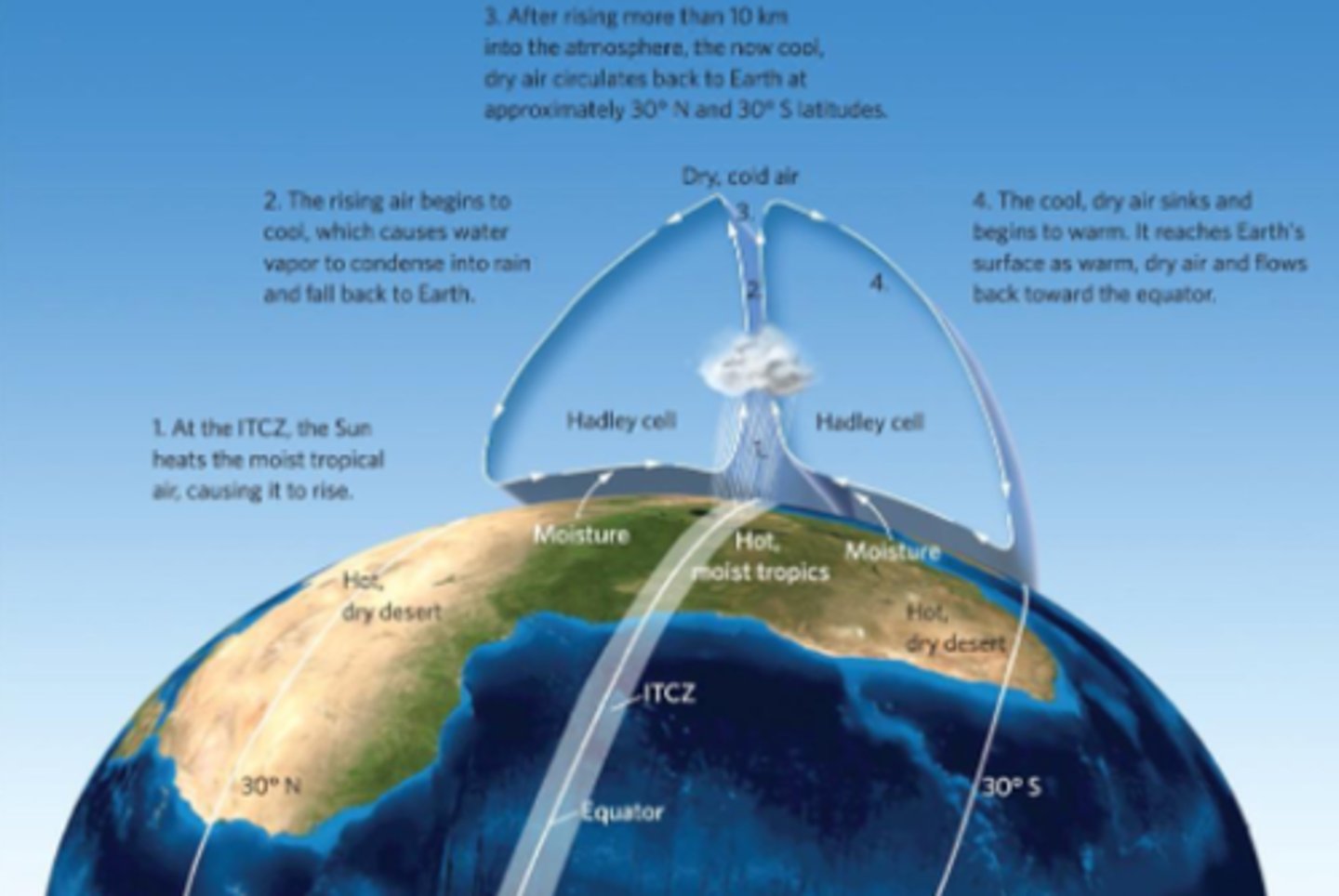
Polar cells
the atmospheric convection currents that move air between 60° and 90° latitudes in the Northern and Southern hemispheres
Hadley cells
the two circulation cells of air between the equator and 30° N and 30° S latitudes
Coriolis Effect
The (apparent) deflection of an object's path due to Earth's rotation
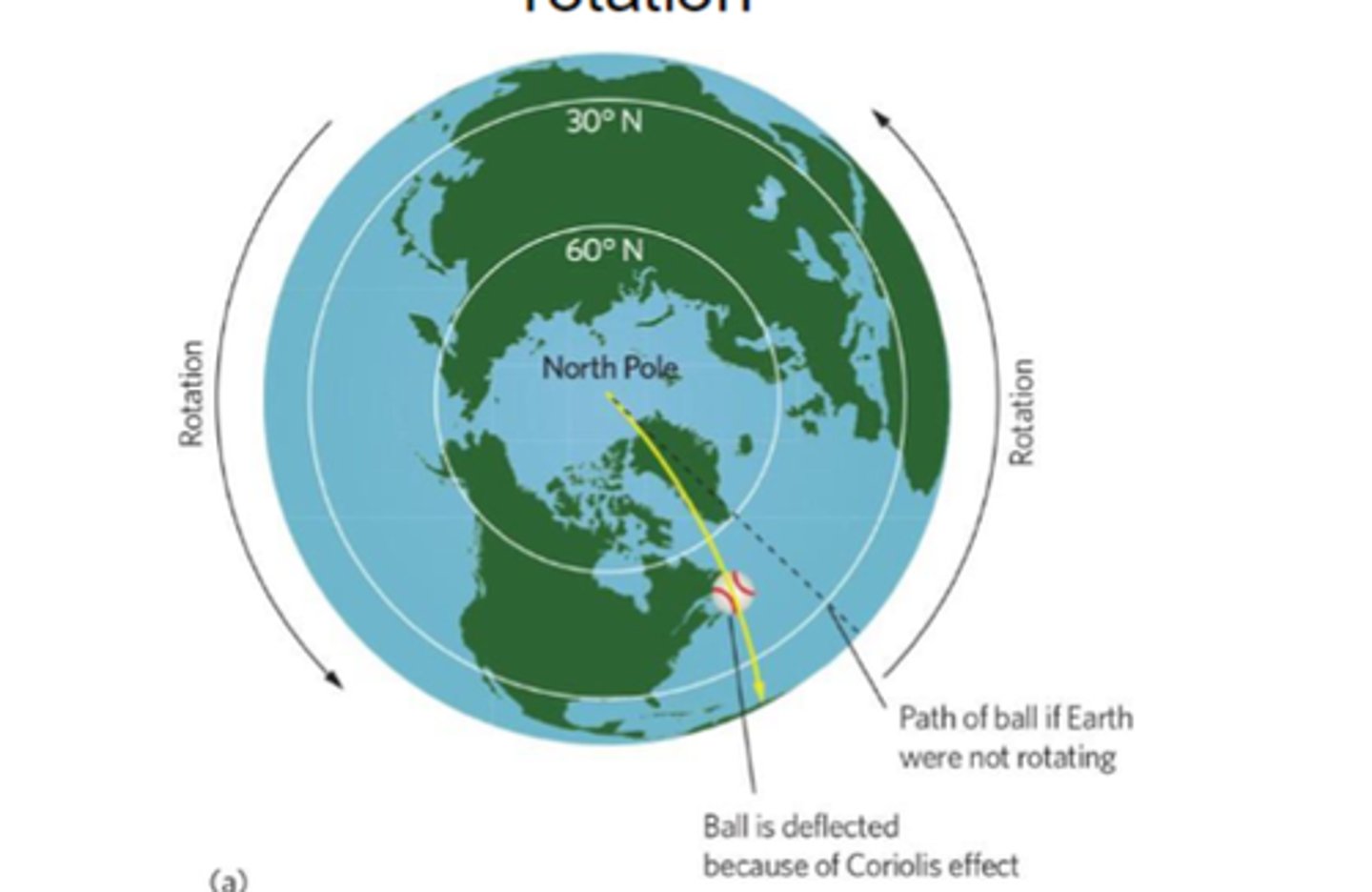
Do smaller-scale geographic features affect regional and local climates?
Yes, smaller-scale geographic features can affect regional and local climates.
Rain Shadow
A region with dry conditions found on the leeward side of a mountain range.
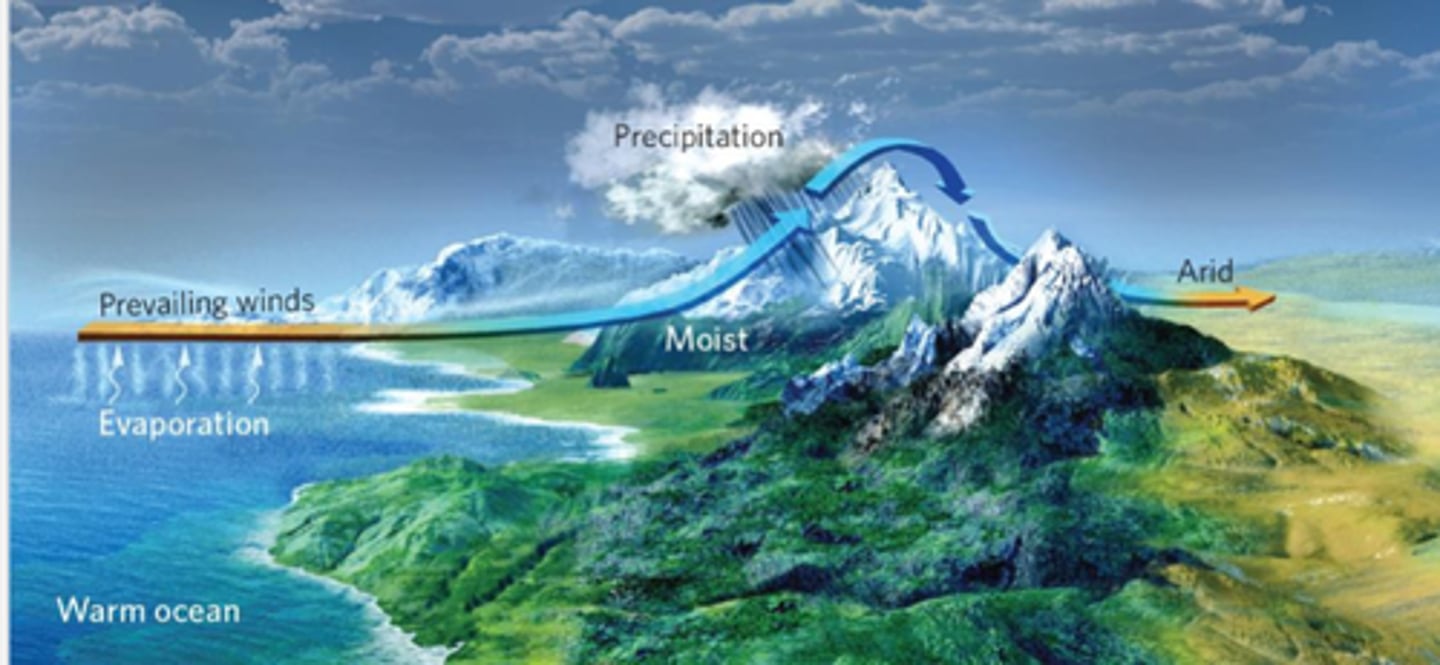

Explain the Lake effect
So basically, the lake effect happens in a similar way that the rain shadow effect happens.
We have open water that's relatively warm, sending moisture up into the atmosphere.
As that air mass moves across the lake, it picks up that moisture.
As it hits the land, it starts to lift that humid air mass and lifts and we get precipitation.
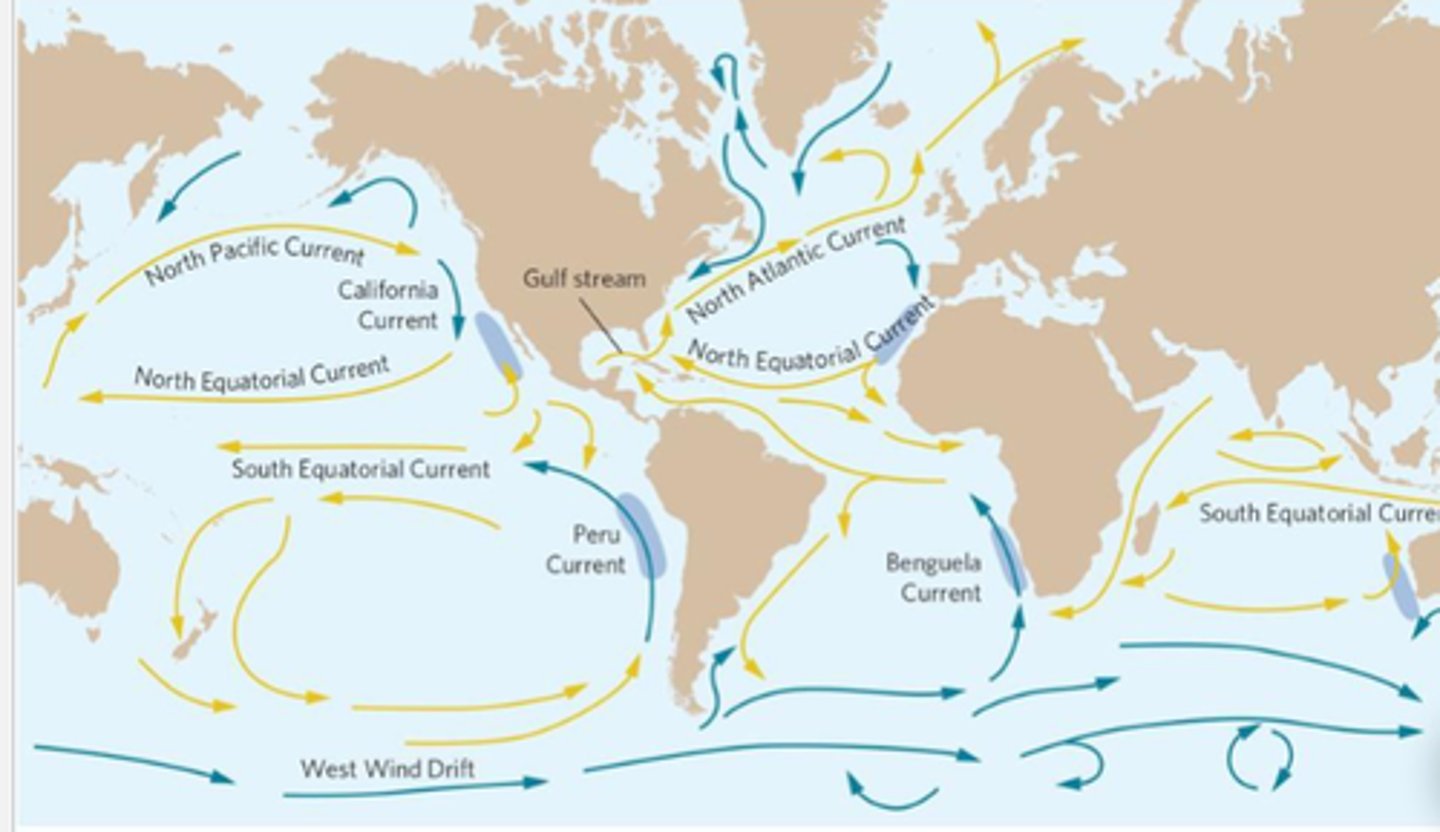
Explain ocean currents
What characteristics are aquatic biomes categorized by?
flow, depth, and salinity
Freshwater wetlands
aquatic biomes that contain standing fresh water, or soils saturated with fresh water for at least part of the year and are shallow enough to have emergent vegetation throughout all depths
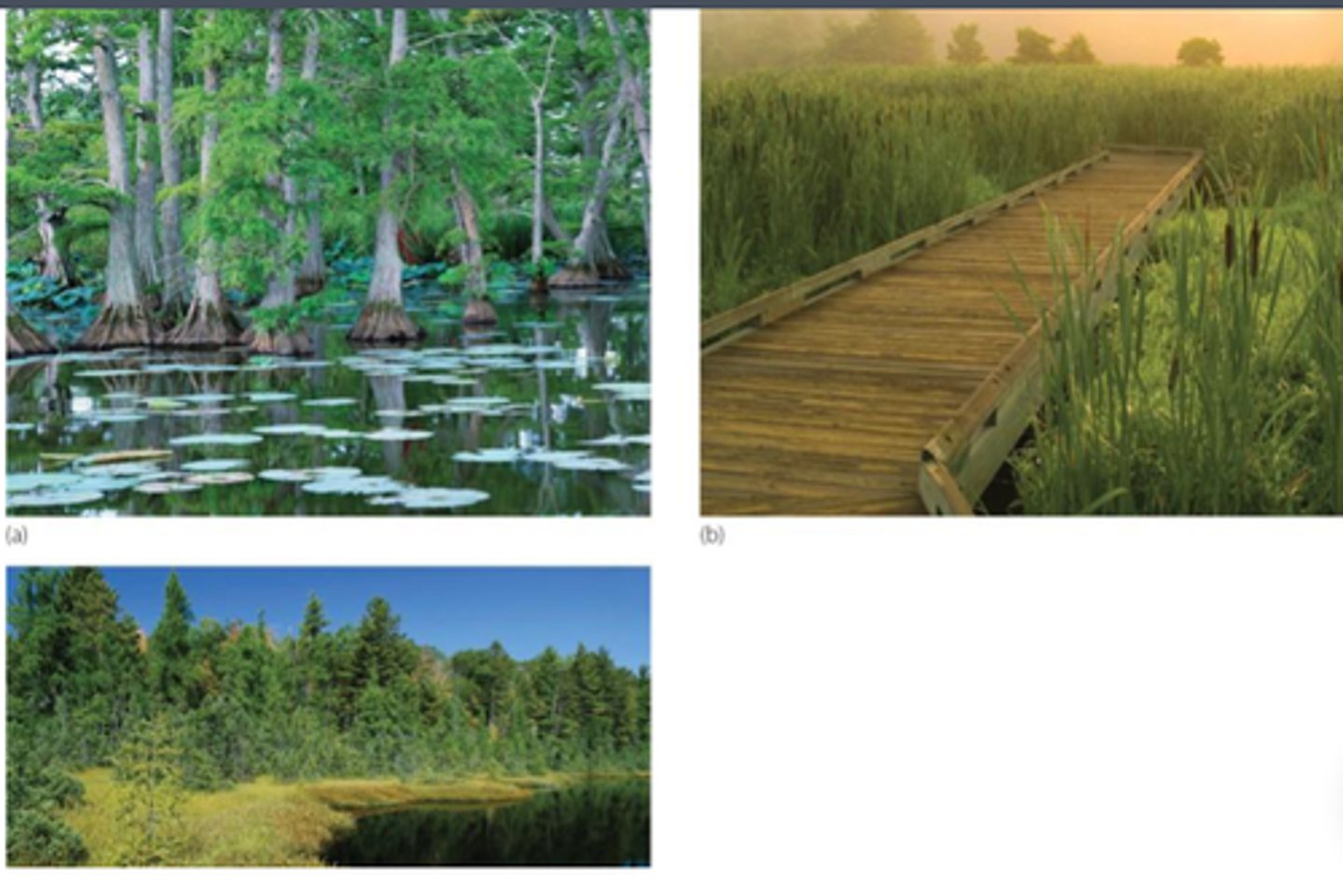

What are streams and rivers characterized by?
characterized by flowing fresh water.
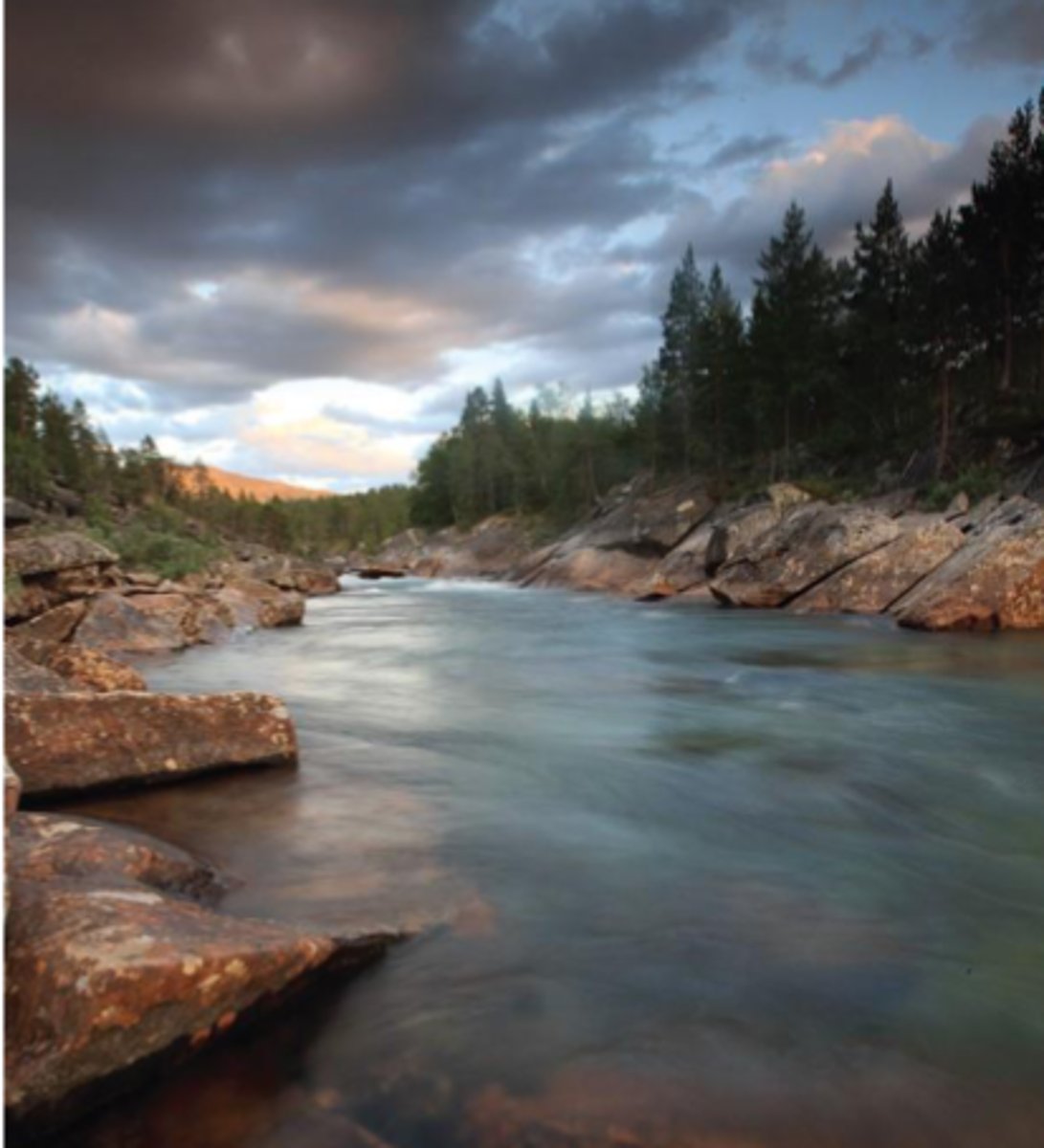

(Picture) Lotic systems branch
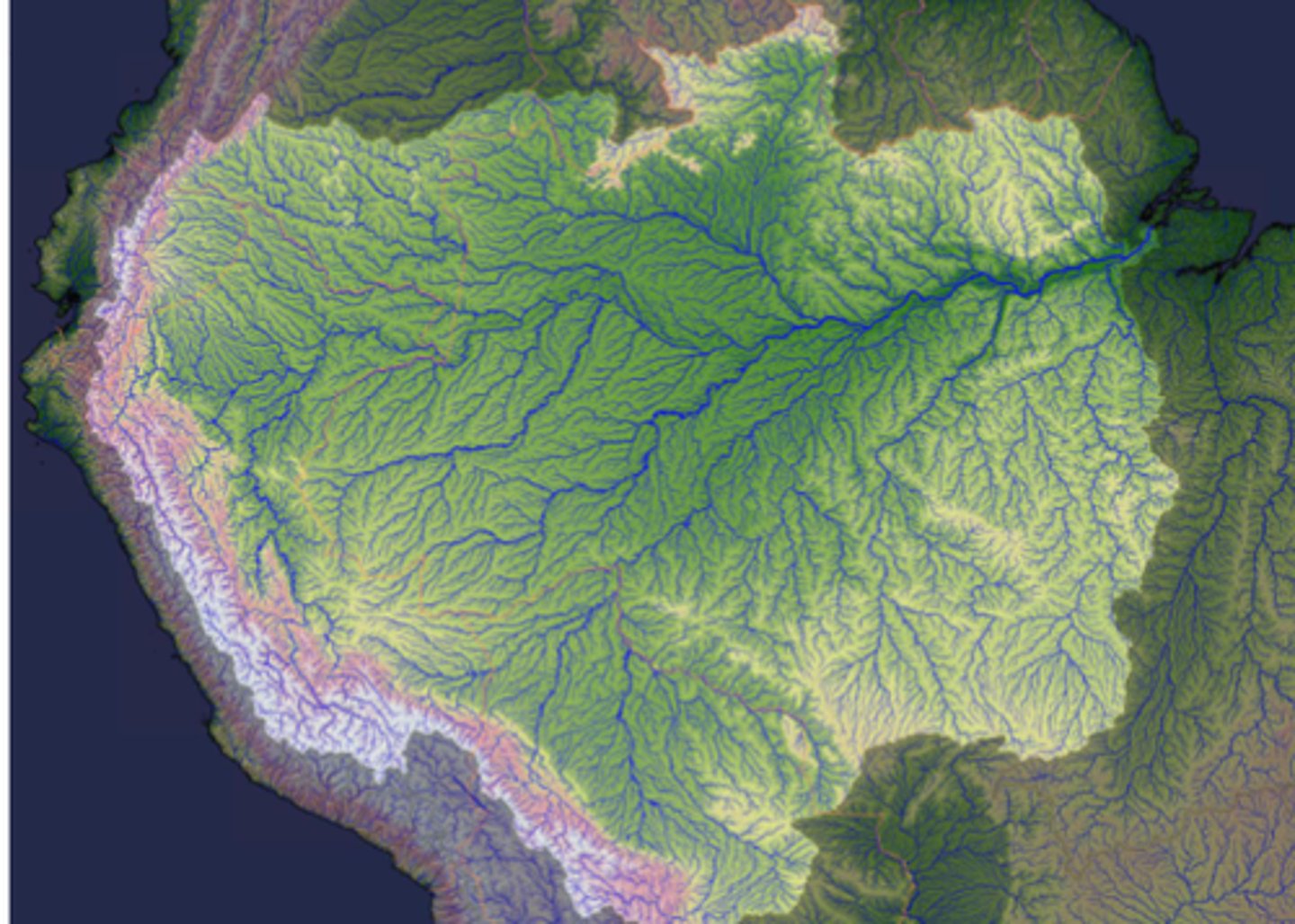
What is Strahler's stream order?
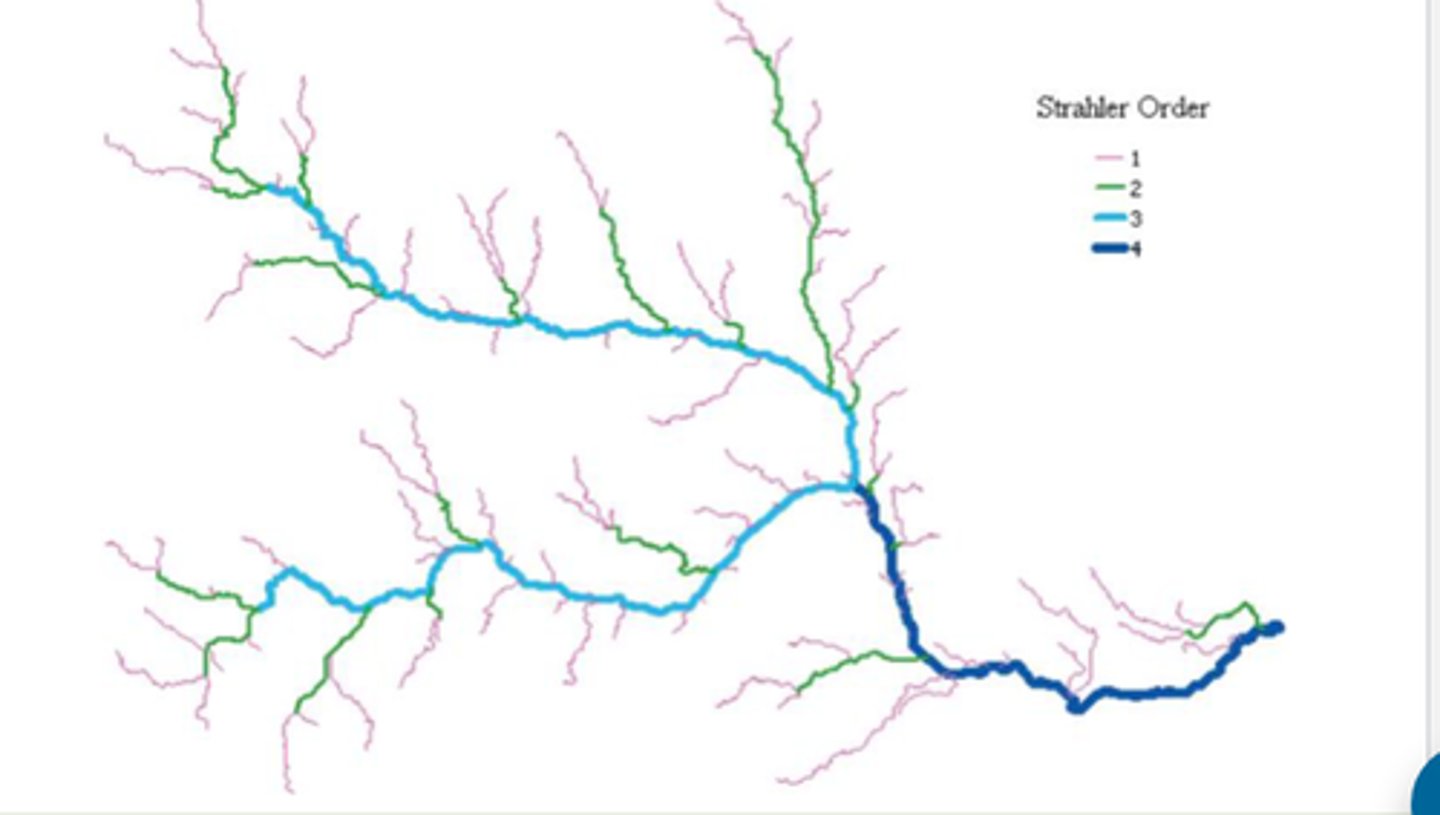
Headwater stream (1st order)
detritivores
high oxygen
low light
low productivity
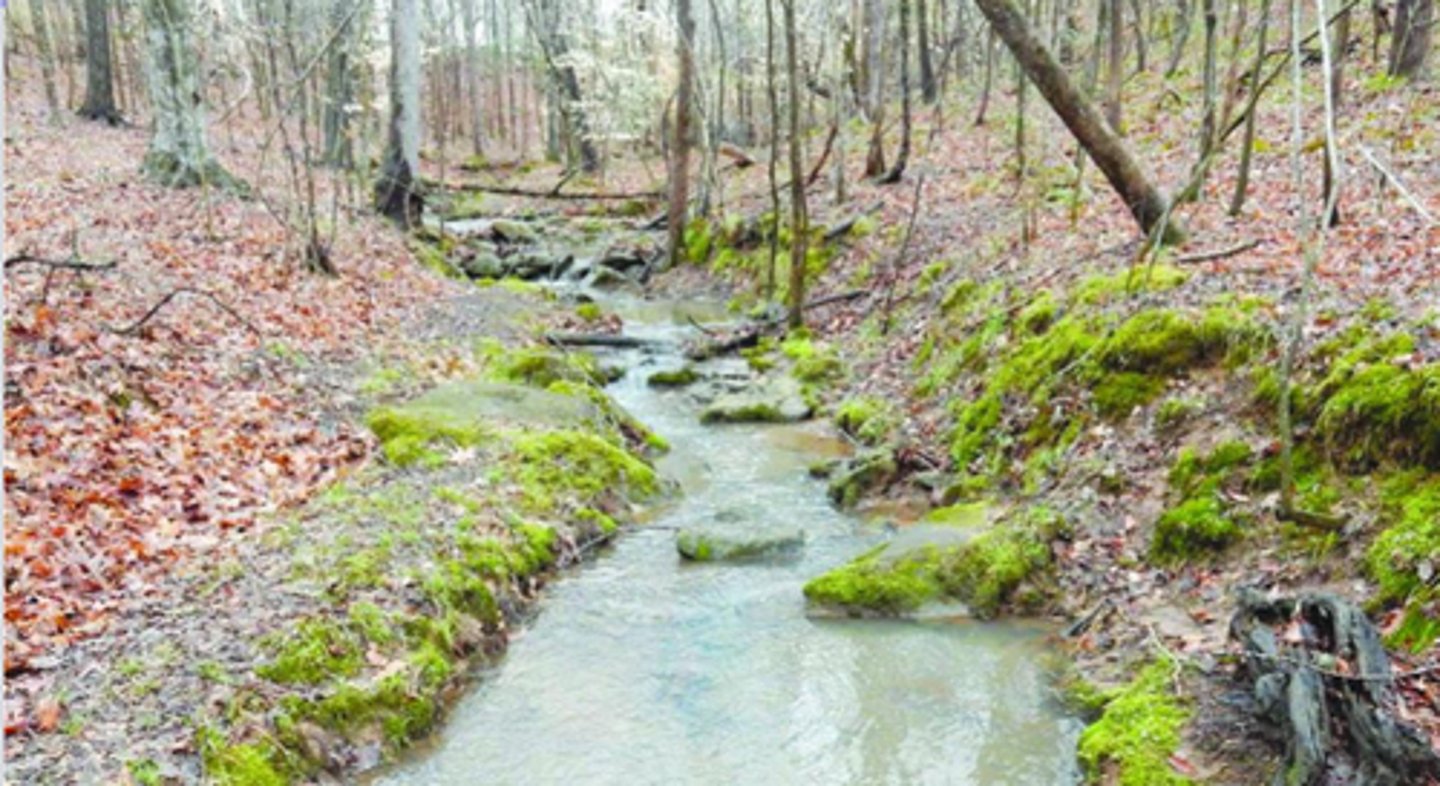

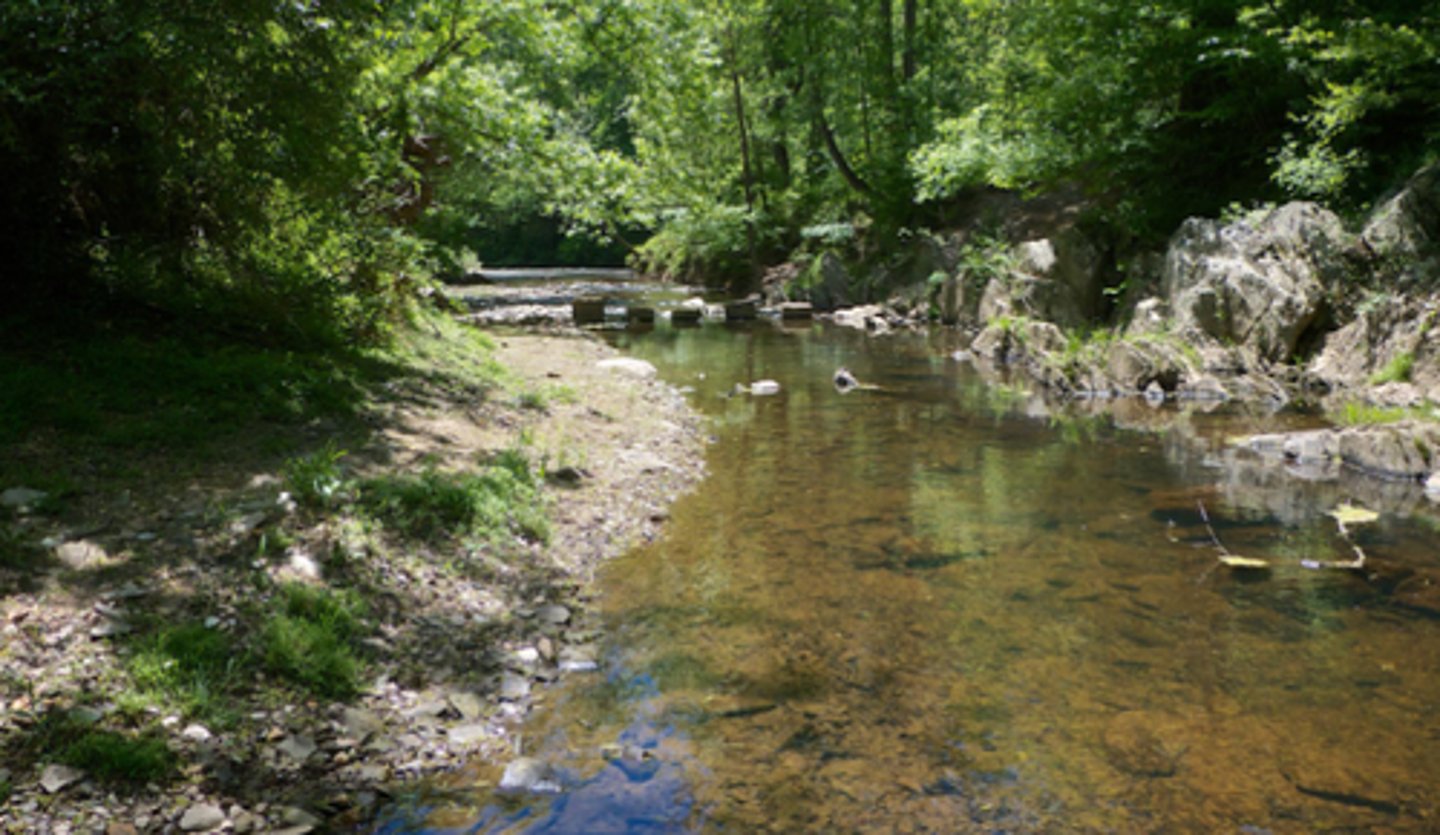
2-3rd order
algae
invertebrate herbivores
shallow
moderate productivity

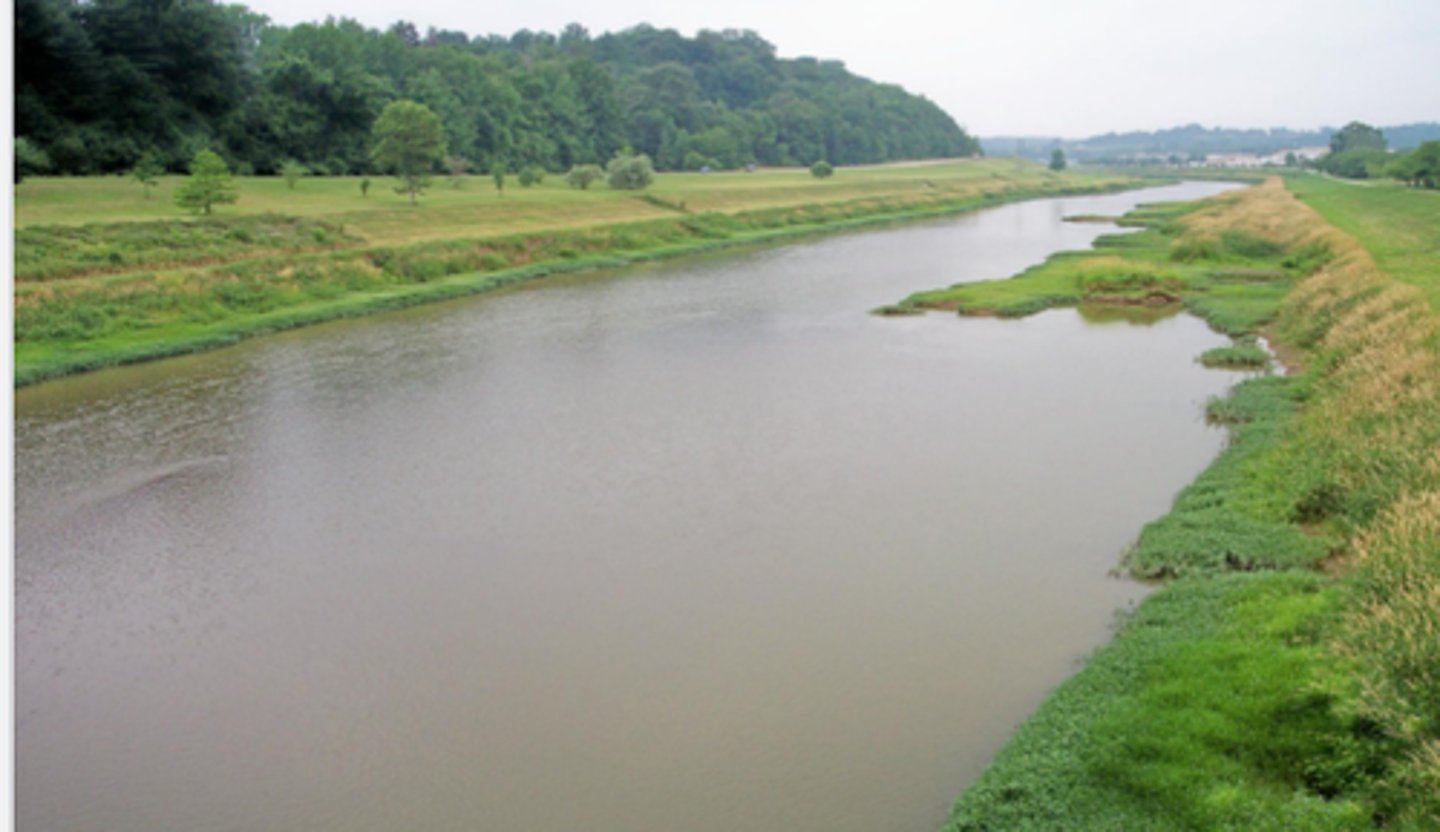
6-7th order
vascular plants
invertebrate herbivores
high light
high productivity

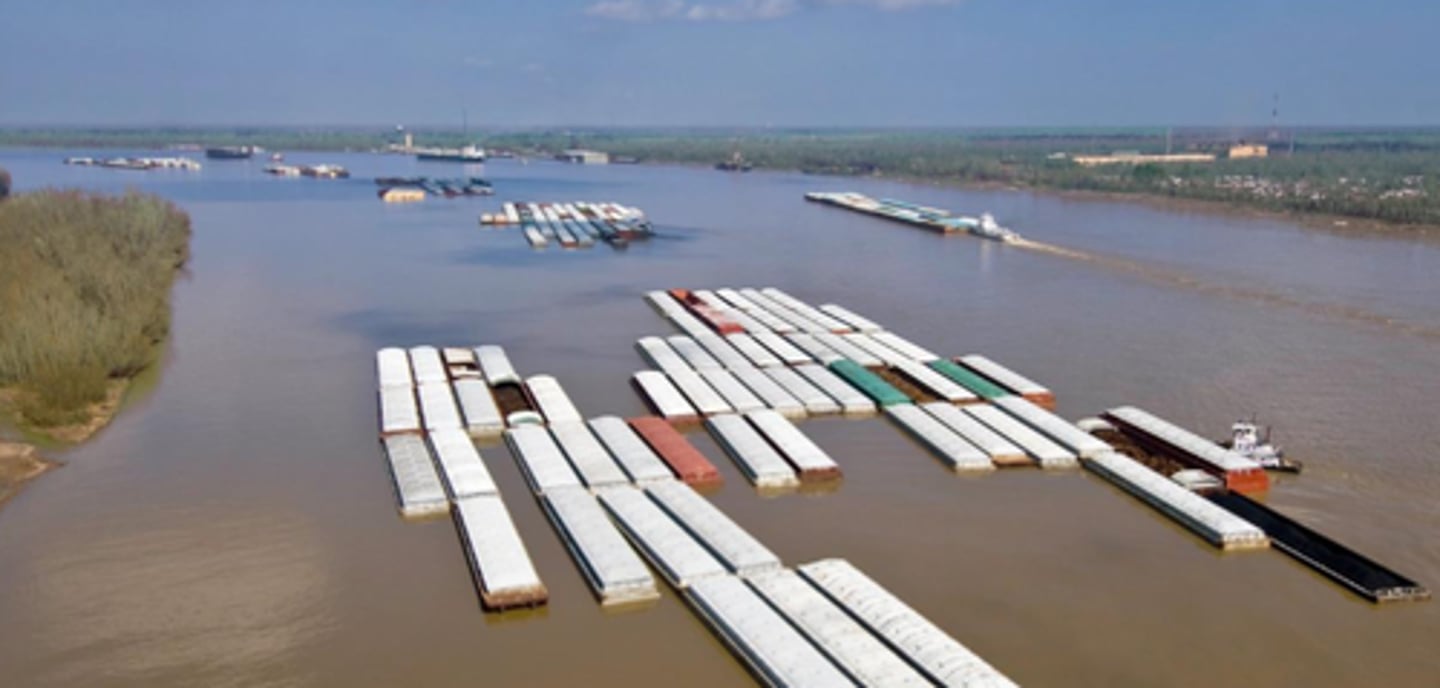
10th Order
planktonic
filter feeders
low oxygen
low light

ponds and lakes
characterized by nonflowing fresh water with at least some area of water that is too deep for plants to rise above the water's surface
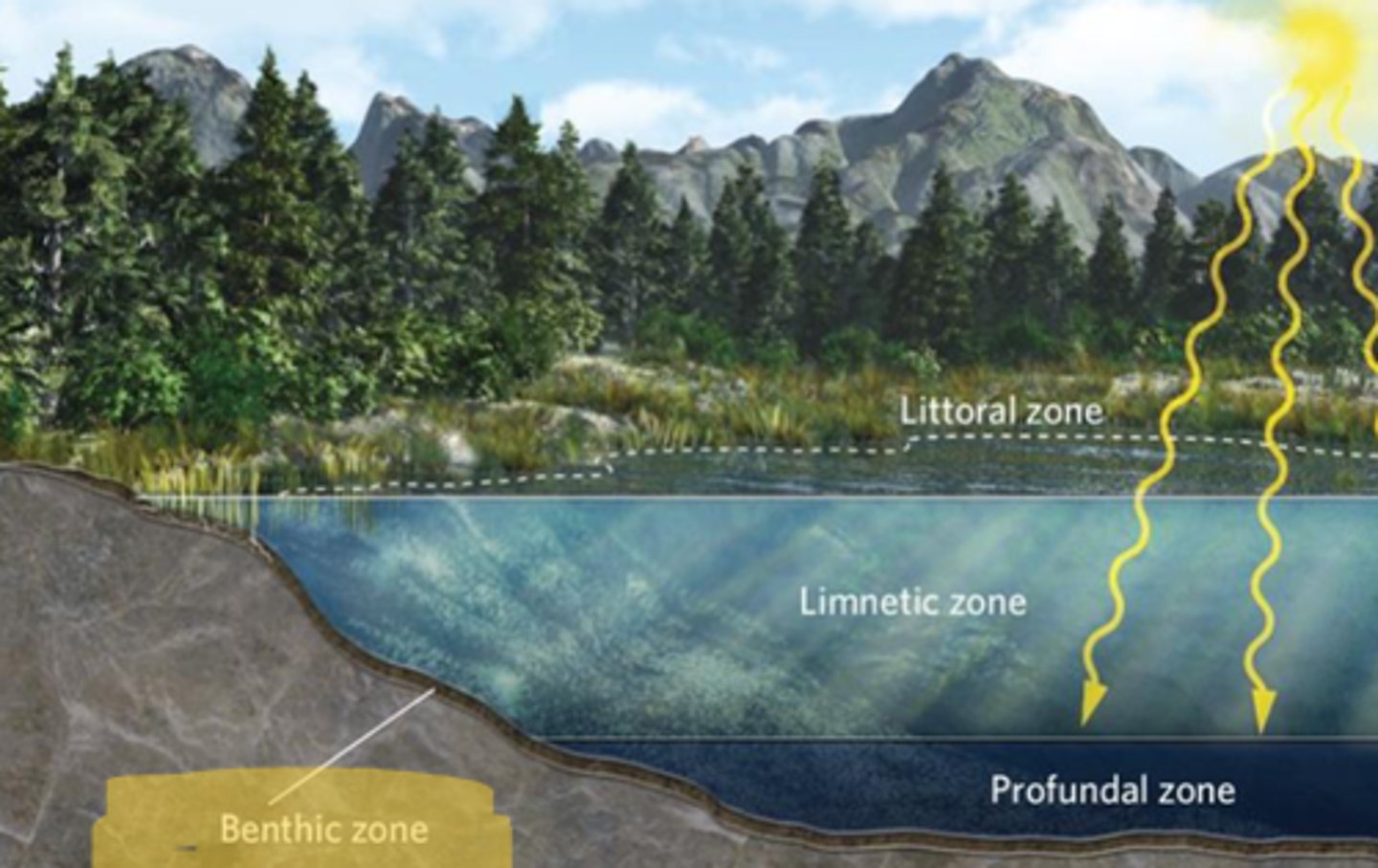
Littoral zone
the shallow area around the edge of a lake or pond containing rooted vegetation
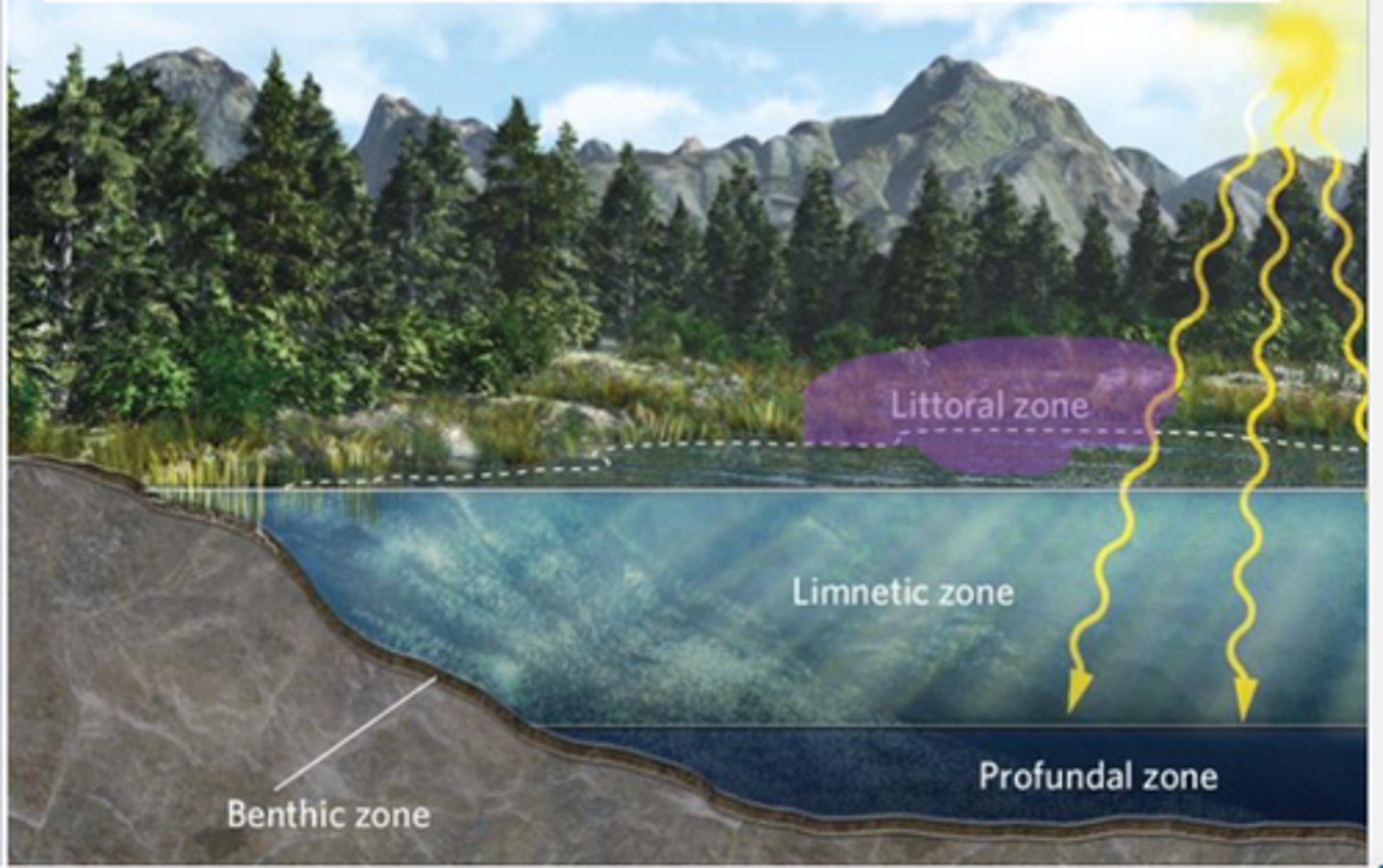
Limnetic zone
he open water beyond the littoral zone, where the dominant photosynthetic organisms are floating algae; also known as Pelagic zone
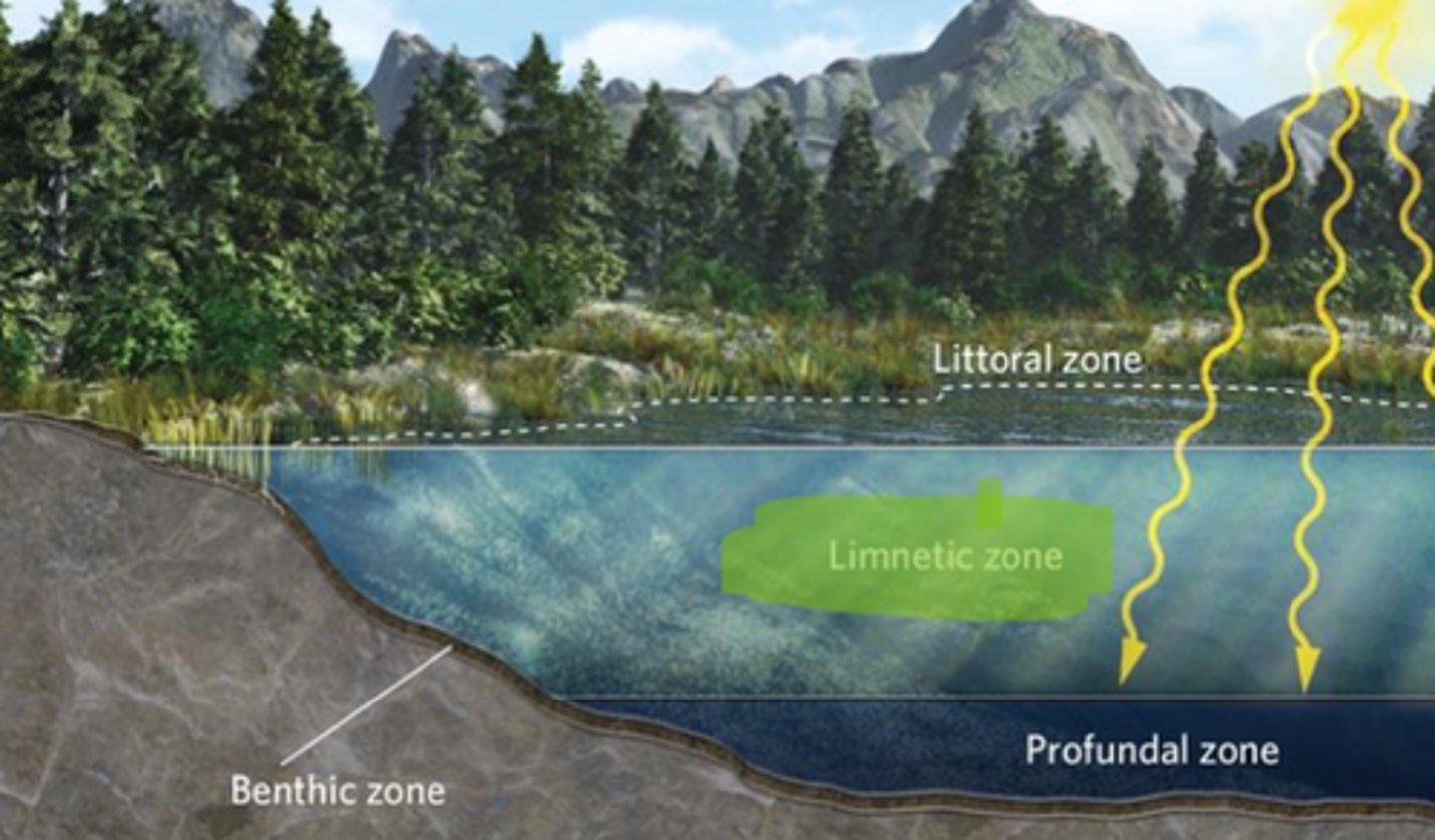
Profundal zone
the area in a lake that is too deep to receive sunlight

Benthic zone
the area consisting of the sediments at the bottoms of lakes, ponds, and oceans