Cell Signaling - AP Biology
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
cell signaling
the molecular mechanisms by which cells detect and respond to external stimuli and send messages to other cells
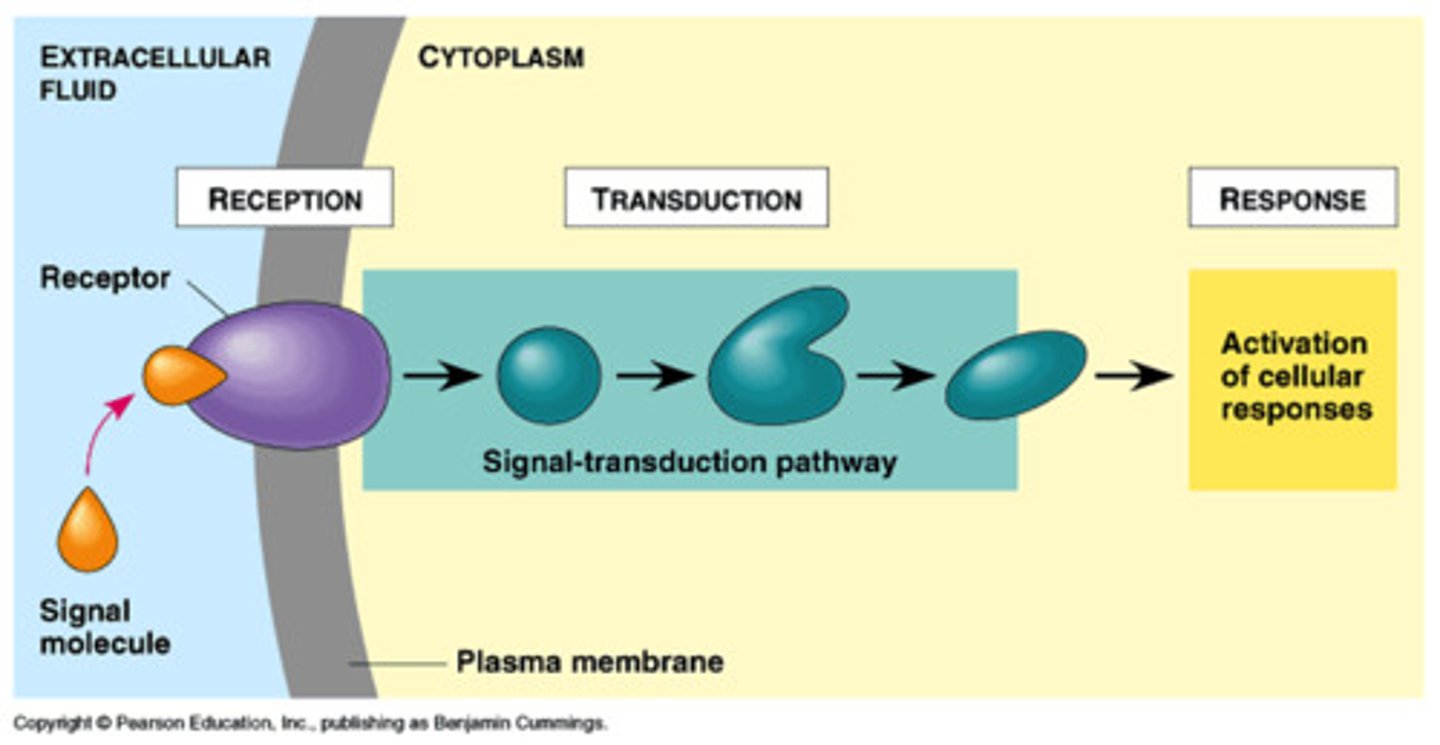
reception
a signaling molecule binds to a receptor protein, causing it to change shape
ligand
A molecule that binds specifically to a receptor site of another molecule.
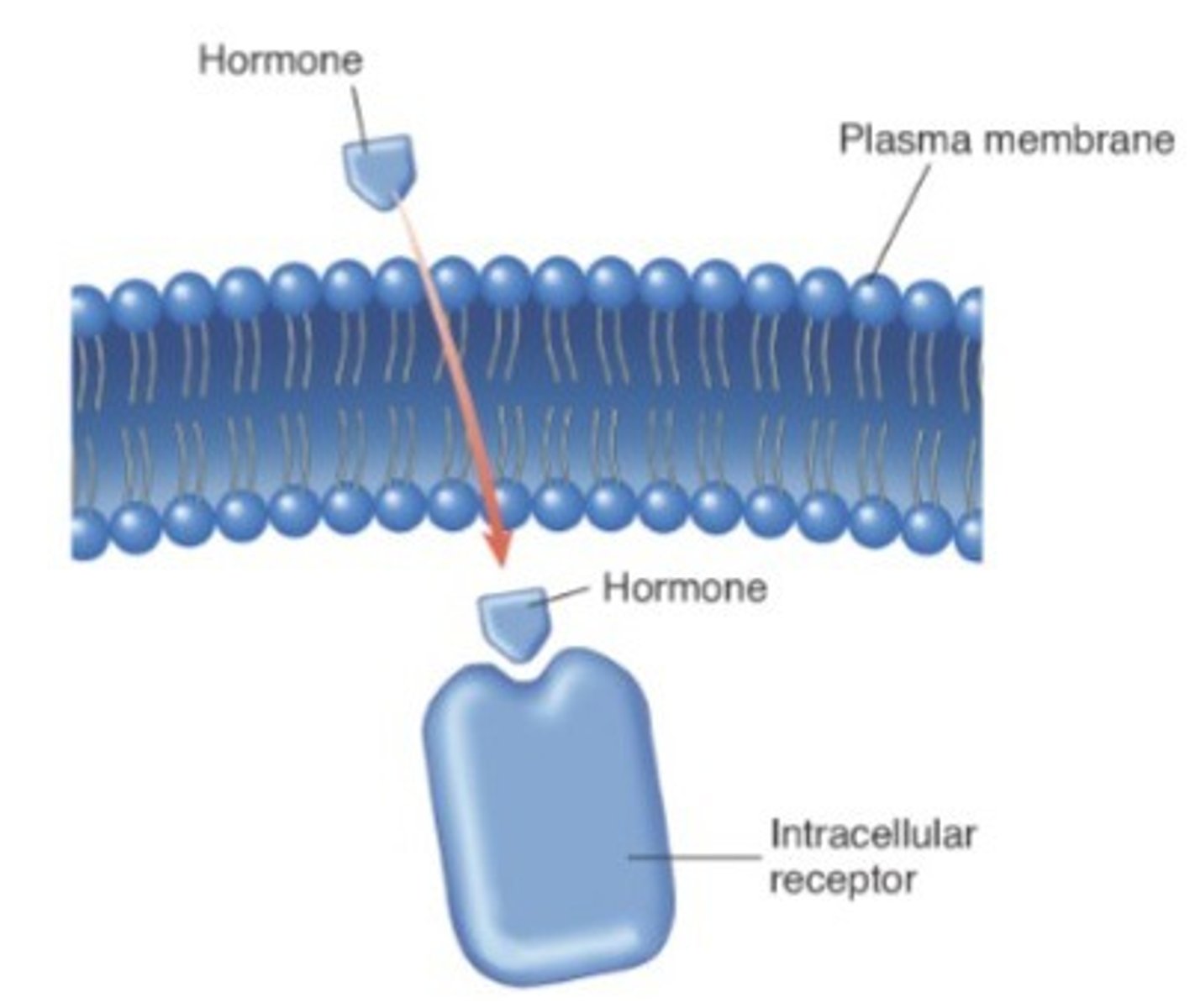
intracellular receptor
receptors located inside the cell rather than on its cell membrane
plasma membrane receptors
receptors embedded in the plasma membrane
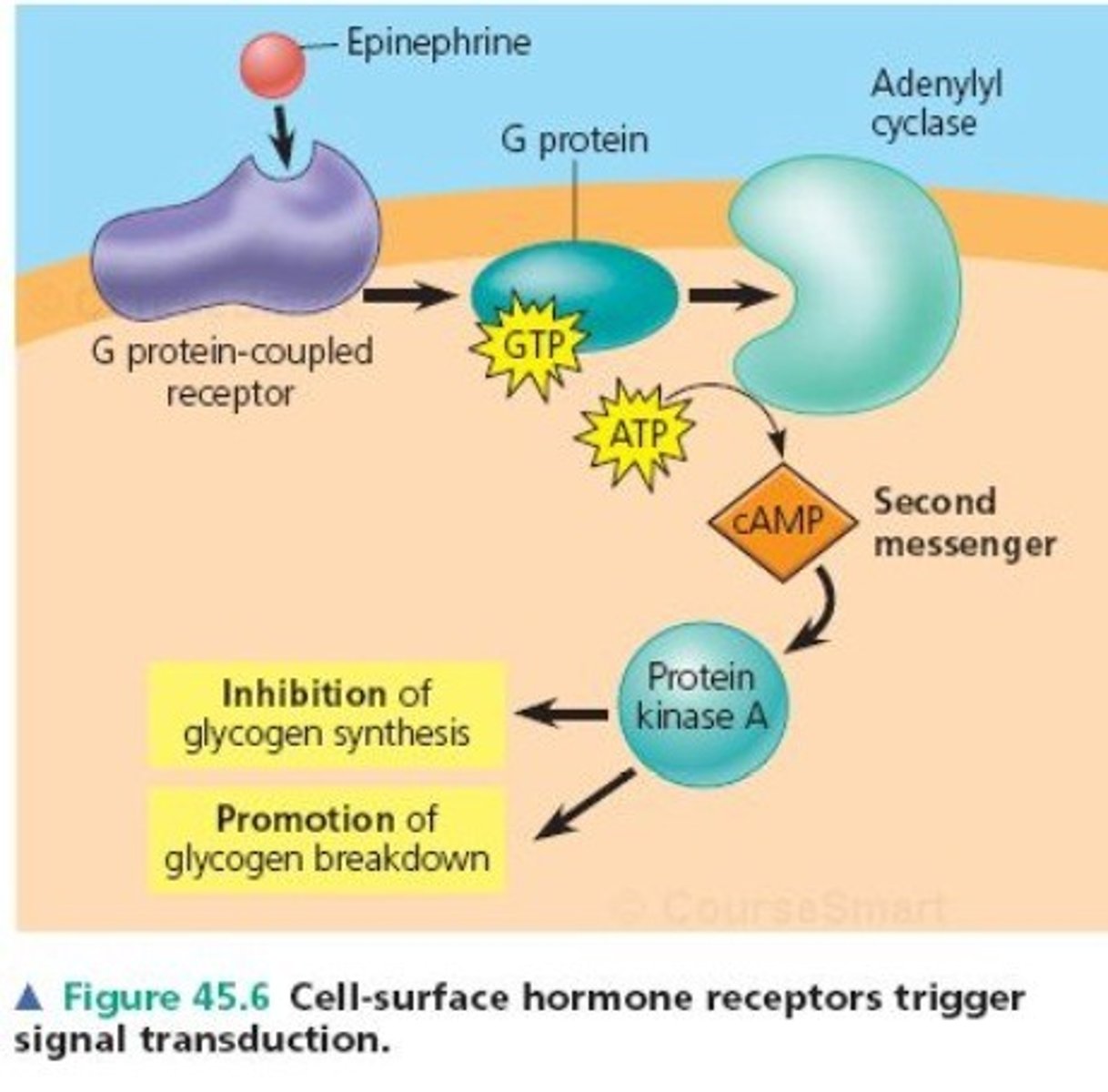
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs)
a large family of proteins that function as receptors; they provide a mechanism for molecules outside a cell to influence the inner workings of the cell
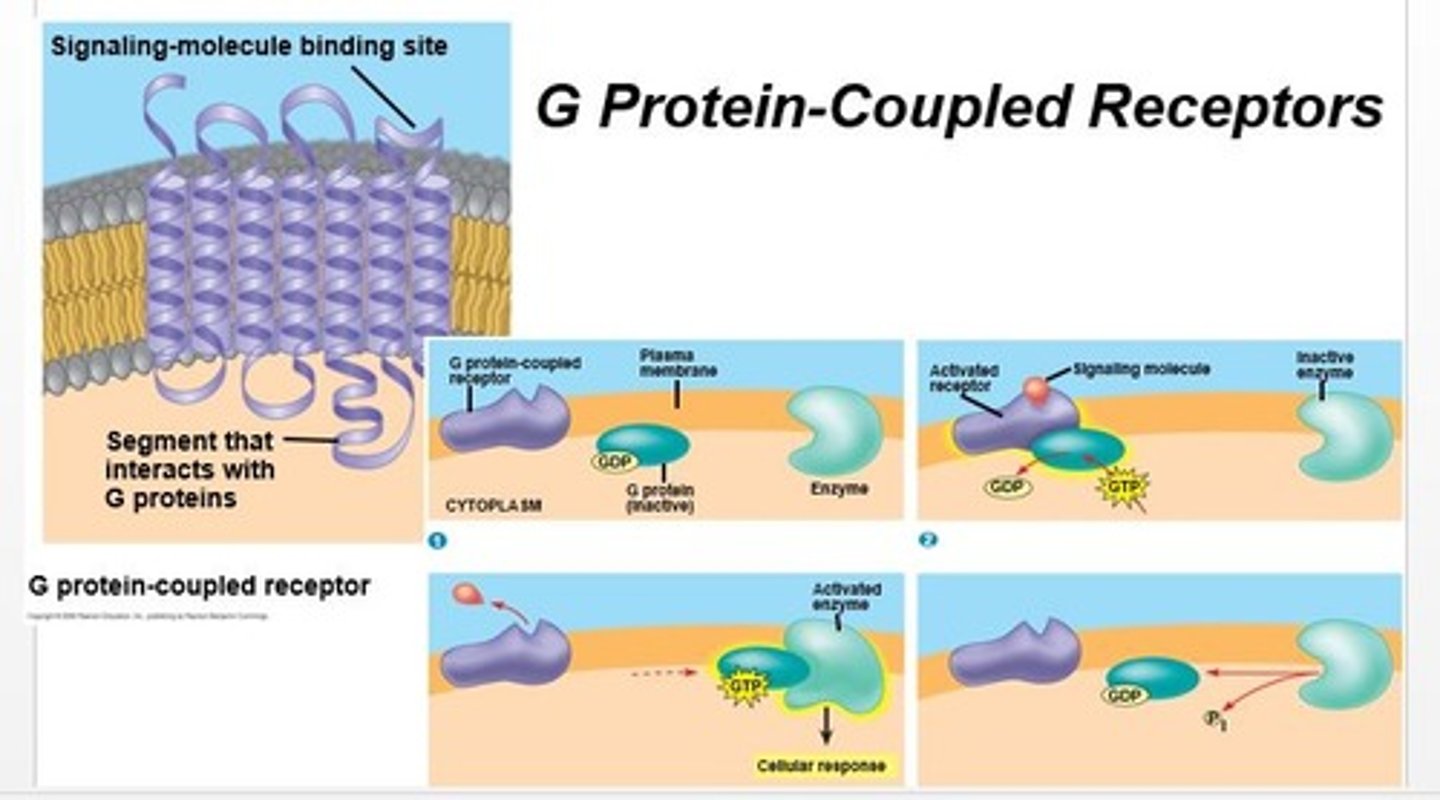
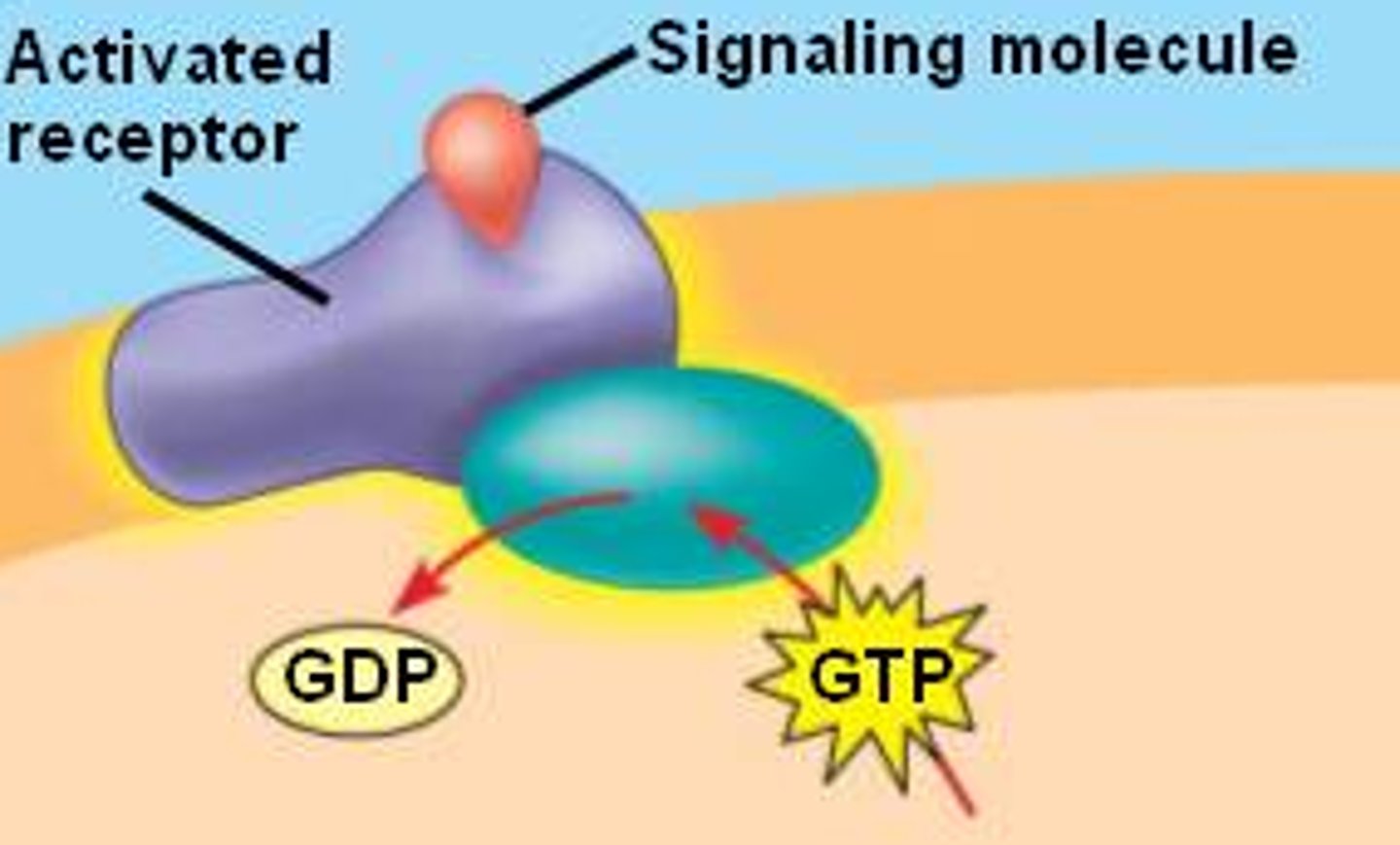
g-protein
A GTP-binding protein that relays signals from a plasma membrane signal receptor, known as a G protein-coupled receptor, to other signal transduction proteins inside the cell.
epinephrine
neurotransmitter and hormone of adrenaline
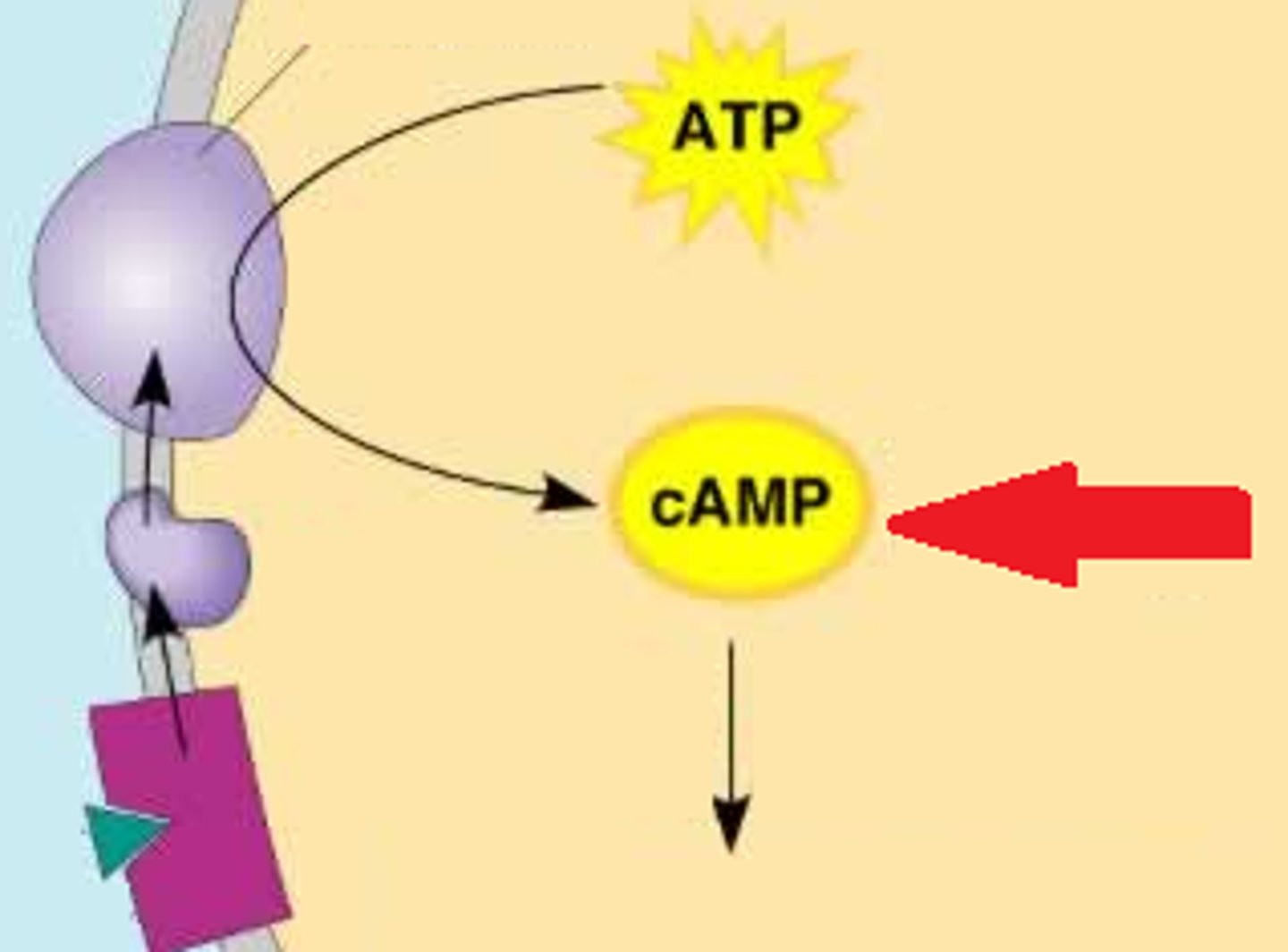
cyclic AMP (cAMP)
secondary messenger that activates protein kinases and initiates phosphorylation cascades.
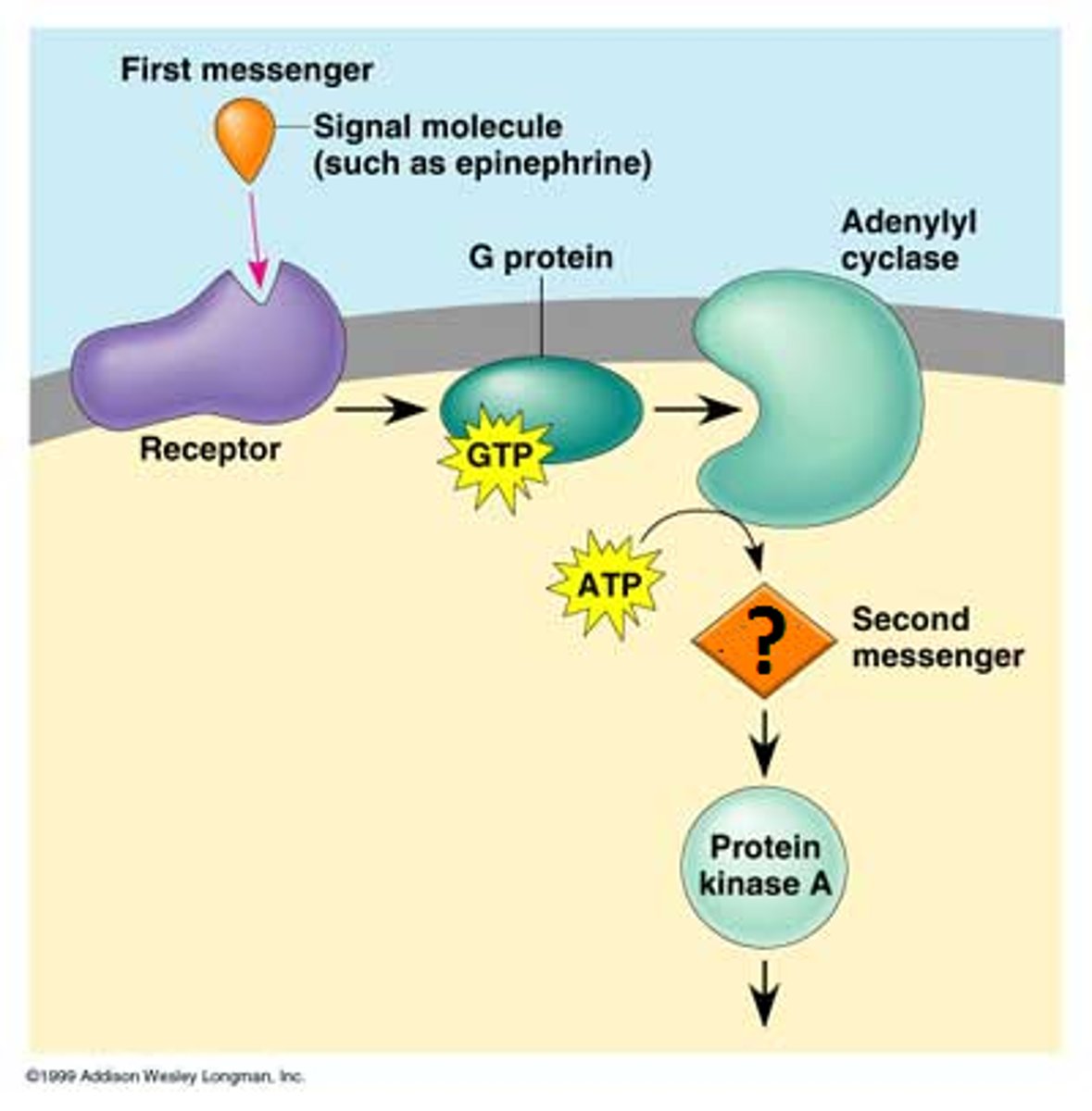
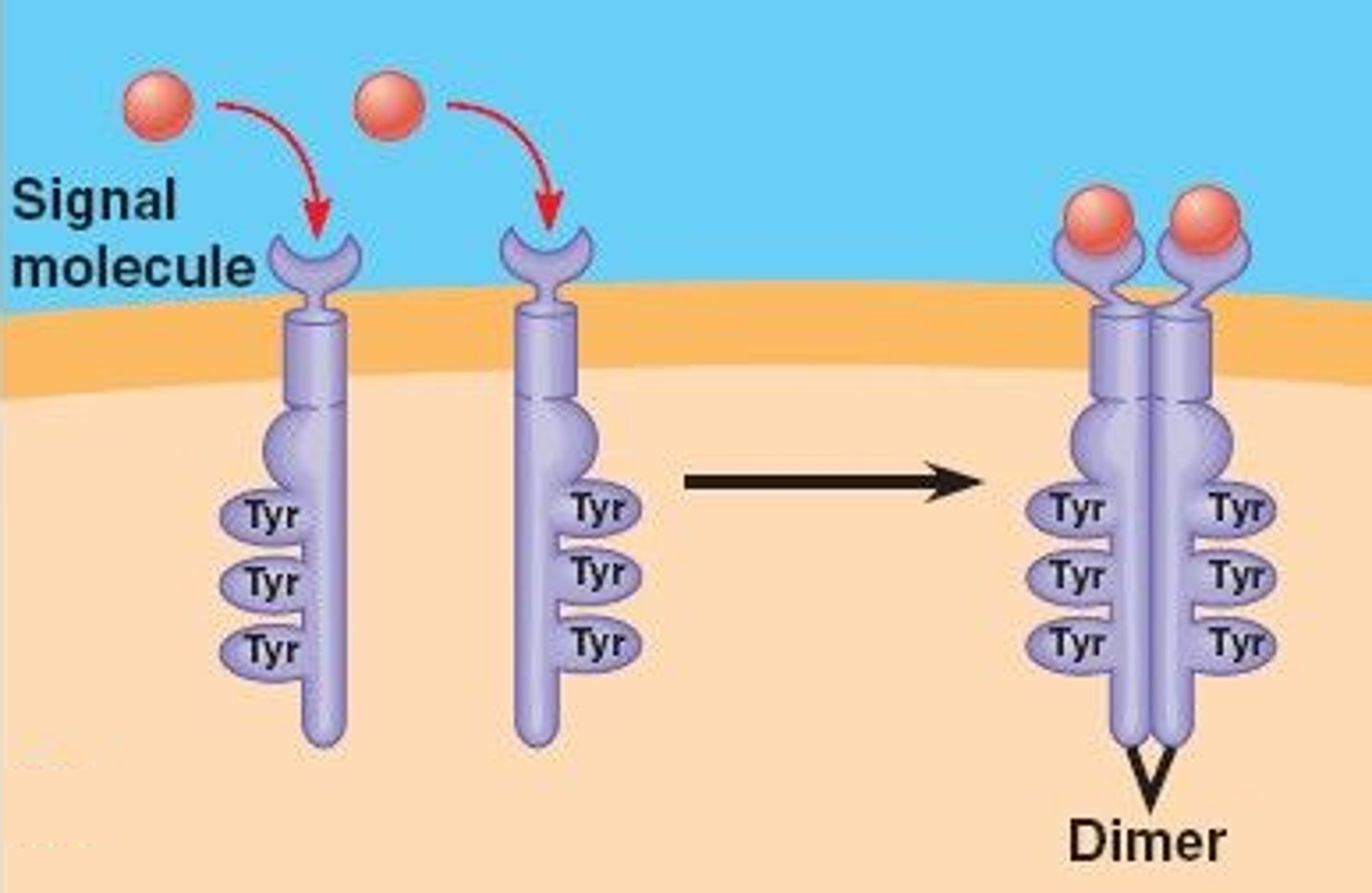
receptor tyrosine kinase
A receptor with enzymatic activity that can trigger more than one signal transduction pathway at once, helping the cell regulate and coordinate many aspects of cell growth and reproduction.
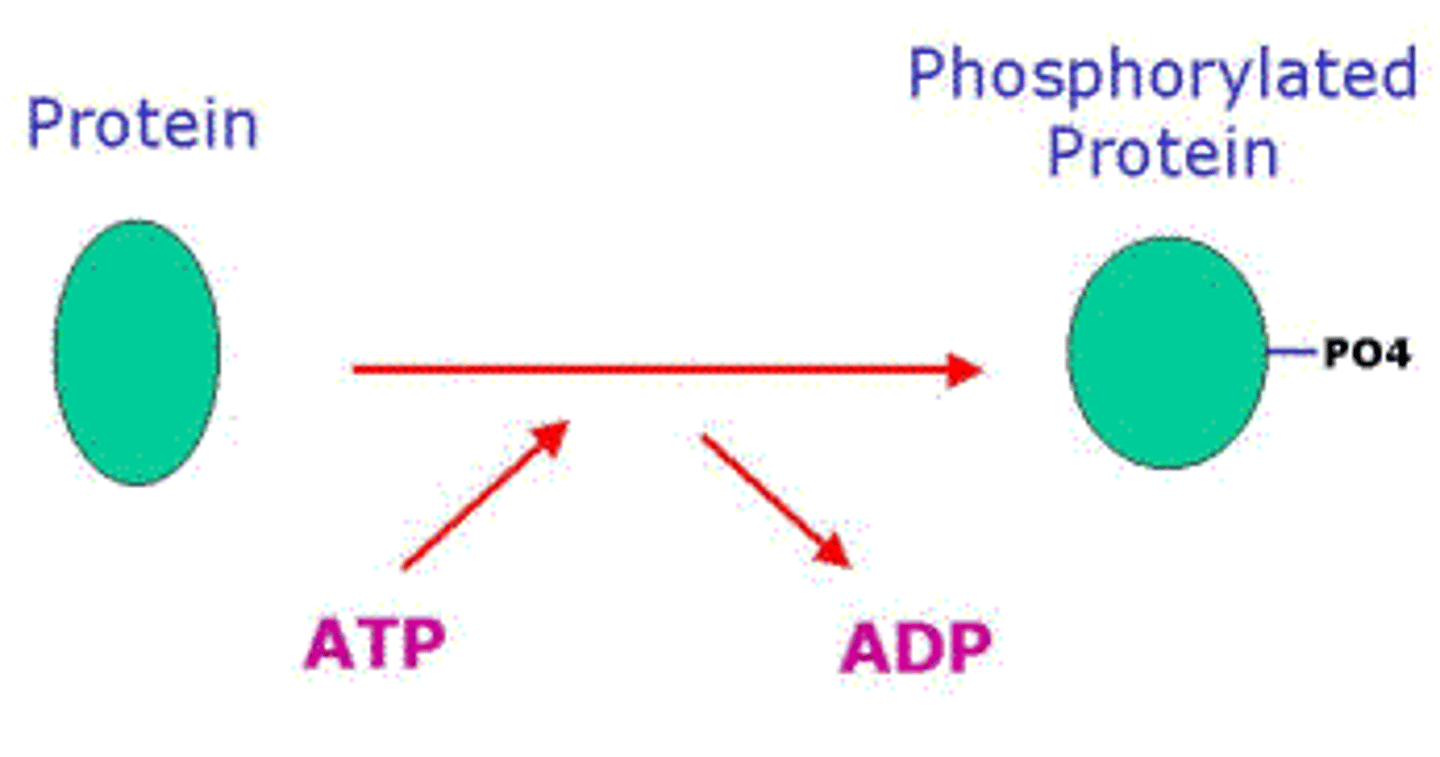
protein kinase
An enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to a protein, thus phosphorylating the protein.
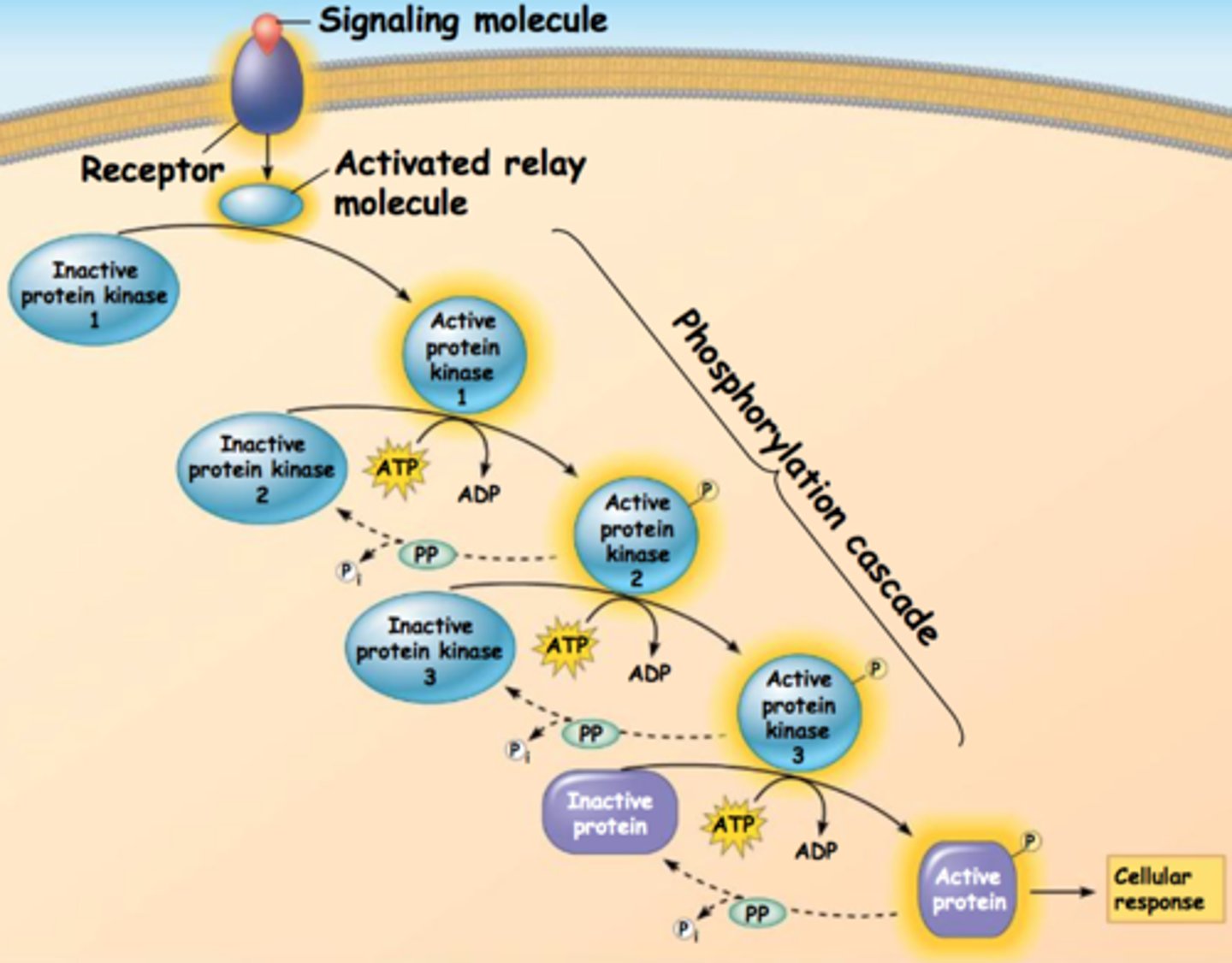
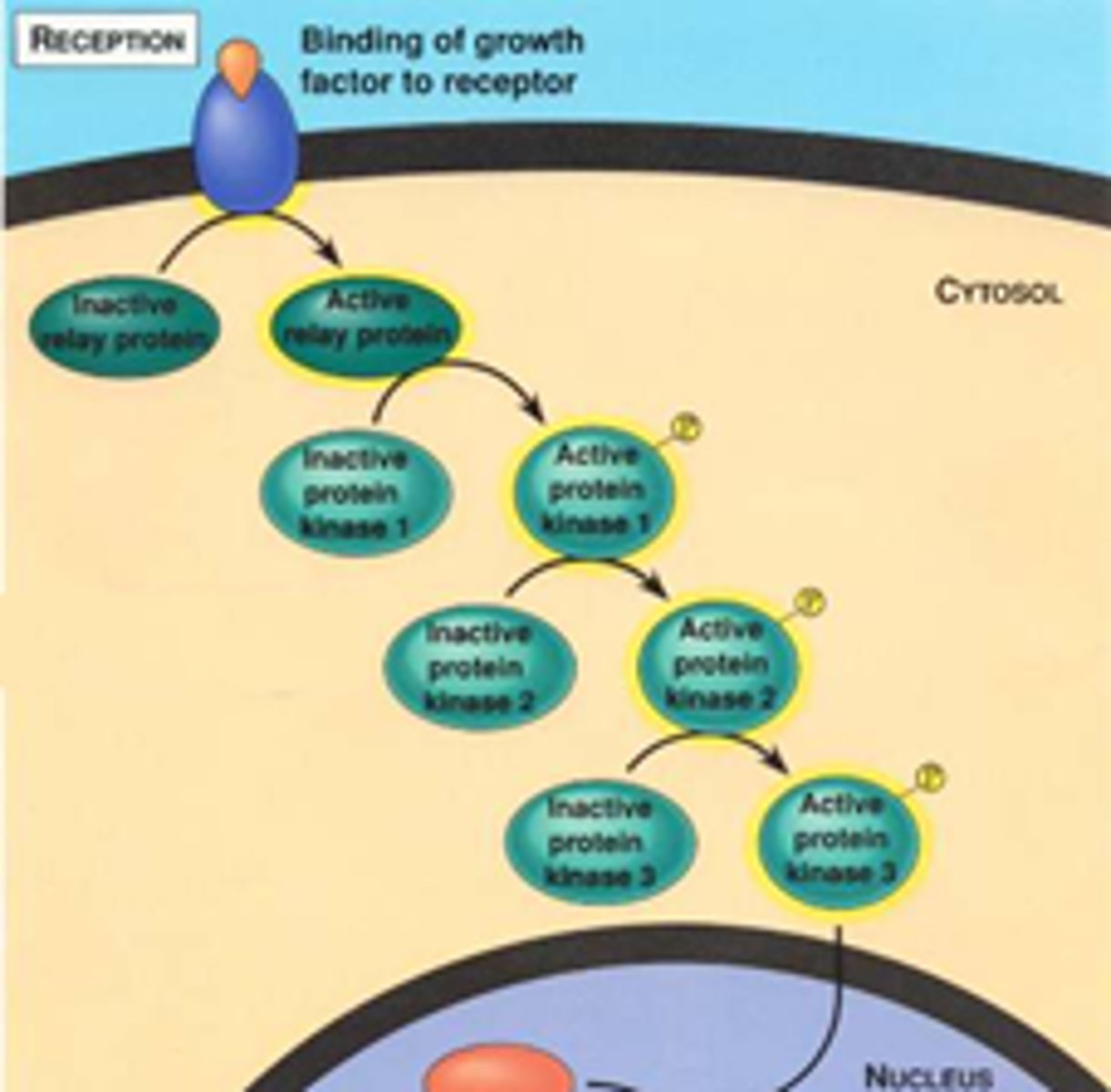
phosphorylation cascades
A series of enzyme-catalyzed phosphorylation reactions commonly used in signal transduction pathways to amplify and convey a signal inward from the plasma membrane.
transduction
chain reactions between many molecules result in the sending of a signal from the receptors to target molecules in the cell
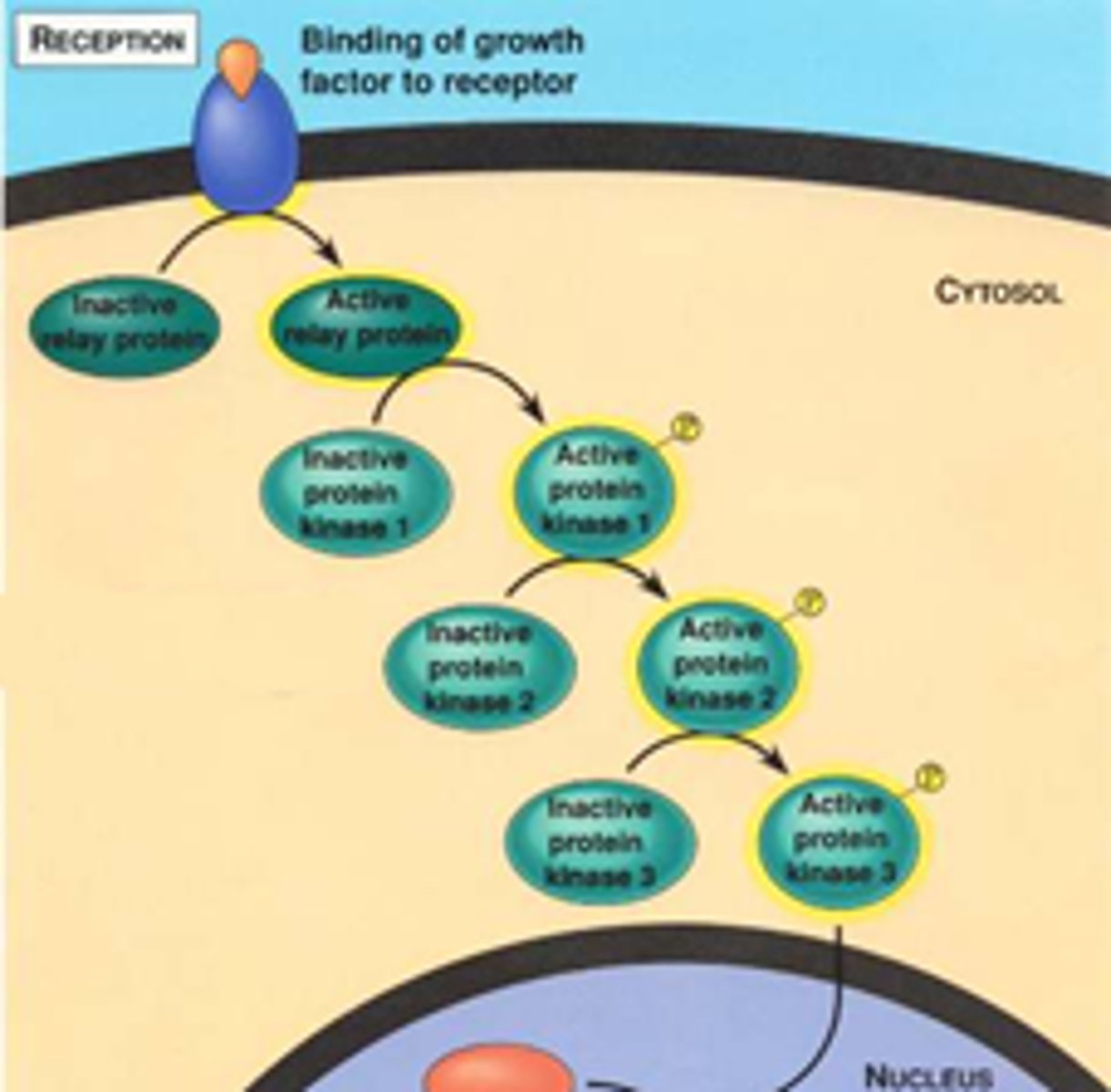
signal transduction pathway
The process by which a signal on a cell's surface is converted into a specific cellular response.
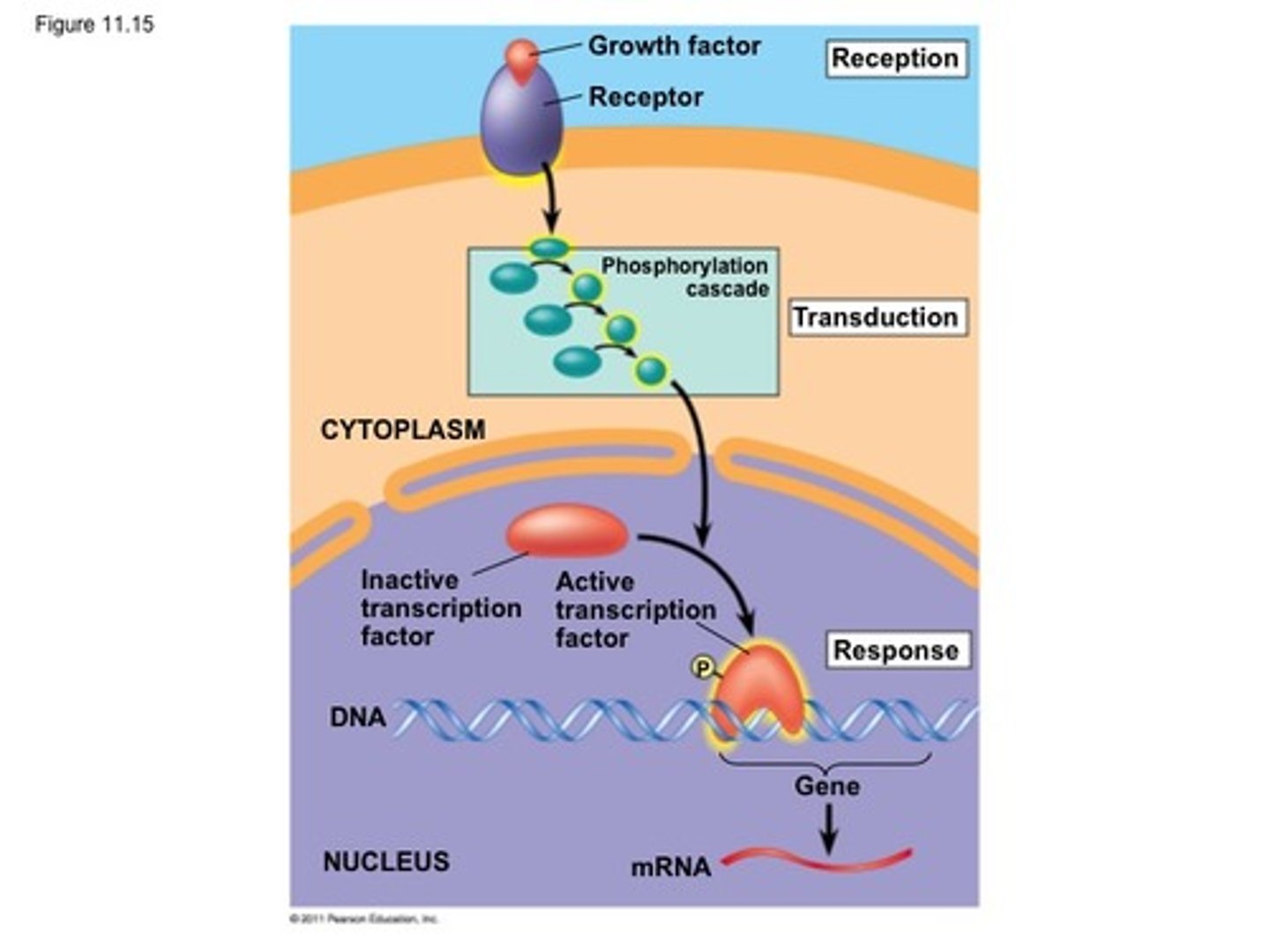
response
cell signaling leads to the regulation of activities that take place in the nucleus or the cytoplasm
nuclear response
turning genes on/off; transcription factors attaches to DNA and causes the creation of mRNA
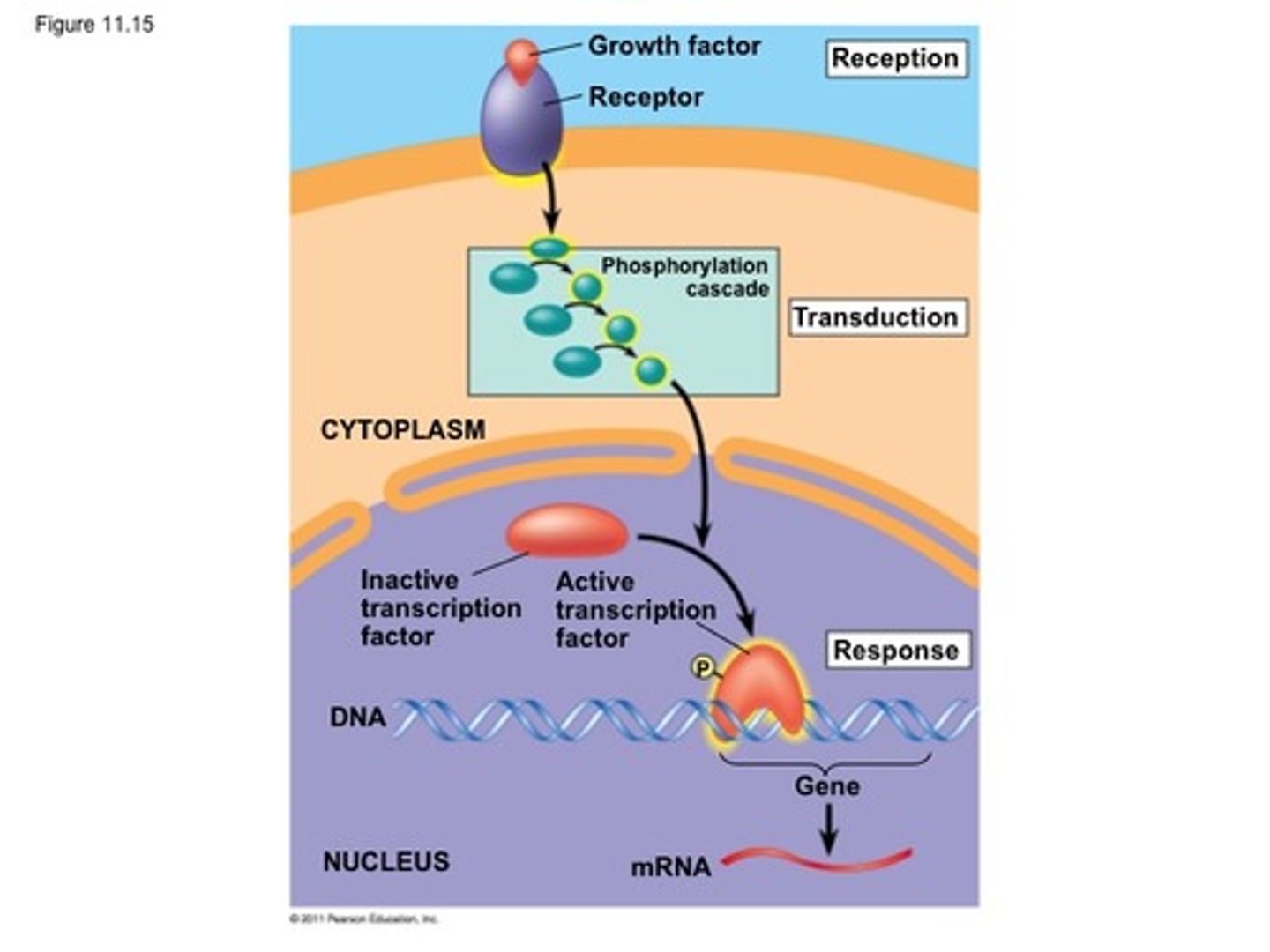
cytoplasmic response
Signaling pathway controls the activity of proteins already present in the cell and does not directly affect transcription of genes
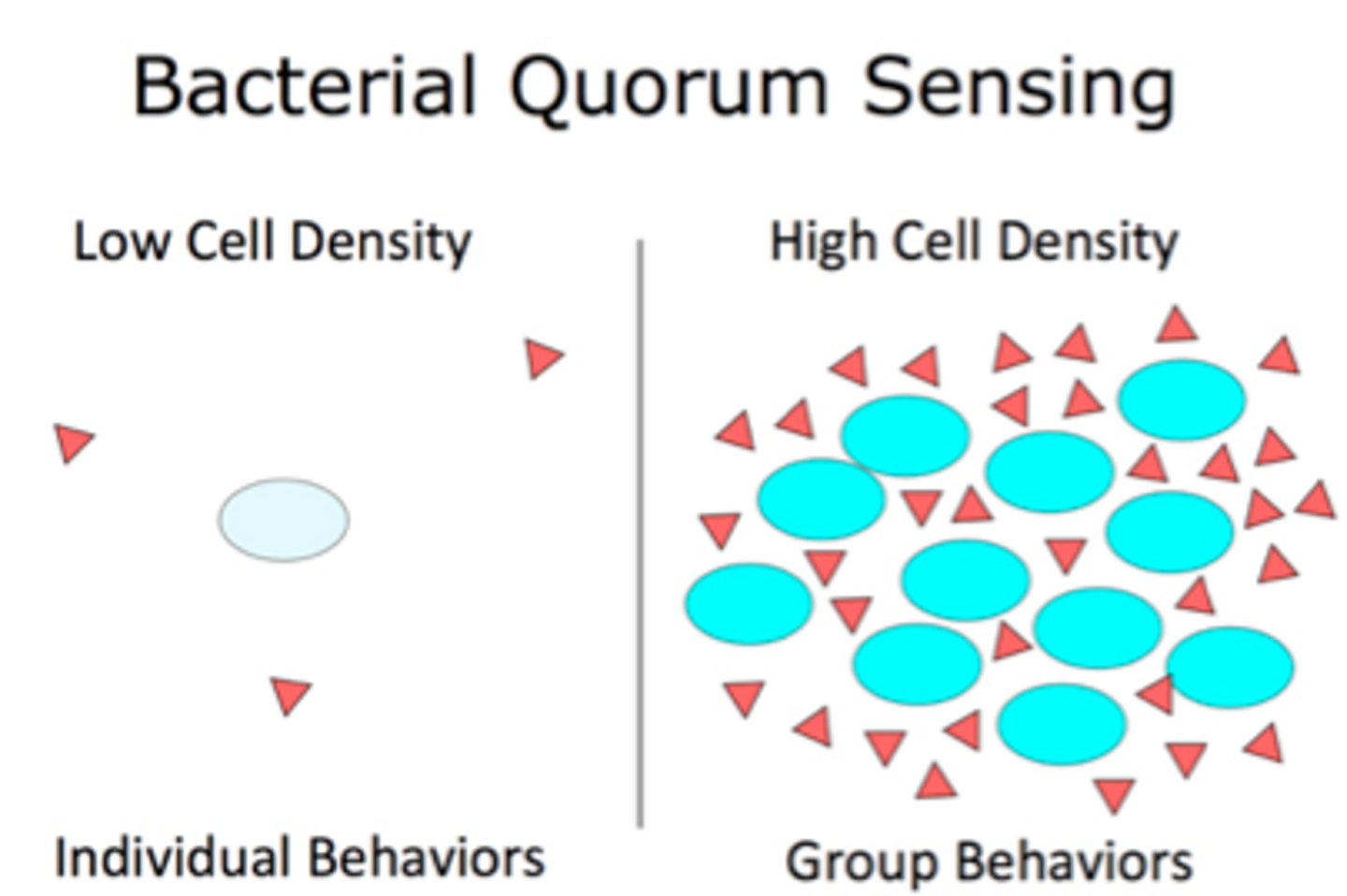
Unicellular or Multicellular organisms communicate with other cells?
BOTH!
bacteria-quorum sensing
release of signal molecules that allows bacteria to respond to changes in their environment
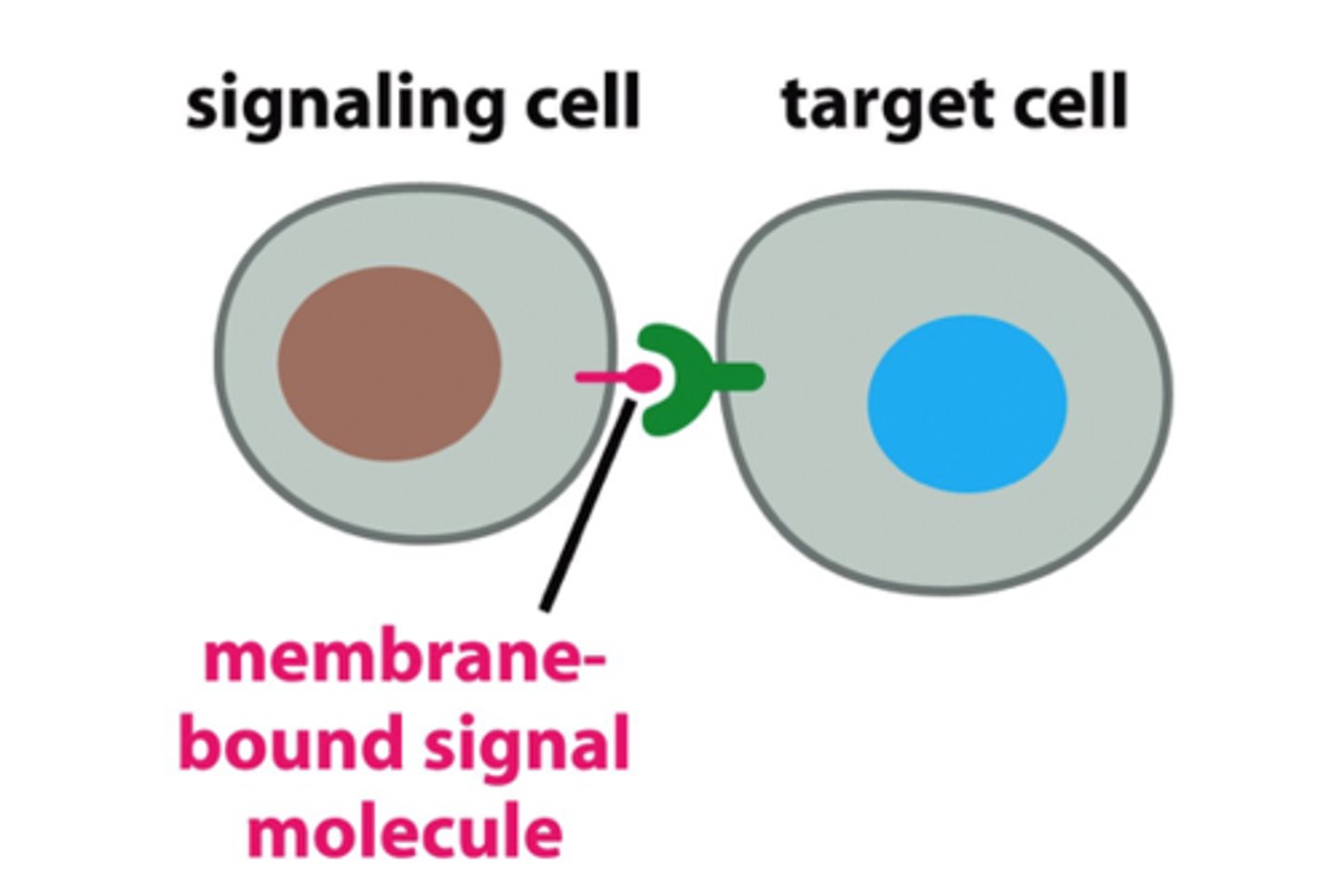
Juxtracrine Cell Signaling
cell signaling by directly touching cells
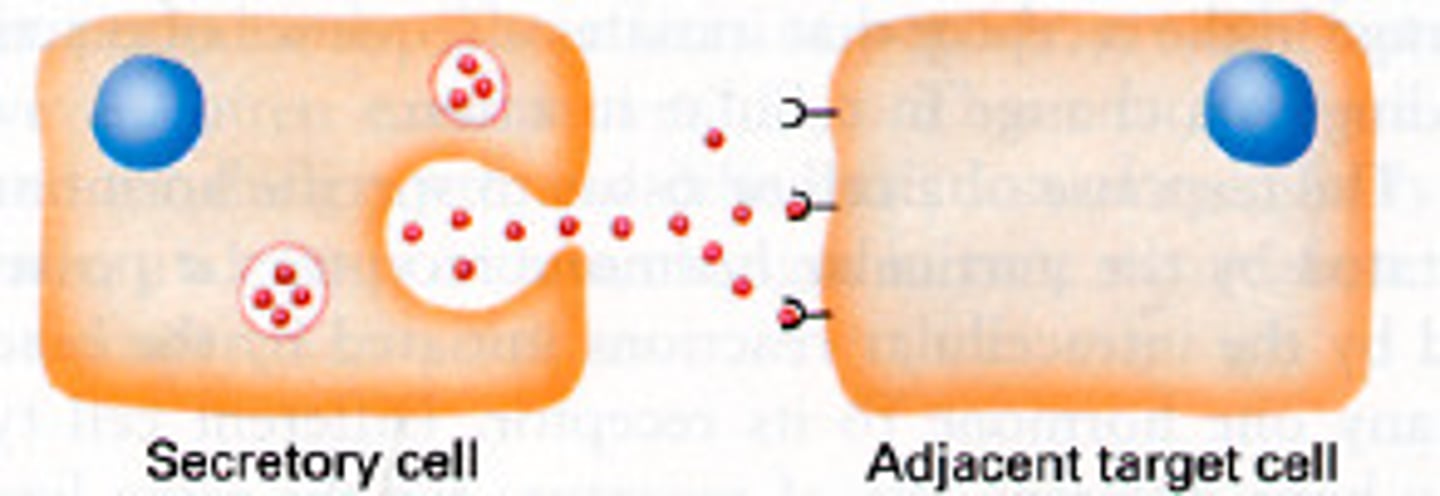
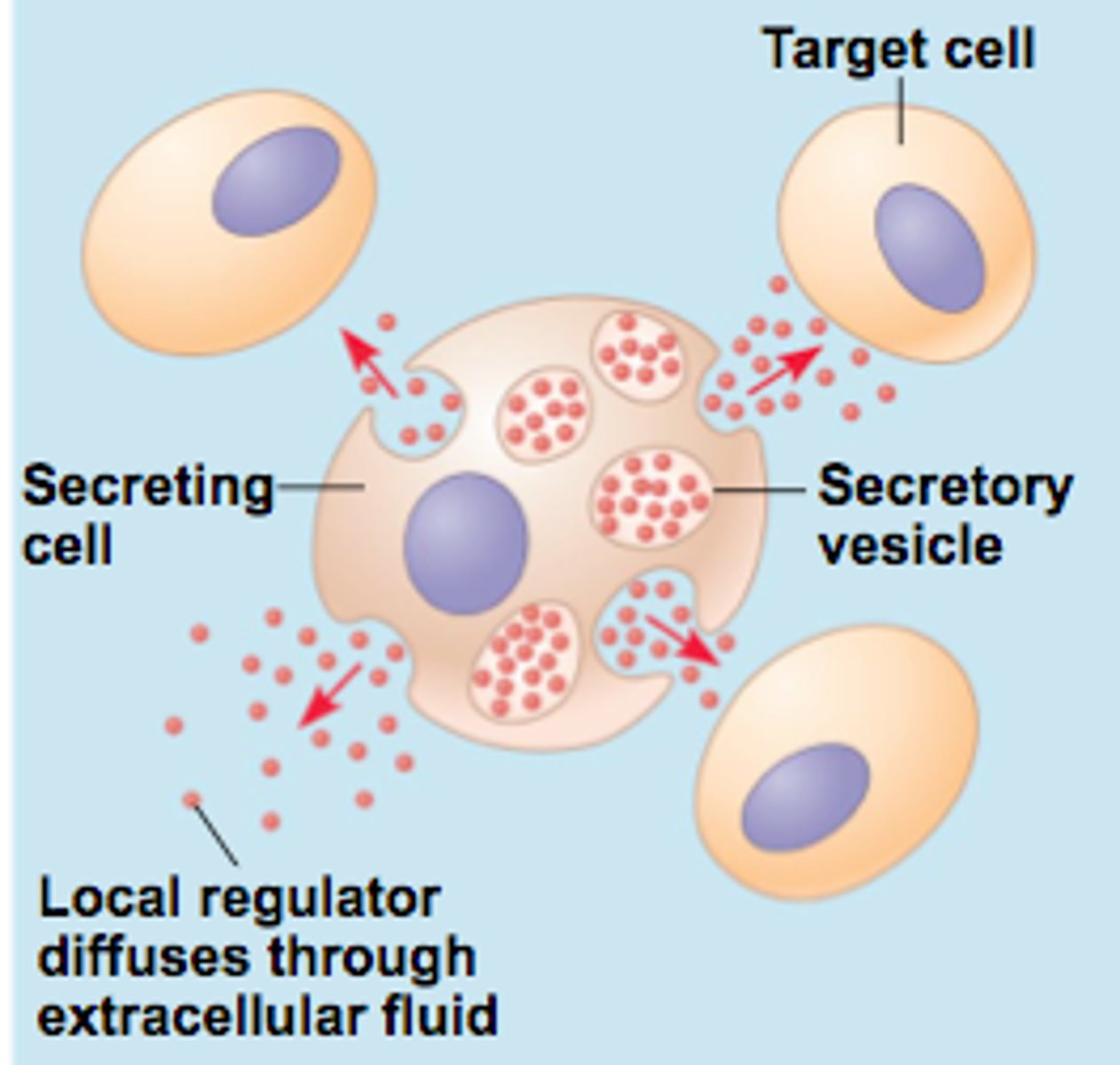
paracrine cell signaling
cell signaling between cells that are in close proximity
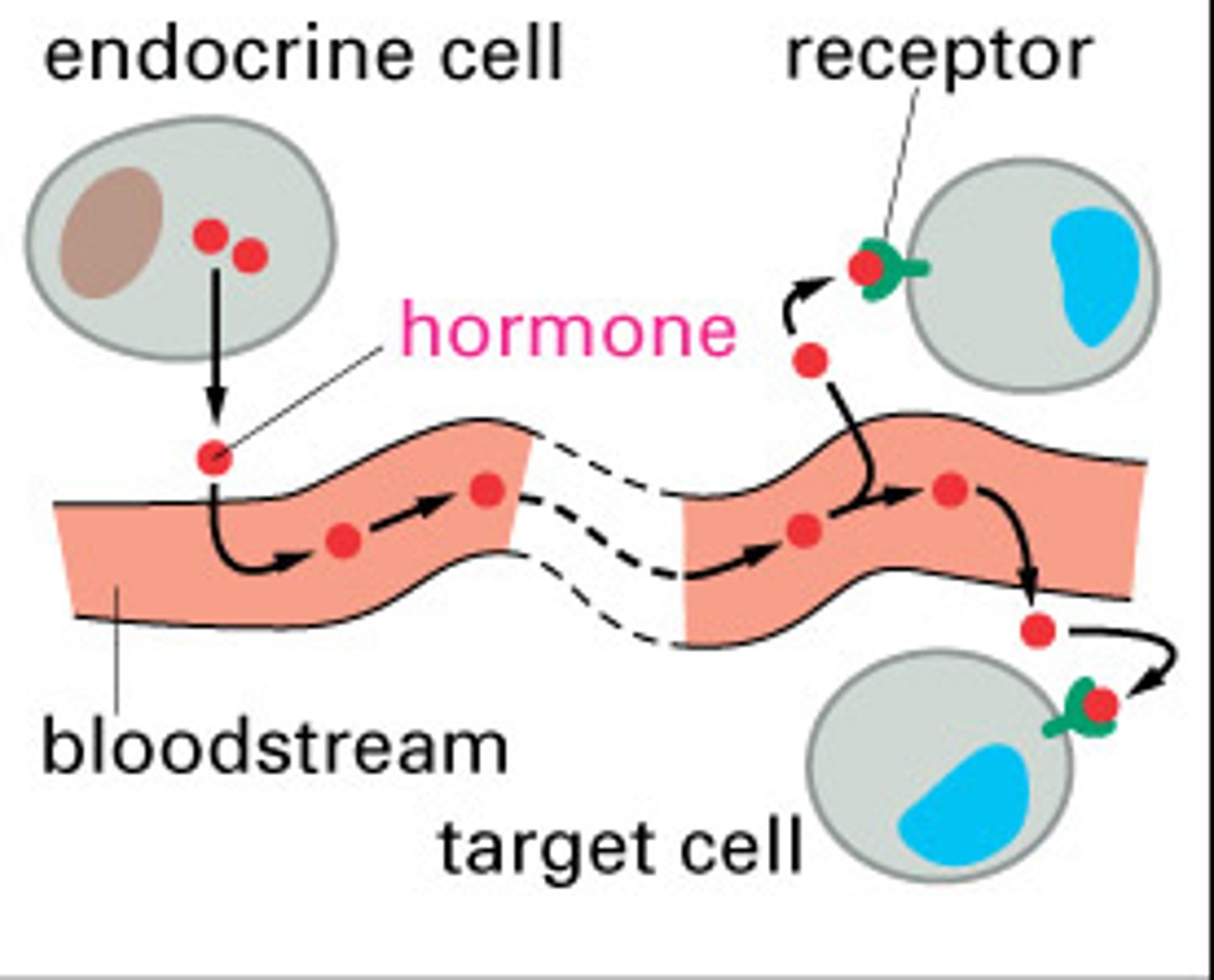
endocrine cell signaling
cell signaling between cells that are farther away
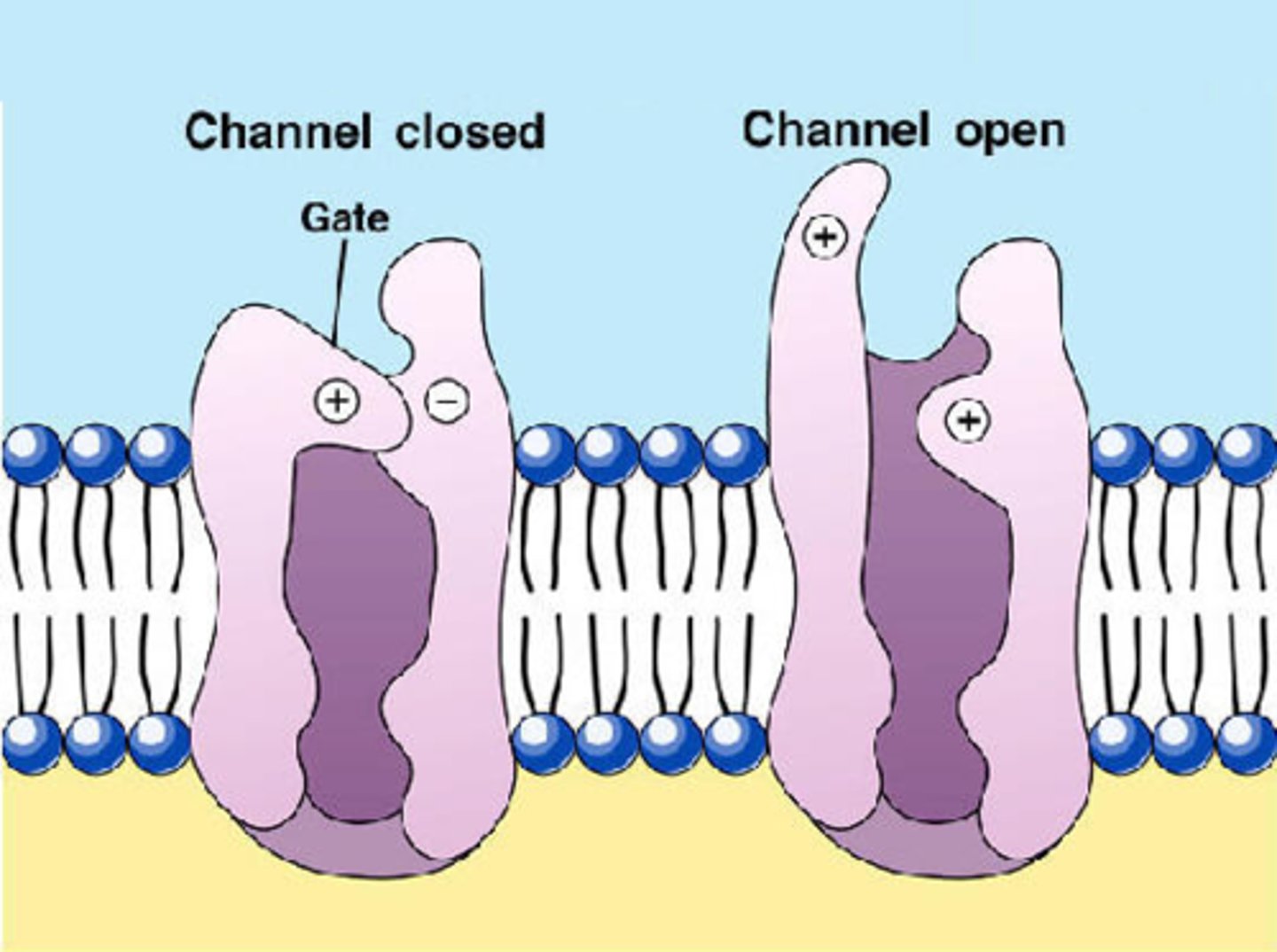
gated ion channels
ion channels that open or close in response to stimuli
second messengers
substances that initiate internal changes when activated by g-proteins or protein kinases
cell identity
signatures on cell that give it specific identity via glycoproteins
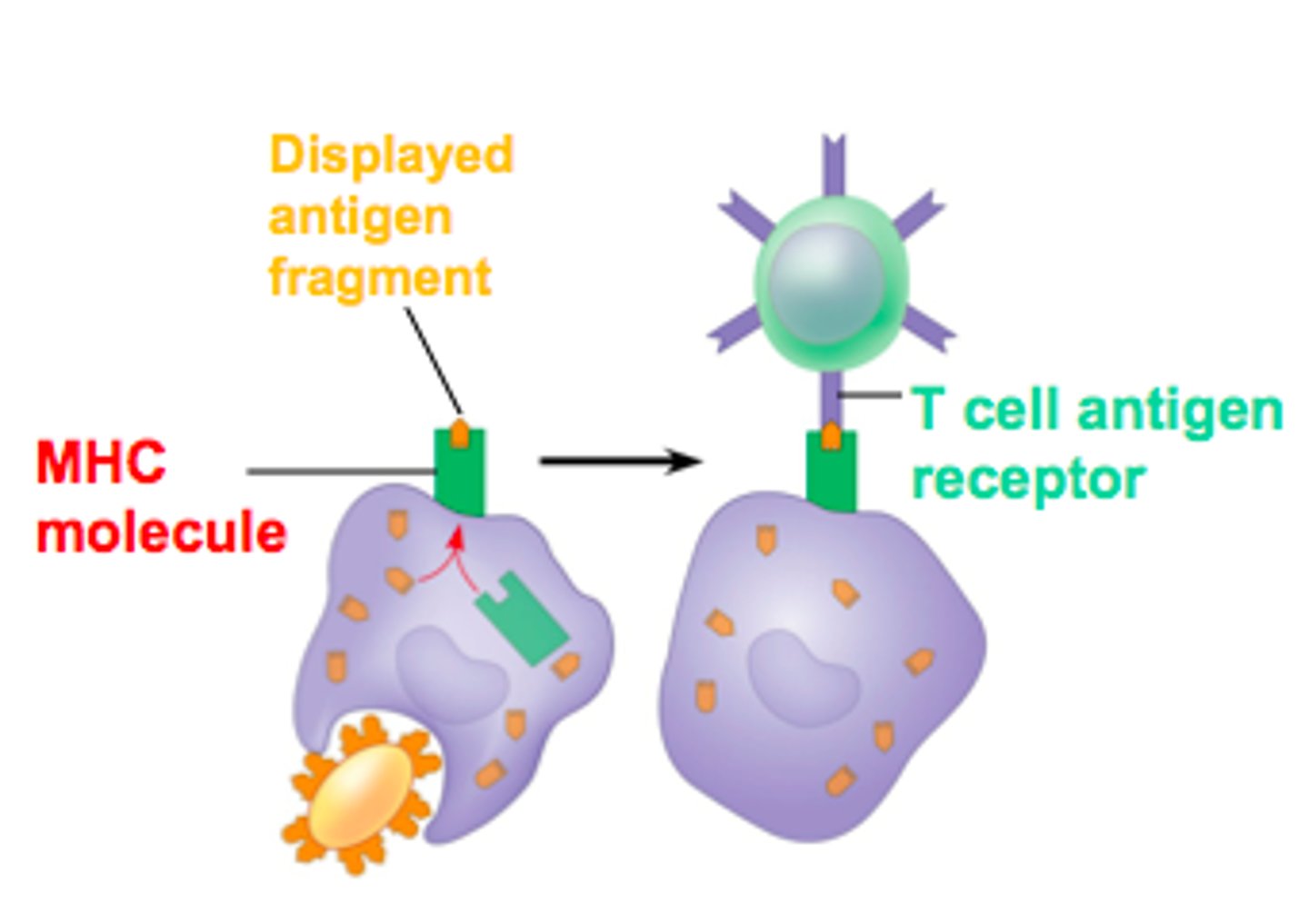
MHC (major histocompatibility complex) proteins
recognition of "self" and "nonself" cells by the immune system
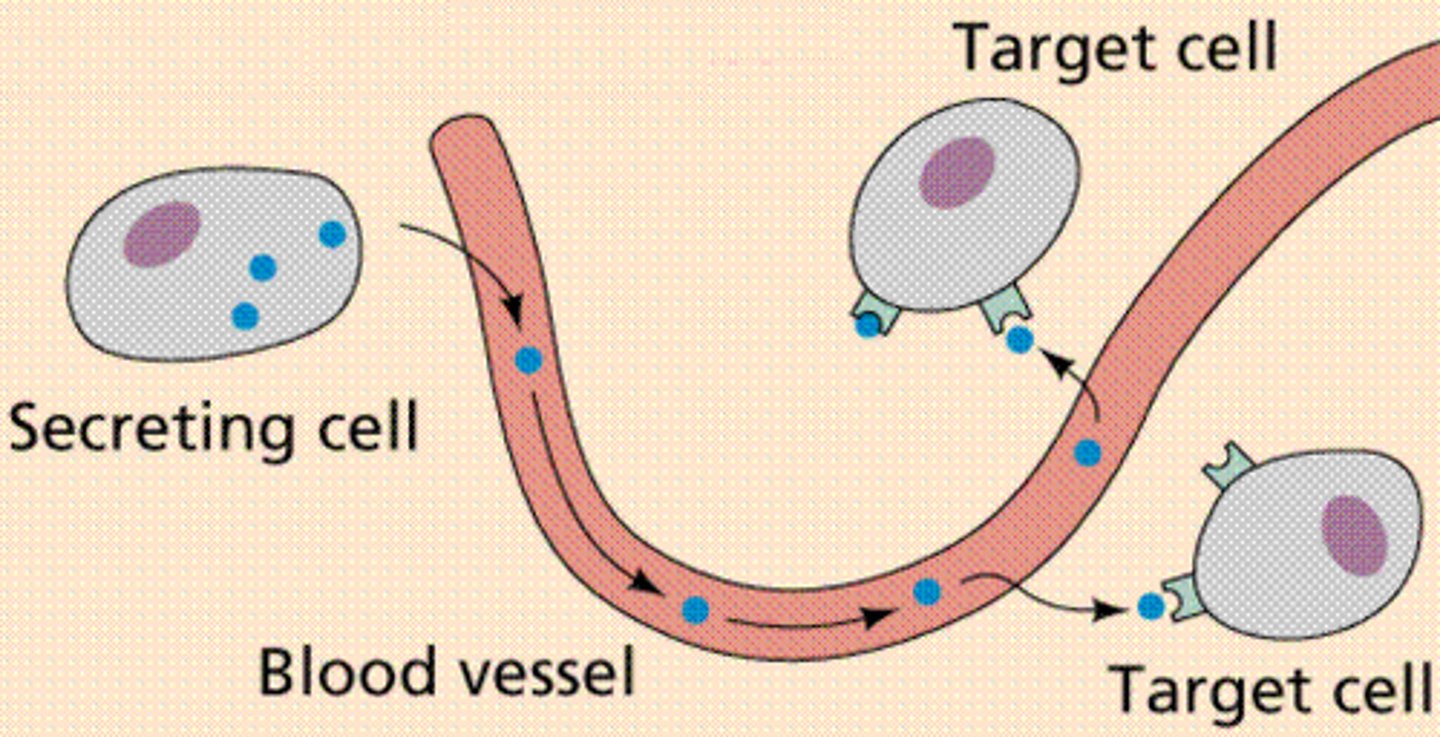
hormones
Chemical messengers, mostly those manufactured by the endocrine glands, that are produced in one tissue and affect another
hormones that can enter cells...
- lipid-soluble or water-soluble
- steroid hormones (lipophilic)
- water-soluble hormones must use membrane receptors in order to control cell activites
- steroid hormones travel in the blood attached to protein carriers
hormones that can't enter cells...
- too large or too polar
- hormones bind to receptor proteins on outer surface of cell membrane
- second messenger needed to produce effects
local signaling
signaling between adjacent cells (paracrine, autocrine, and synaptic)
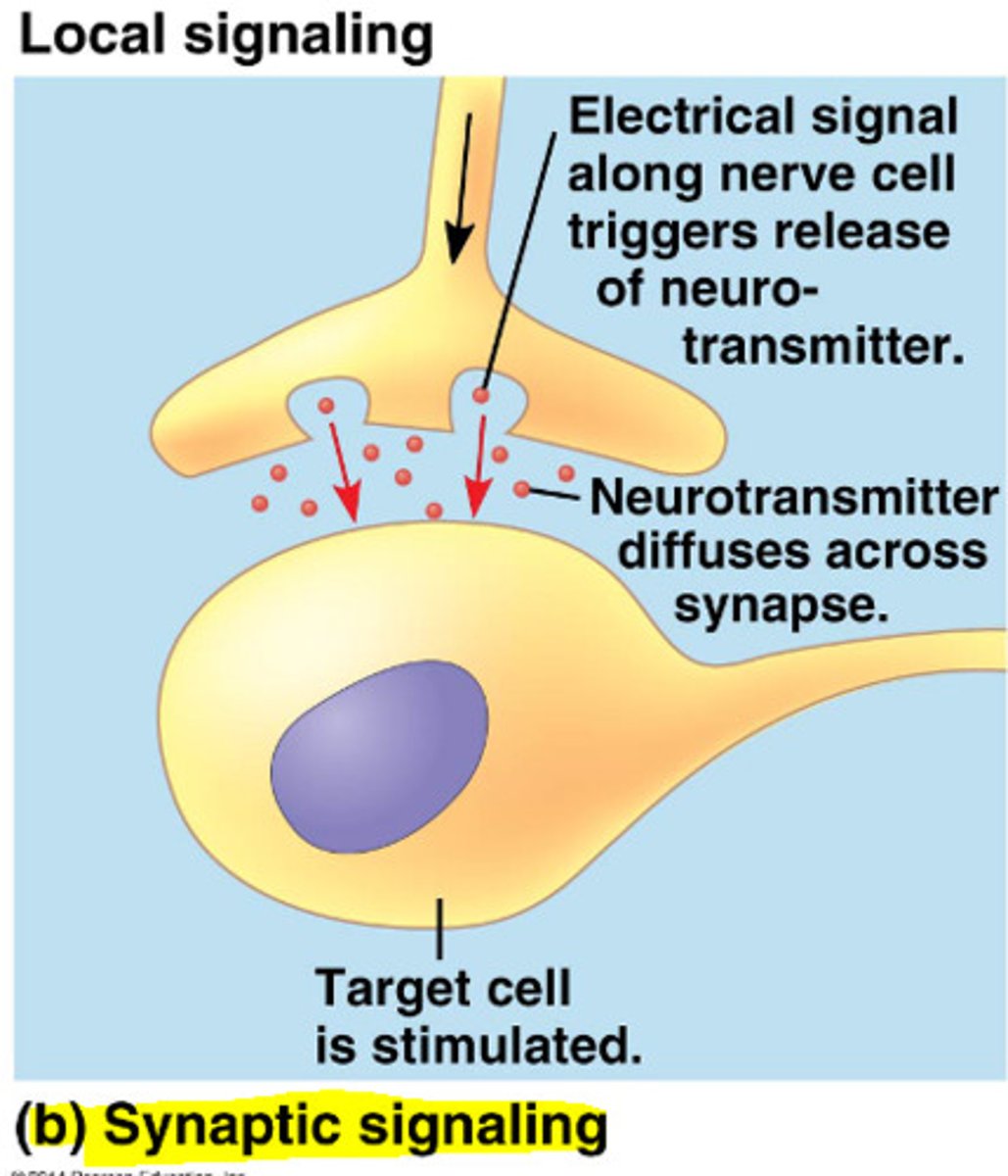
synaptic cell signaling
signal between nerve cells
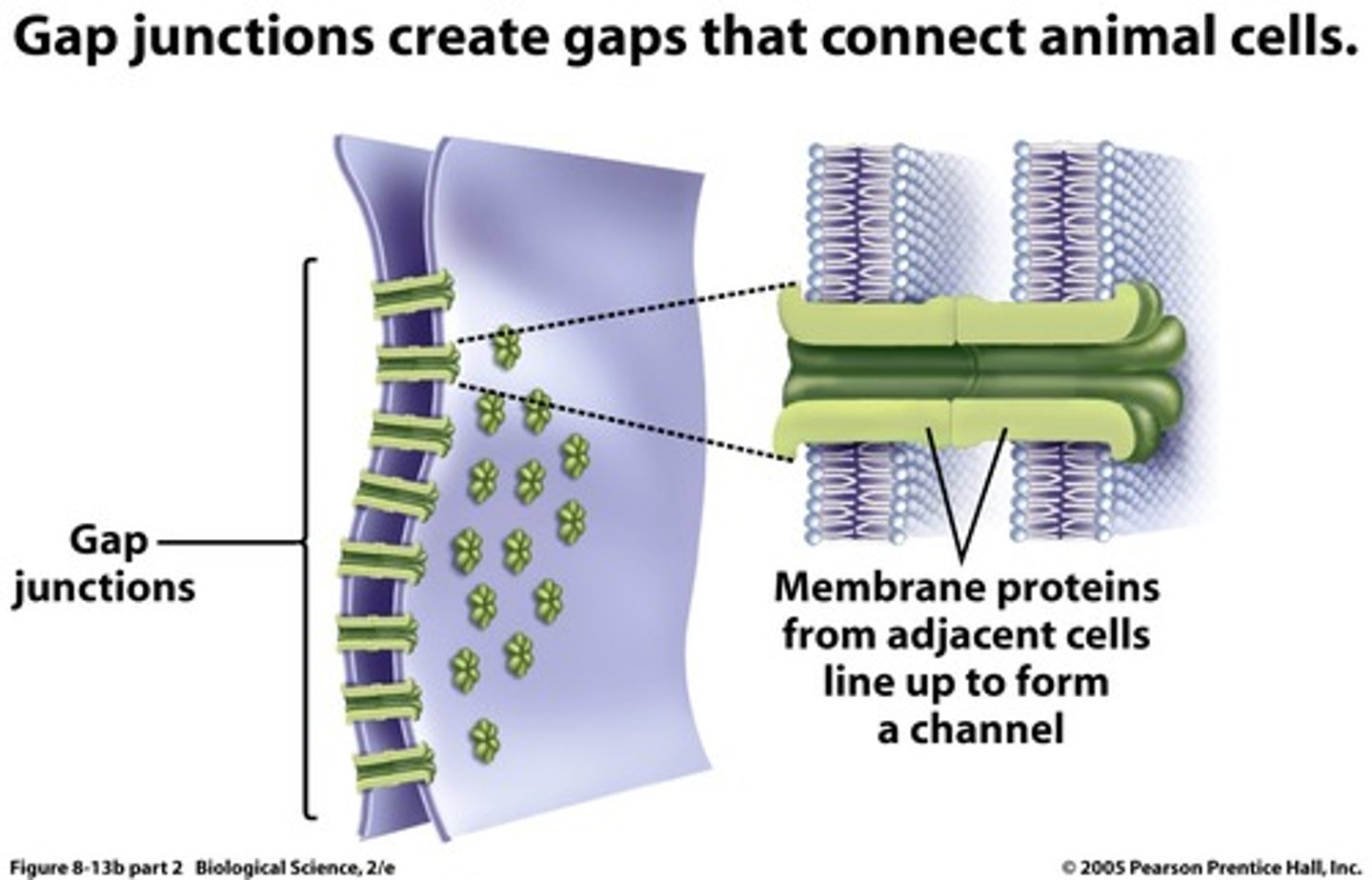
gap junctions
provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent animal cells
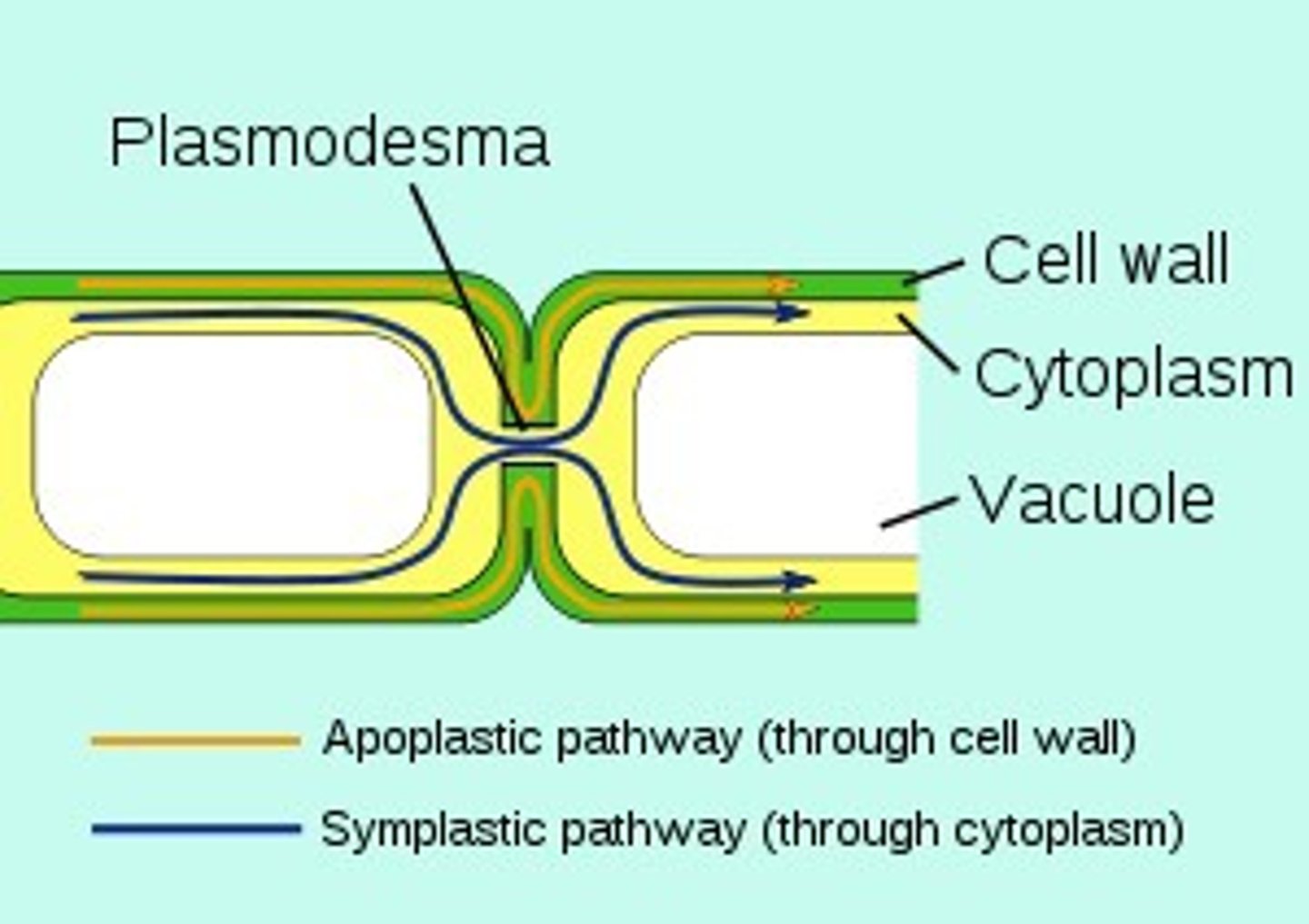
plasmodesmata
channels through cell walls that connect the cytoplasms of adjacent cells
growth factors
Regulatory proteins that ensure that the events of cell division occur in the proper sequence and at the correct rate.
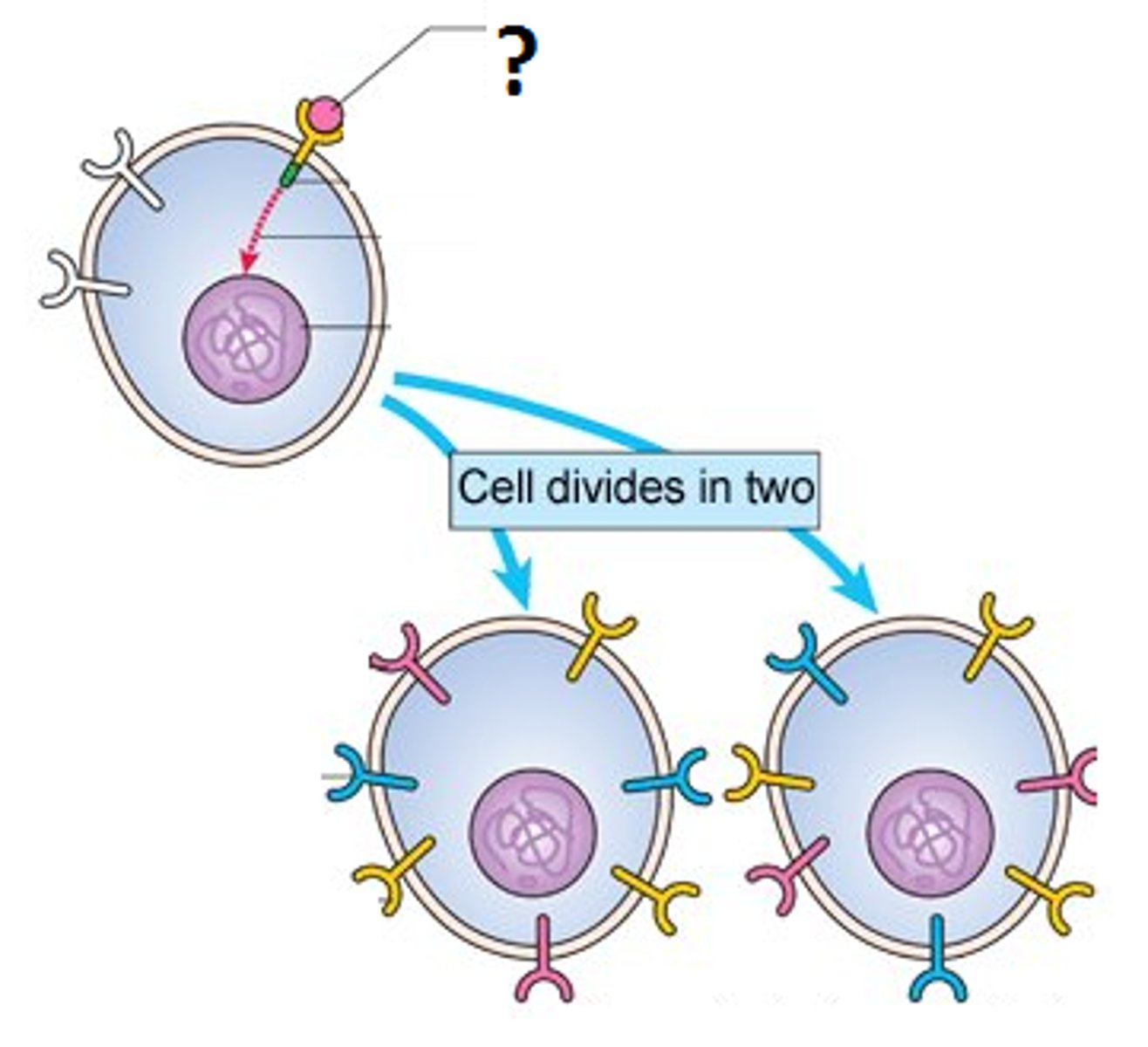
immune system
the system that differentiates self from non-self and protects the body from foreign substances and pathogenic organisms by producing an immune response

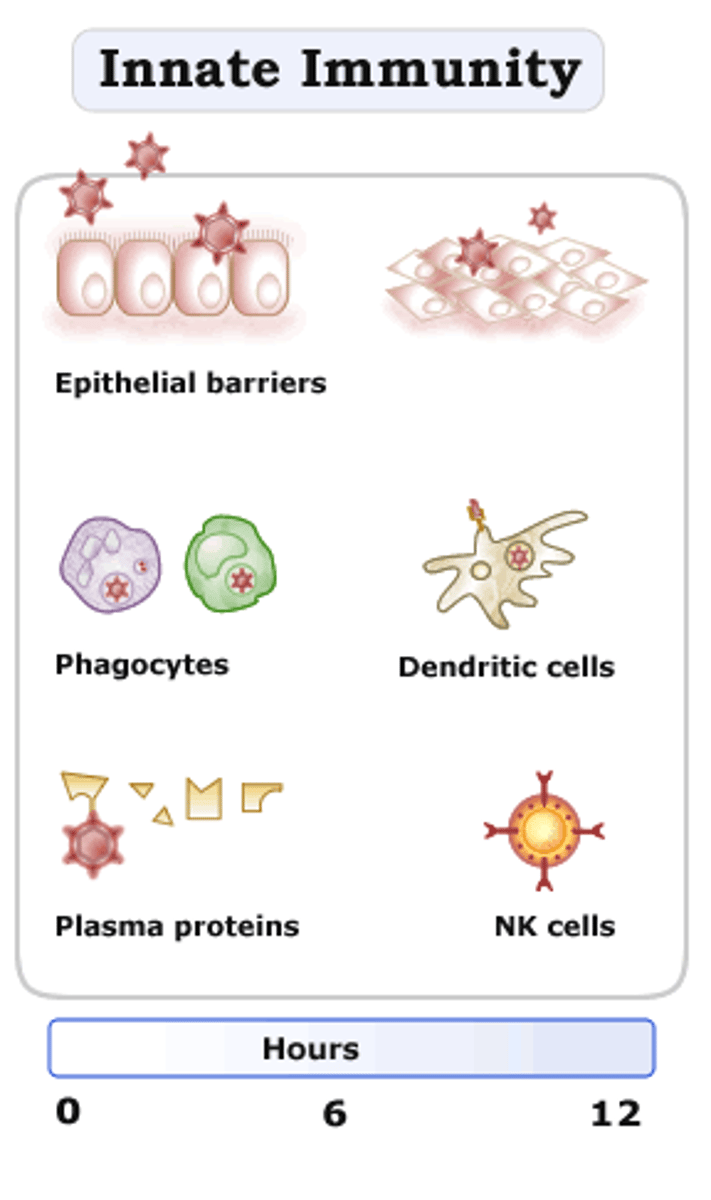
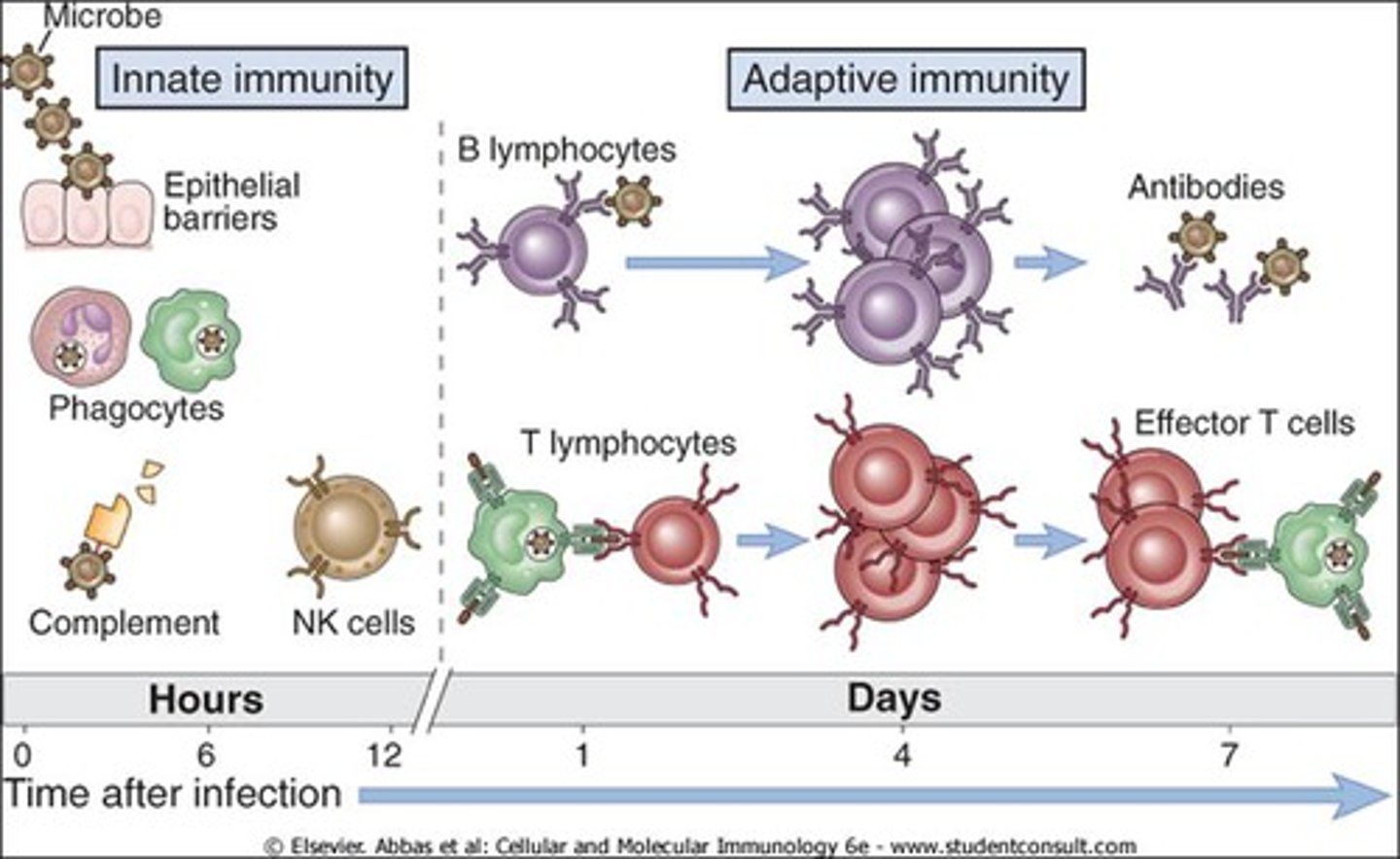
innate immune response
A quick, general immune response that all living things are born with.
adaptive immune response
Cells have 'memory' about previously encountered pathogens and is able to attack based on this memory
pathogen
any organism that can cause disease
lymphocyte
A type of white blood cell that make antibodies to fight off infections
T cell
a lymphocyte that can recognize specific antigens and can activate or deactivate other immune cells
natural killer (NK) cells
can kill cancer cells before the immune system is activated
complement system
proteins in the blood that help antibodies and T cells kill their target
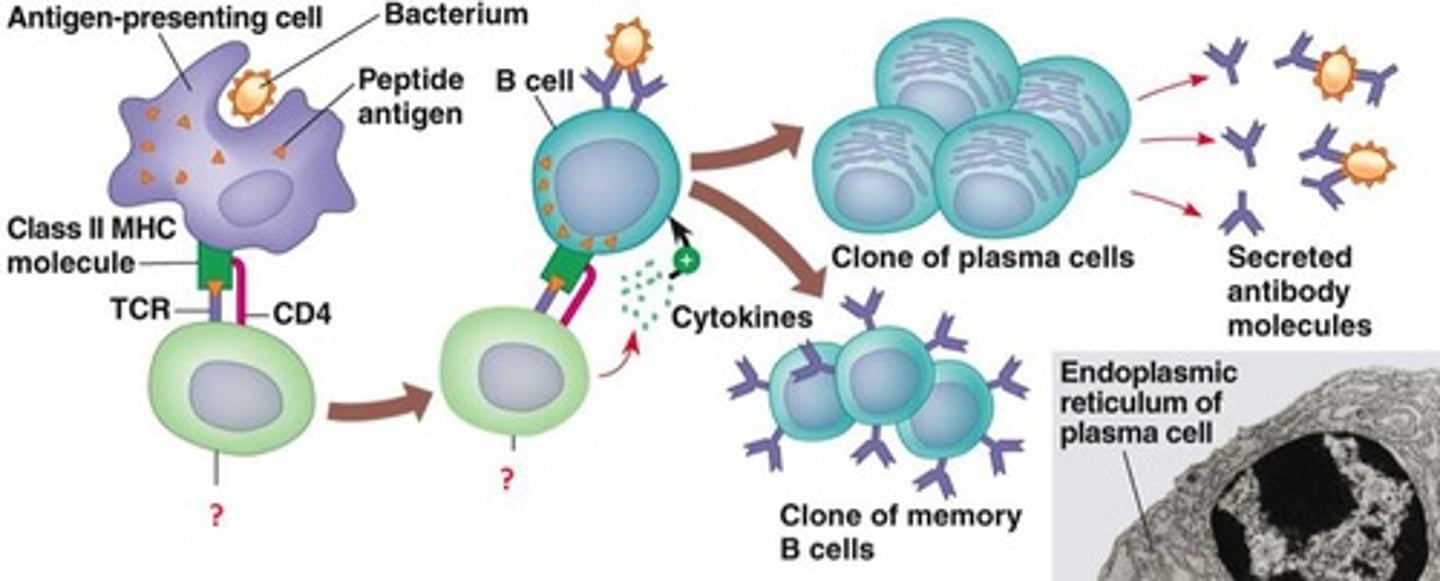
B cells
Cells manufactured in the bone marrow that create antibodies for isolating and destroying invading bacteria and viruses.
antigen
substance that triggers an immune response
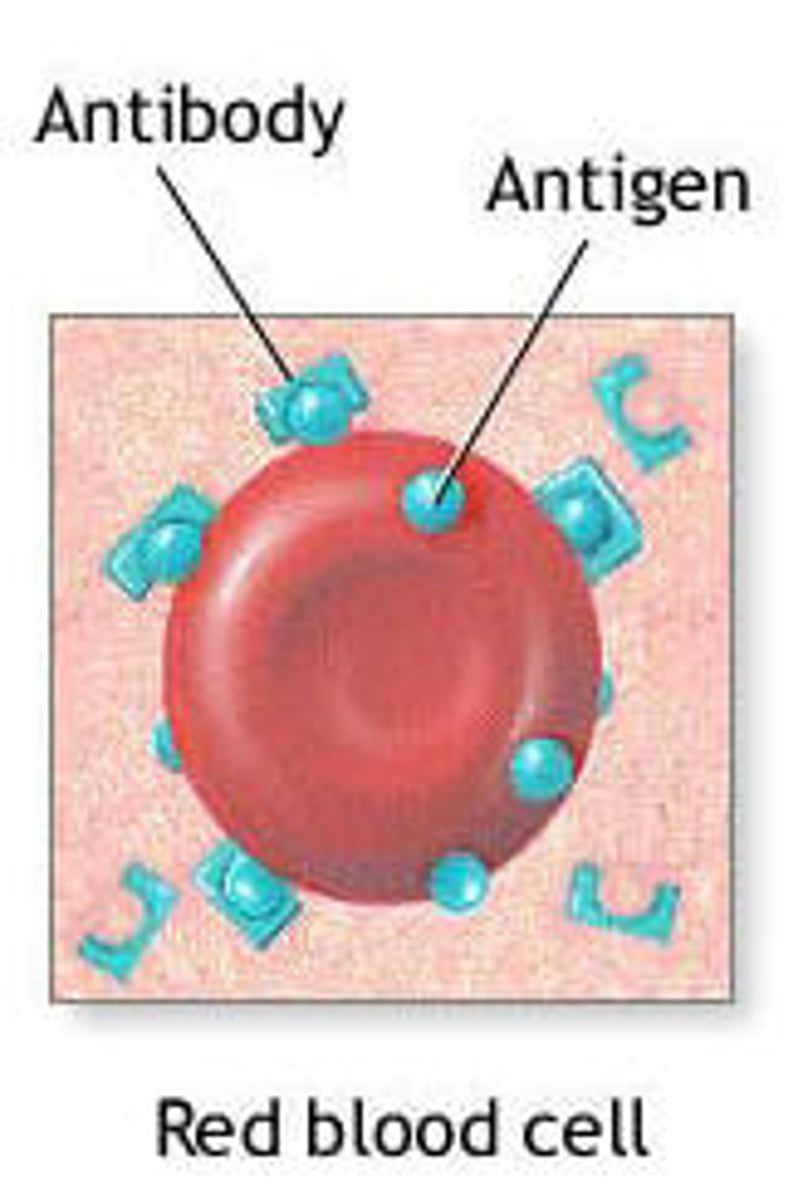
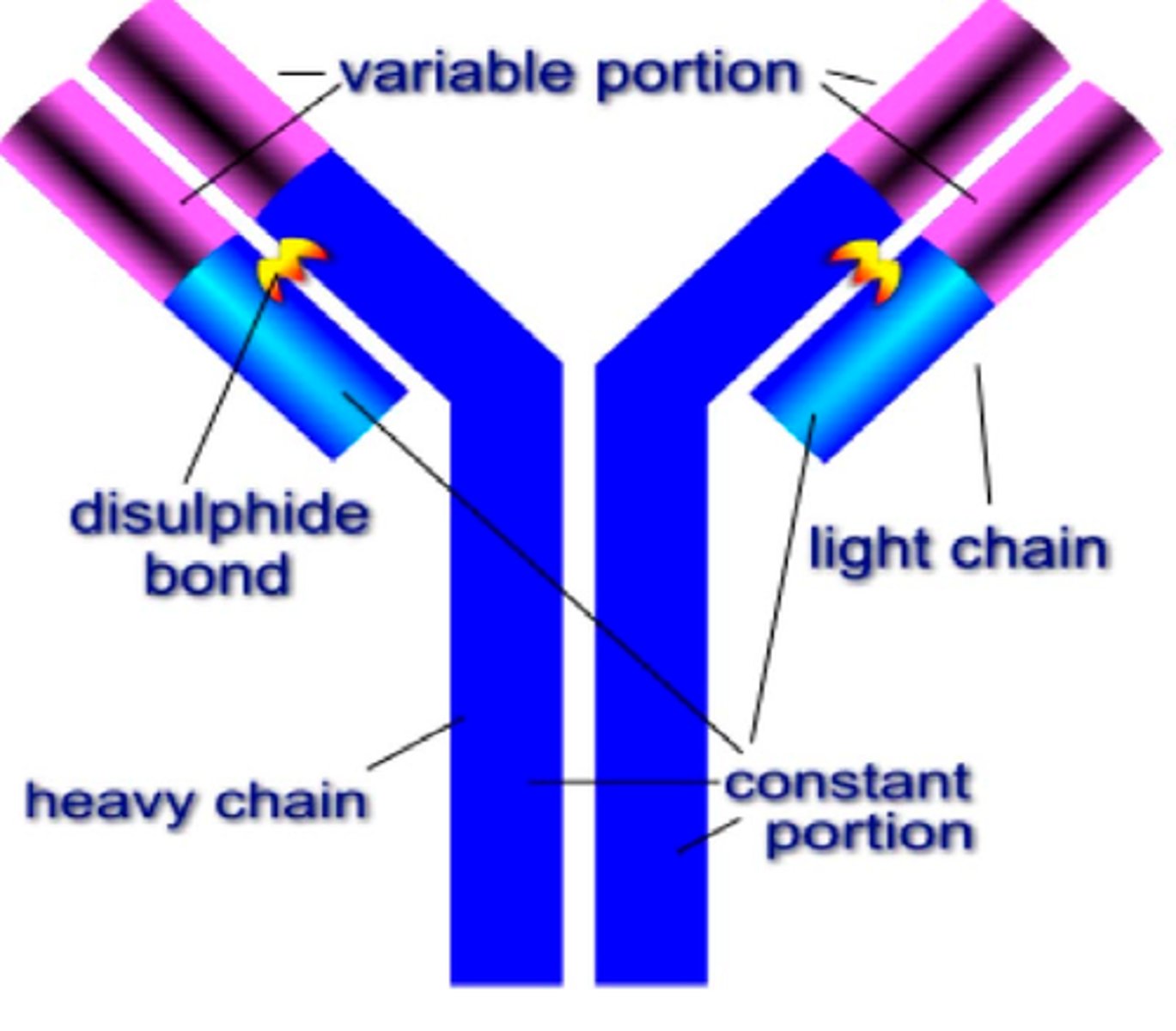
antibodies
Specialized proteins that aid in destroying infectious agents
cell-mediated immunity
type of immunity produced by Tc cells that attack infected or abnormal body cells
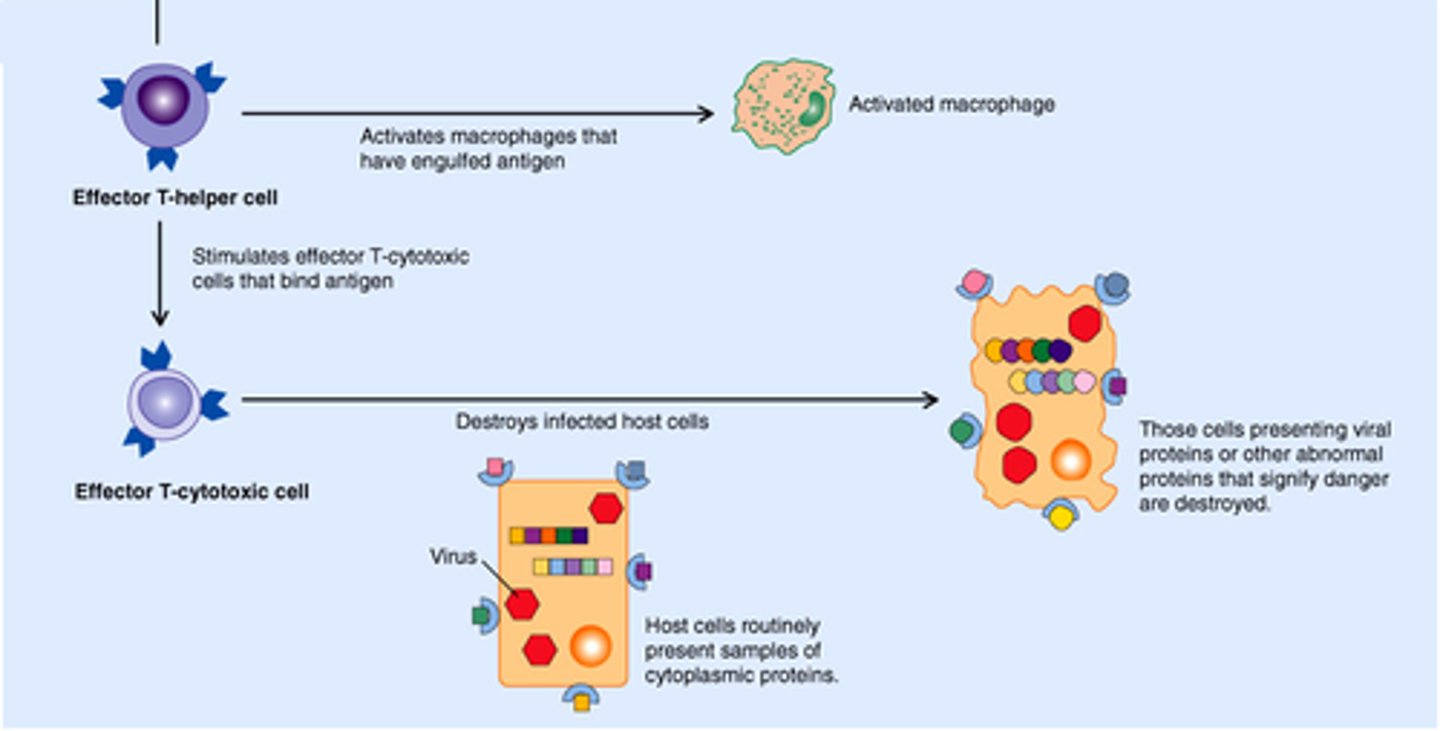
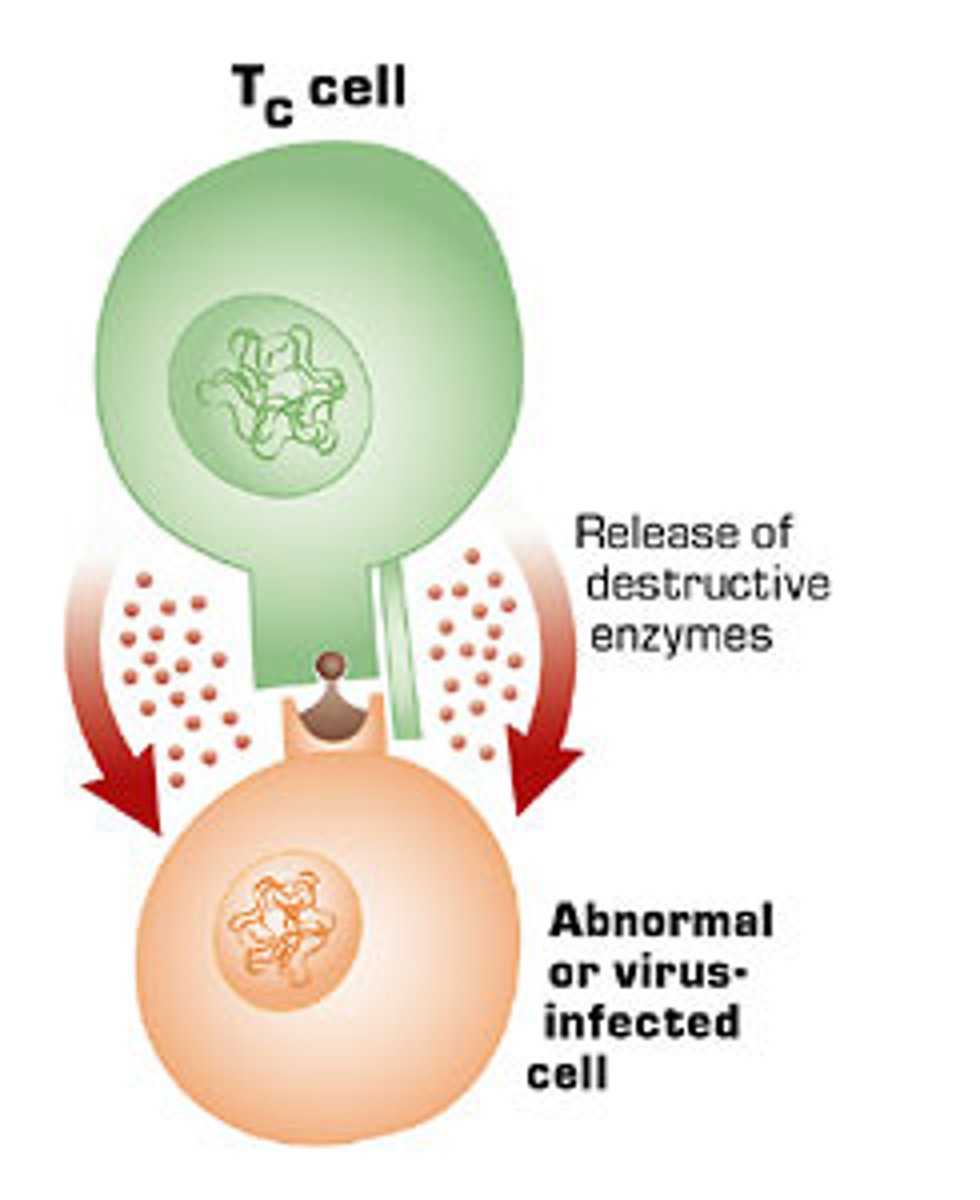
cytotoxic T cell (Tc)
a differentiated T lymphocyte that is responsible for the destruction of infected or abnormal cells
helper T cell (Th)
recognizes presented antigens and secretes cytokines
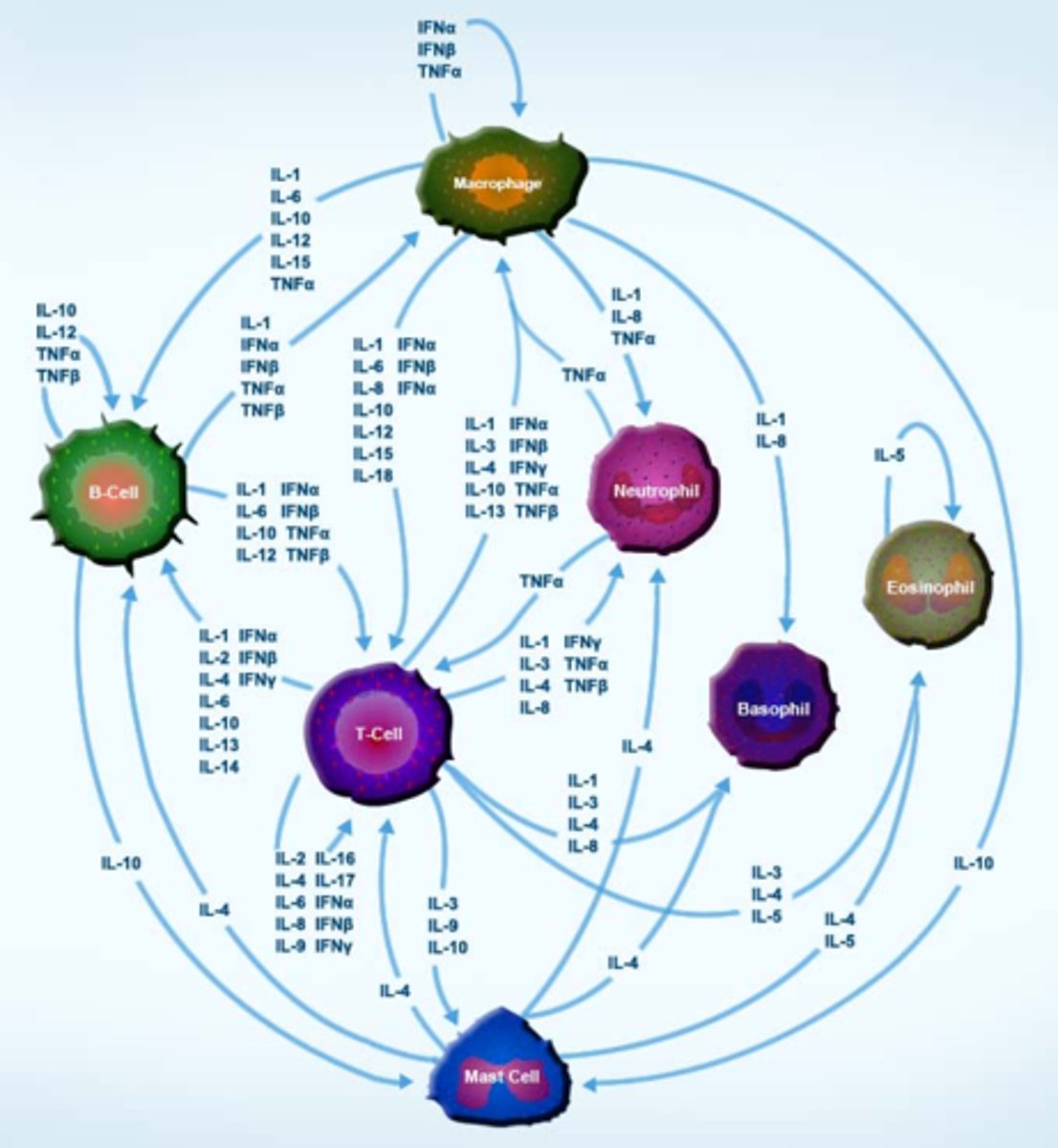
cytokine
chemical substance produced by certain cells that initiates, inhibits, increases, or decreases activity in other cells
lymphatic system
houses large populations of immune cells which are released upon detection of a pathogen
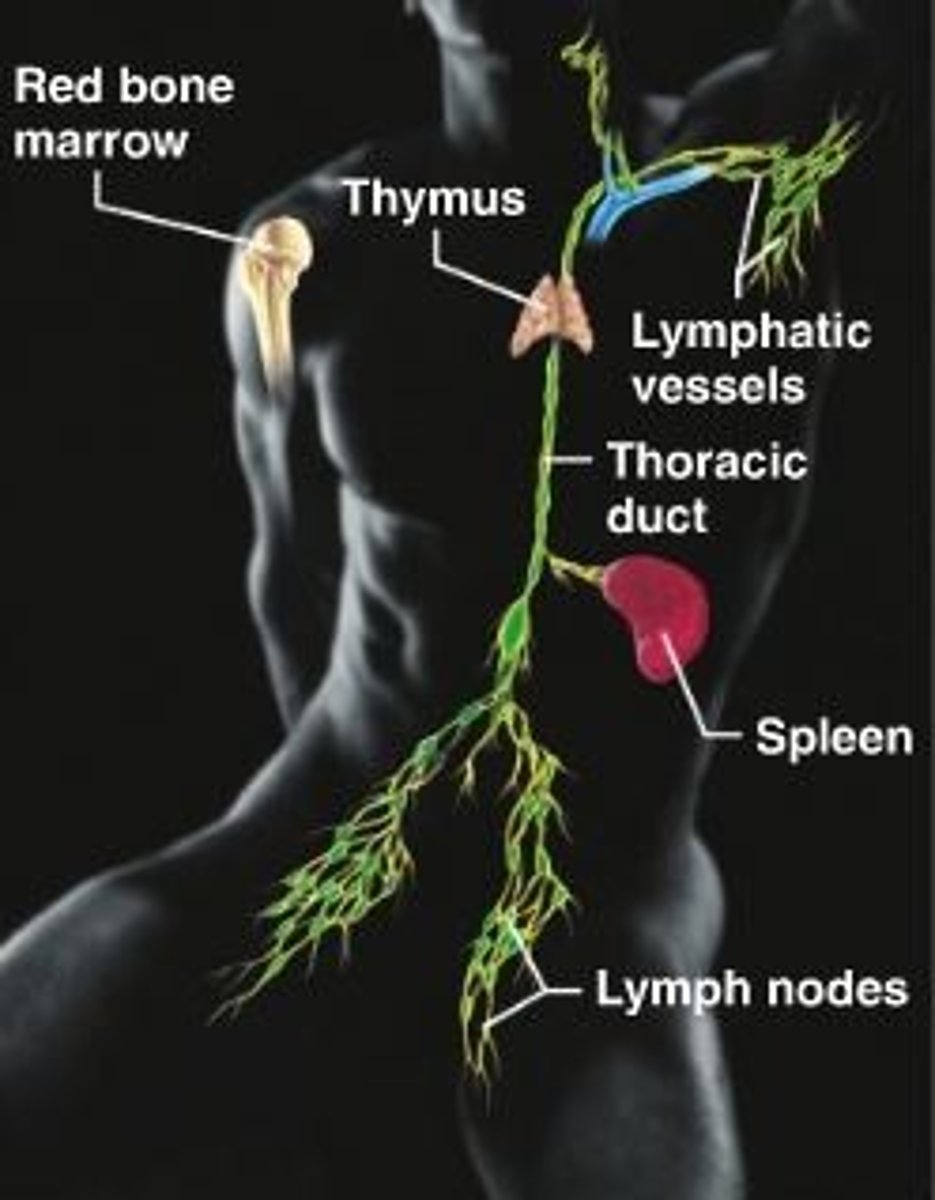
lymph nodes
Bean-shaped filters that cluster along the lymphatic vessels of the body. They function as a cleanser of lymph as wells as a site of T and B cell activation
spleen
Organ near the stomach that produces, stores, and eliminates blood cells
vaccination
injection of a weakened or mild form of a pathogen to produce immunity
effector cell
a plasma B cell or cytotoxic T cell, which are the main types of cells responsible for humoral and cellular immune responses, respectively
binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction in single-celled organisms by which one cell divides into two cells of the same size
budding
A form of asexual reproduction of yeast in which a new cell grows out of the body of a parent.
sprouting
the growth of additional branches on axons or dendrites to enable new connections
parthenogenesis
Asexual reproduction in which females produce offspring from unfertilized eggs.

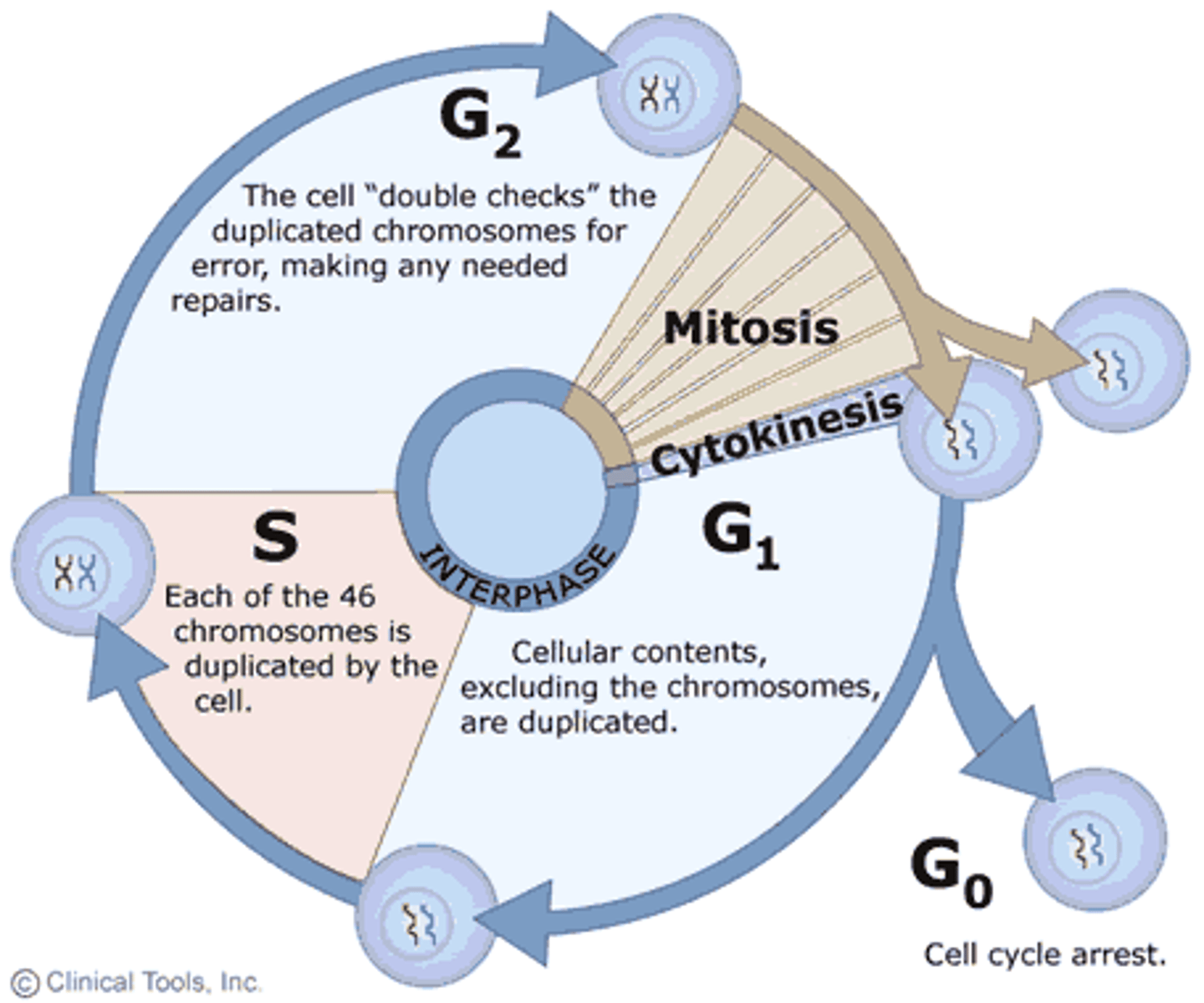
cell life cycle
series of changes a cell goes through from the time it is formed until it divides
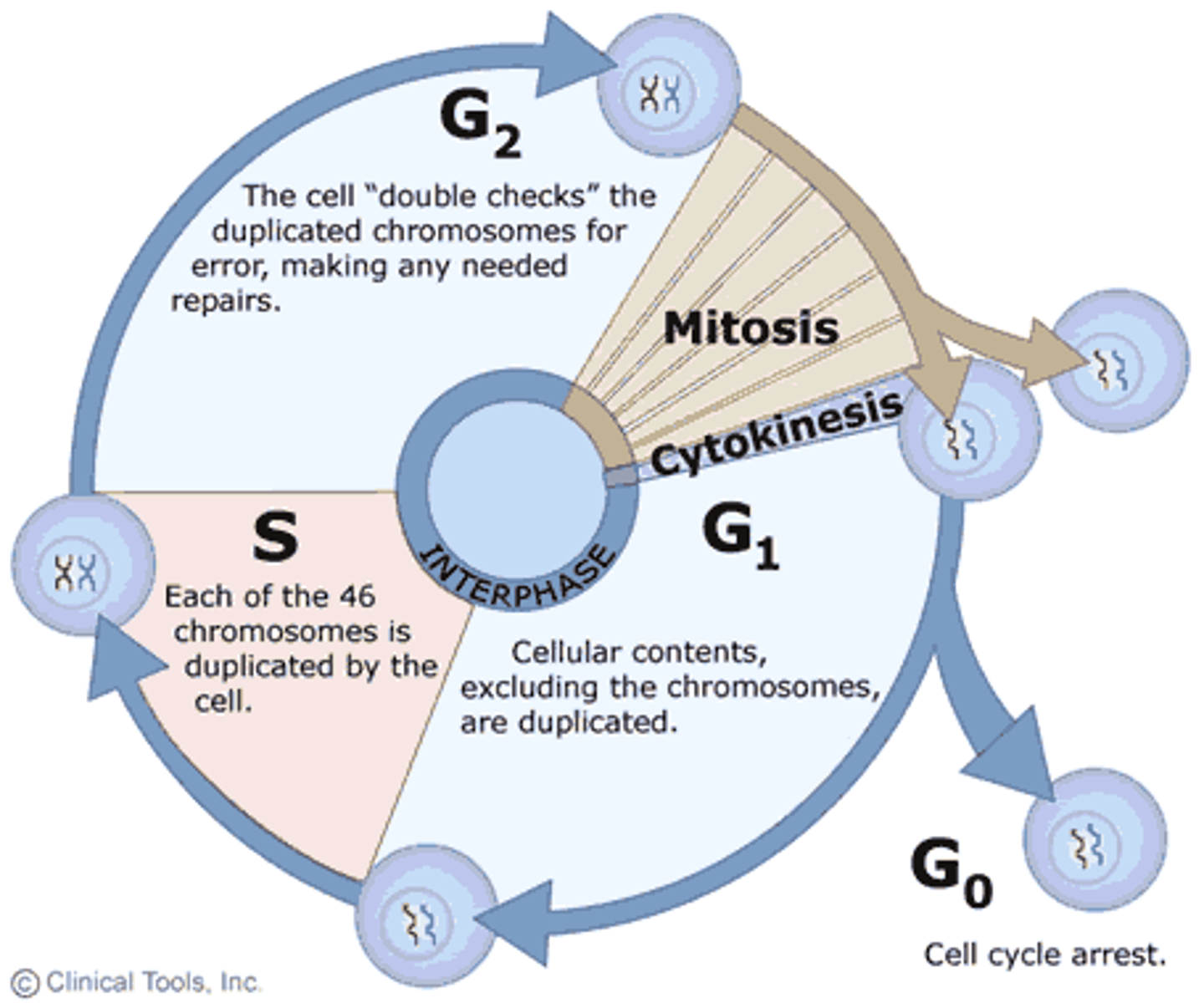
cell life cycle order
interphase --> mitosis --> cytokinesis
mitosis order
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
interphase order
G1, G0, S, G2
interphase
period of the cell cycle between cell divisions
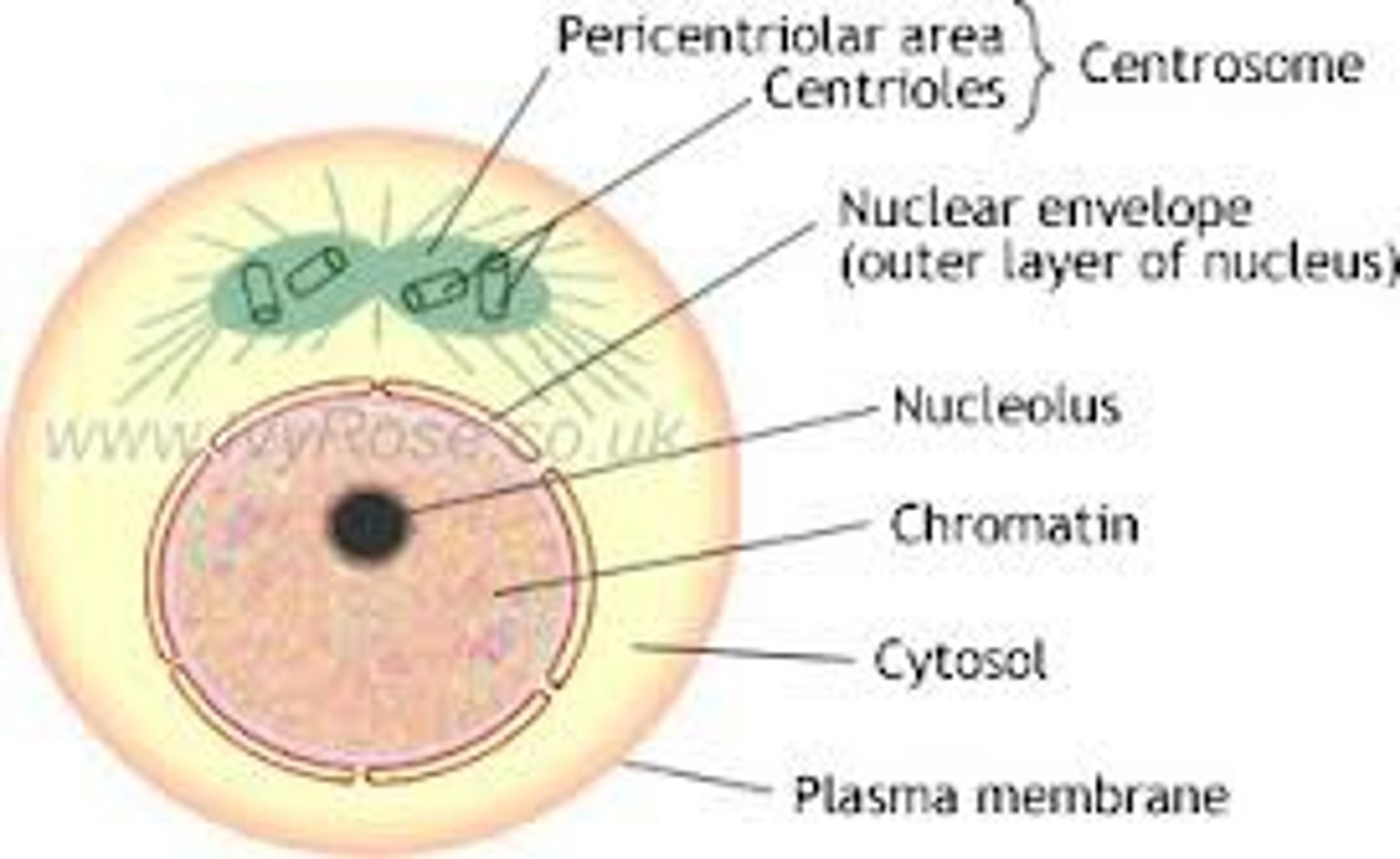
G1
Cell growth
G0
A nondividing state occupied by cells that have left the cell cycle, sometimes reversibly.
S
DNA replication
G2
preparation for mitosis
mitosis
part of eukaryotic cell division during which the cell nucleus divides
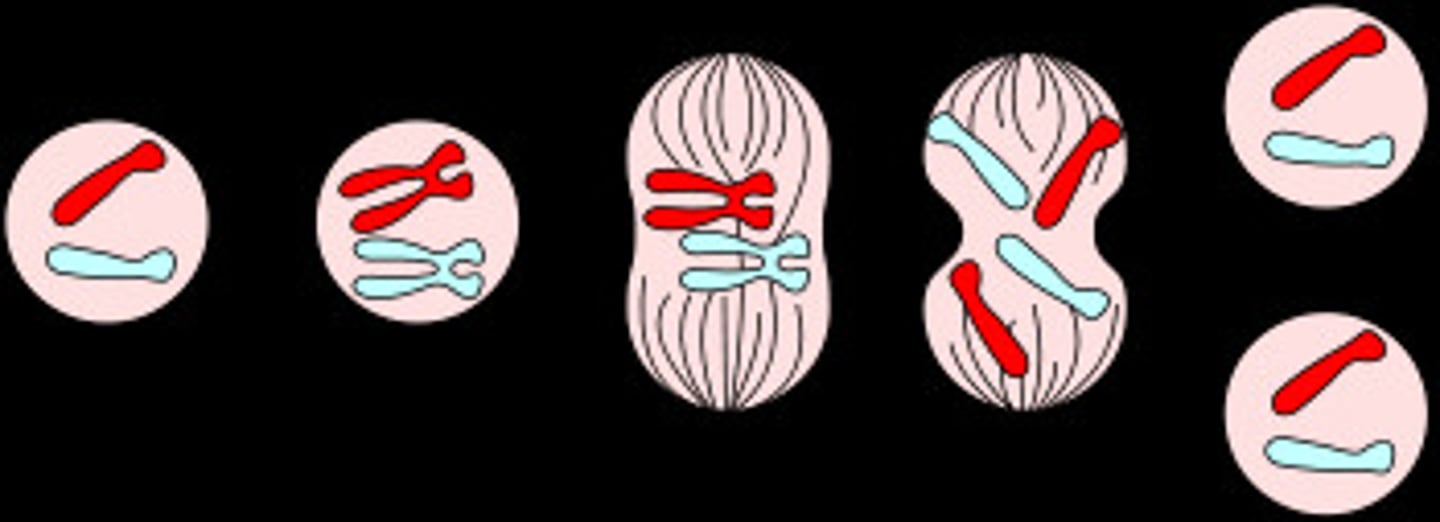
prophase
first and longest phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes become visible and the centrioles separate and take up positions on the opposite sides of the nucleus

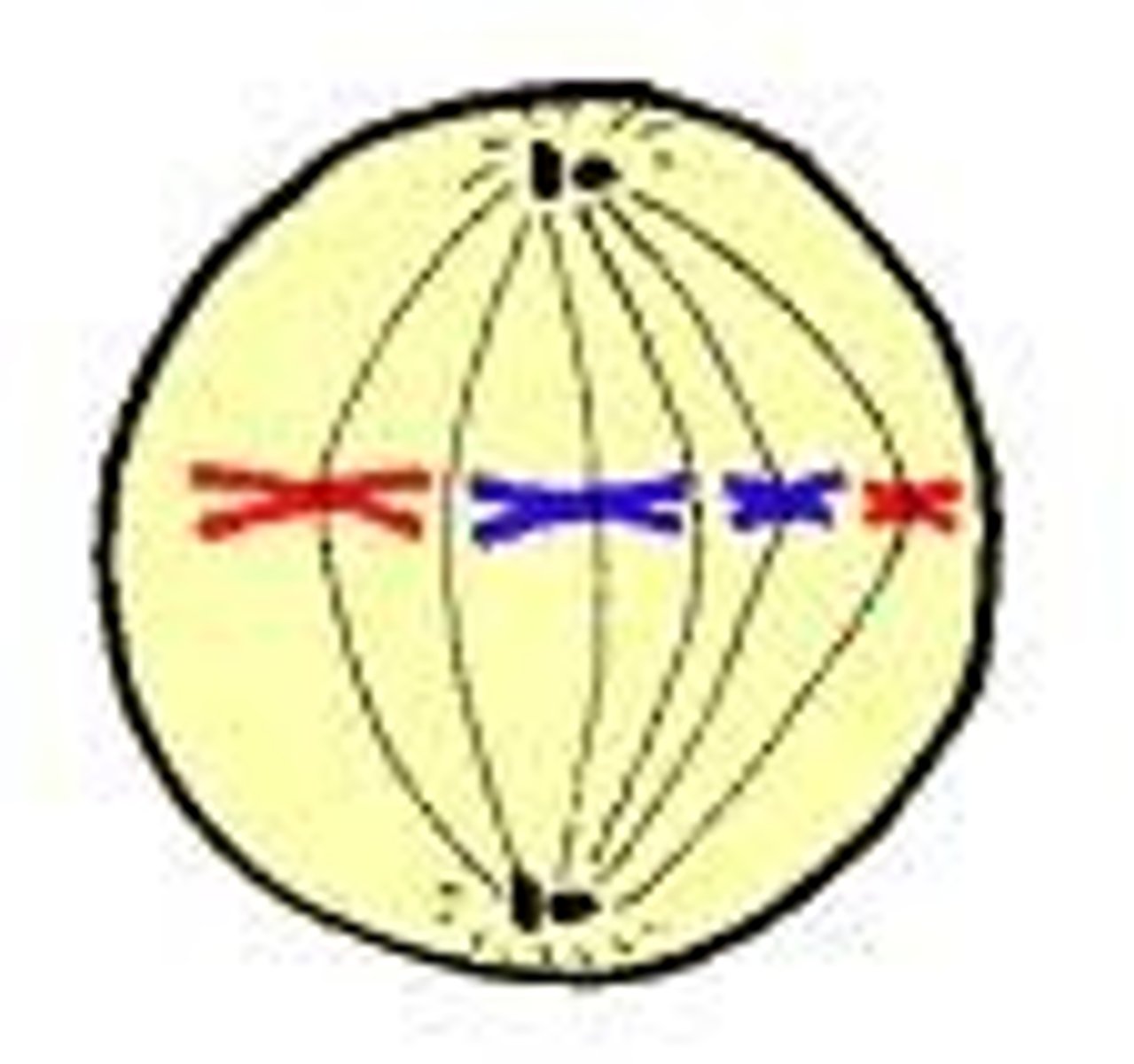
metaphase
second phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
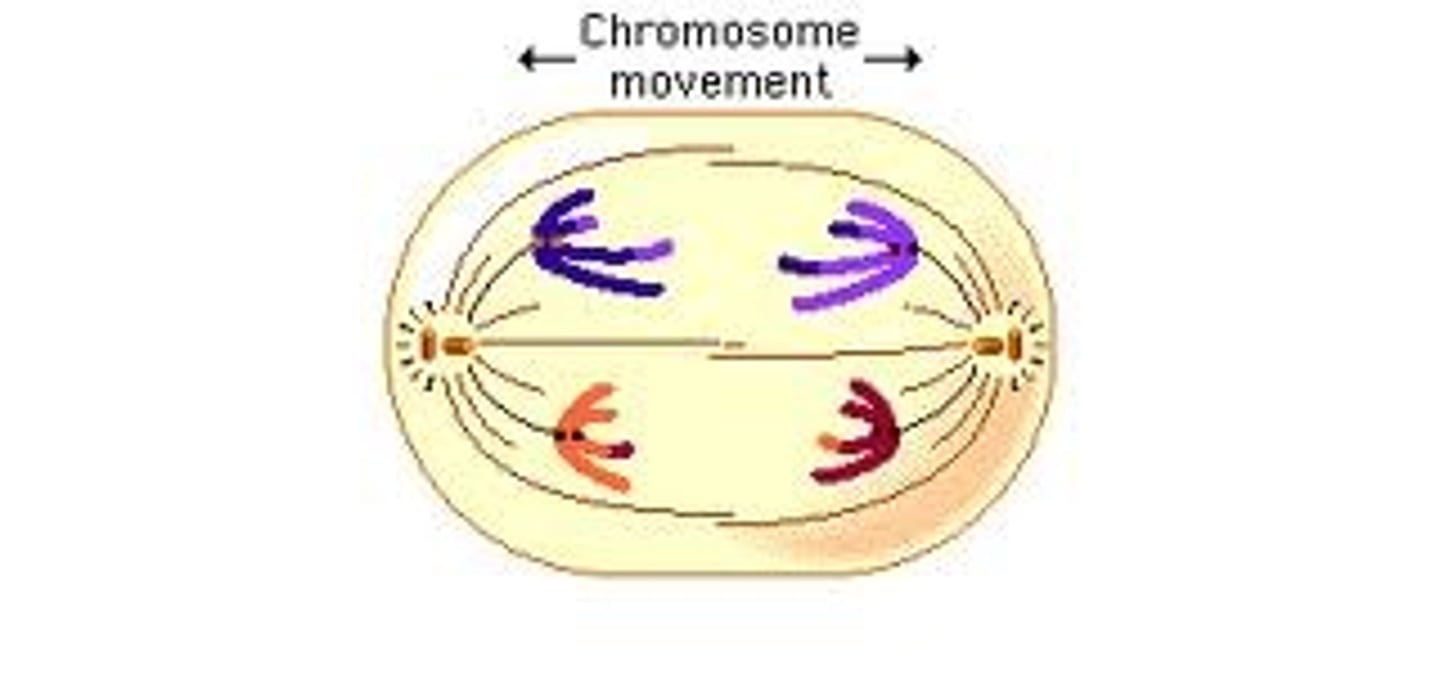
anaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
telophase
After the chromosome separates, the cell seals off, Final Phase of Mitosis.
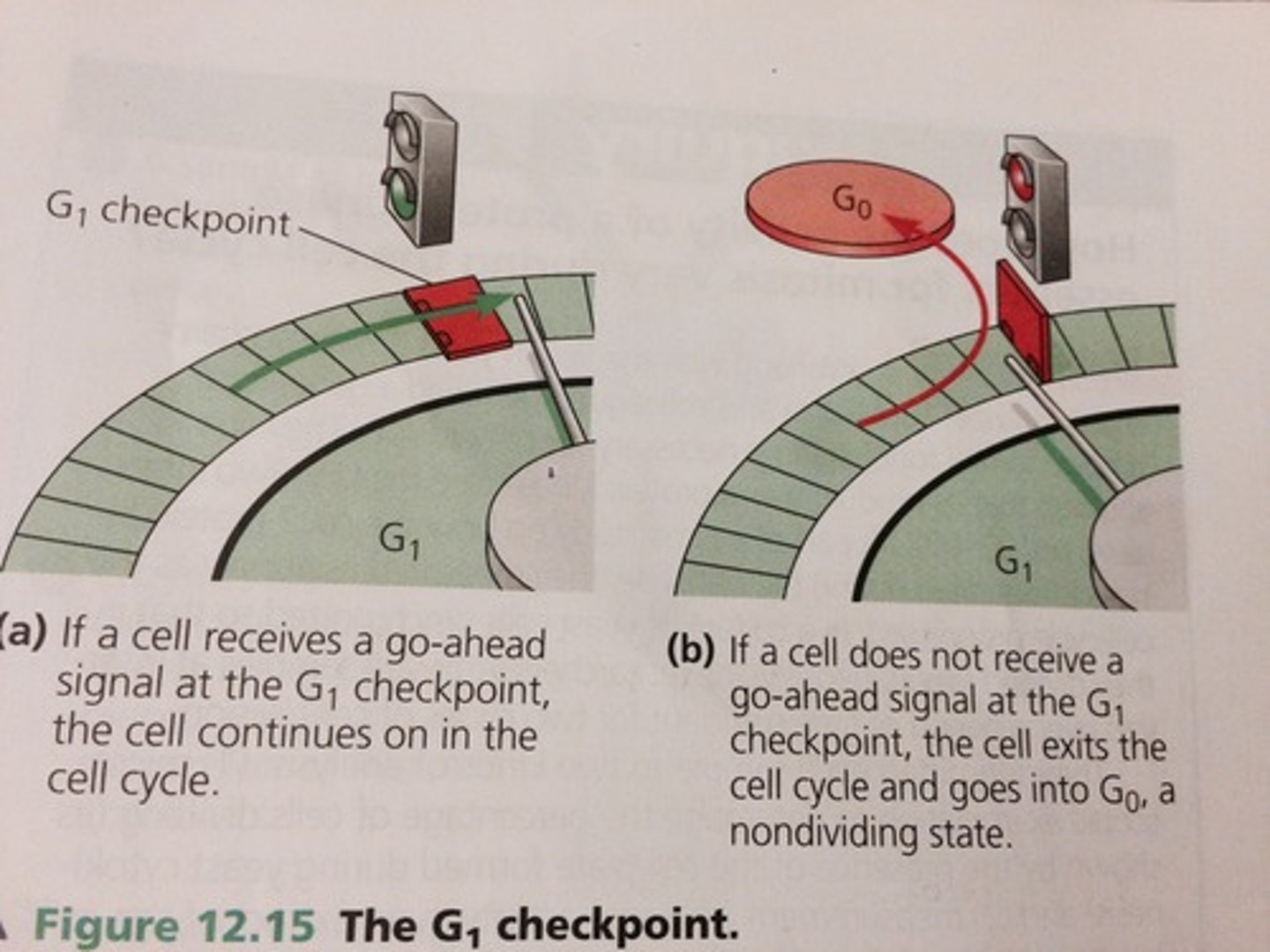
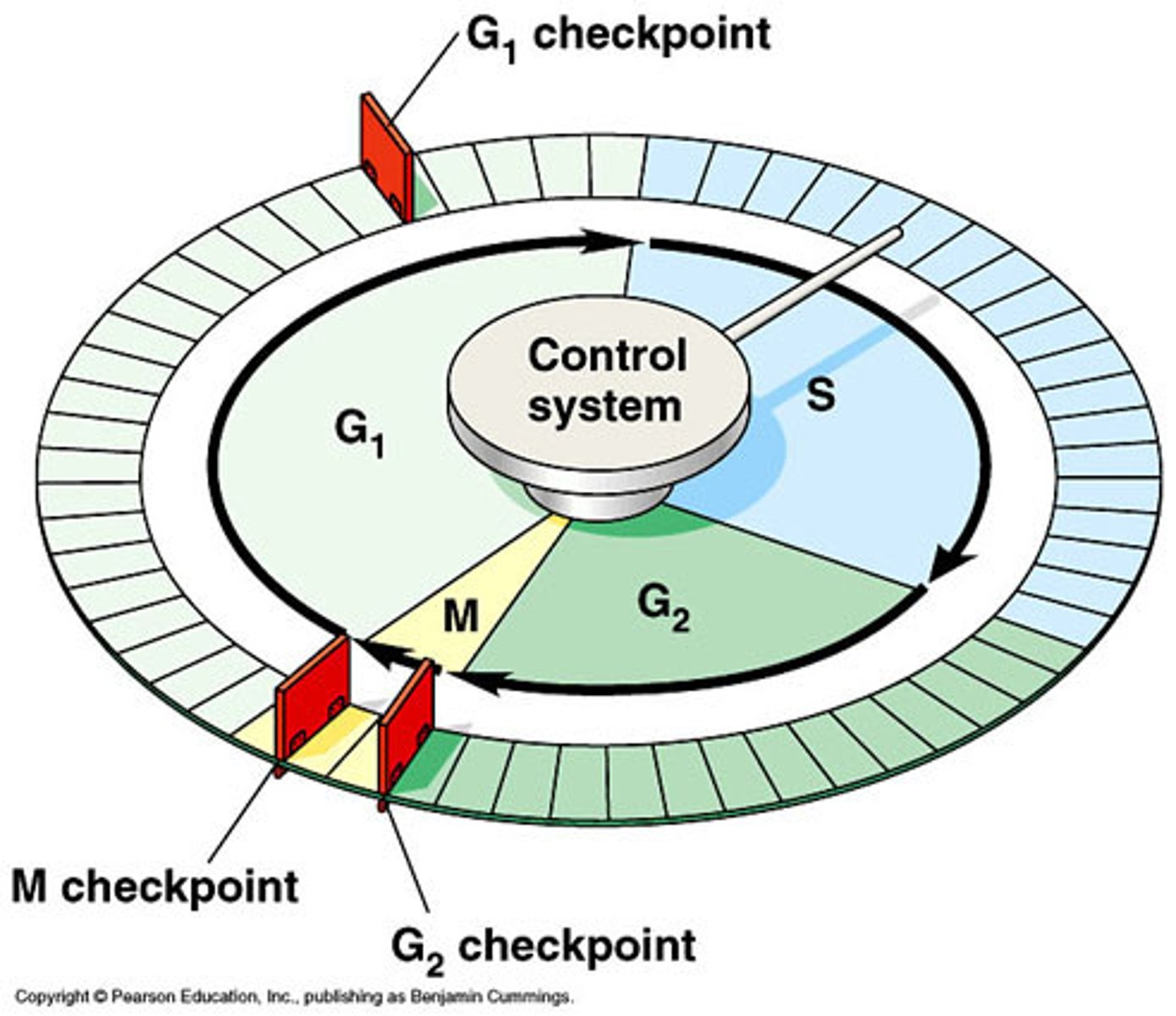
G1 checkpoint
checks for cell size, nutrients, growth factors and DNA damage
G2 checkpoint
The cell checks to make sure the DNA is copied correctly, cell size
M checkpoint
cell monitors spindle formation and attachment to kinetochores
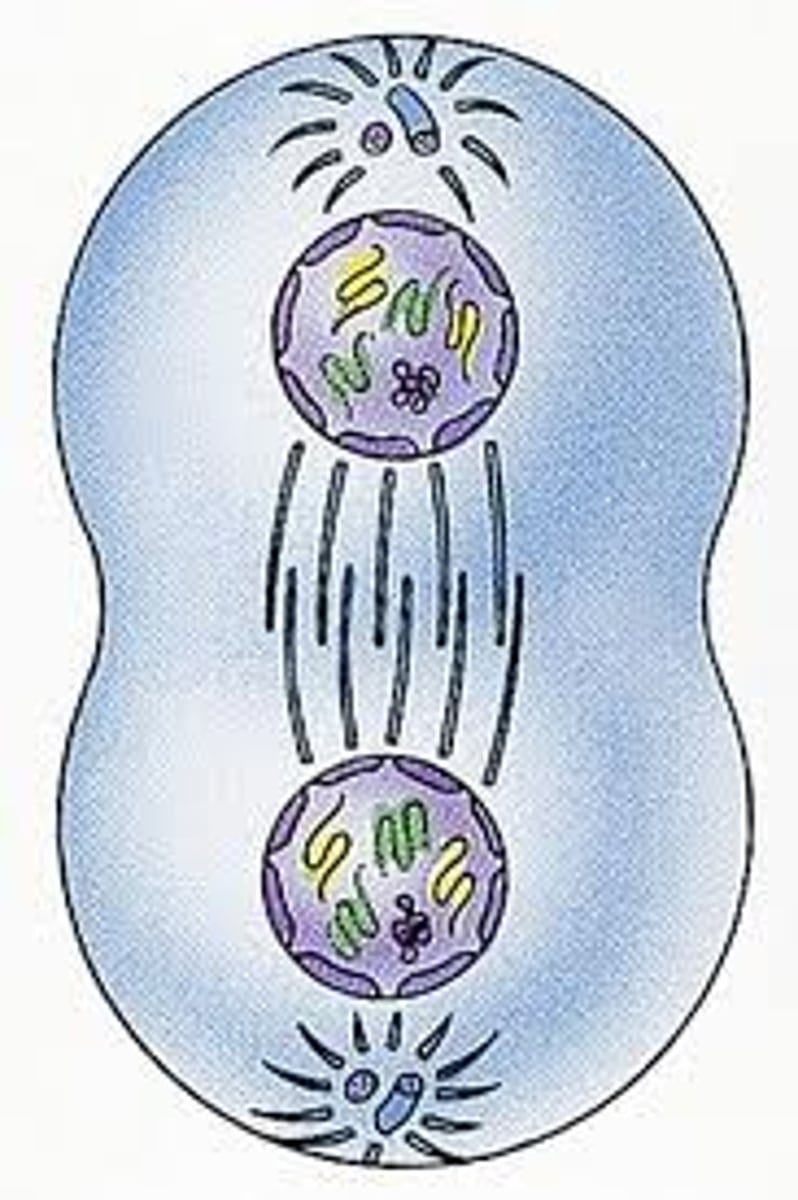
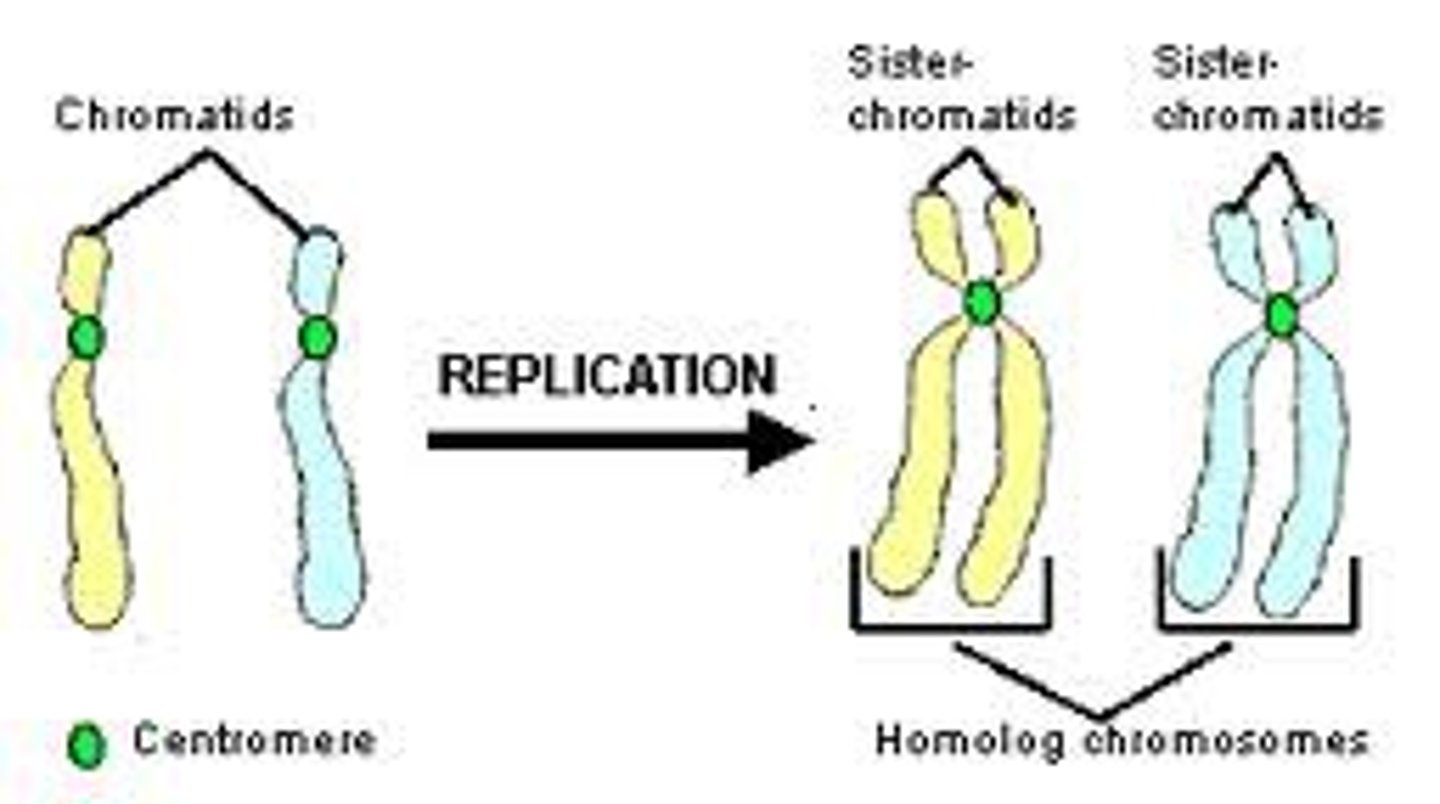
chromatids
two identical chromosomes that split and contain the same genetic material
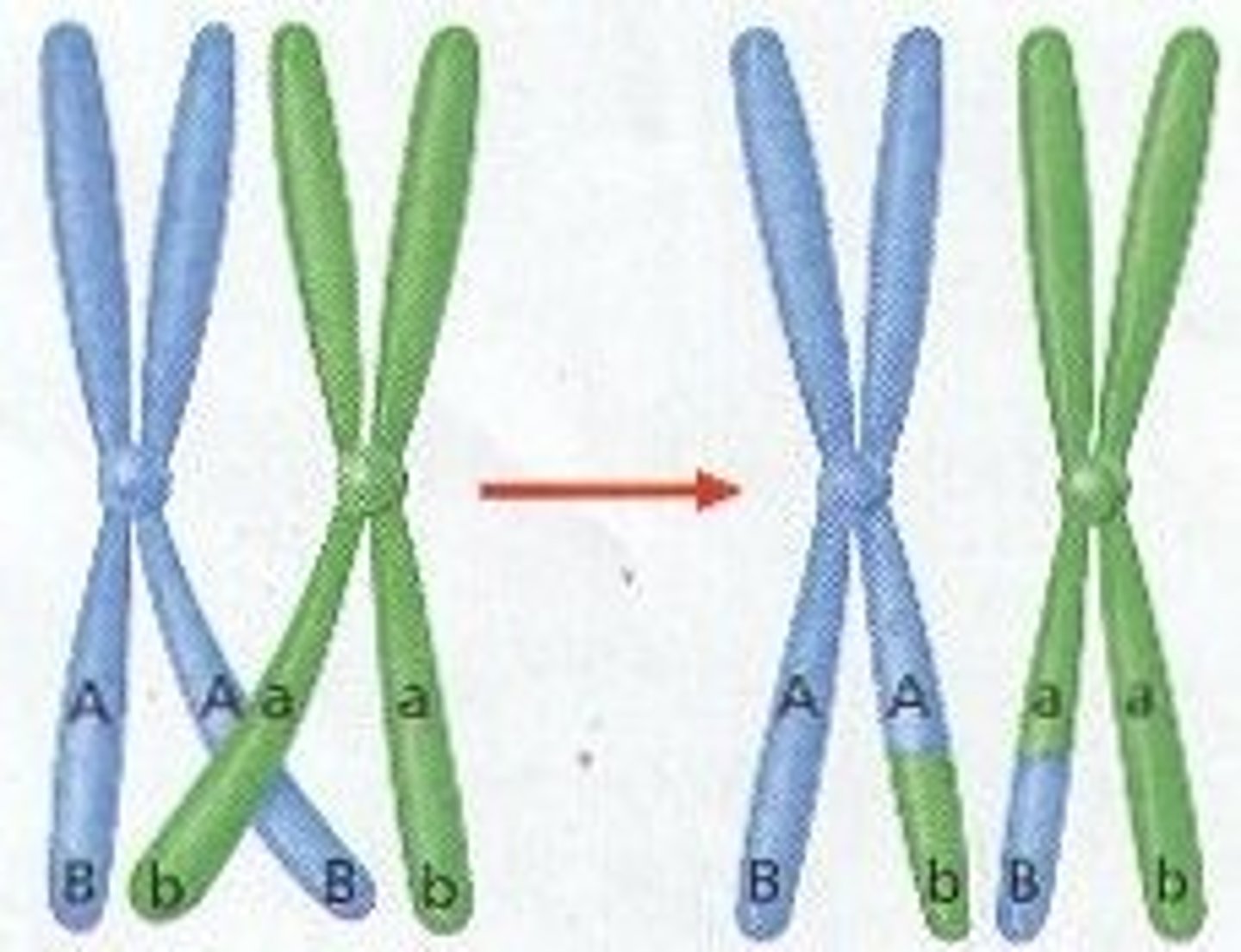
crossing over
Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis.
meiosis
Cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms
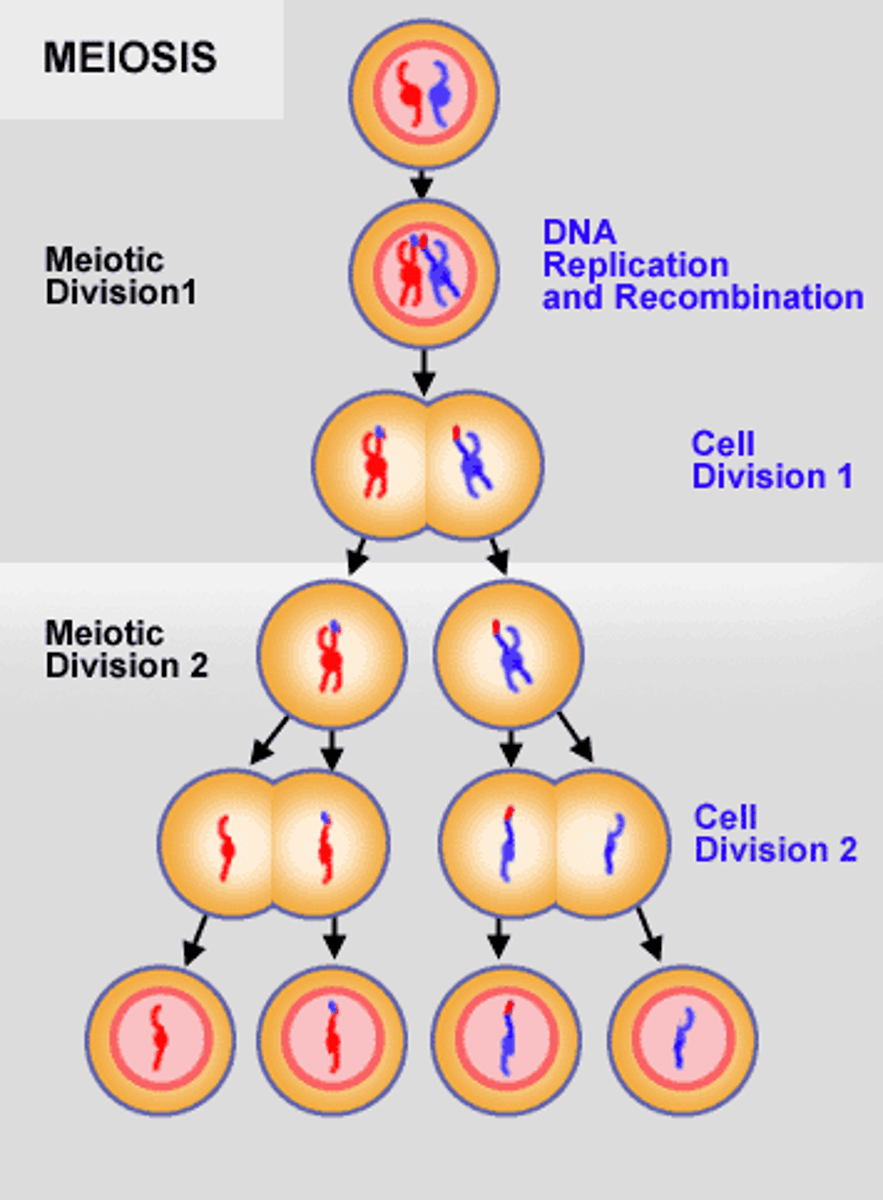
meiosis I
The first division of a two-stage process of cell division in sexually reproducing organisms that results in cells with half the number of chromosome sets as the original cell.
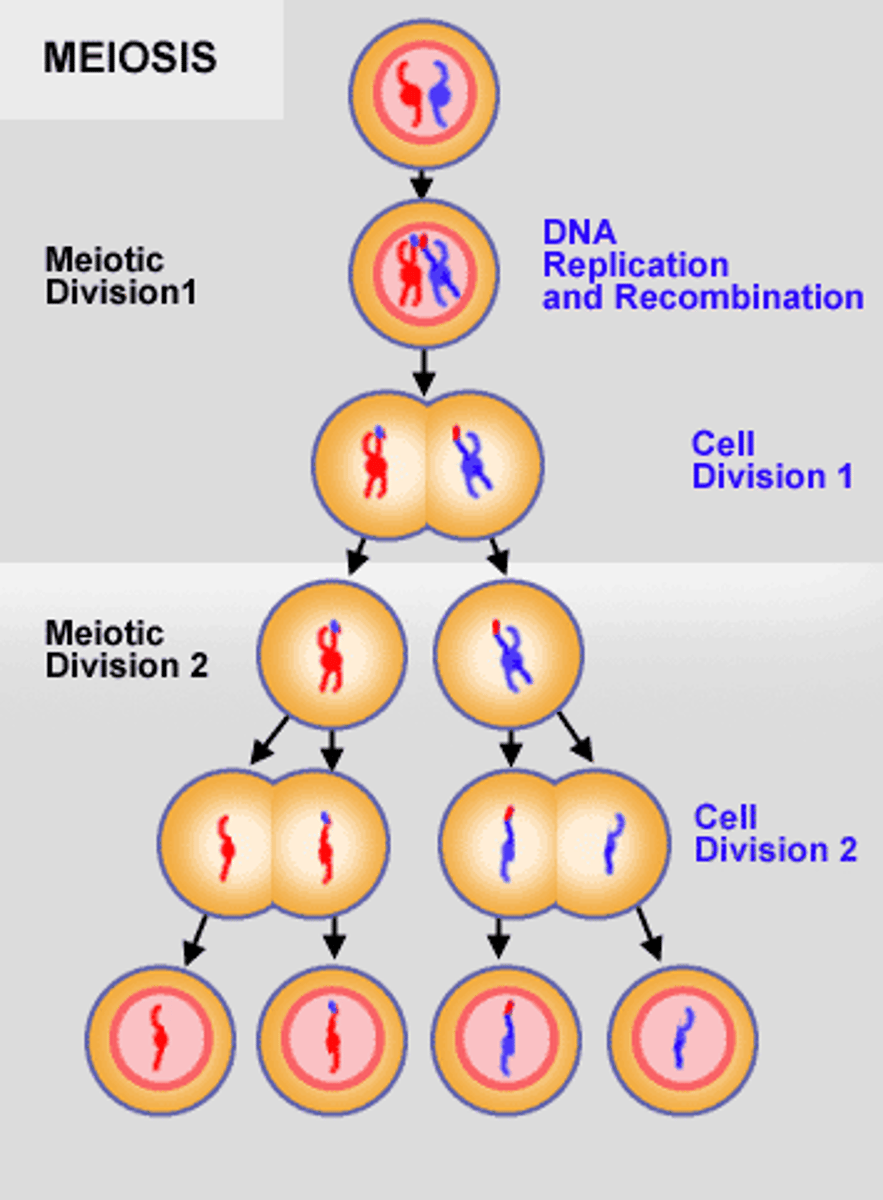
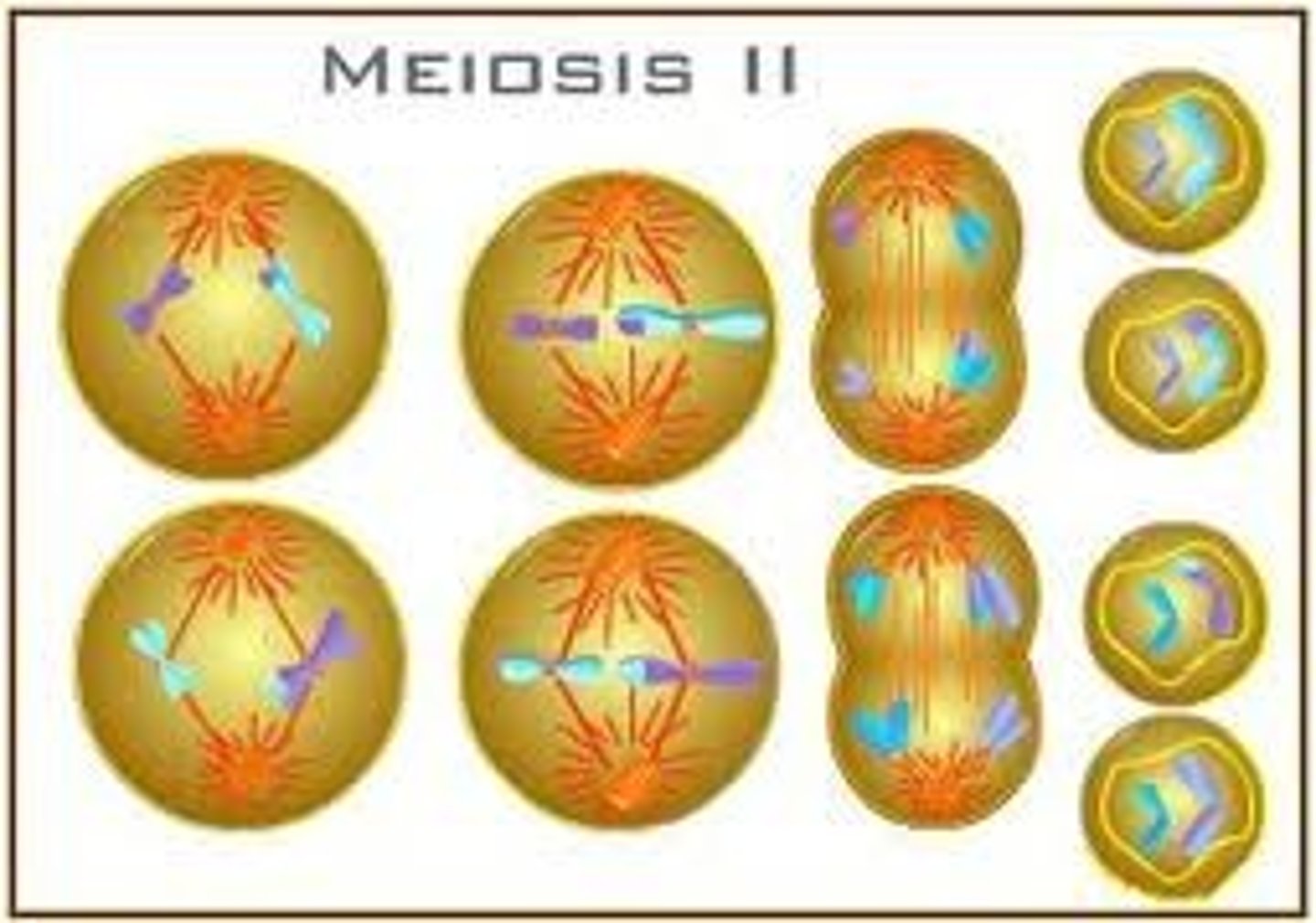
meiosis II
the second phase of meiosis consisting of chromatids separating, along with the two diploid cells splitting in two
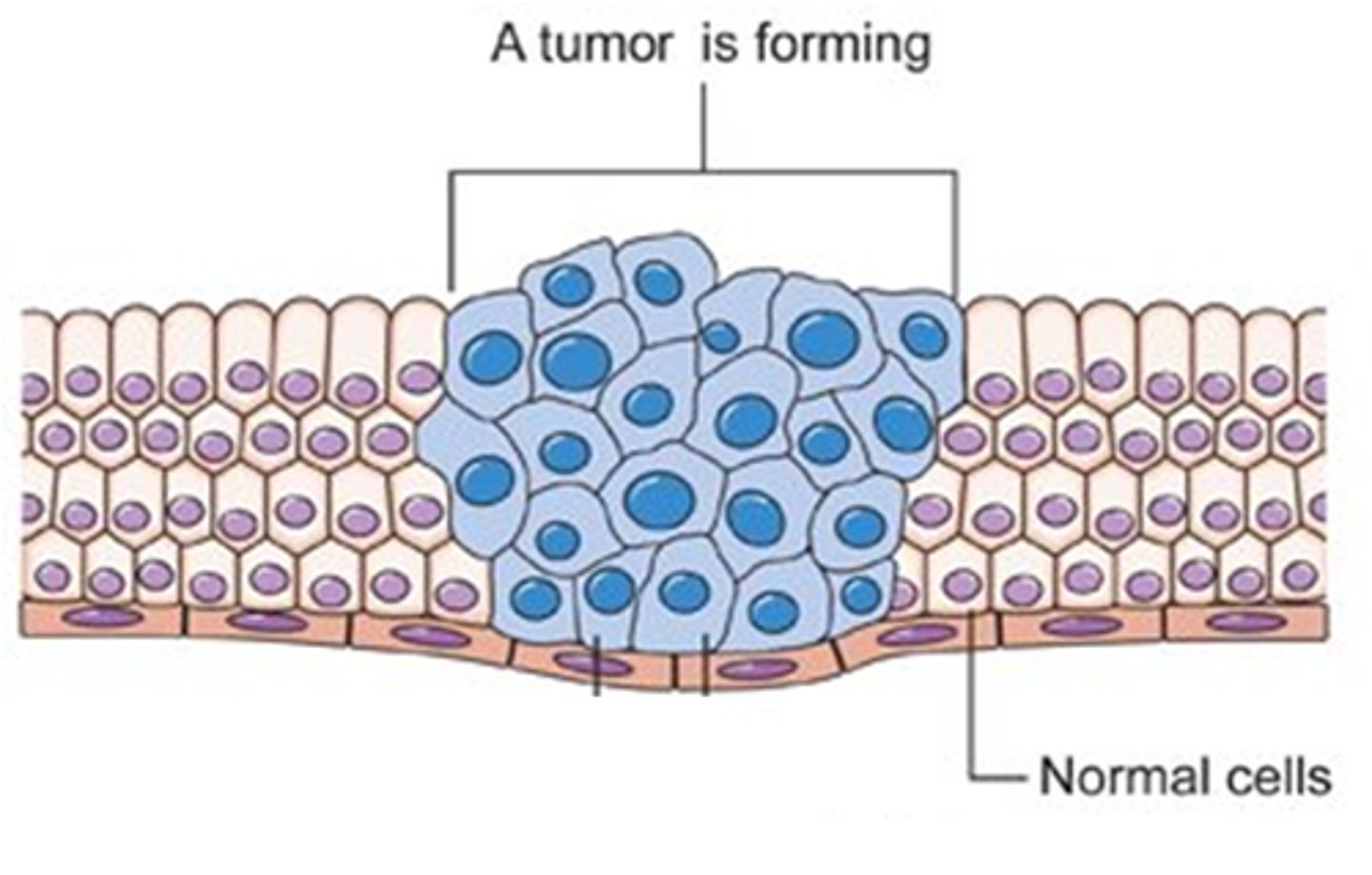
cancer
disorder in which some of the body's cells lose the ability to control growth
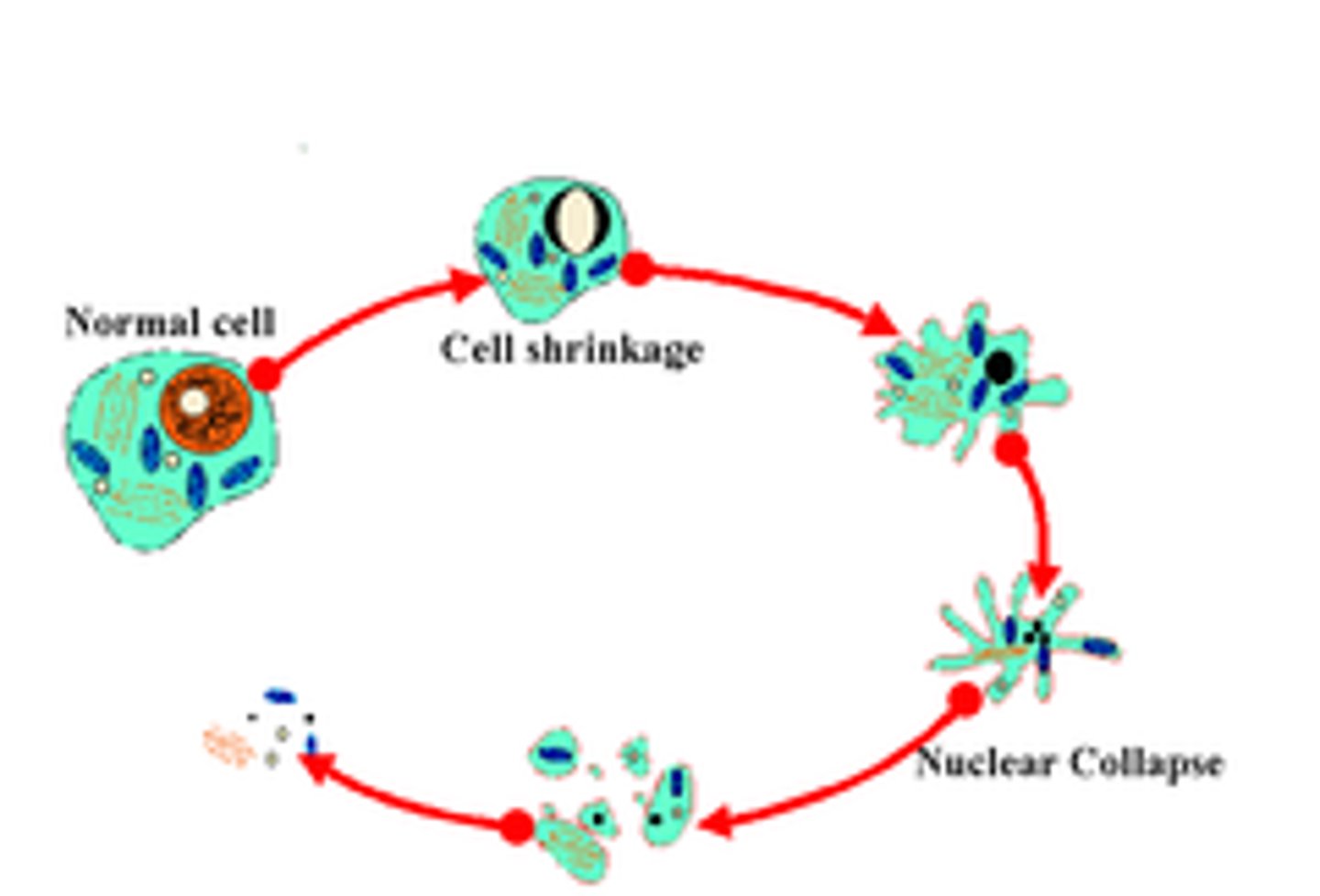
apoptosis
process of programmed cell death
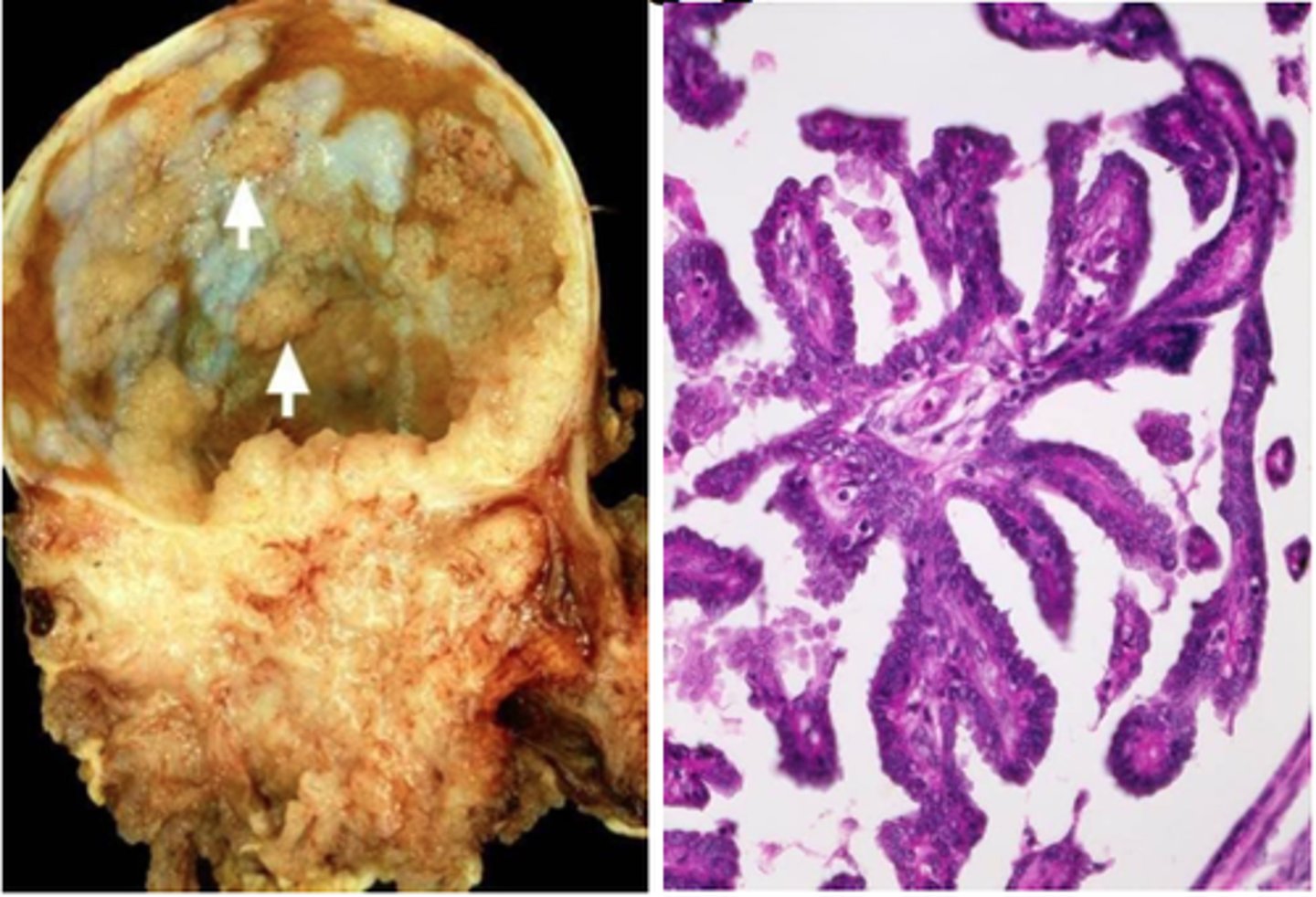
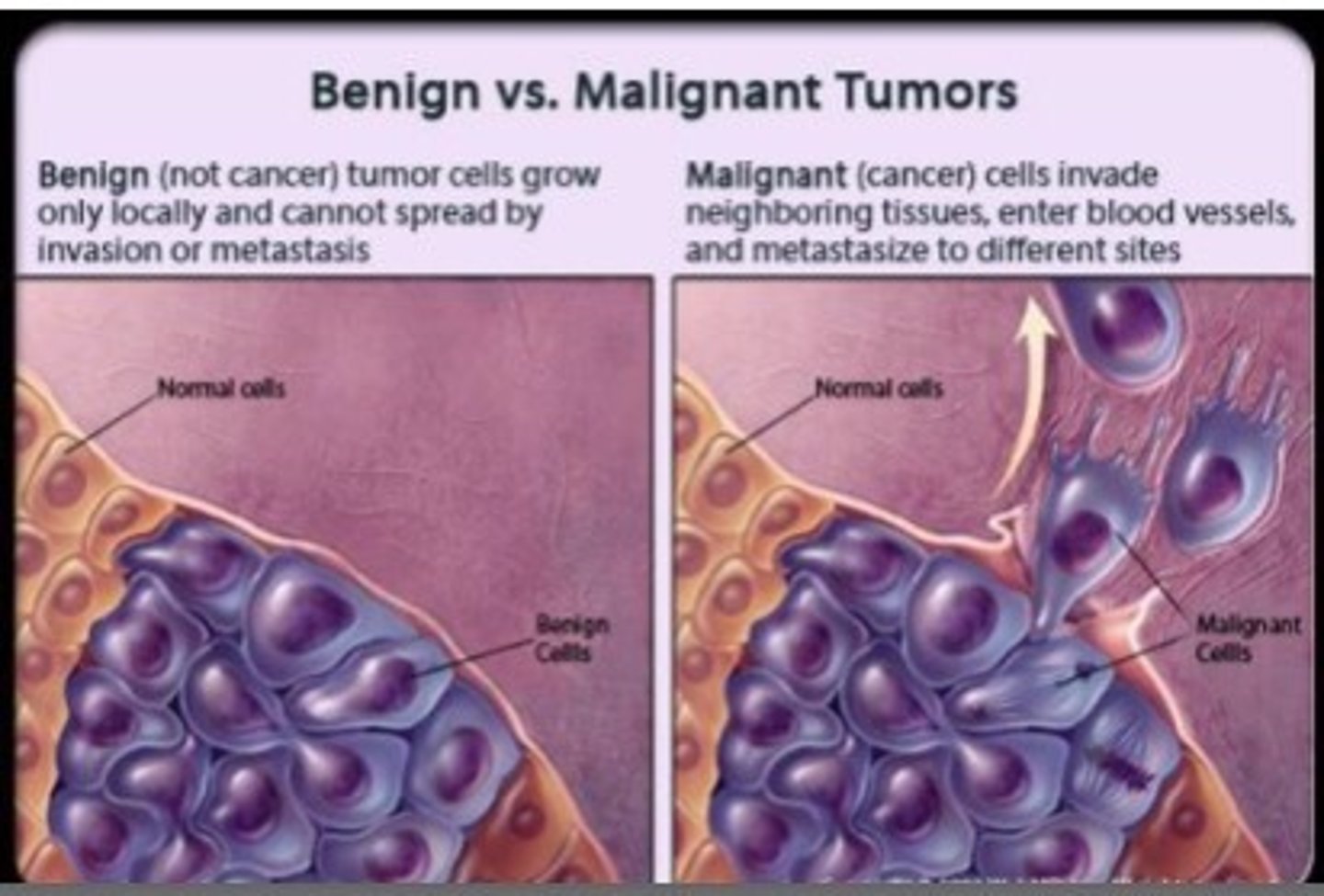
malignant tumor
A cancerous tumor that is invasive enough to impair the functions of one or more organs.
benign tumor
a mass of abnormal cells that remains at the site of origin
chemotherapy
The use of drugs to treat diseases such as cancer
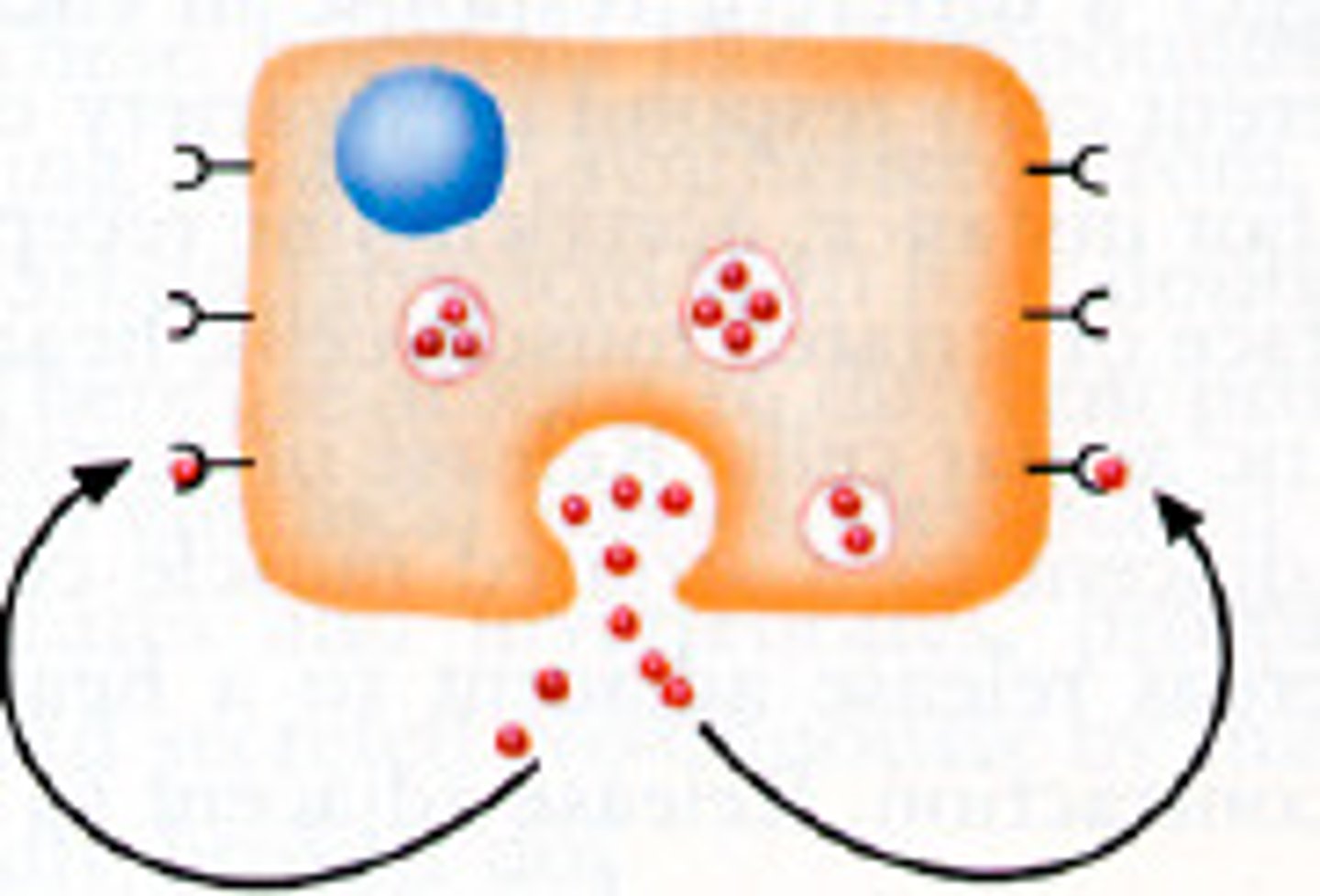
autocrine cell signaling
cell signals itself
pheromones
odorless chemicals that serve as social signals to members of one's species

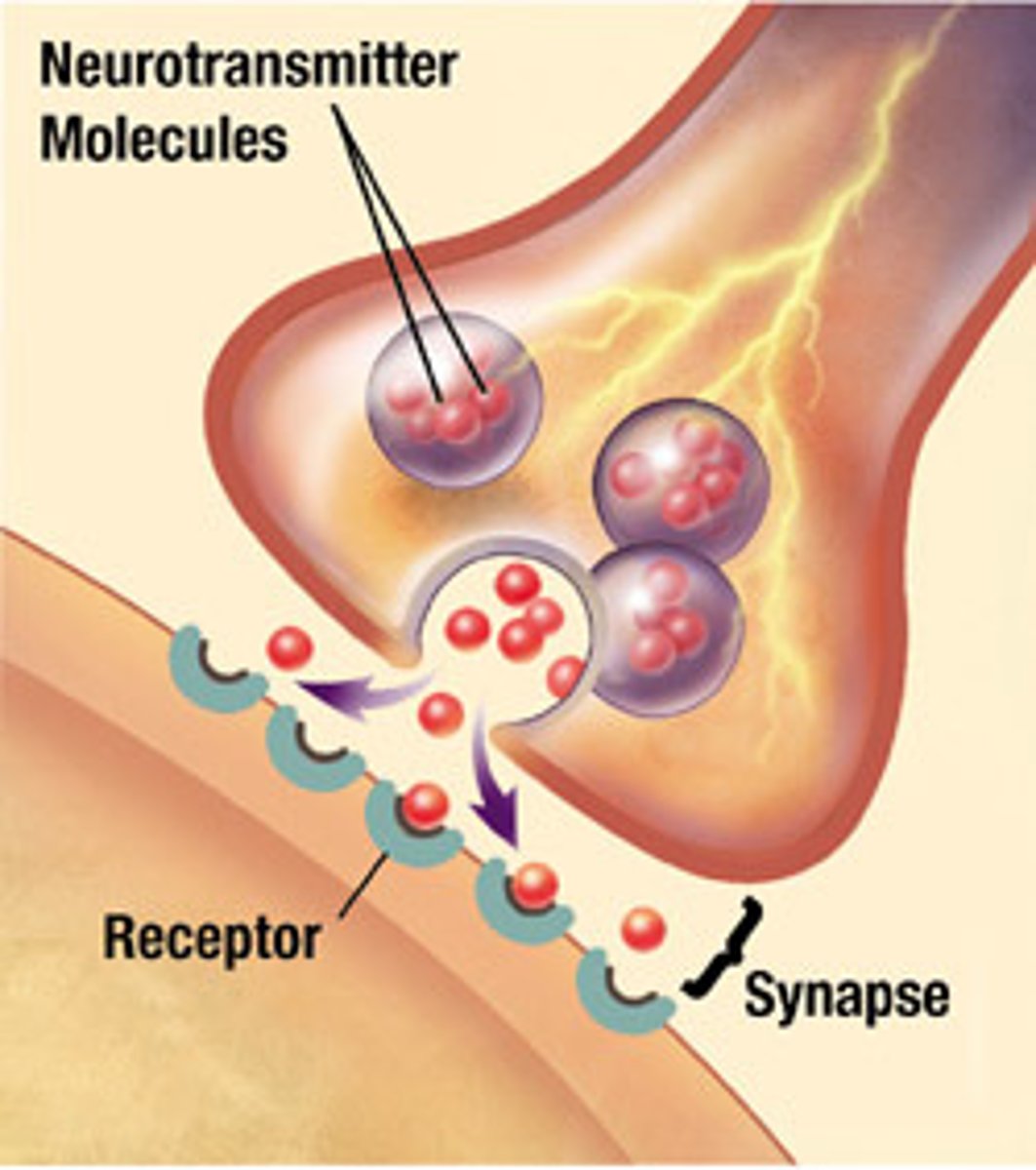
neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
ethylene
The only gaseous plant hormone. Among its many effects are response to mechanical stress, programmed cell death, leaf abscission, and fruit ripening.

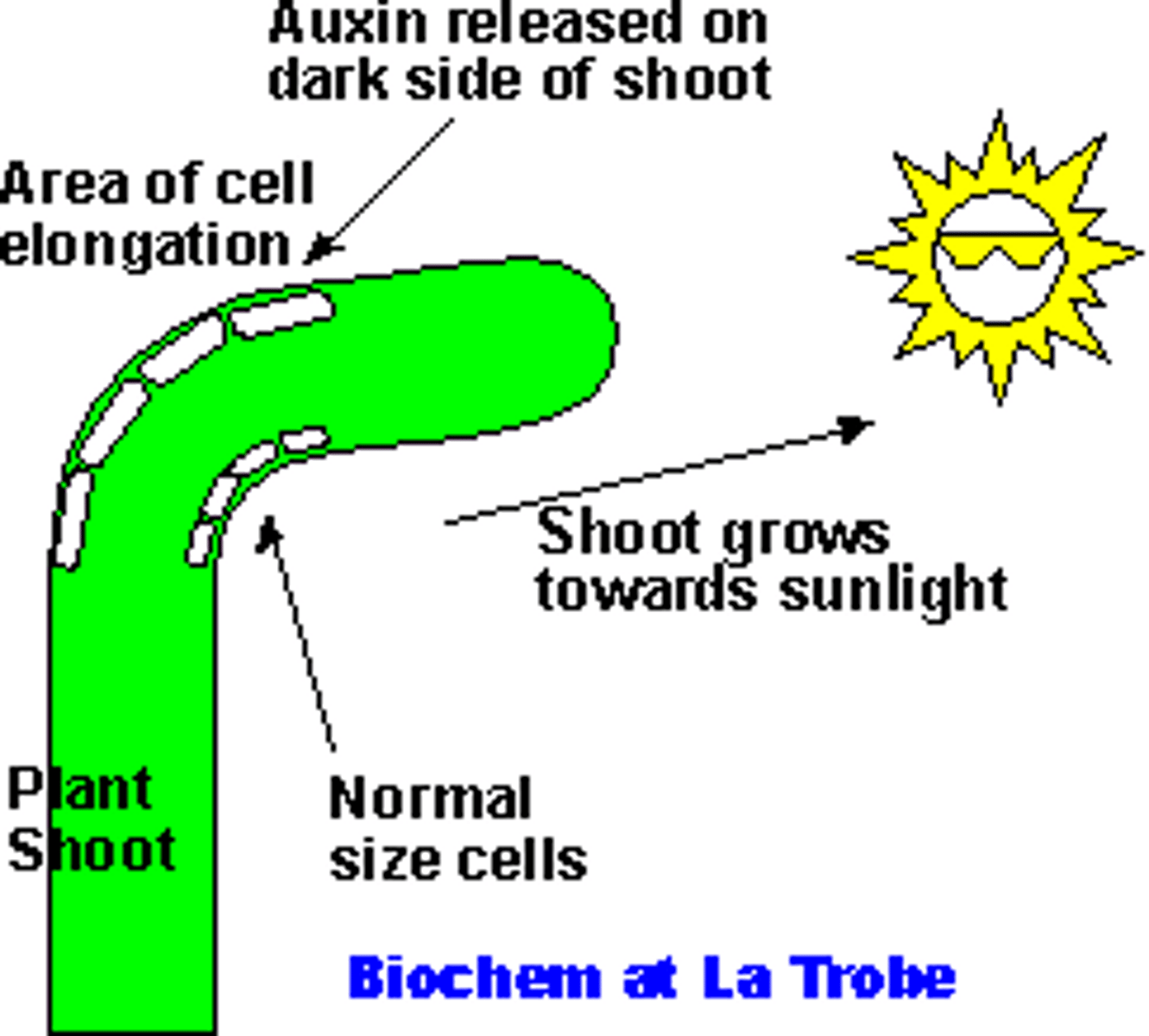
auxin
A plant hormone that speeds up the rate of growth of plant cells
serotonin
Affects mood, hunger, sleep and arousal. Undersupply linked to depression.
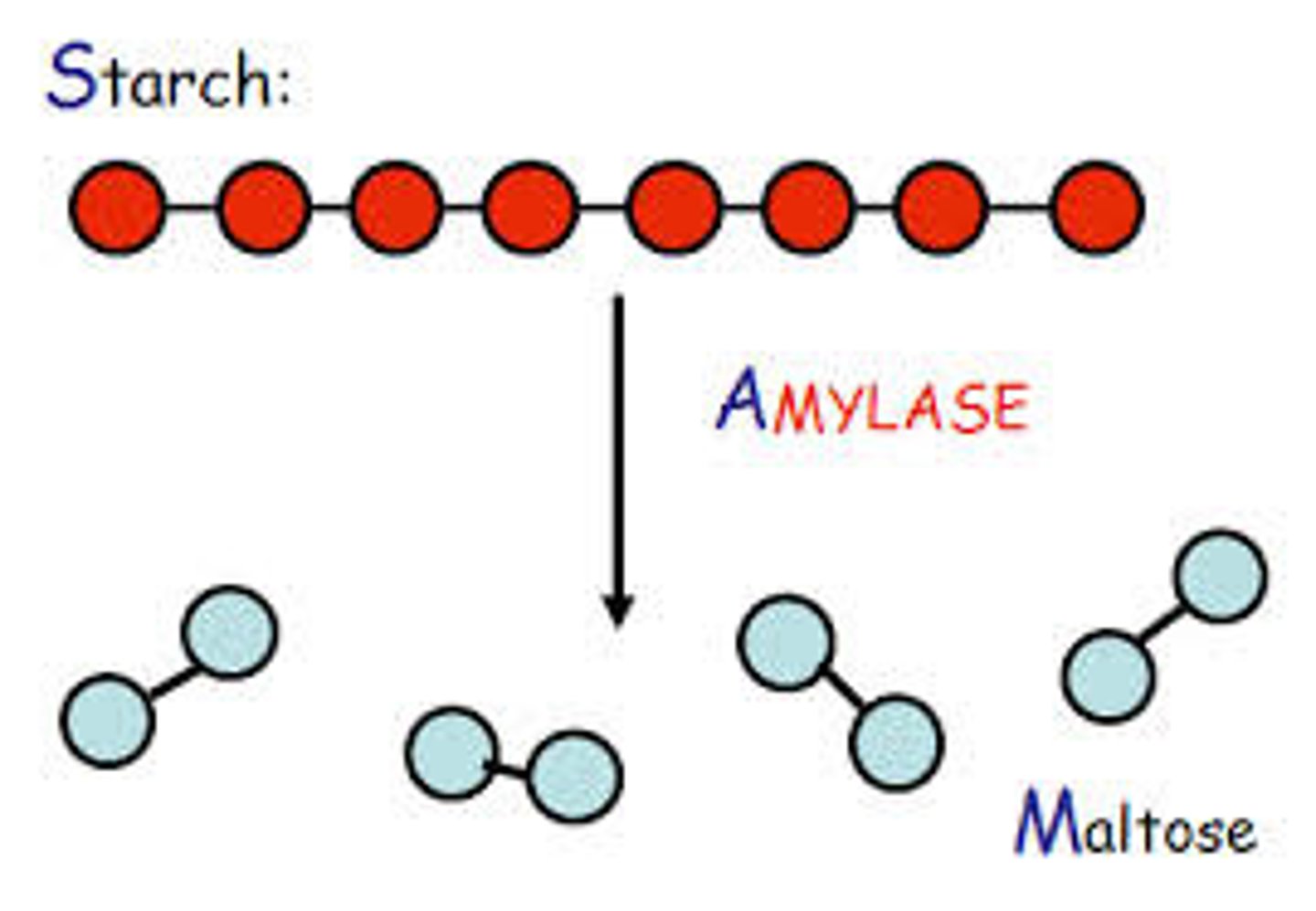
amylase
enzyme that breaks down starch
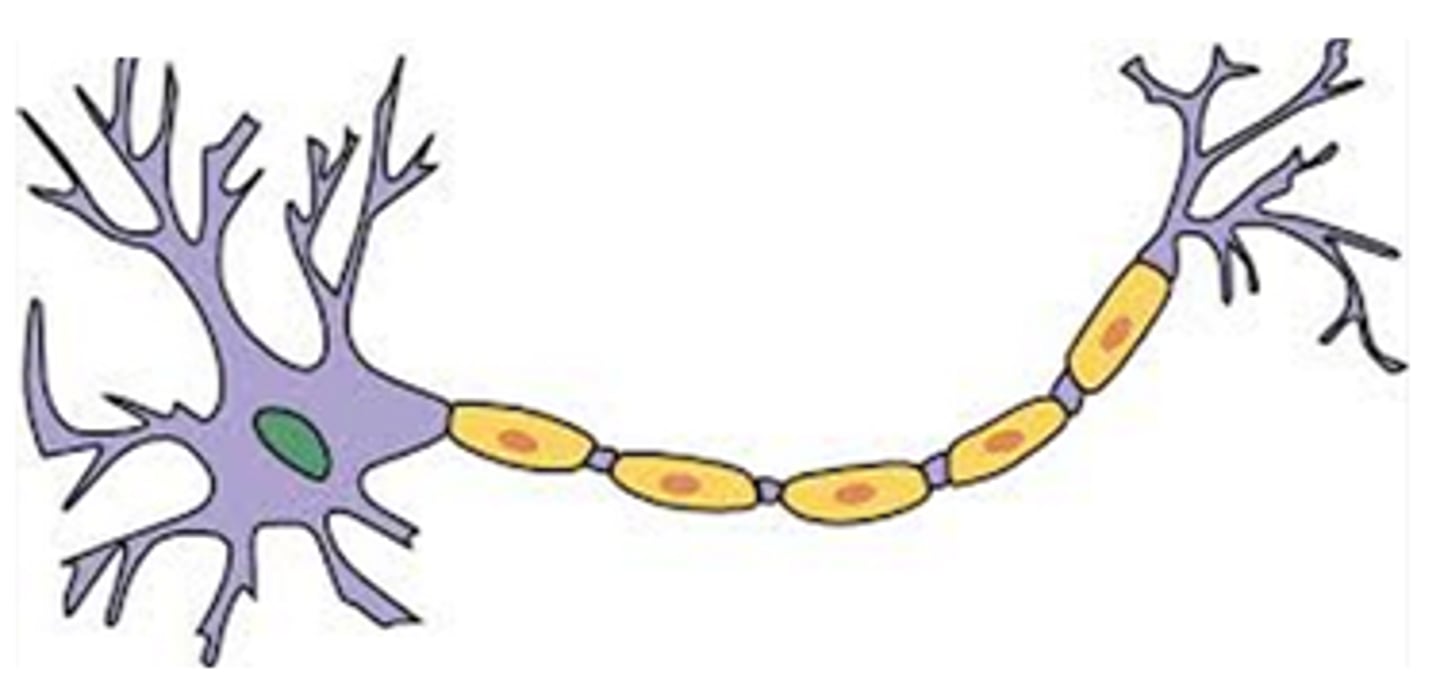
neuron
base unit of the nervous system which carries information throughout the body
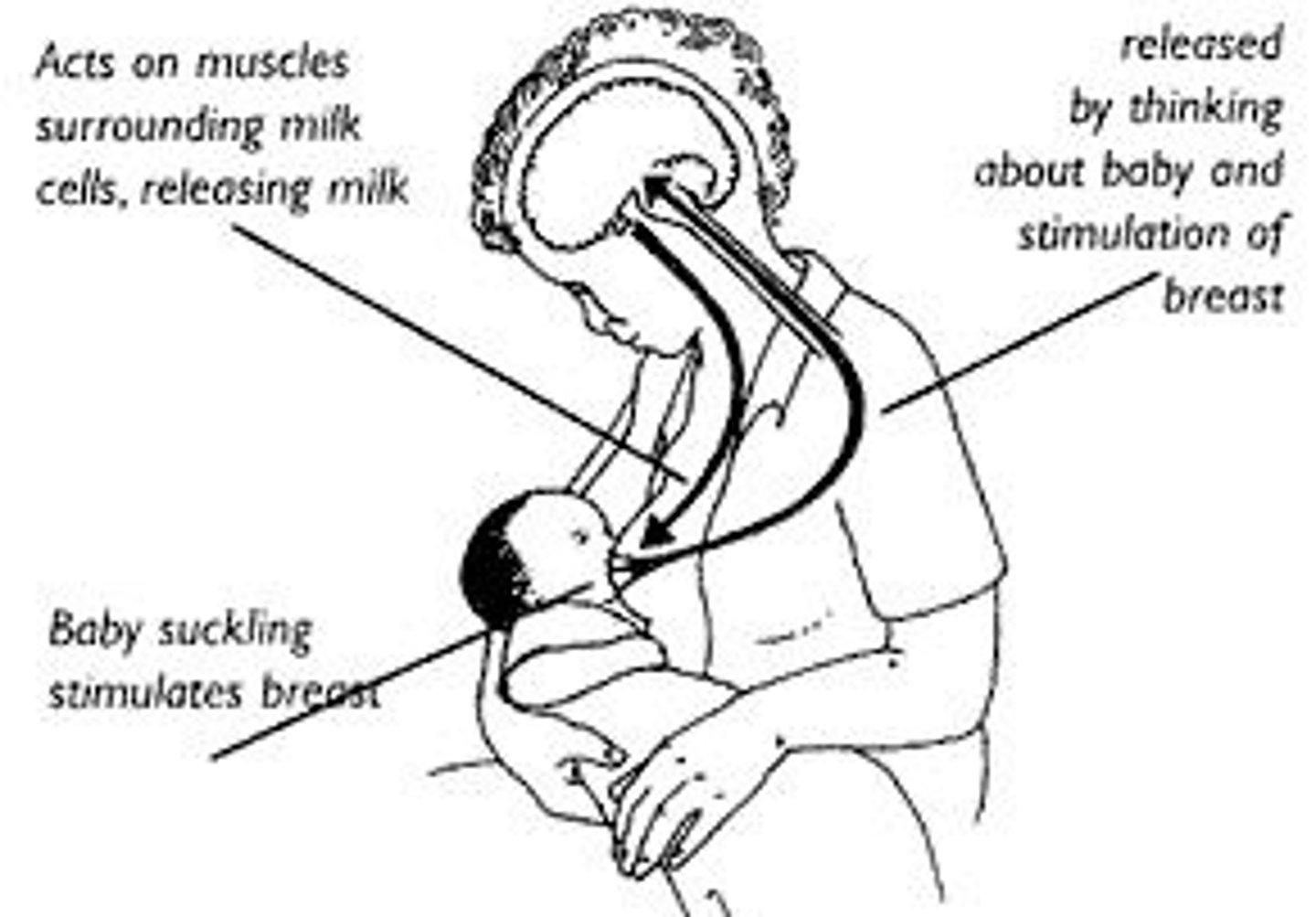
oxytocin
stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth
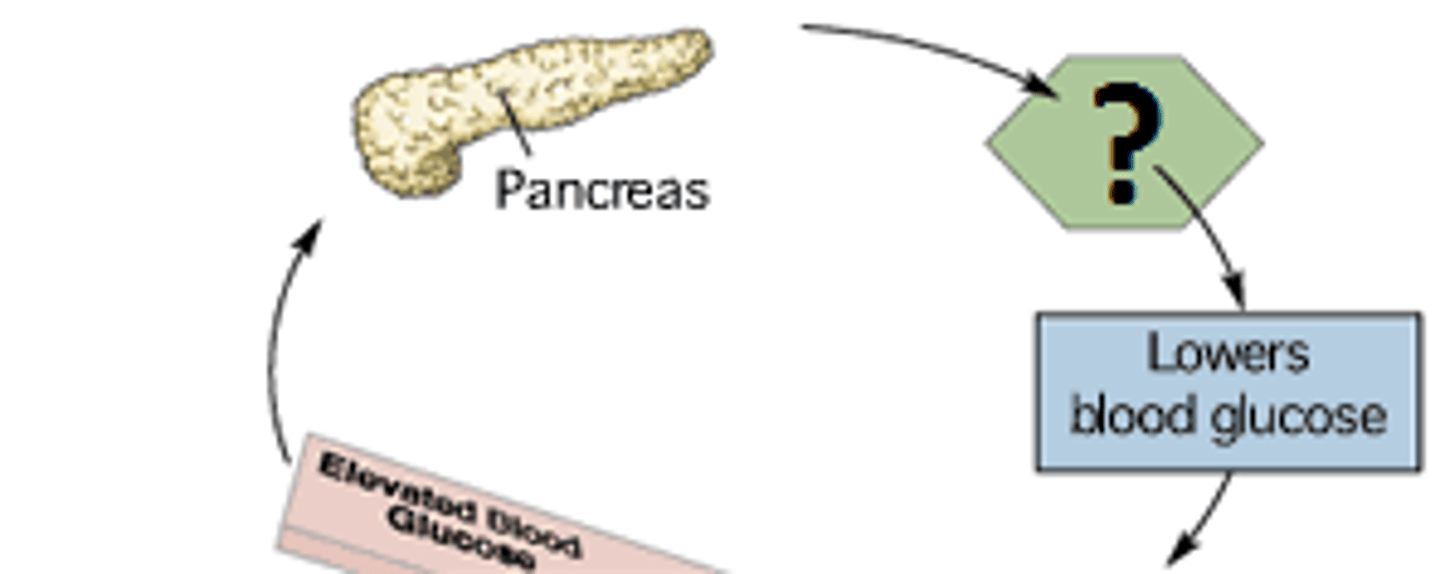
insulin
A protein hormone secreted by the pancreas that is essential for the metabolism of carbohydrates and the regulation of glucose levels in the blood.
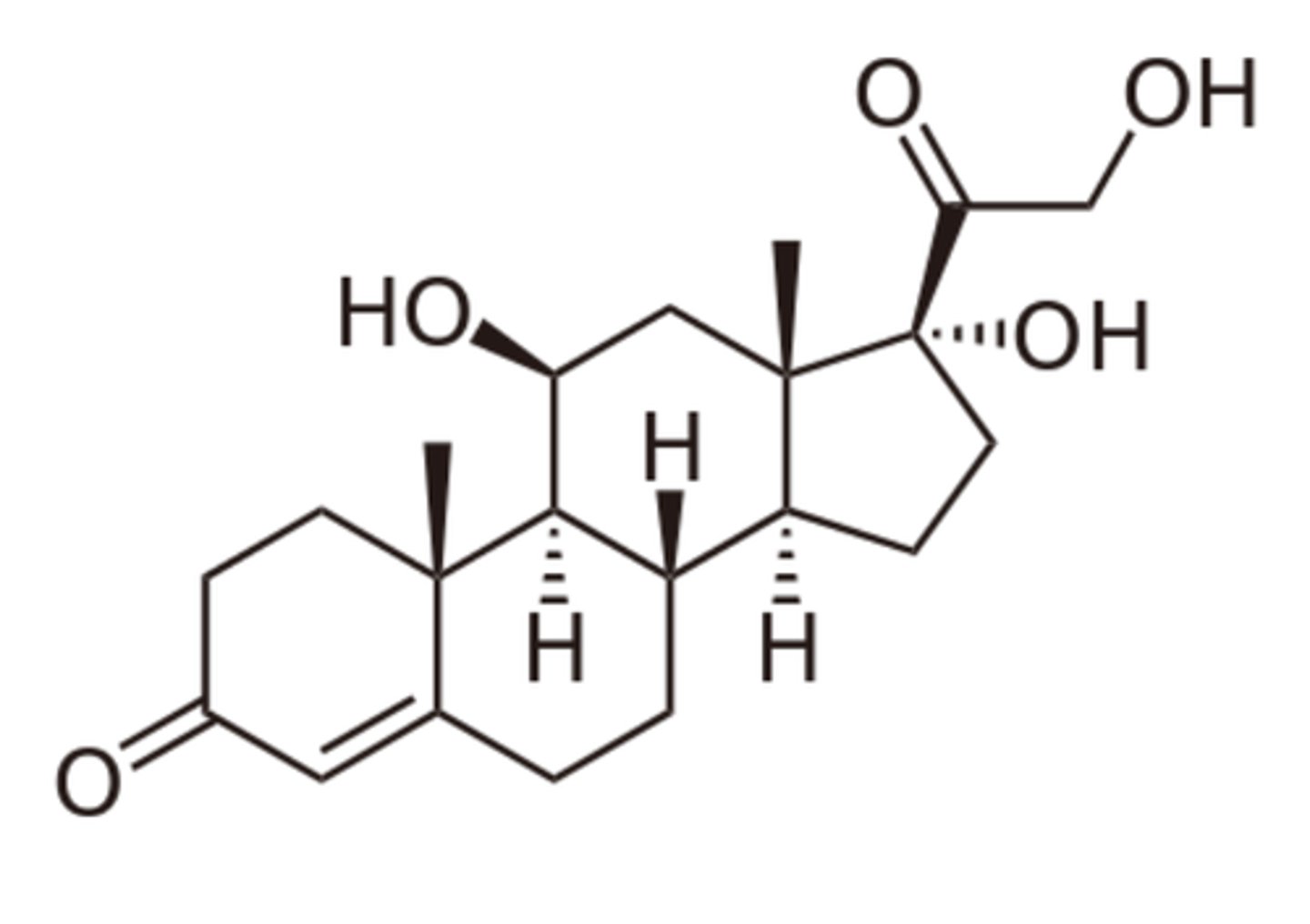
cortisol
stress hormone
melatonin
sleep-inducing hormone

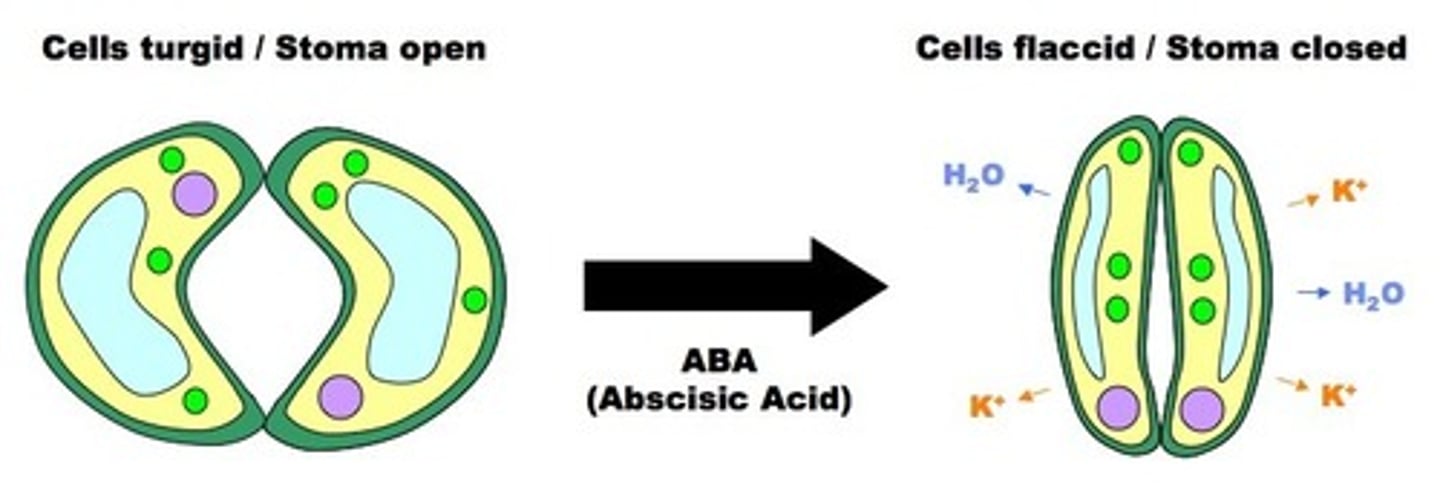
abscisic acid
inhibits cell growth, helps close stomata
GTP
energy source in protein synthesis (ACTIVE)
GDP biology
involved in intracellular signaling processes functioning as a critical regulator in the activity of GTPases (INACTIVE)