Functional Histology of the Integumentary System
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Epidermis
Outer skin layer, stratified squamous epithelium, providing protection and water retention.
Epidermis characteristics
continuity and hardness (keratin)
Waterproofing due to glycolipids
pigmentation to protect against UV rays
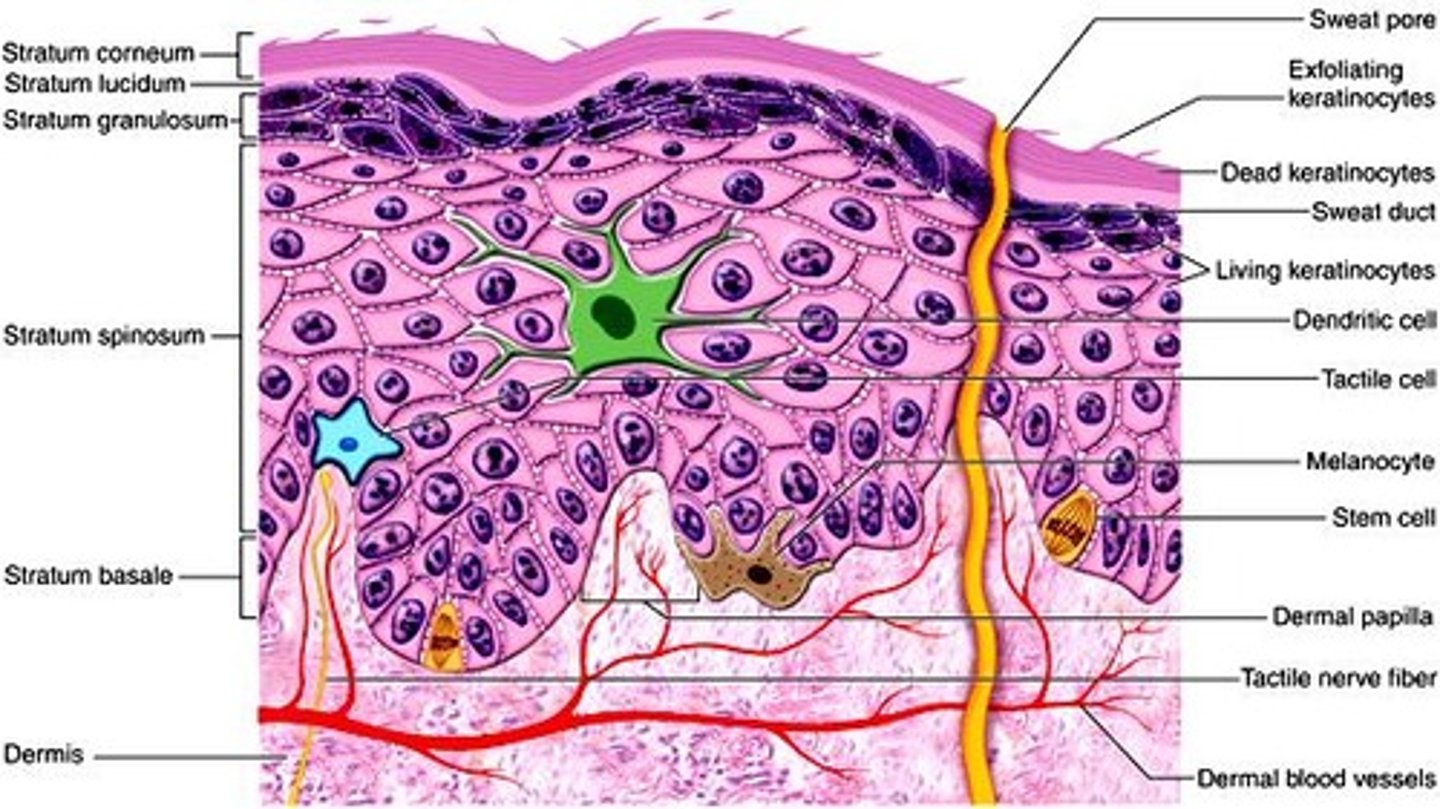
Stratum Basale
the deepest layer of the epidermis consisting of stem cells capable of undergoing cell division to form new cells, anchors epidermis to dermis
Cell Types: stem cells, melanocytes (pigment), Merkel cells (sensory)
Stratum Spinosum
Varies in thickness, a layer of the epidermis that provides strength and flexibility to the skin, produces keratin, secrete lipids, and serves immune function
Cell types: keratinocytes, dendritic cells (immune function)
stratum granulosum
a layer of the epidermis that marks the transition between metabolically active strata and the dead cells of the more superficial strata, appears as a dark band
Cell types: keratinocytes, which produce keratohyalin granules
stratum lucidum
a layer of the epidermis found only in the thick skin of the fingers, palms, and soles
Cell types: similar to stratum corneum, dead or dying keratinocytes
stratum corneum
outermost layer of the epidermis, which consists of flattened, keratinized cells, THICK in thick skin
Cell types: DEAD keratinocytes
Keratinocytes
The most abundant epidermal cells, function mainly to produce keratin. (produce glycolipids)
Keratin
Protein that contributes to skin hardness and continuity.
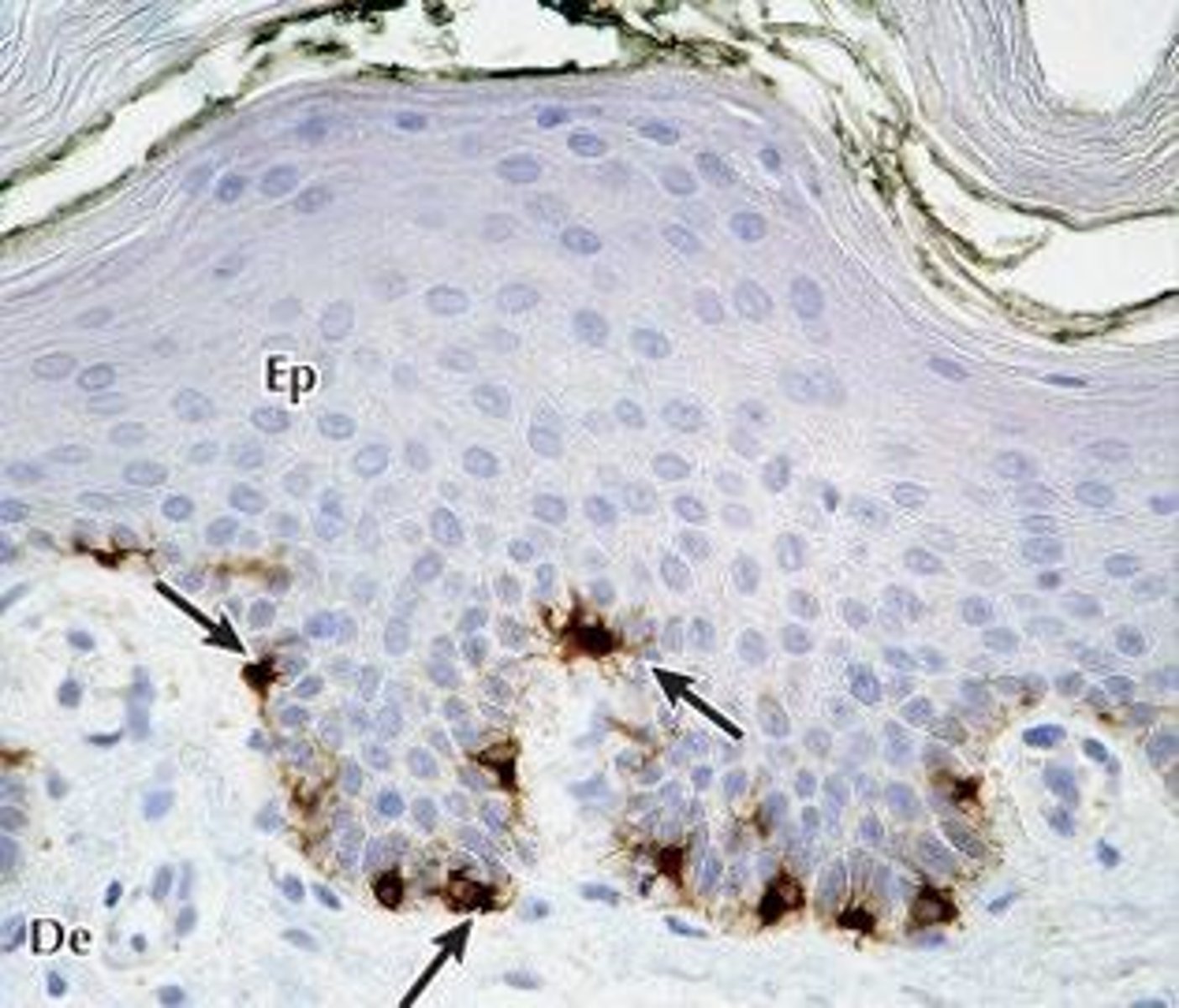
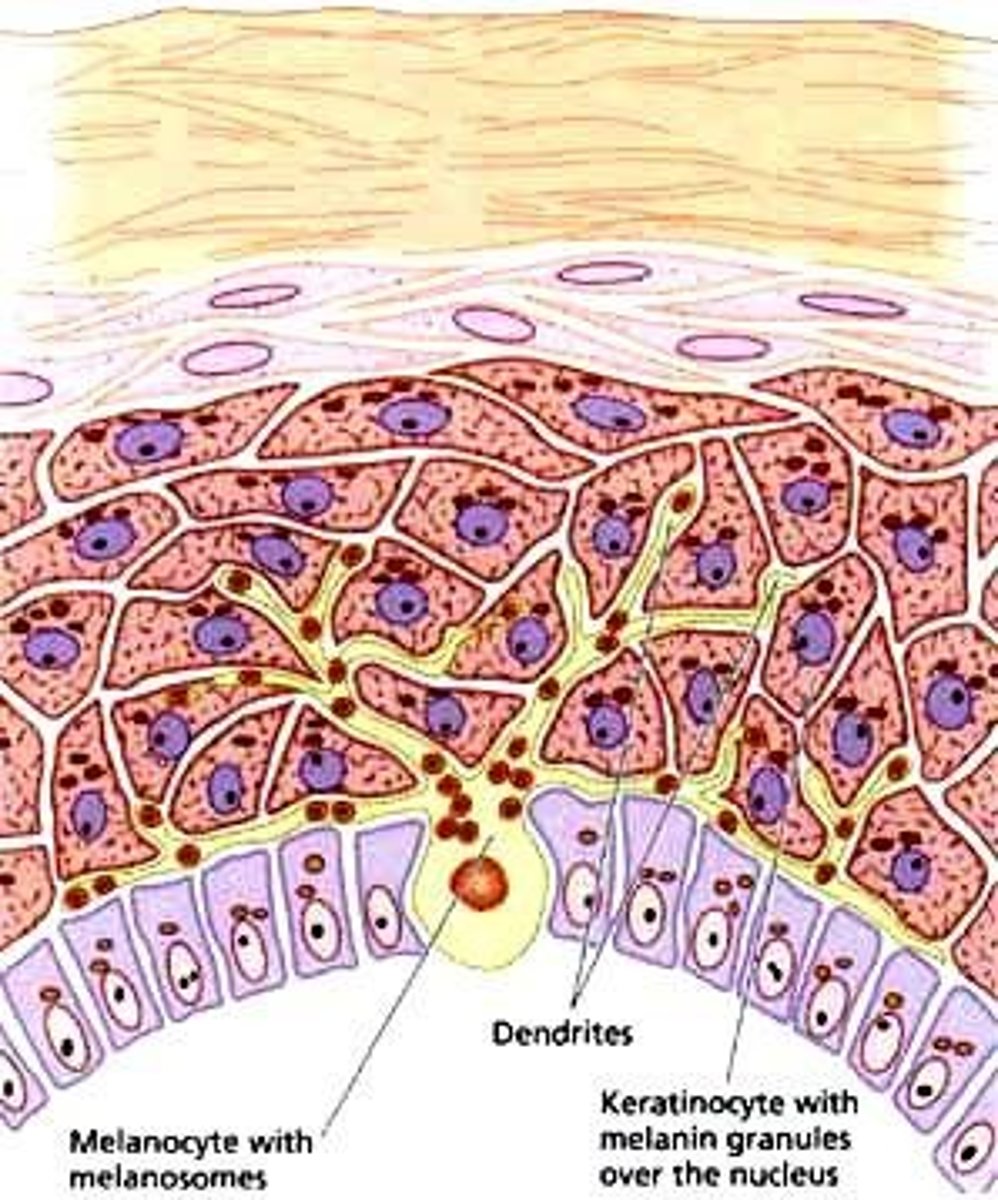
Melanocytes
Cells producing melanin for skin pigmentation. Stimulated by exposure to UV radiation.
Melanin
A pigment that gives the skin its color, it functions to prevent UV from damaging DNA.
Albinism
Genetic condition causing lack of melanin in skin.
Other sources of skin color
Carotene (food-derived), bilirubin (from Hb breakdown), "flushed" skin, or cyanosis (blueish skin) (changes in oxygenation that change skin color)
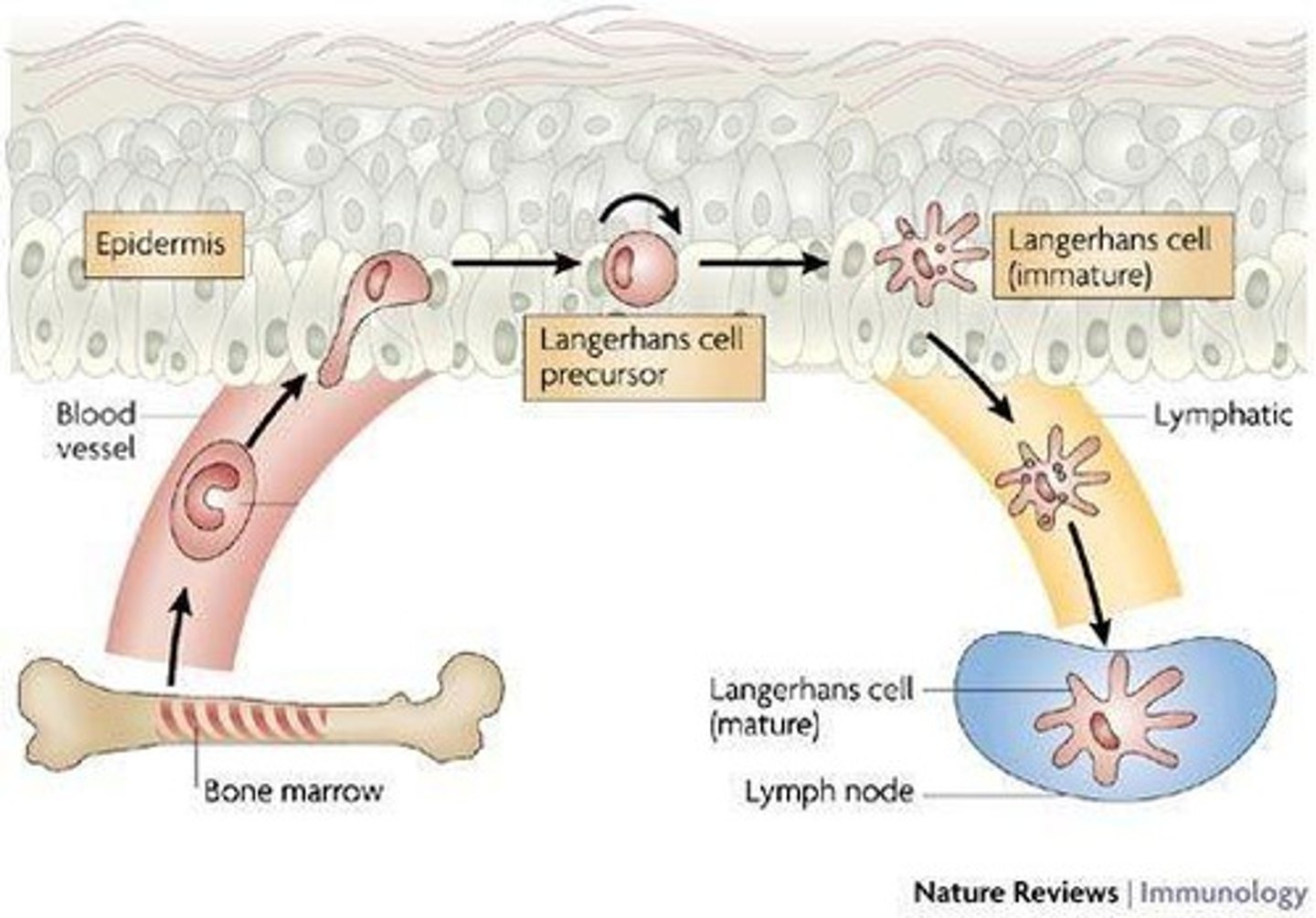
Dendritic cells
Immune cells in the epidermis, also known as Langerhans cells. Patrolling stratum spinosum for potential pathogens.
epidermal-dermal junction
Stratum basale is anchored to the dermis at the epidermal-dermal junction. The Basal Lamina contains hemidesmosomes and anchoring filaments on type 3 collagen, type 7 collagen loops tether BM to the dermis
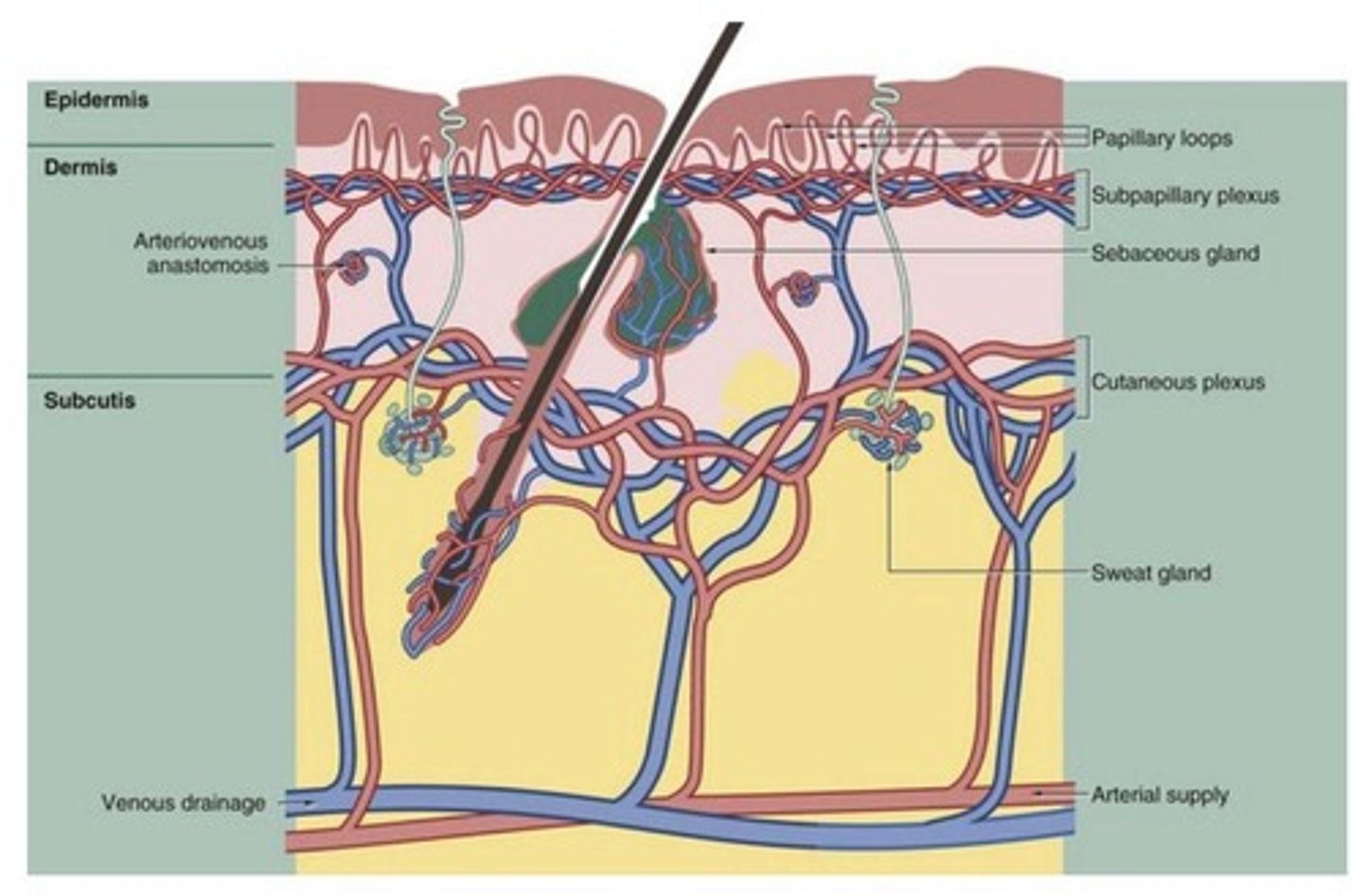
Dermis-blood supply
-Supply nutrients to the avascular epidermis
-important in controlling body temperature
papillary dermis
layer of dermis directly under the epidermis; rich in blood vessels and capillaries
reticular dermis
thicker area of the dermis that forms the bulk of the dermal layer, less vascularized than the papillary dermis
papilla in papillary dermis
small, nipple-like projections that increase surface area and enhance the exchange of nutrients and oxygen between the dermis and epidermis.
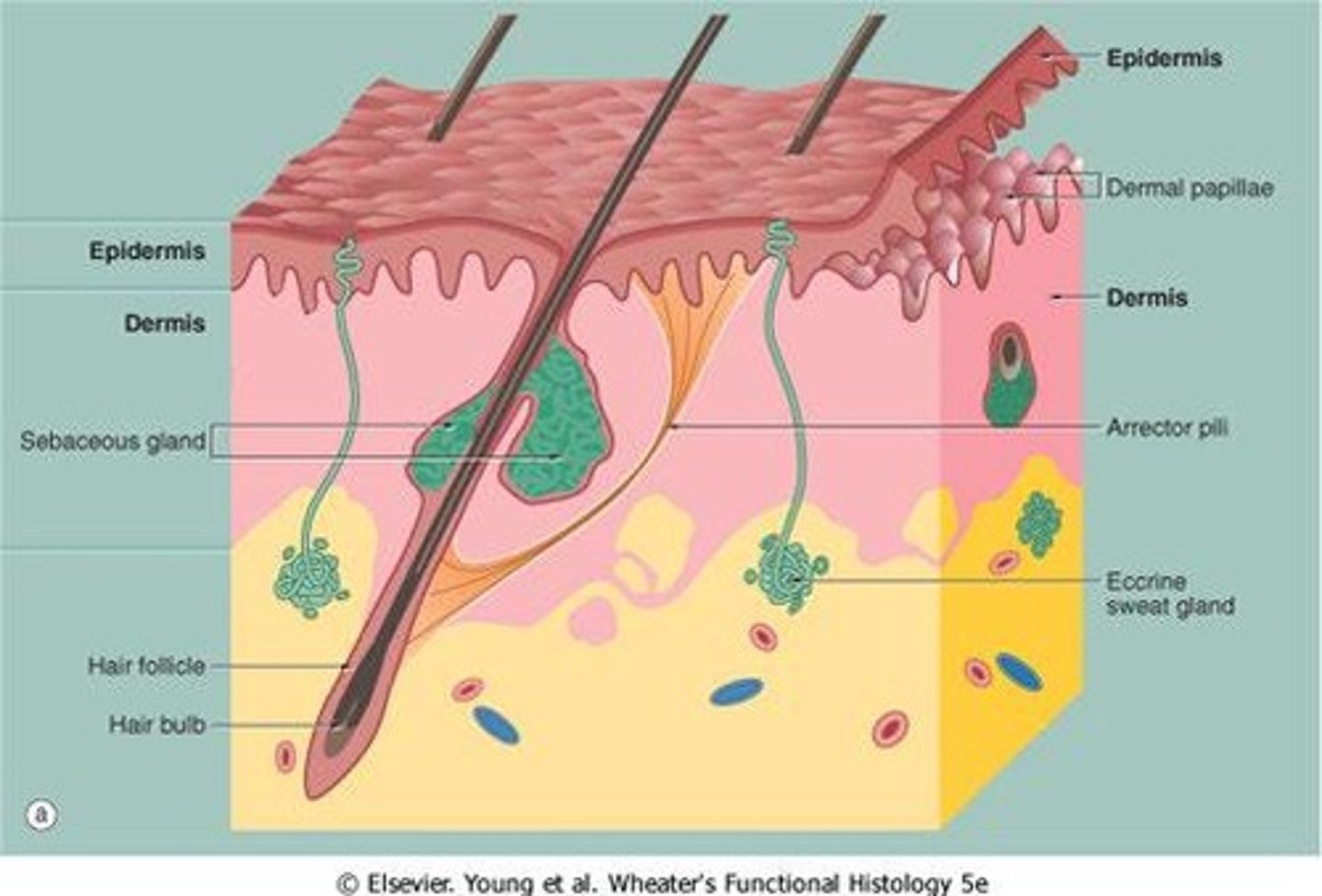
Eccrine sweat glands
Simple tubular glands secreting watery fluid for thermoregulation. Secretory regions stain lighter pink than ducts. Stratified-simple cuboidal.
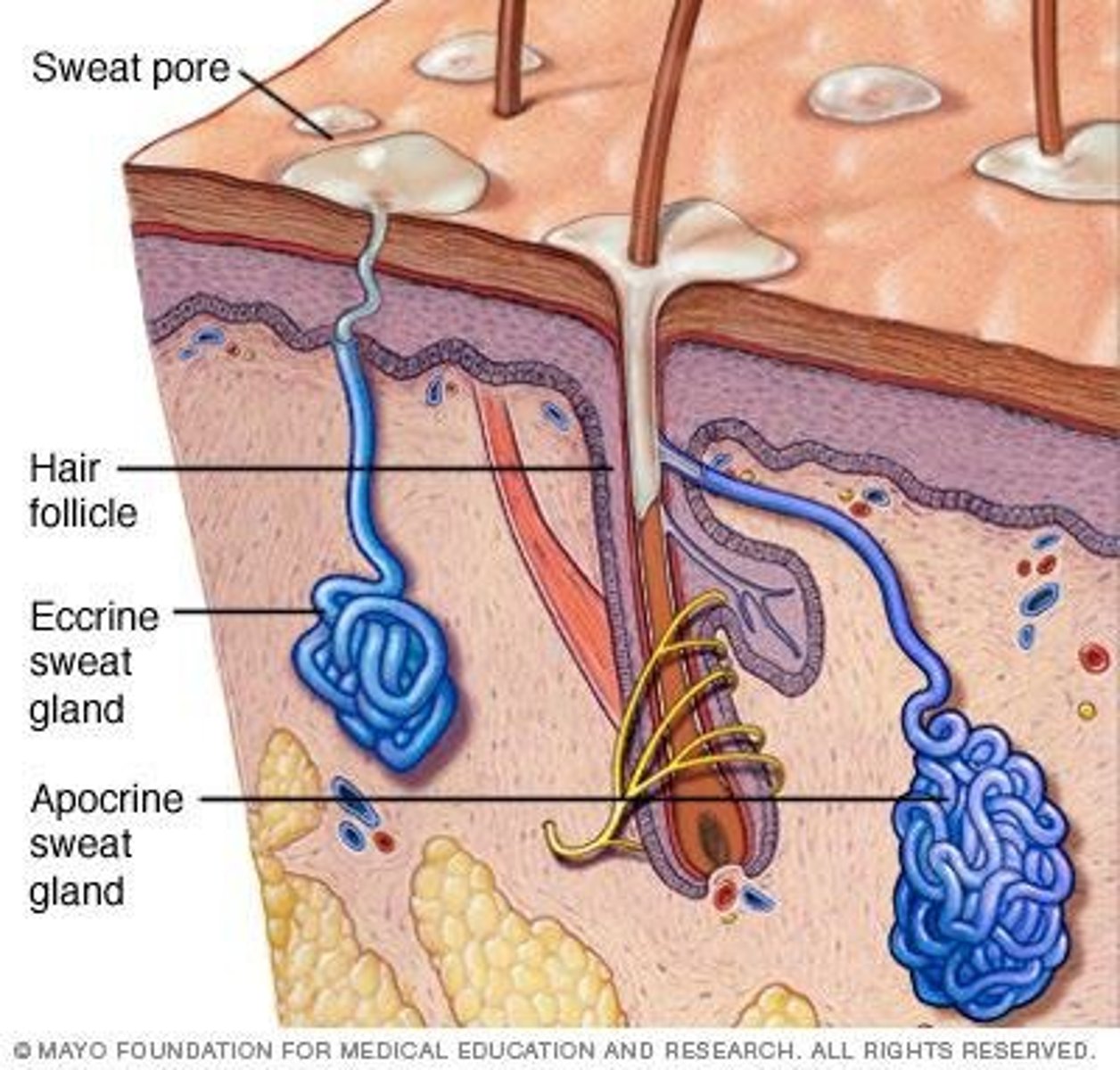
Apocrine sweat glands
Glands secreting lipid-rich fluid, with limited distribution. Contribute to body odor (provide food for surface bacteria). Much more rare (not in our slides). Glands have way larger lumens.Also stratified-simple cuboidal epithelium.
Body Temperature Regulation
The blood vessels in the skin help the body retain (vasoconstriction) or lose heat (vasodilation). Sweating and the evaporation of water from the skin contribute to cooling the skin.
hair follicle structure, bulb:
The follicle wall (epidermis) surrounds the hair follicle, the hair root includes the cuticle (superficial), cortex, and medulla. The hair matrix is deep in the hair bulb, where stem cells are dividing.
internal epithelial root sheath
firmly attaches the hair root to the follicle
external epithelial root sheath
portion of the epithelial root sheath that has all strata found in thin skin, gets thicker as you approach the surface.
Sebaceous glands
Glands producing oil to lubricate skin and hair, associated with hair follicles, secrete by holocrine excretion into the follicle.
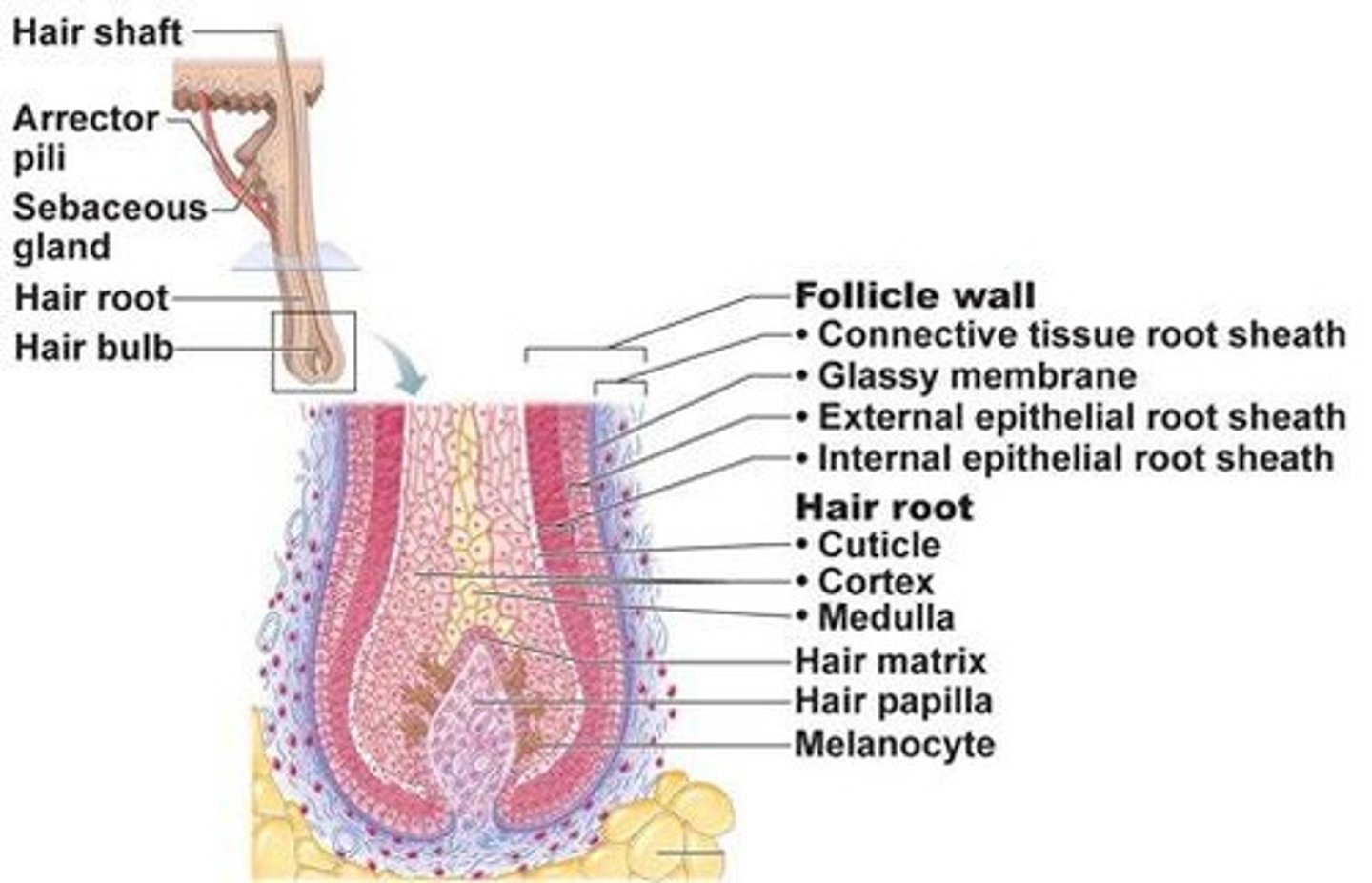
Arrector pili muscle
Smooth muscle causing hair to stand on end. Mostly a vestigial trait in humans, it connects the root sheath to the CT below the epidermis.
Where are most sensory receptors?
Dermis
Glycolipids
Substances that waterproof the skin's surface.
Basal lamina
Thin layer anchoring epidermis to dermis.
Type VII collagen
Protein connecting the basal membrane to the dermis.
Meissner's corpuscle
Sensory receptor for light touch in the most superficial dermis. Found ONLY in the dermal papilla, more superficial than Pacinian corpuscles. (modified glial cells +capsule +axon)
Pacinian corpuscle (lamellar corpuscles)
Sensory receptor for deep pressure and vibration in the deeper region of the reticular dermis. (modified glial cells +receptor proteins)
Merkel Cells
individual mechanoreceptor cells that release neurotransmitters that stimulate free nerve endings, associated with the stratum basale (not identifiable in our slides)
Free nerve endings
respond to pain and temperature,
Cutaneous sensation
Ability to perceive stimuli through skin receptors.
Body temperature regulation
Mechanisms like sweating and blood vessel adjustment.
Thick skin
Skin type with multiple epidermal layers, found on palms.
Thin skin
Skin type with fewer layers, covers most body areas.
Cyanosis
Bluish skin color due to low oxygenation.
Flushed skin
Redness from increased blood flow.