EOY Science - Medical Science
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
cells
the basic units of life
tissues
a group of cells that work together to perform a particular function

organs
a group of different tissues working together to perform a particular function
organ system
a group of organs working together
What is the organization of the human body from smallest to largest structures?
cells, tissues, organs, organ systems.
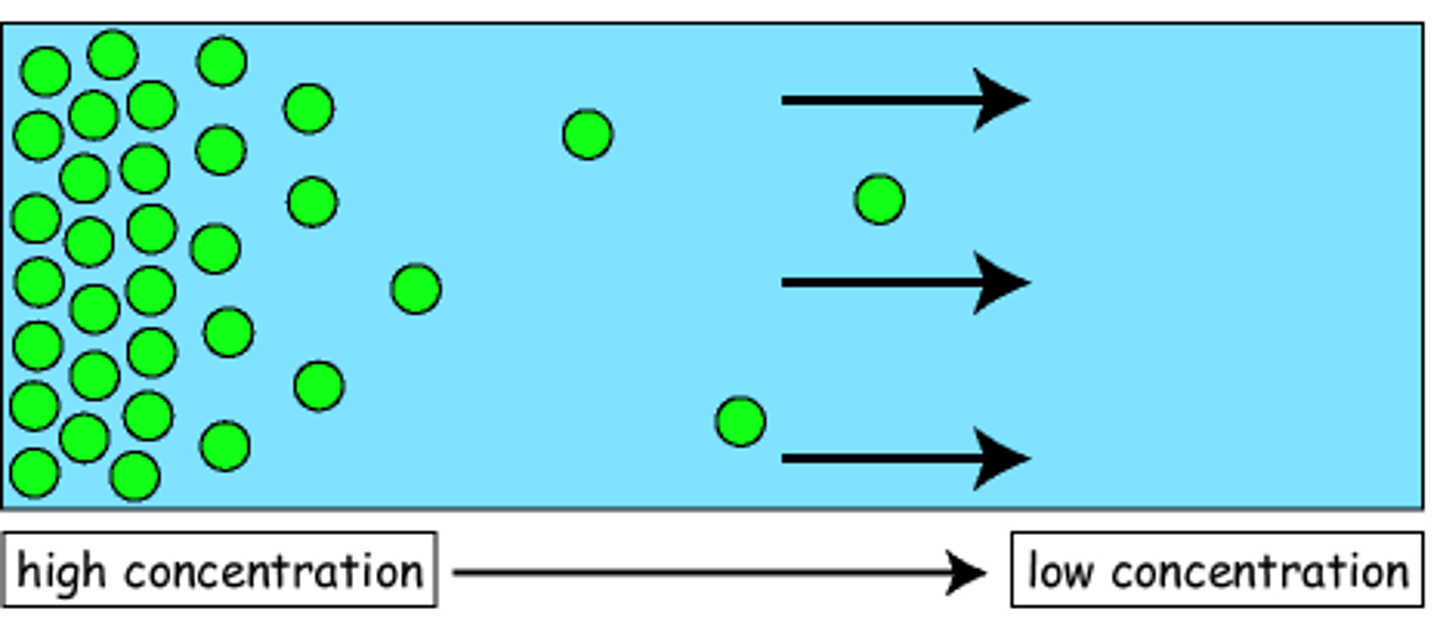
what is diffusion
the spreading out of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the concentrations are equal.
does diffusion require energy
no
how does oxygen get to the cells
oxygen enters the body through the lungs, diffusing from the lungs into the bloodstream. Oxygen then binds to red blood cells, which transports it through the circulatory system to body tissues. At the tissues, oxygen diffuses from the blood into cells.
what process allows oxygen to get to the cells?
diffusion
why is oxygen needed for life processes?
because oxygen is essential for respiration which cells use to generate energy. Without oxygen, energy production is reduced and energy is crucial for all life processes.
define respiration
a chemical reaction that takes place in every living cell to provide useable energy to carry out life processes.
what is aerobic respiration
respiration with more than enough oxygen
aerobic respiration chemical formula
glucose + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + energy
what is anaerobic respiration?
producing energy without oxygen
anaerobic respiration chemical formula
glucose = lactic acid + a small amount of energy
what does the mouth do?
it is an entry point for air.
what does the nose do?
it is an entry point for air and filters, warms, and moistures air before it enters the respiratory tract.
what is the epiglottis and what does it do?
it is a flap of tissue that covers the trachea when swallowing, preventing food from entering airways.
what is the trachea and what does it do?
also known as the windpipe, carries air from the throat to the bronchi.
what is the bronchi and what does it do?
bronchi are two large tubes that branch from the trachea into each lung, allowing air to move into the lungs.
what are the bronchioles and what do they do?
smaller branches of the bronchi that spread throughout the lungs, leading to the alveoli.
what is the alveoli and what does it do?
they are tiny sacs where gas exchange occurs between air and blood. They have thin walls and are surrounded by capillaries.
what is the diaphragm and what does it do?
a muscle below the lungs that contracts and relaxes to help air move in and out of the lungs.
what are the ribs and what do they do?
bones that form the rib cage, protecting the lungs and other organs.
what is the inter-coastal muscle and what does it do?
muscles between the ribs that help with breathing by expanding and contracting the chest.
why is the respiratory system so important?
because the respiratory system supplies oxygen to the body and removes carbon dioxide from the body.
what is gas exchange
the process where oxygen moves from the alveoli in the lungs into the blood stream and carbon dioxide moves from the blood stream into the alveoli to be exhaled.
what two processes are involved in breathing?
inhalation and exhalation
define breathing
the physical process of moving air in and out of the lungs.
what are some effects on the respiratory system from smoking?
cancer, heart disease, strokes, and shortness of breath.
what is emphysema
a lung disease where alveoli are damaged, reducing the lungs ability to exchange gases effectively, leads to difficulty breathing.
define carcinogenic
refers to something that can cause cancer
define addictive
describes something that can make someone dependent on it, making it difficult to quit.
what is the function of the left atrium?
receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via pulmonary veins.
what is the function of the left ventricle?
pumps oxygenated blood to the body through the aorta.
what is the function of the septum?
A wall that separates the left and right sides of the heart to prevent oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from mixing.
what is the function of the right atrium?
recieveies deoxygenated blood from the body via the vena cava.
what is the function of the right ventricle?
pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery for oxygenation.
what is the function of the aorta?
the largest artery, carrying oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body.
what is the function of vena cava?
large veins that return deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium.
what is the function of the pulmonary artery?
carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
what is the function of the pulmonary vein?
brings oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the left atrium.
why is the circulatory system so important?
The circulatory system is important as it transports oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to cells and removes waste products like carbon dioxide.
how does exercise affect heart rate?
exercise affects heart rate because your muscles need more oxygen, making your heart pump faster to supply the necessary oxygen and nutrients.
what are the three types of blood vessels?
arteries, veins, and capillaries.
what are arteries ?
Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body.
what are the structures of arteries?
they have thick, elastic walls to withstand high pressure from the heart.
what are veins?
veins are blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart
what are the structure of veins?
they have thin walls and valves to prevent the backflow of blood.
what are capillaries?
tiny blood vessels that allow for the exchange of gases, nutrients, and wastes between blood and tissues.
what is the structure of a capillary?
they have thin walls to allow gas exchange
why is blood so important?
because blood is vital for transporting oxygen. nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body.
what is the function of white blood cells?
they help fight infections, protect the body, and helps your immune system.
what is the function of red blood cells.?
carries and transports oxygenated blood.
what is the function of platelets?
helps blood clot.
what is the function of the plasma?
transports nutrients, hormones, and waste products around the body.