VM 581 CR III Midterm
1/193
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
194 Terms
A castrated male goat
Wether
The act of determining where a cancer is located and whether or not it has spread.
Staging
Surgical procedure to create an incision into the urinary bladder for visual inspection, stone retrieval, or mass removal
Cystotomy
What does the abbreviation PCR stand for when referring to DNA identification and multiplication?
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Abnormally high blood potassium, which can result from a urinary obstruction
Hyperkalemia
Abbreviation for bacterial colonization of portions of the urinary tract that are normally sterile
UTI
Straining to urinate
Stranguria
Frequent urination (small volumes)
Pollakiuria
Surgical procedure to create a connection between the urinary bladder and the skin; used to drain urine in patients with obstructed outflow
Tube cystotomy
The act of describing the appearance of cancer cells in tissue in order to predict risk of recurrence and/or metastasis.
Grading
Where do dysuria and pollakiuria localize?
Lower urinary tract
T/F: Absence of bacteria on a urinalysis effectively rules OUT a urinary tract infection.
False
Gold standard urine collection method for urinalysis
Cystocentesis
What is the most common cause of dysuria and pollakiuria in dogs?
Bacterial UTI
What is the most common cause of dysuria and pollakiuria in cats?
Idiopathic - FIC/FLUTD
What is MIC?
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration: the lowest concentration of an antimicrobial that inhibits visible growth of a microorganisms
Lady weights 11.4kg, Amoxicillin dose range is 11-22mg/kg Q8-12 for 5 days, there are 100mg and 200mg tablets, if you select Q8 dosing, what size and quantity of tablet will you dispense?
200mg, #15 tablets
What is the most common organisms causing UTIs in dogs and cats?
Fecal flora and skin contaminants
A recurrent UTI is _____ or more infections within ____ months
3
12
Which of the following antibiotics do NOT concentrate well in urine?
A. Penicillins
B. Aminoglycosides
C. Chloramphenicols
D. Macrolides
E. Fluoroquinolones
D.
Which antibiotic should be reserved for resistant UTIs, prostatic disease and/or pyelonephritis?
Fluoroquinolones (Enrofloxacin)
Which antibiotic is effective as a first line of treatment for sporadic cystitis bacterial agents?
Amoxicillin
Early castration in male goats increases the risk of obstructive urolithiasis primarily due to which effect?
Reduced testosterone leading to decreased urethral diameter
What are the most common parasites in adult goats?
A. Haemonchus Contortus
B. Coccidia
C. Fasciola Hepatica
D. Dictyoculus
A.
What is polioencephalomalacia?
A. A polio virus
B. A clostridial sp
C. Thiamine deficiency
C.
What type(s) of urolith is/are least common in goats?
A. Amorphous magnesium-calcium-phosphate
B. Amorphous magnesium-calcium-phosphate + struvite
C. Calcium carbonate
D. Silicates
D.
Which of the following findings is most consistent with a diagnosis of uroabdomen?
A. Peritoneal fluid creatinine equal to serum creatinine
B. Peritoneal fluid urea lower than serum urea
C. Peritoneal fluid creatinine ≥ 2× serum creatinine
D. Increased peritoneal fluid glucose compared to blood
C.
Potassium levels are key to identifying if diuresis is needed. This is important because, hyperkalemia puts the animal at risk of what complication?
Fatal arrythmias
Which ultrasonographic finding is most consistent with hydronephrosis?
A. Hyperechoic renal cortex with acoustic shadowing
B. Reduced corticomedullary distinction
C. Dilated renal pelvis with hypoechoic fluid
D. Irregular renal capsule with perinephric fat inflammation
C.
Which of the following venous blood gas (VBG) findings would you NOT expect in a patient with urinary obstruction?
A. Azotemia
B. Hyponatremia
C. Hyperkalemia
D. Hypoglycemia
D.
What sedation drug should be avoided in an animal with urinary obstruction?
Alpha 2 agonists can cause an increase in urine production
What is the gold standard surgical treatment of choice for a goat with urinary obstruction?
Tube cystotomy
Intermittent administration of ammonium chloride is most appropriate in which of the following situations?
A. Management of uroliths that are soluble in acidic urine
B. Prevention of calcium carbonate urolith formation
C. Long-term maintenance therapy in all obstructed ruminants
D. Management of uroliths that are soluble in alkaline urine
A.
Diets high in __________ have an inappropriate __________ ratio which puts goats at higher risk for developing stones
grain/legumes
calcium/phosphorus
Which calcium to phosphorus ratio is most appropriate to help prevent urolith formation in herbivores?
A. 1:1
B. 1:2
C. 2:1
D. 4:1
C
Pelleted and grain-based diets increase the risk of urolith formation primarily because they:
Lack the proper calcium:phosphorus proportions, decrease saliva formation, increasing phosphorus excretion in urine
Which forage is most associated with calcium-based urolith formation due to high calcium content?
Alfalfa hay or clover pastures
Castration at approximately what age is most associated with increased risk of urolith obstruction in goats?
< 6 months
Most common type of urolith in horses
Calcium carbonate
A 3-year-old male castrated goat is presented for acute onset dysuria and progressive ventral swelling. On physical examination, the prepuce is markedly swollen that is firm on palpation. The goat is straining to urinate, and the tail is held elevated. Urine dribbling is minimal to absent.
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Preputial abscess
B. Cystitis
C. Bladder rupture
D. Urethral rupture
D.
In small animal and large animal emergency medicine, potassium levels that warrant immediate treatment are generally:
> 6.5 mEq/L
Which of the following treatments for hyperkalemia can help correct the severe acidosis in a patient with urinary obstruction?
A. IVF therapy with LRS
B. Dextrose 2.5%
C. Sodium bicarbonate
D. IVF therapy with 0.9% NaCL
C.
What structure in small ruminants makes it difficult to catheterize? What about in pigs?
Small ruminants: urethral diverticulum
Pigs: preputial diverticulum
T/F: Urethral process amputation in goats in a permanent treatment for obstructive urotliths
False
Surgical treatment for uroliths where the uretha is incised in order to relieve the obstruction
Urethrotomy
Surgical treatment for urolithiasis in which the bladder is sutured to the body wall and a permanent stoma is created, allowing urine to drain directly to the exterior while bypassing the urethra
Marsupialization
Surgical treatment for urolithiasis where the urethra is transected in the perineal region and masupialized to the skin, allowing urine to exit through a new opening, losing use of normal anatomy
Perineal urethrostomy
T/F: Hydropulsion of uroliths is an appropriate treatment option for urolith obstruction in goats
False - retrograde can oush into urethral recess
A 12-year-old gelding is presented for straining to urinate and frequent attempts with minimal output over the past week. On physical exam:
Large, firm bladder palpable per rectum
Mild hindlimb weakness, otherwise neurologically normal
No signs of systemic infection
Ultrasound shows sediment in the bladder.
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Cystolithiasis
B. Idiopathic urinary incontinence
C. Sabulous cystitis
D. Urethral obstruction due to urolith
C. — Calcium carbonate sediment due to inadequate emptying
Which of the following breeds is predisposed to urolith formation and obstruction?
A. Boer
B. Pygmy
C. Nubian
D. Alpine
B.
Prevention methods for urolith formation in goats
Increase water intake
Ammonium chloride to acidify urine
Free choice feeding
Delay castration
Breed predisposition
Which of the following would least likely be indicative of urolith obstruction in goats?
A. Hematuria
B. Bruxism
C. Crystals on prepuce hair
D. Colic
E. All of the above are indicative
E.
What are the ingredients of Simparica Trio?
A. Fluralaner
B. Selamectin
C. Spinosad, milbemycin oxime
D. Sarolaner, moxidectin, pyrantel
D.
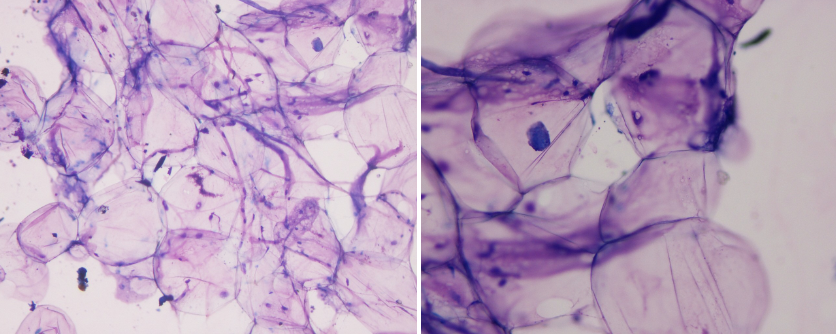
What is your cytologic diagnosis?
A. Epidermal inclusion cyst
B. Lipoma
C. Sebaceous adenoma
D. Mast cell tumor
B.
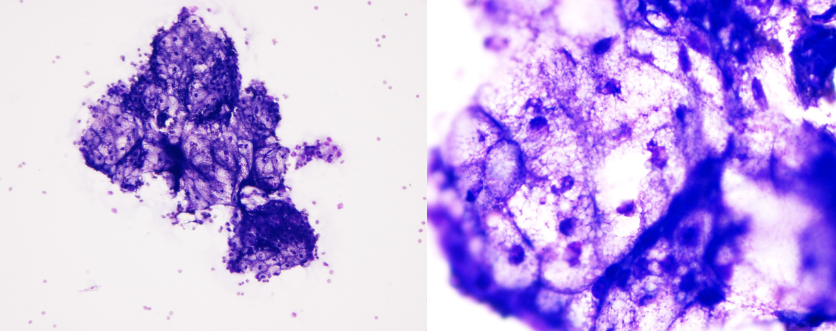
What is your cytologic diagnosis?
A. Epidermal inclusion cyst
B. Lipoma
C. Sebaceous adenoma
D. Mast cell tumor
C,
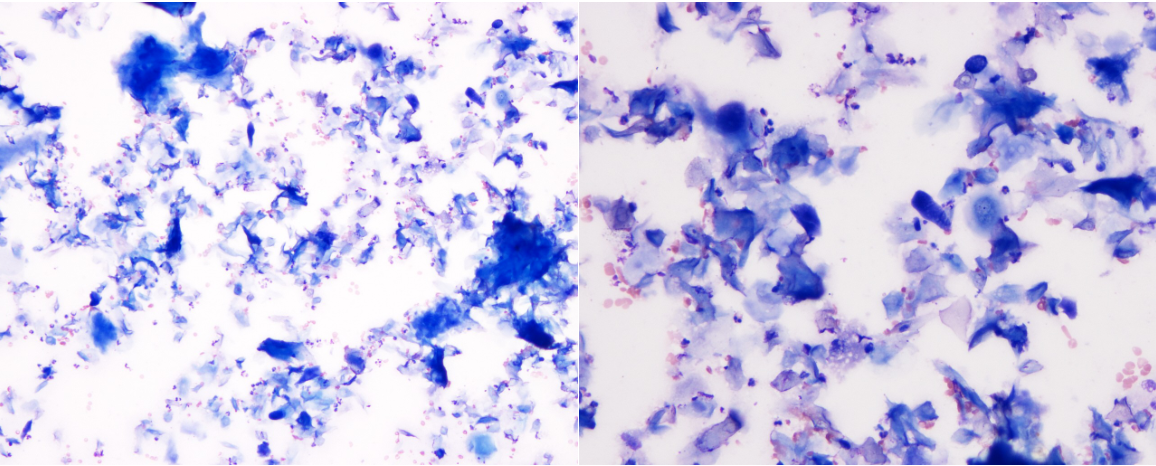
What is your cytologic diagnosis?
A. Epidermal inclusion cyst
B. Lipoma
C. Sebaceous adenoma
D. Mast cell tumor
A.
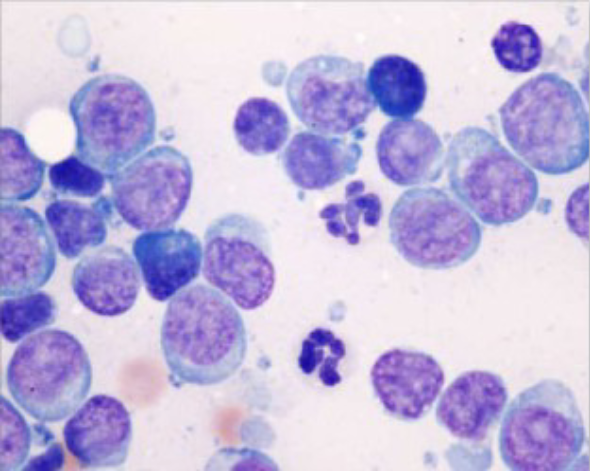
What is your cytologic diagnosis?
A. Reactive LN
B. Suppurative inflammation with bacterial sepsis
C. Normal LN
D. Lymphoma
D.
3 differential categories for peripheral lymphadenopathy
Infectious disease
Inflammatory
Neoplasia
Which of the following would NOT be a differential for hypercalcemia?
A. Neoplasia
B. Idiopathic
C. Addison’s disease
D. Vitamin D toxicosis
E. Primary hypoparathyroidism
E.
A 9-year-old dog presents for lethargy, PU/PD, and decreased appetite. Bloodwork reveals a marked hypercalcemia. Thoracic radiographs and lymph node aspirates are pending.
Which of the following is the first-line treatment for hypercalcemia in this patient?
A. Furosemide (Lasix) IV
B. Prednisone PO
C. 0.9% NaCl IV fluid therapy
D. L-asparaginase
E. Dexamethasone IV
C.
How do glucocorticoids help reduce serum calcium levels?
Decrease bone resorption and reduce intestinal calcium absorption
T/F: Steroids should be started after diagnostics are complete when lymphoma is suspected
True
What is the most common cancer in dogs and cats?
Lymphoma
What is the most common paraneoplastic syndrome of lymphoma?
Anemia ± thrombocytopenia
Which of the following is considered the gold standard for clinical staging of lymphoma in dogs and cats?
A. Fine needle aspirates of enlarged peripheral lymph nodes
B. Biopsy of lymph nodes
C. Abdominal ultrasound
D. PARR
B. — usually unnecessary but gold standard
T/F: Substaging of lymphoma is a more important prognostic factor than clinical stage.
True
Treatment of choice in most lymphoma cases
CHOP chemotherapy protocol
Most dogs remain in remission for _______ to _______ months without chemotherapy following completion of CHOP
3 to 6
T/F: Most tumors do not need a histopathology diagnosis to move forward with surgery
True
Which type of neoplasia is most likely to provide a high-quality, diagnostic sample when evaluated by cytology?
A. Round cell neoplasia
B. Mesenchymal neoplasia
C. Epithelial neoplasia
D. Neuroendocrine epithelial neoplasia
A.
In which of the following sample types would aspiration instead of fenestration be preferred for cytology sampling?
A. Spleen
B. Liver
C. Pulmonary
D. Lymph node
C. — best for intracavitary and poorly exfoliative masses (sarcoma)
4 questions to ask when obtaining a cytology sample suspect for neoplasia
Is it cellular?
Is there evidence of inflammation?
What is the predominant cell type?
Is there criteria for malignancy?
An FNA of a mass would be considered inflammatory if what cell type is found?
Neutrophils and/or macrophages
A bening epithelial neoplasia is called:
adenoma
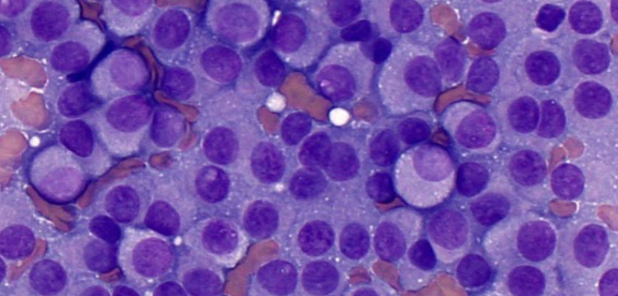
The cytology slide pictured is most consistent with which of the following cell types?
A. Neuroendocrine epithelial neoplasia
B. Mesenchymal neoplasia
C. Lymphoma
D. Plasma cell
A. — naked nuclei in a sea of cytoplasm, cluster together
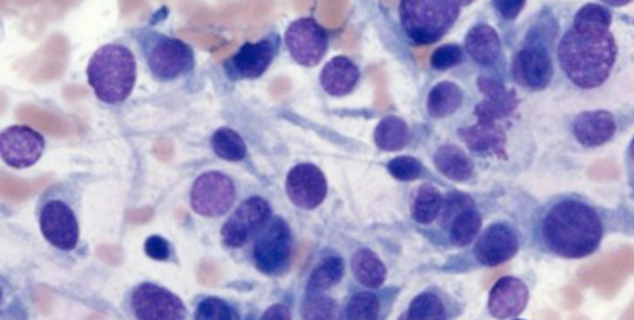
The cytology slide pictured is most consistent with which of the following cell types?
A. Neuroendocrine epithelial neoplasia
B. Mesenchymal neoplasia
C. Lymphoma
D. Plasma cell
B.
Osteosarcoma and hemangiosarcoma originate from which cell type?
Mesenchymal
Name the 6 types of round cell neoplasia
Lymphoma
Mast cell
Plasma cell
Histiocytoma
TVT
Melanoma
T/F: Melanoma can spread through the blood stream and the lymphatics
True — also carcinoma
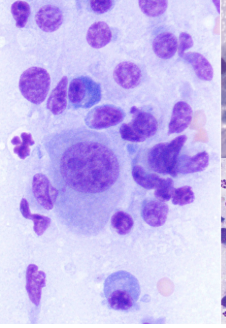
Name characteristics of malignancy seen in this slide
Multinucleation
Anisocitosis
Anisokryosis
Large prominent nuclei
Pleomorphic
Dx: Histiocytic Sarcoma
When differentiating between lymphoma and normal/reactive lymphoid tissue on cytology, which feature is the most distinguishing?
Monomorphic population of lymphoid cells: >50% intermediate/large lymphocytes
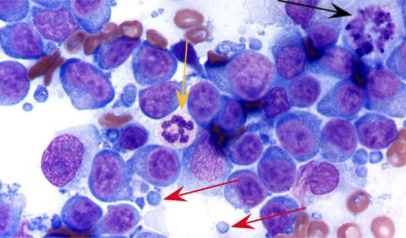
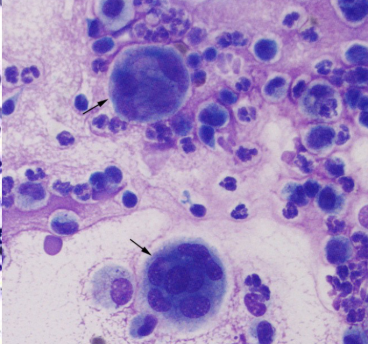
What cell is the black arrow pointing to?
Multinucleated giant cells → specialized mnacrophages
Which of the following is a criterion of malignancy that is specific to squamous cell carcinoma?
A. Anisocytosis
B. Anisokaryosis
C. Increased mitotic figures
D. Asynchronous maturation
D.
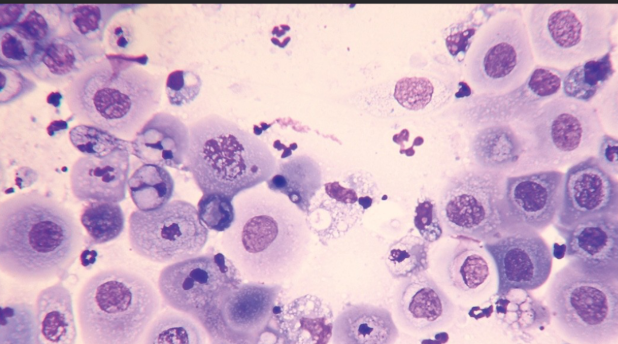
Basal reserve cells in epithelial tissue are:
A. Fully differentiated cells that make keratin
B. Undifferentiated progenitor cells located in the basal layer
C. Mesenchymal stem cells in connective tissue
D. Inflammatory cells that migrate into epithelium
B.
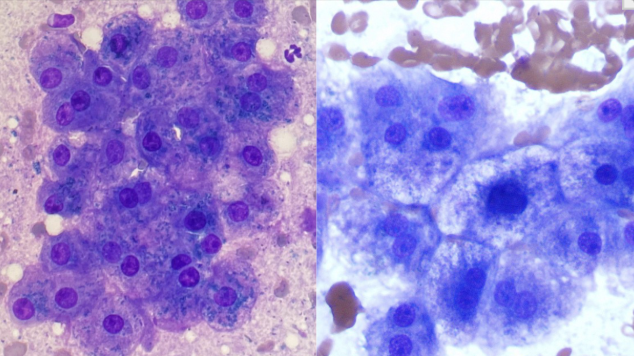
The cytology slide pictured is most consistent with which of the following cell types?
A. Epithelial neoplasia
B. Mesenchymal neoplasia
C. Lymphoma
D. Plasma cell
A. — hepatocellular carcinoma
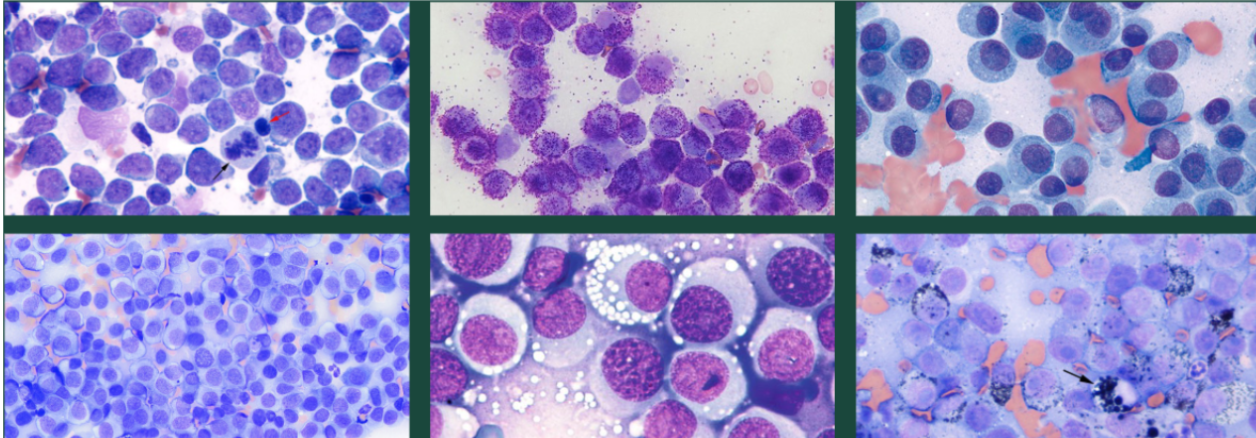
Label the round cell neoplasia
Lymphoma
Mast cell
Plasma cell
Histiocytoma
TVT
Melanoma
What approach do you choose when a dog has a single cutaneous mass that is less than 5 cm in diameter?
A. FNA to guide next step
B. Incisional biopsy to guide your next step
C. Excisional biopsy with submission for routine examination
D. Excisional biopsy with submission for routine examination including full margin evaluation
E. Excisional biopsy, but no further testing in order to keep costs low
A.
Which of the following statements is correct?
A. Bread loafing is least expensive method to evaluate margins
B. Tangential sections provide most accurate information regarding complete tumor excision
C. Tangential sections give distance of tumor to margins
D. Routine biopsies that provide tumor distance to margins include a full assessment of tumor margins
E. Knowing tumor distance to marks as determined in quarter and half sections if sufficient to determine complete excision
B.
Why perform an MCT prognostic panel?
A. To predict response to TKI therapy (Palladia)
B. To determine if additional local therapy is needed
C. To better predict survival time
D. All of the above
D.
T/F: PCR testing for lymphocyte clonality determines if a lymphoma is B cell or T cell in origin
False — IHC does
Malignant epithelial neoplasia is called:
Carcinoma
T/F: When sampling an ulcerative or necrotic lesion, a quality biopsy would include normal and diseased tissue
True
What is the appropriate tissue-to-fixative ratio for submitting most tissues for histopathology?
1 part tissue to at least 10 parts 10% neutral buffered formalin
Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding submission of eyes for histopathology?
A. All extraocular tissue should be removed prior to fixation
B. The globe should not be incised or injected for fixation
C. A 1:10 tissue-to-formalin ratio should be used
D. In winter, isopropyl alcohol should be added to the formalin specimen container
C. — 1:20 ratio
T/F: You can submit a spleen for histopathology in multiple sections
True — center of mass, borders of mass, hemangiosarcoma → around perimeter
Which of the following is NOT required when completing a histopathology submission form?
A. Signalment (age, breed, sex)
B. Relevant clinical history and reason for biopsy
C. Gross description of the sample submitted
D. Definitive treatment plan and prognosis
D.
Why is complete surgical margin evaluation often not recommended for soft tissue sarcomas?
Soft tissue sarcomas have tentacle-like microscopic projections that extend beyond the gross tumor margins, making complete margin assessment unreliable
What are the main disadvantages of cross-sectioning a tumor for margin evaluation?
Cross-sectioning assumes symmetrical, expansile tumor growth and only evaluates a very limited portion of the surgical margins, which can lead to inaccurate assessment of true tumor extent.
Which of the following tissue-processing methods is BEST for evaluation of lymph nodes?
A. Bread loaf sectioning
B. Tangential sections
C. Cross-sectioning (radial method)
D. Trimming
A.
Which marker is central to the melanoma prognostic panel?
Ki67