General Science
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Scientific Notation
To express a number in scientific notation, you move the decimal as many places as necessary until there is only one digit to the left of the decimal.
-For 832,000, you move the decimal to the left by 5 decimal places.
Momentum
Momentum equals mass (amount of matter in an object) times velocity (speed in a given direction).
velocity
speed in a given direction
a deciduous forest
a type of forest characterized by trees that lose their leaves seasonally, typically in the autumn

a tropical rainforest
Tropical rain forests are one of the most important areas on Earth. These special ecosystems are home to thousands of species animals and plants. Rain forests are not only densely packed with plants, but are also full of tall trees that form a ceiling from the the Sun above. This ceiling keeps smaller plants from growing. Areas where sunlight can reach the surface are full of interesting plants.

Tundra
a treeless plain especially of arctic regions having a permanently frozen layer below the surface soil and plant life made up mostly of mosses, lichens, herbs, and very small shrubs

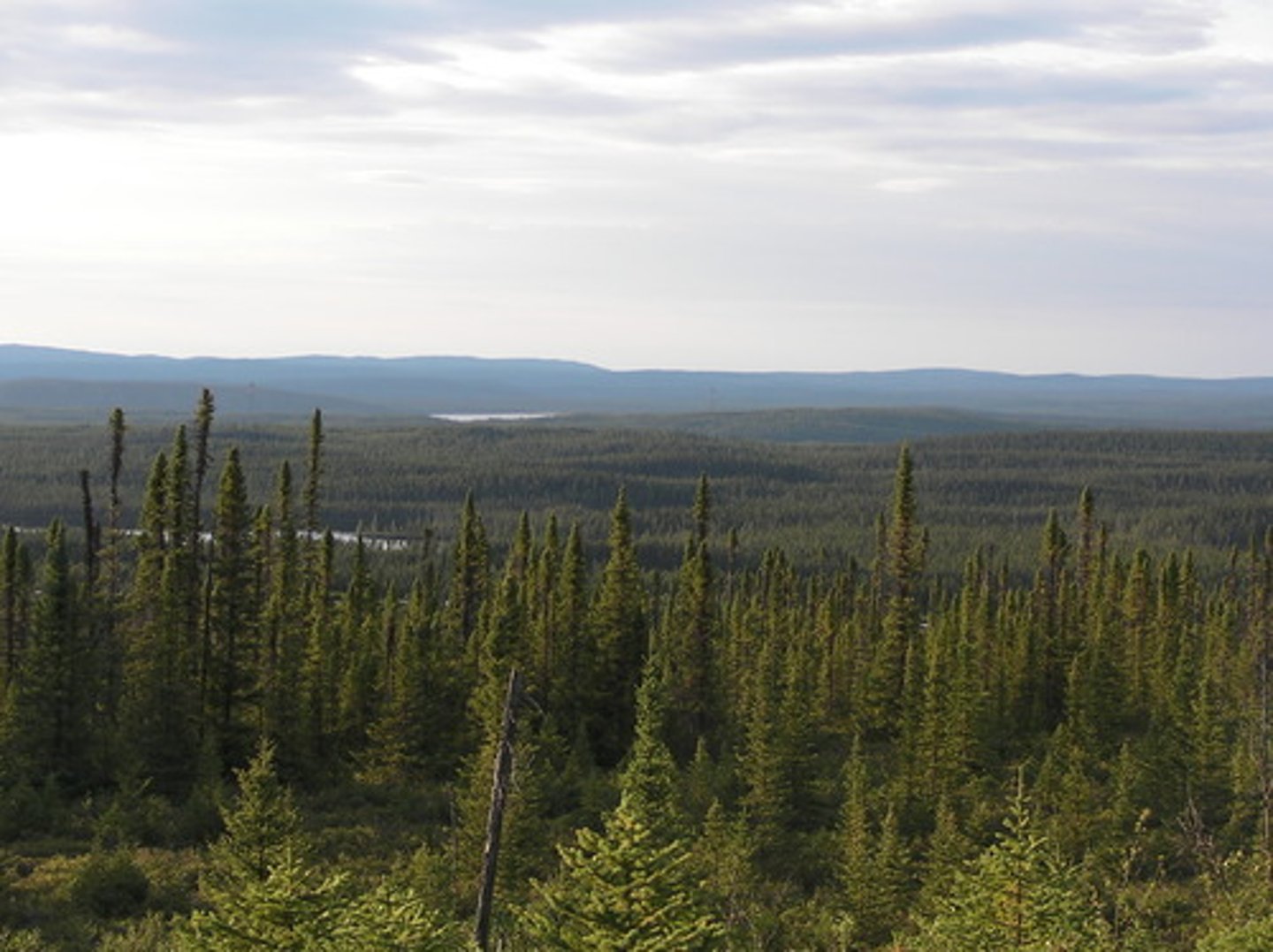
Taiga
a moist subarctic forest dominated by conifers (such as spruce and fir) that begins where the tundra ends.

unoxygenated blood
Unoxygenated blood (also called deoxygenated blood) is blood that has low oxygen content and high levels of carbon dioxide
veins
Veins carry blood devoid of oxygen to the right atrium of the heart.
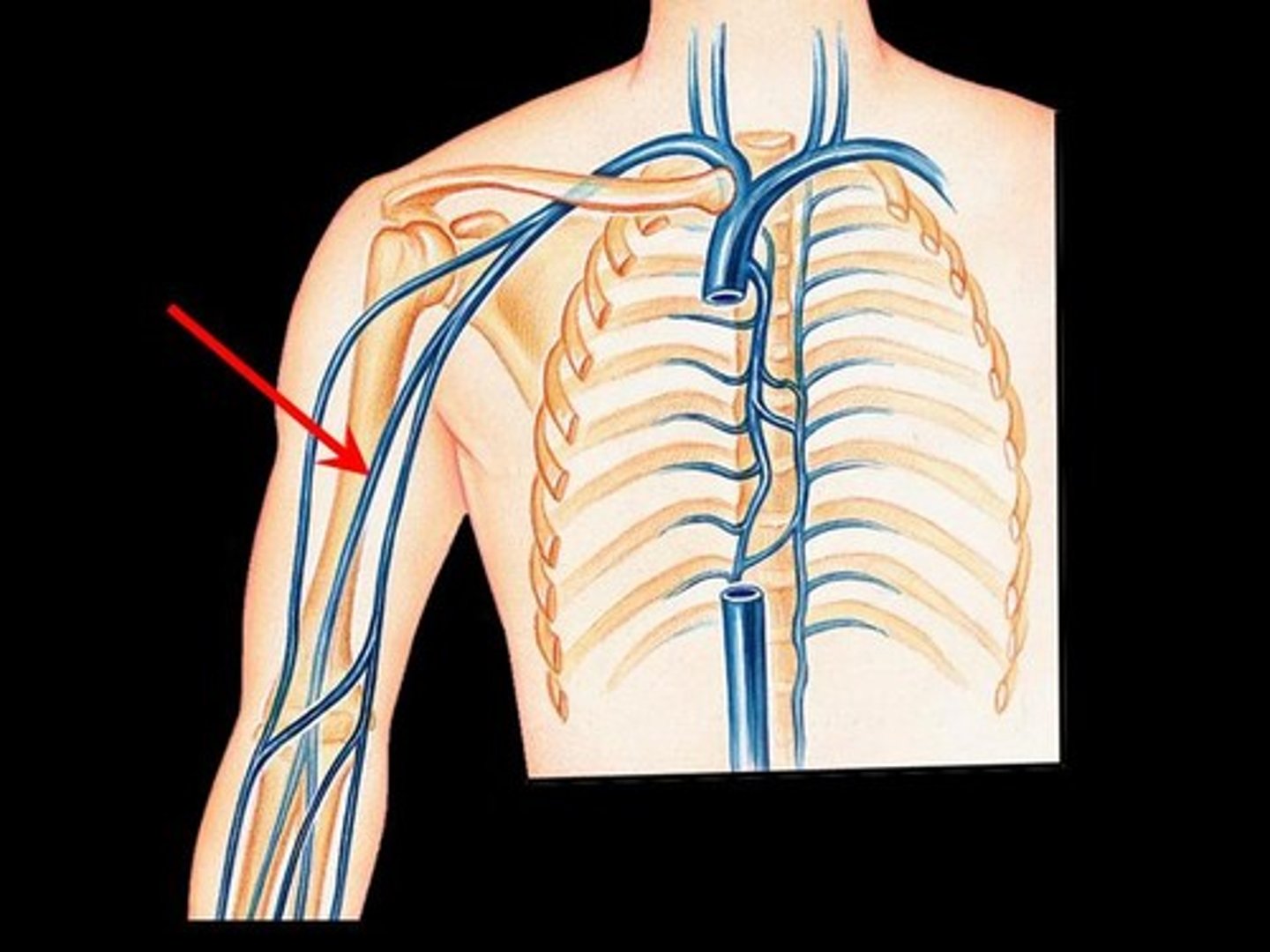
arteries
Arteries, capillaries, and the aorta carry oxygenated blood from the heart to blood cells throughout the body.
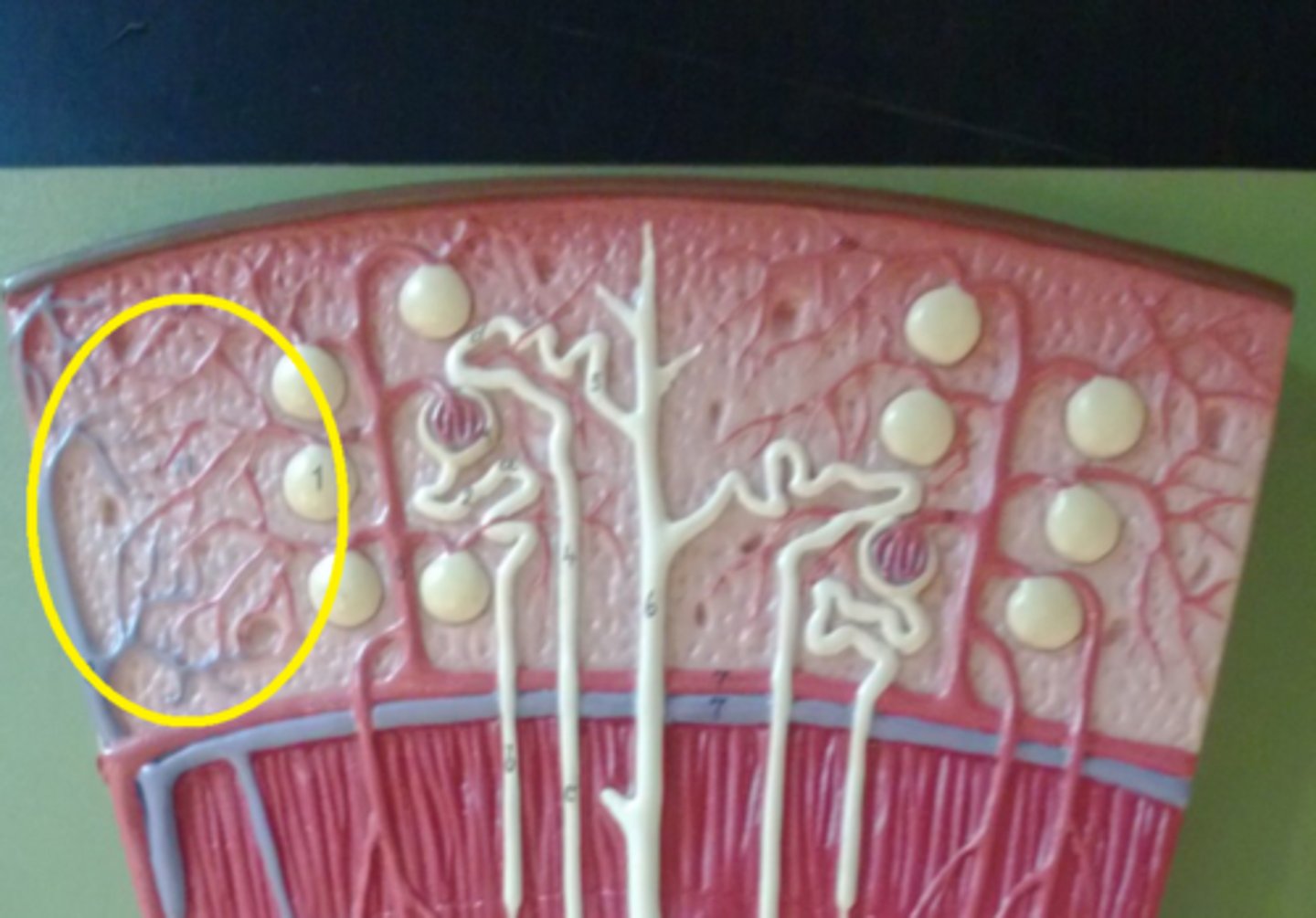
capillaries
Arteries, capillaries, and the aorta carry oxygenated blood from the heart to blood cells throughout the body.
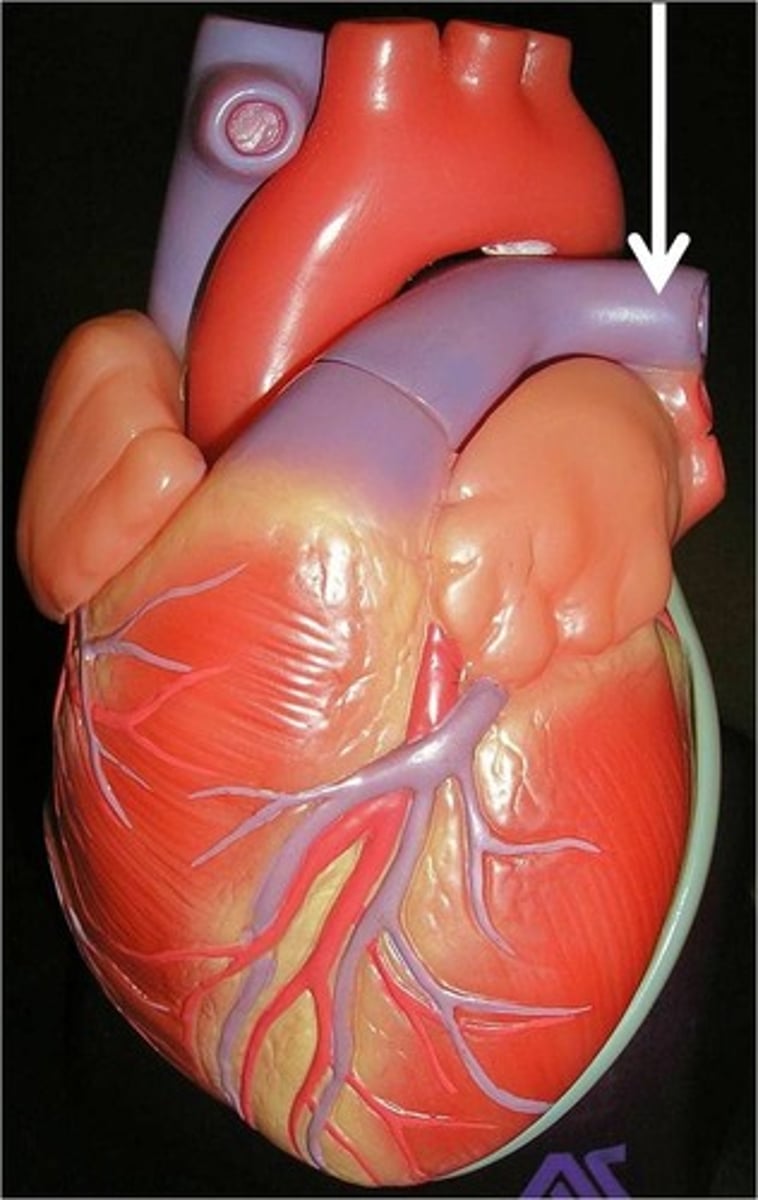
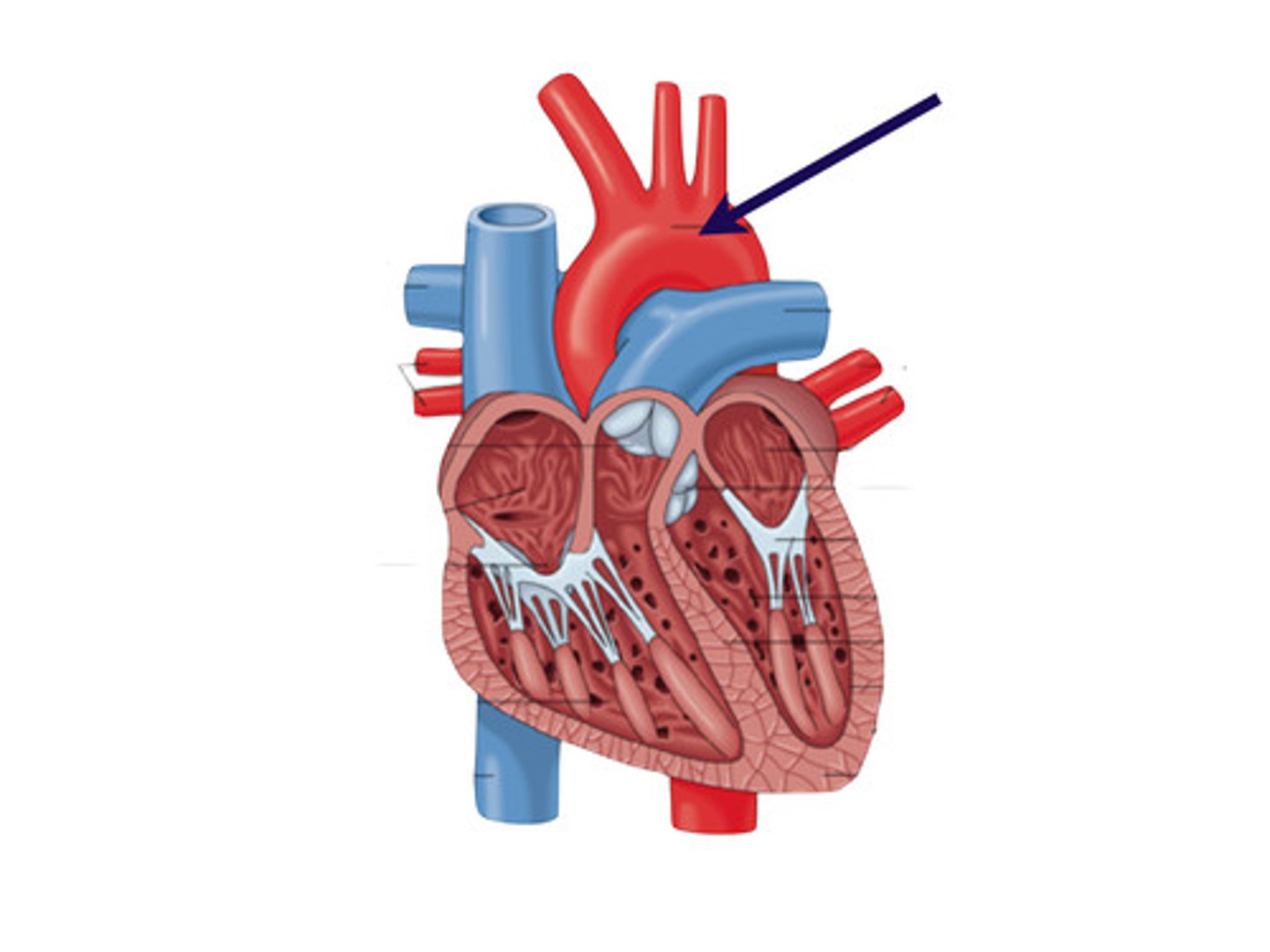
aorta
Arteries, capillaries, and the aorta carry oxygenated blood from the heart to blood cells throughout the body.
vertebrates
Vertebrates are animals that have a backbone or spinal column
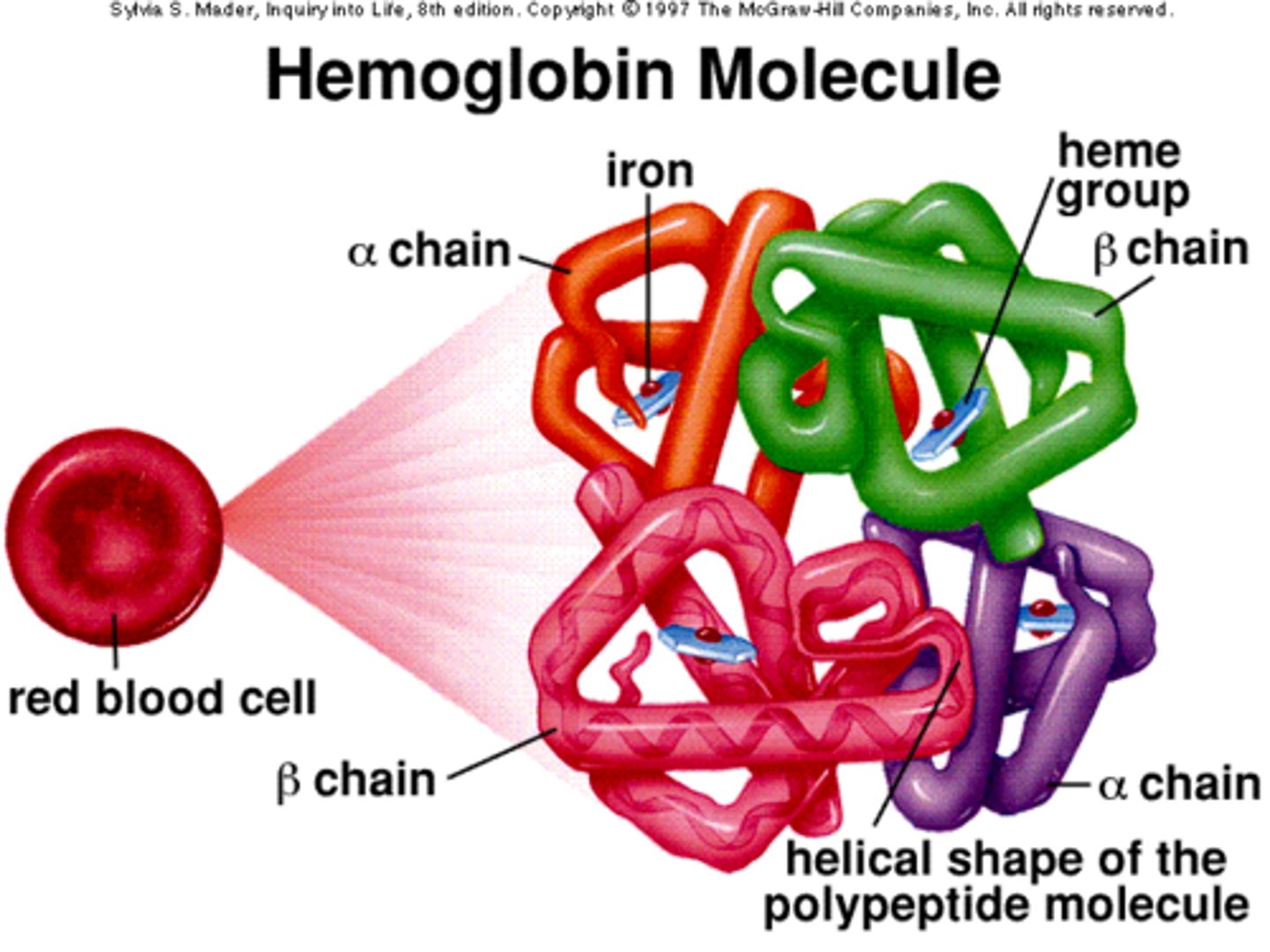
heoglobin
Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that is responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body and returning carbon dioxide back to the lungs to be exhaled.
carotene
Carotene is a natural pigment found in many plants and fruits, especially those that are orange, yellow, or red. It belongs to a group of compounds called carotenoids.
dopamine
Dopamine is a chemical messenger (neurotransmitter) in the brain that plays a major role in how we feel pleasure, motivation, and reward. It also helps regulate movement, mood, attention, and learning.
melanin
Melanin is a natural pigment found in the skin, hair, and eyes of humans and animals. It's what gives them their color.

hemoglobin
Hemoglobin, used by all vertebrates and some invertebrates to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body, gives red blood cells their color.
On the pH scale, any substance below what number is considered acid
The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is considered neutral. Anything below 7, then, is acidic. 0-6.9
Dna has which of the following structures
a double helix
-The Watson-Crick model of DNA is a double-stranded twisted ladder, or double helix.
a helix
A helix is a spiral-shaped structure, like a coil or spring. It's a common shape in nature and science.
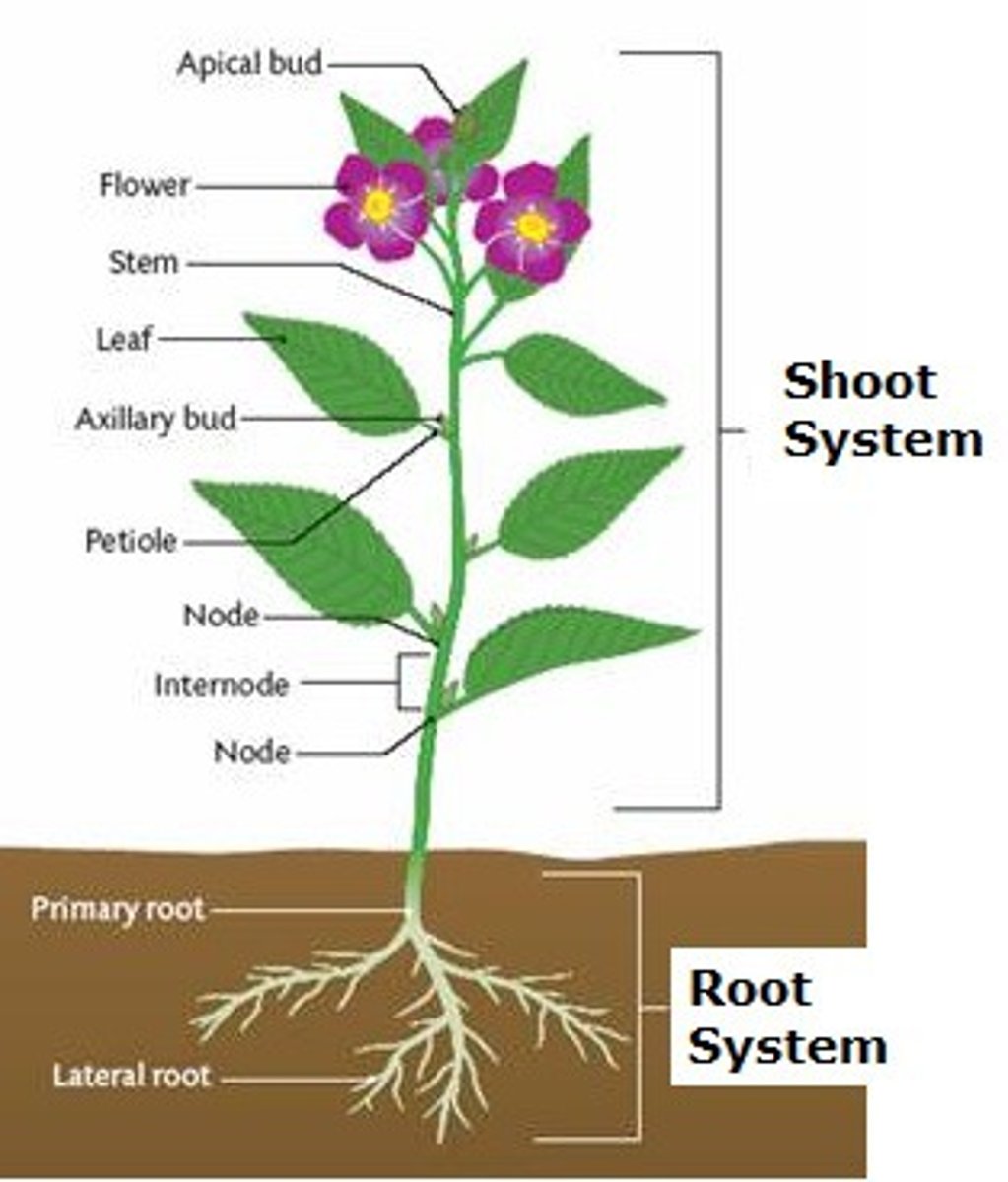
Vascular system in plants
The vascular system in plants is a network of tubes that transports water, minerals, and nutrients throughout the plant — kind of like a plant's version of blood vessels.
anticoagulant
An anticoagulant is a substance that stops blood from clotting
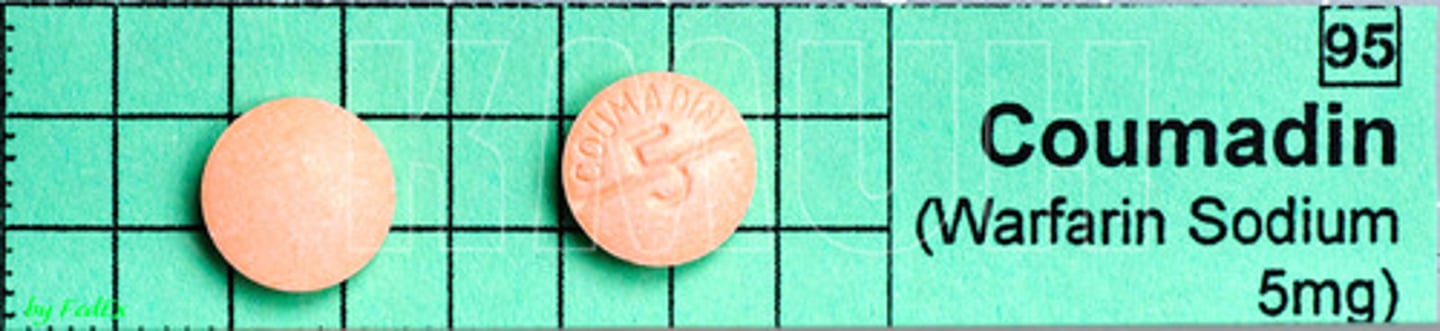
Heparin is an anticoagulant. What is the primary purpose of drugs like Heparin
To prevent the blood from clotting
glucose (C6H12O6)
Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) is a simple sugar and a key source of energy for living organisms.
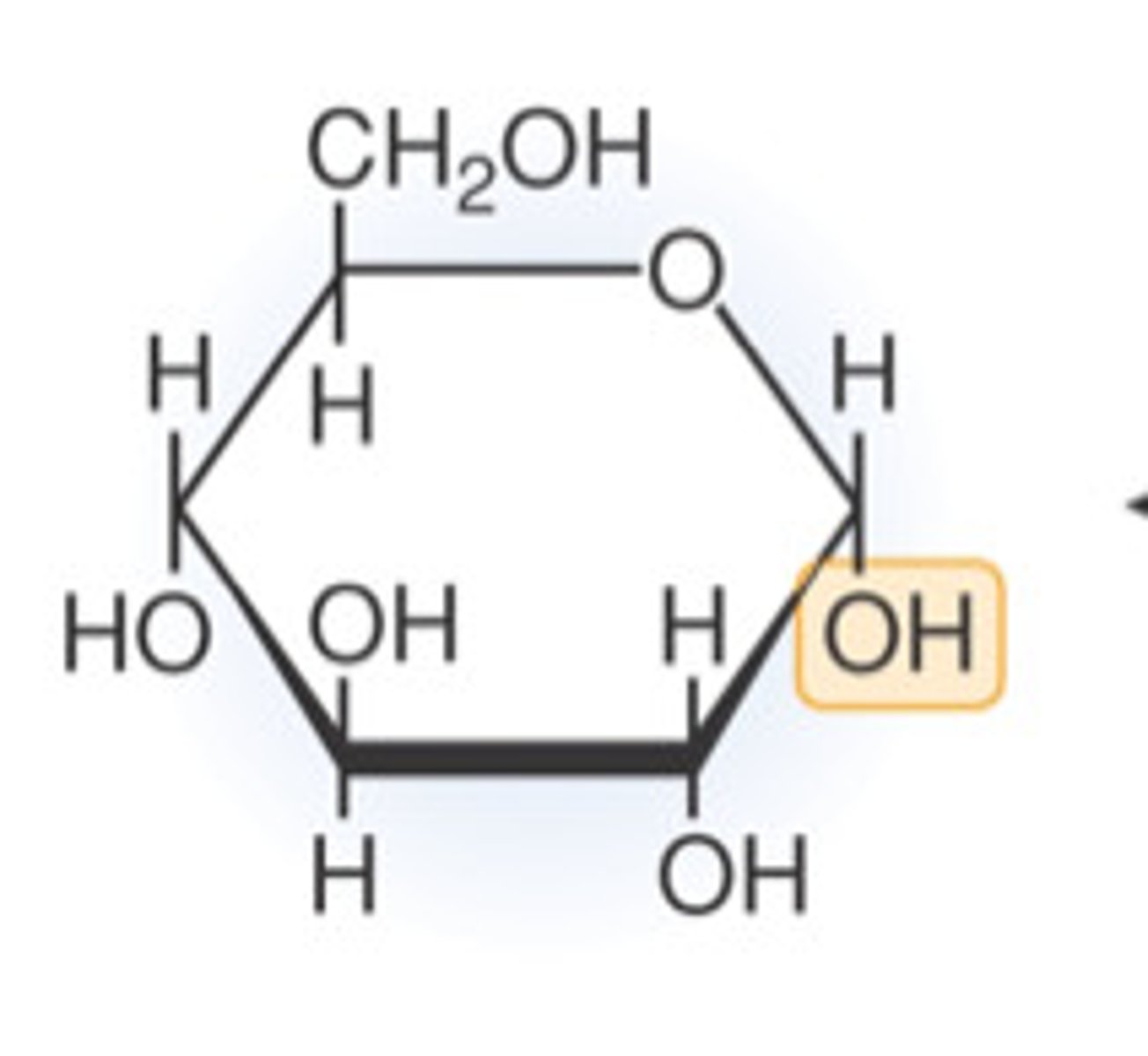
Which of the following is an organic compound?
glucose (C6H12O6)
-All organic compounds contain carbon (C). Potassium (K) is only a single element, and it does not contain carbon.
Latitude
Latitude is a geographic coordinate that tells you how far north or south a place is from the Equator.
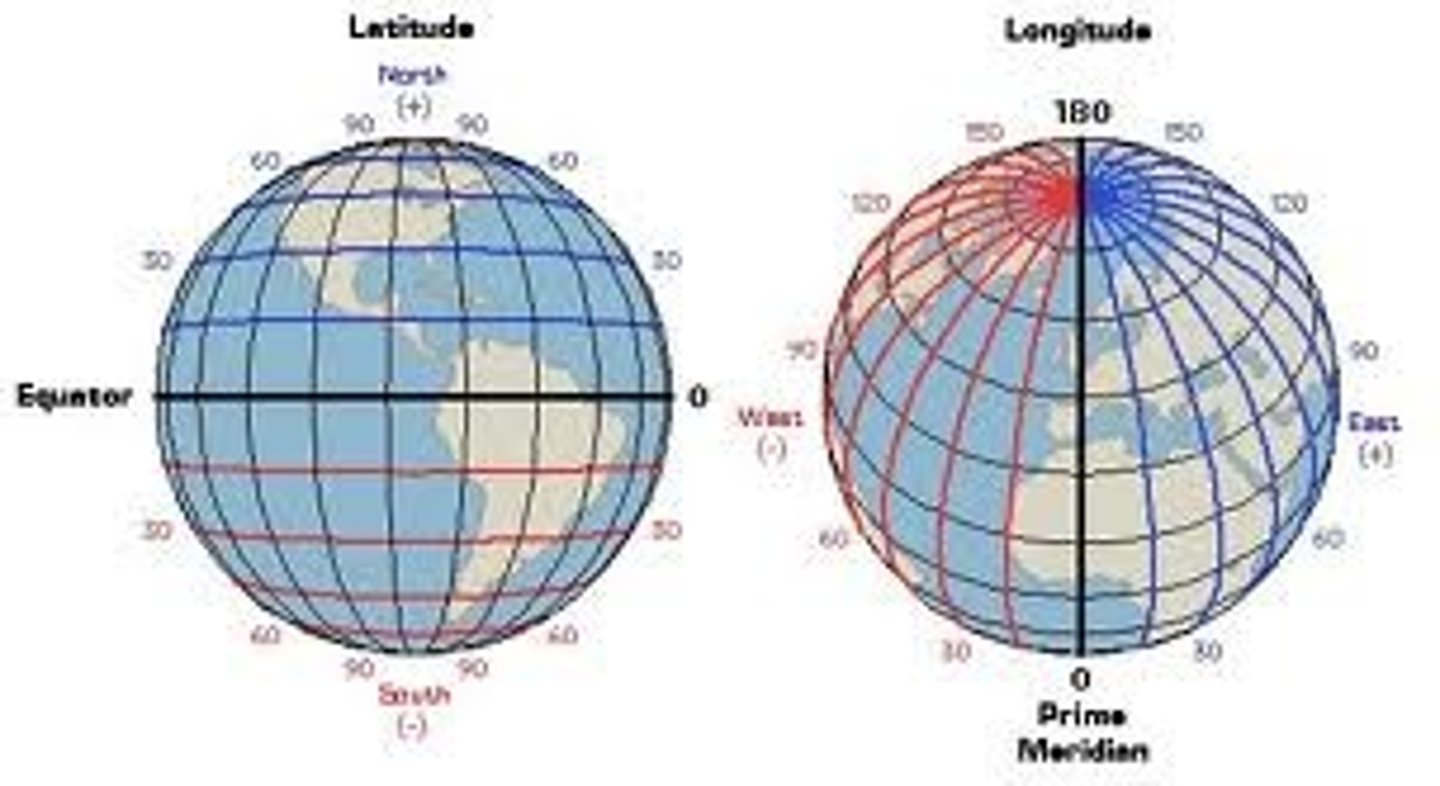
Longitude
Longitude is a geographic coordinate that tells you how far east or west a place is from the Prime Meridian.
-The longitude of a point on Earth's equator can be any value between 0° and 180° east or west — because longitude measures east-west position, and the equator only tells us the latitude (which is always 0°).
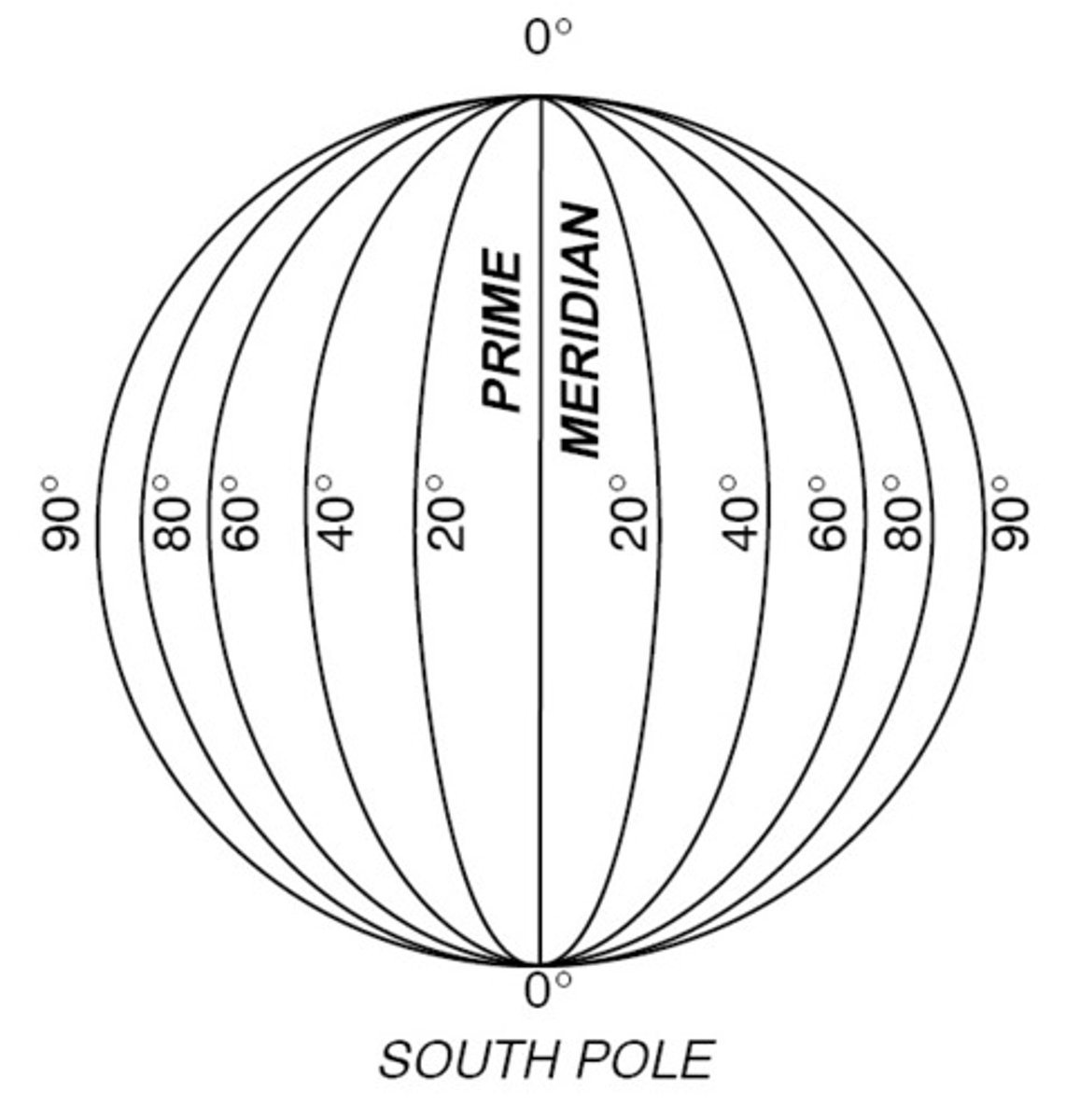
What is the latitude of any point on the earth's equator
0
-All points on the equator have a latitude of 0 degrees. The North Pole has a latitude of 90 degrees North. The South Pole has a latitude of 90 degrees South.
anemoneter
Measures wind speed

Hygrometer
measures humidity

Barometer
measures air pressure or atmospheric

Thermometer
Measures temperature
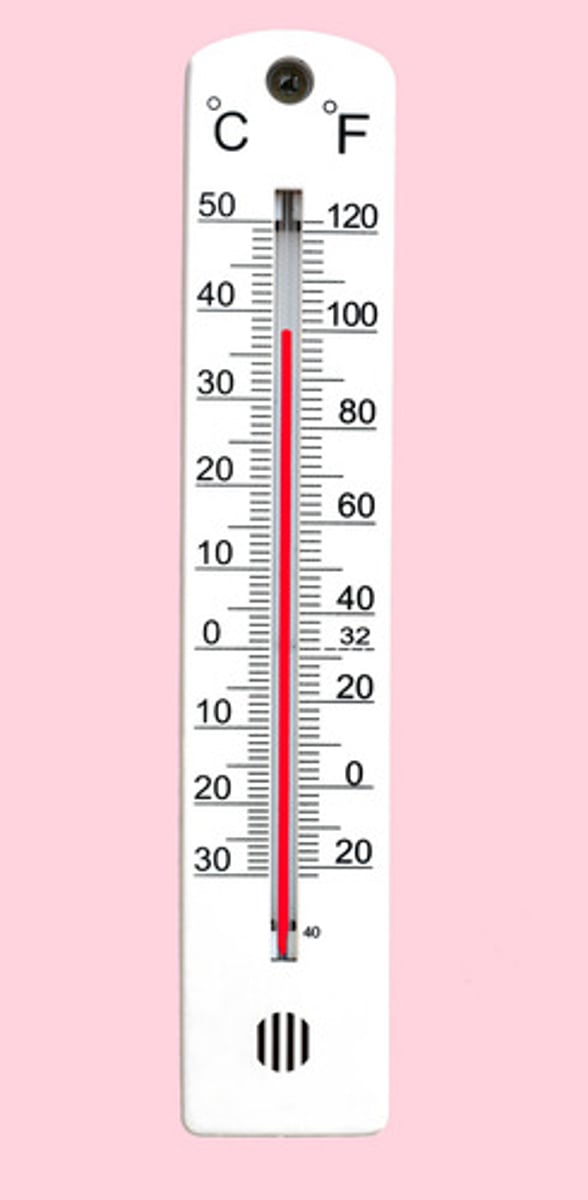
On the pH scale, any substance above 7 is considered
Basic (alkaline)
-7.1-14
pH
pH stands for "potential of hydrogen" or "power of hydrogen". It is a scale used to measure how acidic or basic (alkaline) a solution is.
pH affects chemical reactions, plant growth, digestion, enzyme function, and more.
- 7 netural, pure water
Earthquake scale
3.0 = minor
5.0 = moderate
7.0+ = major and potentially destructive
-Richter Scale (Magnitude)
Measures the energy released at the earthquake's source
How many bones does the human body have
206
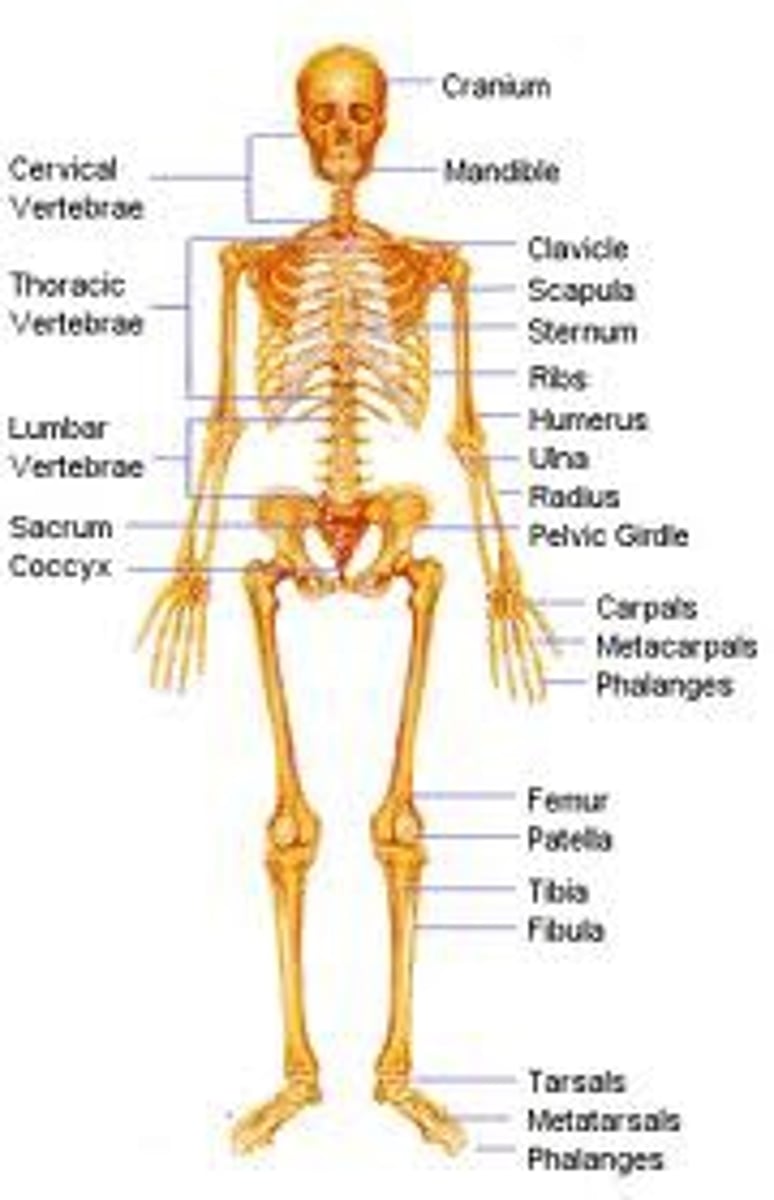
how bones do babies have
300 bones
How many teeth do adults have?
32
How many teeth do kids have
20
-Children typically have 20 primary (baby) teeth. These teeth usually erupt between the ages of 6 and 30 months. By the age of 3, most children have a full set of 20 baby teeth. As children grow older, their baby teeth are gradually replaced by 32 permanent teeth.
Torando scale
*EF0, 65-85 mph (105-137 km/h)Light damage - broken branches, minor roof damage
*EF1, 86-110 mph (138-177 km/h)Moderate damage - roof tiles off, moving cars
*EF2, 111-135 mph (178-217 km/h)Considerable damage - roofs torn off, trees uprooted
*EF3, 136-165 mph (218-266 km/h)Severe damage - entire buildings destroyed
*EF4, 166-200 mph (267-322 km/h)Devastating - houses leveled, cars thrown
*EF5, Over 200 mph (322+ km/h)Incredible - strong structures completely destroyed
-The tornado scale most commonly used is the Enhanced Fujita (EF) Scale, which rates tornadoes based on the damage they cause, which helps estimate their wind speeds.
Flood scale
he flood scale is used to describe the severity of a flood based on water levels, impact, and risk to life or property. While there's no universal flood scale like the Richter scale for earthquakes, most regions use a 3-level classification based on river height and effects.
1-4
Flood stage = 10 meters
10.1-11.0 m = Minor 1
11.1-12.5 m = Moderate 2
12.6+ m = Major 3
Extreme 4
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight to make their own food by converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose (sugar) and oxygen.
Photosynthesis equation
6CO2+6H2O+sunlight energy→C6H12O6+6O2
CO₂ = Carbon dioxide (from the air)
H₂O = Water (from the soil)
C₆H₁₂O₆ = Glucose (plant food/energy)
O₂ = Oxygen (released into the air)
How many chromosomes do humans have?
40 chromosomes, 23 pairs
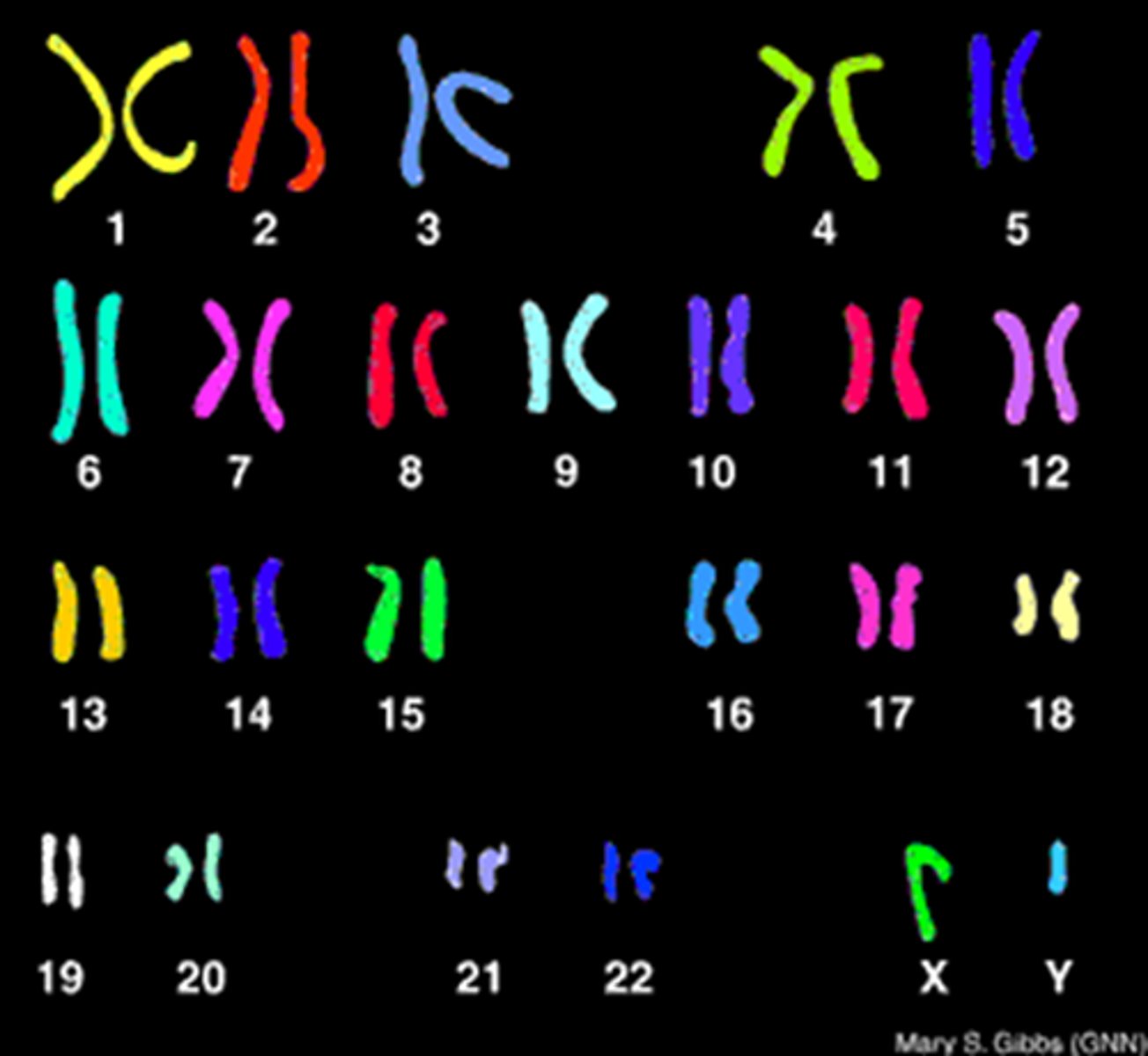
Which chromosomes do you inherit from your parents
XX = Female
XY = Male
An X chromosome from your mother
An X or Y chromosome from your father, which determines your biological sex
Hibernation
Hibernation is a state of deep rest or sleep that some animals enter during winter to survive cold temperatures and food shortages.

Nocturnal
Nocturnal means active at night and resting during the day.

How many planets are there? What's their order (closest to the Sun)?
8 Planets
1.Mercury
2. Venus
3. Earth
4. Mars
5. Jupiter
6. Saturn
7. Uranus
8. Neptune
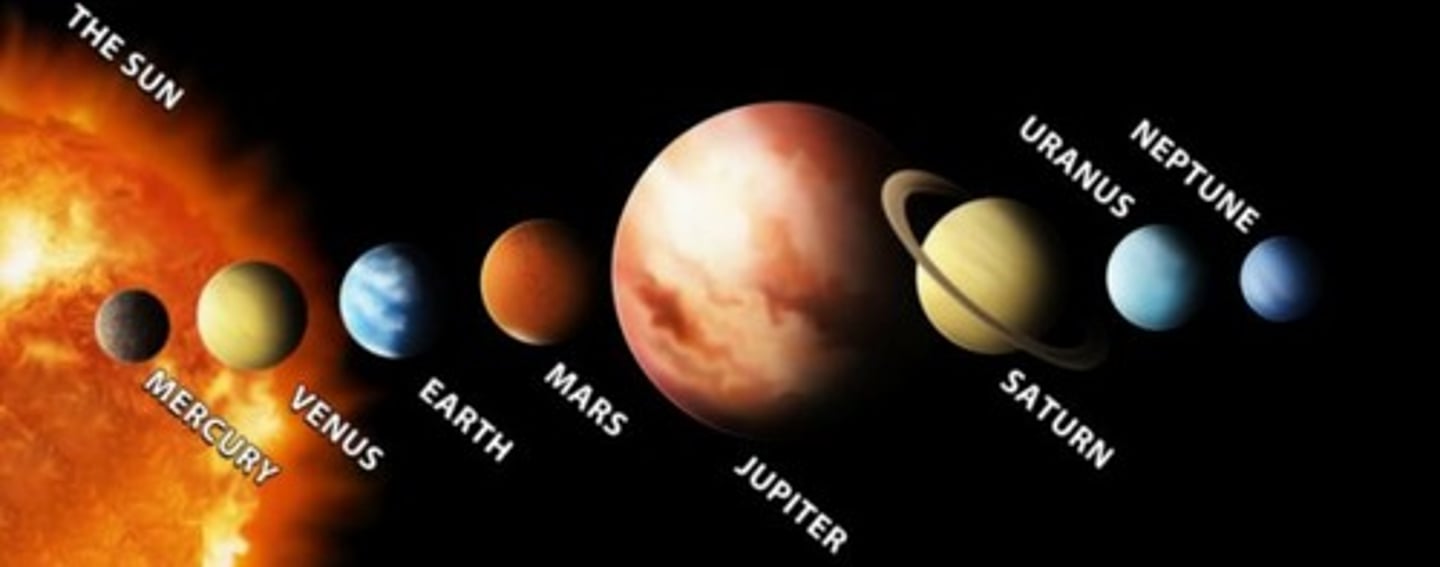
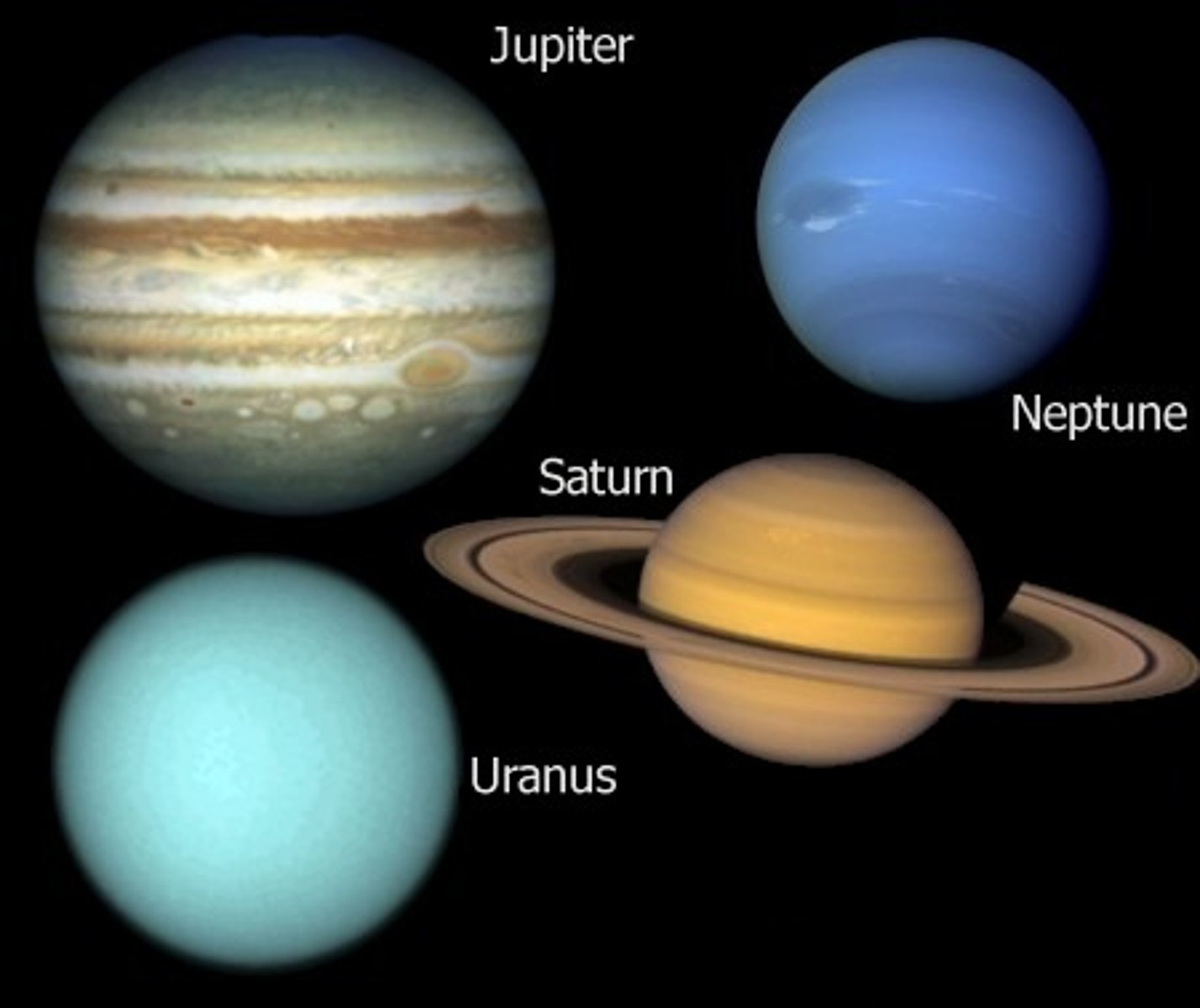
which planets have rings?
1. Jupiter - Has faint, thin rings made of dust
2. Saturn - Has the most visible and largest ring system, made of ice and rock
3. Uranus - Has dark, narrow rings, hard to see
4. Neptune - Has faint, dusty rings with some bright arcs
