Zoology
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
hierarchy of biology organization
atoms → bio molecules → subcellular organelles → cells → tissues → organs → organ system → organism → group → population → community → ecosystem → biome → biosphere
emergent properties of systems
arise from interactions between components
H-Bs, spontaneous peptide folding
kingdoms
bacteria
archaea
eukarya
plantae
fungi
animalia
protists
Darwin’s natural selection observations
individuals in a population vary in heritable traits
populations potentially produce far more than they can support
2 methods of classification
phenetic - species grouped by overall similarity
phylogenetic - classified by shared ancestors
agreement vs disagreement between phenetics and phylogenetics
agree
constant rate of evolution
divergent evolution
disagree
differential evolution rate
convergent evolution
cladistics
relationships determined by synapomorphies
synapomorphies
shared, derived characteristics
pleisiomorphic
primitive/original state
apomorphic
derived state
autapomorph
trait unique to a taxon
synapomorph
trait derived from nearest common ancestor
Symplesiomorph
trait derived from older common ancestor
monophyletic
clades sharing synapomorphies
Non-monophyletic clades
share symplesiomorphies, due to convergent evolution
paraphyletic group
a group containing a hypothetical common ancestor + some, but not all, of its descendants
polyphyletic
a group of taxa not including their hypothetical common ancestor
protist nutrition
some aerobic
some photoautotrophs
some heterotrophs
a few mixotrophs
euglena
a mixotrophic protists that absorbs organic material from the environment when no light is available
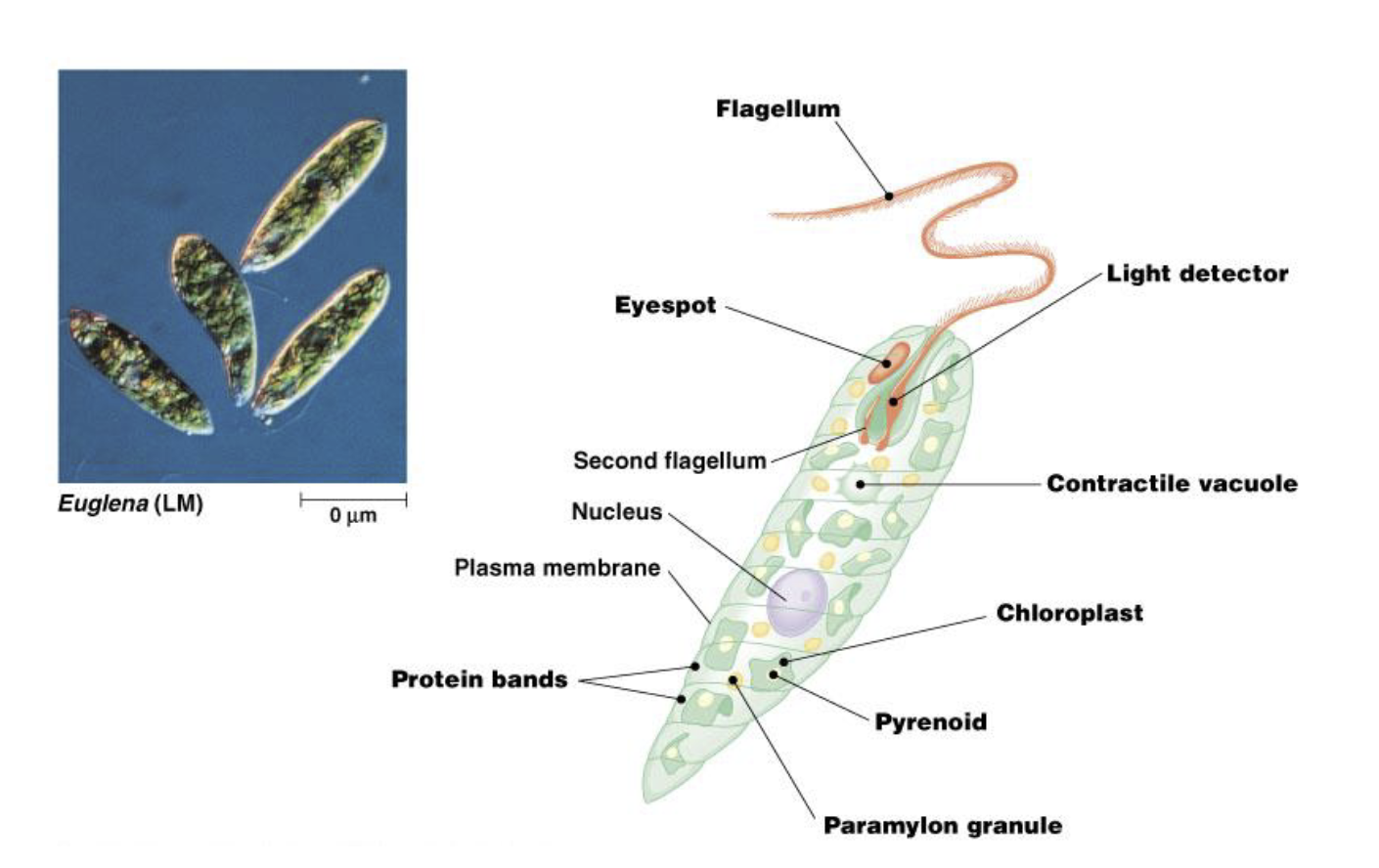
protozoa defining characteristics
unicellular eukaryotes without collagenous and chitinous cell walls
non-photosynthetic in primitive condition
plasmalemma
outer membrane of protists
protists cytoplasm components
ectoplasm - gelatinous outer layer
endoplasm - inner fluid region
spongiome
system of tubules and vacuoles that collects water in protists
contractile vacuoles
expel excess water from cytoplasm of protists (osmotic regulation)
galvanotaxis
electrical stimulus
geotaxis
gravity stimulus
thigmotaxis
touch stimulus
rheotaxis
currents stimulus
ciliates
phylum ciliophora
live solitary in fresh water
externally ciliated body some point during life
reproduce via binary fission
ciliary movement
power stroke followed by recovery stroke
Metachronal Rhythm
beat of cilia where wave moves through it one way and the organism is propelled the opposite direction
paramecium
cilia used to draw in food along oral groove
expel water via contractile vacuole
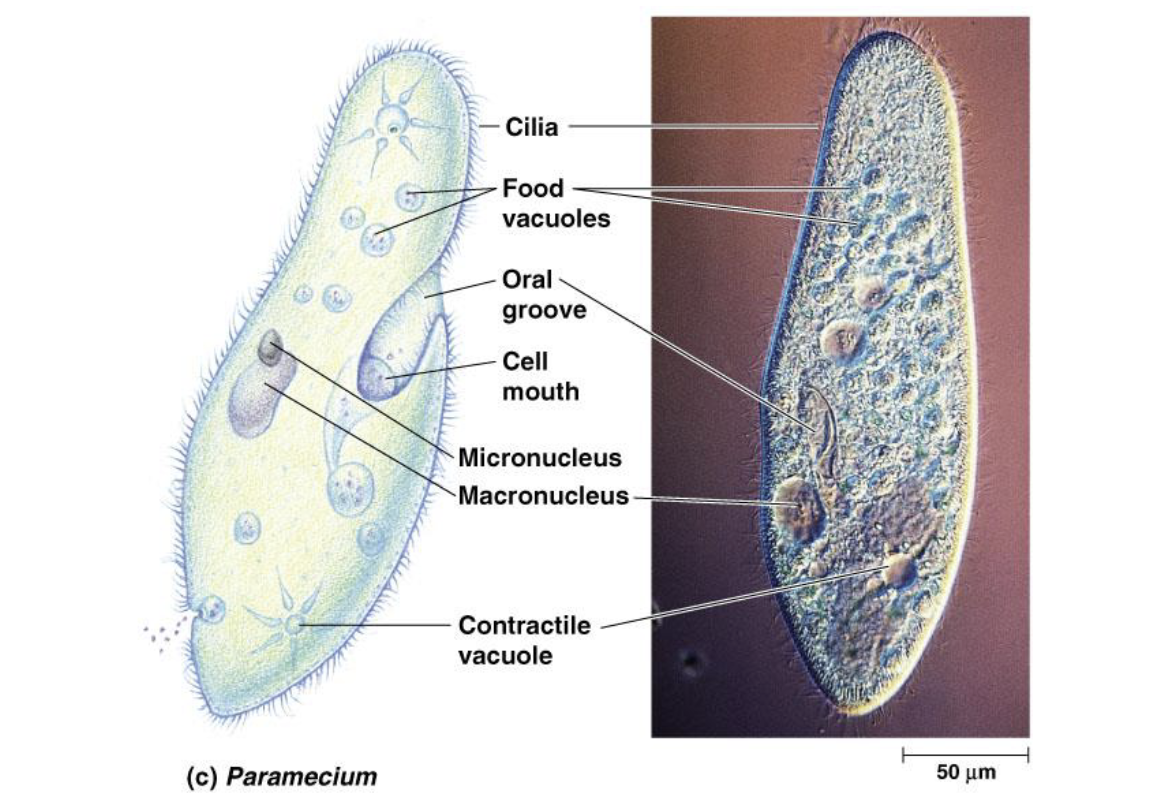
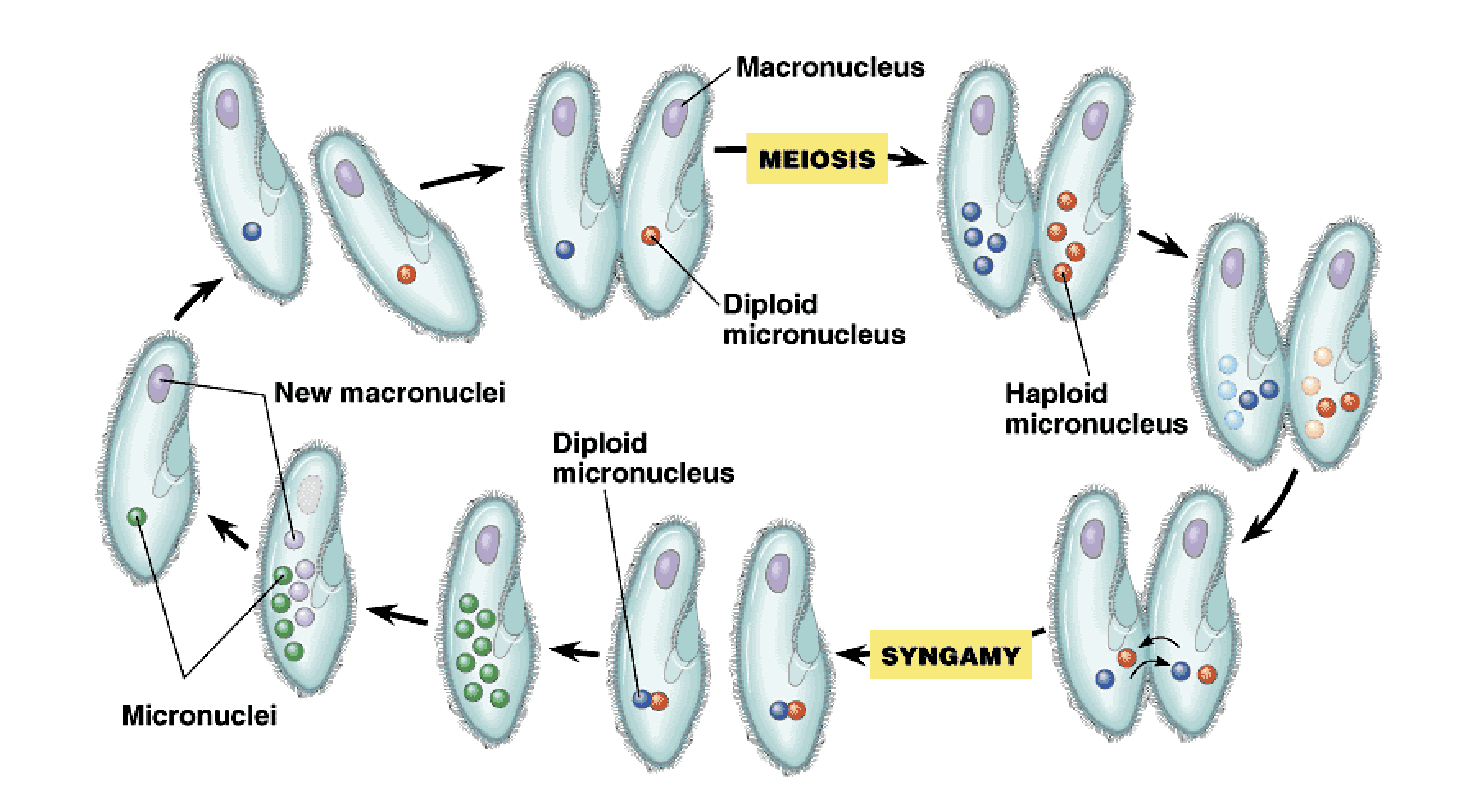
macronucleus
50+ copies of genome
control everyday function by synthesizing RNA
necessary for asexual reproduction
micronuclei
1-80 copies
required during sexual process to create genetic variation
conjugation
sexual shuffling of genes in protists where micronucleus undergo meiosis and are exchanged
pseudopodia
cellular extensions used to move and feed
Sarcodinids
amoeboid protozoans
have pseudopodia
most free-living
2% parasitic
Amoebozoa
protozoans
inhabit freshwater, marine, and soils
most are free-living heterotrophs
called amoeboid due to constantly changing body
most naked, some have a test (shell)
posses pseudopodia for movement/feeding
Class Archamoebae
phylum amoebozoa → protozoans (kingdom)
Class Mycetozoa
phylum amoebozoa → protists
cellular and acellular slime molds
Entamoeba histolytica
parasite that causes amoeboid dysentery via contaminated water/food/utensils
AMEBIASIS
amoeboid dysentery caused by Entamoeba histolytica
test (shell)
secreted by body or consists of small sand/particles
cytoplasmic streaming
pseudopodia emerges → anchor its tip → streams more cytoplasm into pseudopodia
involves transition between gel and solid form
mimivirus
virus that infects ameboid
larger genome than many bacteria - blurs barrier between viral and cellular world
encodes a few proteins involved in protein synthesis that belong to a set of universally conserved genes in cellular life
acquired genes from HGT from ameboid hosts
sputnik
grows in mimivirus-infected amoeba to decrease yield of mimivirus
slime molds classification
class mycetozoa → phylum protozoa
Mycetozoa
slime molds → convergent role in decomposition of organic material
feed and move via pseudopodia (like amoeba), but protein sequences close to fungi and animals
plasmodial slime molds classification
Myxogastrida → class mycetozoa → phylum amebpzpa → protists
plasmodial slime molds
brightly pigmented heterotrophic organisms
feeding stage is amoeboid mass, plasmodium
plasmodium
single mass of cytoplasm with multiple nuclei
diploid nuclei undergo synchronous miotic divisions thousands of times
cytoplasmic streaming distributes nutrients/O2 in cytoplasm
phagocytosis food from: moist soil, leaf mulch, rotting logs
differentiates into stages for sexual reproduction when habitat dries/food disappears
cellular slime molds
Dictyostelida → Mycetozoa → amebozoa → protozoa
feeding stage - solitary
form aggregate unit when food is scarce - pseudoplasmodium
pseudoplasmodium
aggregate that forms when food is scarce in cellular slime molds
each cell remains its identity
aggregates of amoebas form fruiting bodies → produce spores in asexual reproduction
acrasin
cAMP in clime molds
phylum radiozoa
radiolarians (7700 fossil, 3300 extant)
acantharians (500 extant)
perforated membrane separated in 2 zones
intracapsular - nucleus
extracapsular - food vacuoles and digestion
axopodia - psudopodia supported by thin microtubules
rigid exoskeleton
silica - radiolarians
strontium sulphate - acantharians
acantharians classifications
in phylum radiozoa → protozoa
radiolarians classification
phylum radiozoa → protozoans
axopodia
pseudopodia supported by thin microtubules, in radiozoans
Heliozoa
protists
sun animals, life in fresh water
skeleton is unfused siliceous or chitinous plates
distinct inner and outer region with no physical boundary
reproduce via autogamy
foraminifera
protists
mostly marine and benthic (live in sand or attach to rock/algae)
some abundant in plankton
multichambered porous shells consisting of materials hardened by calcium carbonate
shells referred to as tests since some forms the protoplasm covers exterior of shell
pseudopodia (reticuopodia) extend through pores for
swimming
shell formation
feeding
symbiotic with algae
reticulopodia
pseudopodia that extends through pores in forams for swimming, shell formation, and feeding
flagellated protozoa
pedicle and one+ flagella
flagella longer and fewer than cilia + have hair like projections
Trichozoa
mostly symbiotic
hydrogenosomes instead of mitochondria
Trichomonadea classification
subphylum parabasal → phylum Trichozoa → flagellated protozoa
Trichomonas vaginalis
infect vaginal lining if acidity is disrupted
infect male urethrae without symptoms
spread sexually
saccostomae
kinetoplastids
phylum euglenozoa → flagellated protists
single large mitochondrion with unique organelle kinetoplast
symbiotic and include pathogenic parasites
kinetoplast
housed extracellular DNA
found in saccostomae (kinetoplastids)
metamonada
multiple flagella (2,4,8)
lack mitochondria
intestinal symbionts
ex Giardiais
Giardiais
parasite that infects human intesine, in phylum metmonada
Dinoflagellates
abundant components of phytoplankton
foundation of food chains
some heterotrophic
most unicellular, some colonial
characteristic shape reinforced by internal plates of cellulose
2 flagella sit in grooves of armor and spin it
lead to blooms that produce toxins
deadly to fish and humans
some bioluminescent driven by ATP
sporozoa / apicomplexa
spore forming protozoa
endoparasites of animals
intricate life cycle with sexual and asexual stages
requires 2+ hosts for completion
2 major groups
gregarines - parasites of insects/invertebrates
coccidians - parasites of invertebrates (intermediate hosts) and vertebrates
subphylum coccidiomorpha
plasmodium, parasite that causes malaria
in phylum sporozoa
plasmodium falciparum life cycle
malaria
sexual cycle (in mosquito)
female mosquito bites human and ingest gametocytes oocyst → sporogony occurs → sporozoites develop in oocyte → migrate and released in salivary gland
Asexual cycle (in human)
sporozoite released in saliva → migrate to liver → enter liver cells and undergo schizogony → merozoites released
in RBC
→ merozoites enter blood cells and undergo schizogony → macrogametocyte → microgametocyte → trophozoite → merozoites released and cycle continues
choanoflagellates
metazoans
150 spp
no fossil record
smore secrete delicate Loricae
outer coverings of interwoven silica bars
some are colonial for part of their life (proterospongia)
proterospongia
choanoflagellates → metazoans
colonial for part of their life
cells embedded in jelly-like matrix
primitive cell differentiation
flagellated cells with colors move colony through water
amoeboid cells on inside grow and divide to grow colony
protostome development
spiral and determinate cleavage
schizocoelous
solid masses of mesoderm spits to form coelom
blastopore → mouth
deuterostomes development
radial and intermediate cleavage
enterocoelous
folds of archenteron forms coelom
blastopore → anus
occluding cell junction
seal off intracellular space from environment
septate junctions - all invertebrates
tight junctions - vertebrates, tunicates, some arthropods
desmosomes cell junctions
used for adhesion
gap junctions
chemical and electrical communication → in hydrozoa and bilateria
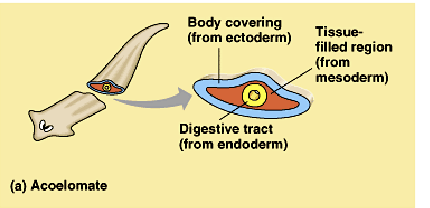
acoelomate
body covering from ectoderm
tissue filled region from mesoderm
digestive tract from endoderm
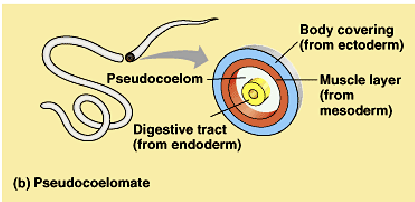
pseudocoelomate
body covering from ectoderm
muscle layer from mesoderm
digestive tract from endoderm
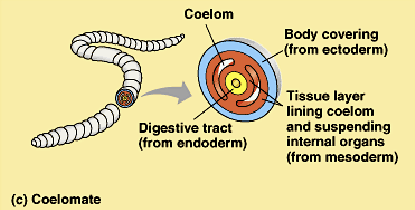
coelomate
body covering from ectoderm
tissue layer lining coelom and suspending organs from mesoderm
digestive tract from endoderm