Physics & Weather Test Review
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/78
Earn XP
Last updated 10:48 PM on 2/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
1
New cards
Force
Push or pull
2
New cards
Mass
The amount of matter in an object.
3
New cards
Net Force
the sum of all forces acting on an object
4
New cards
Equilibrium or Balanced Force
the state in which the net force on an object is zero/combined forces that result in a zero net force on an object
5
New cards
Unbalanced Force
combined forces that result in a non-zero net force on an object.
Can cause objects to accelerate.
Can cause objects to accelerate.
6
New cards
Normal Force
the perpendicular force that a surface exerts on an object that is pressing on it
7
New cards
2. George was walking with a force of 10 Newtons. All of a sudden, a strong gust of wind with a force of 5 Newtons started in the opposite direction. How did this affect George?
The gust of wind will cause George to slow down.
8
New cards
David kicked a soccer ball. Name some unbalanced forces that could cause it to stop.
**friction** from grass, pebbles, etc; **air resistance**; **gravity**
9
New cards
Ms. Bottin went to the grocery store. She grabbed an empty shopping cart, which had a mass of 14 kg. While walking down one of the aisles, she noticed a full shopping cart that had a mass of 25 kg. If Ms. Bottin applied the same force to both shopping carts, which one would accelerate faster? Explain why.
**The 14 kg shopping car would accelerate faster since it has a smaller mass.**
10
New cards
2. Trent decided that he wanted to learn how to skateboard. He applied force to his back foot, so he could roll forward. How is this an example of action-reaction?
Action - he pushed back
Reaction - he goes forward
\
Reaction - he goes forward
\
11
New cards
Identify if the following refers to speed, velocity, or acceleration.
speed, velocity, or acceleration.
15 mph
speed, velocity, or acceleration.
15 mph
Speed
12
New cards
Identify if the following refers to speed, velocity, or acceleration.
speed, velocity, or acceleration.
\
32 m/s east
speed, velocity, or acceleration.
\
32 m/s east
Velocity
13
New cards
Identify if the following refers to speed, velocity, or acceleration.
speed, velocity, or acceleration.
\
12 cm/s2
speed, velocity, or acceleration.
\
12 cm/s2
Acceleration
14
New cards
A car travels 528 km in 6 hours. Calculate the car’s speed.
S=D/T
88 km/h
88 km/h
15
New cards
A soccer ball takes 20 s to roll 10 m. What is the average speed of the soccer ball?
S=D/T
0\.5m/s
0\.5m/s
16
New cards
How is velocity different from speed?
Velocity is a vector that contains a direction, speed does not.
17
New cards
What are the two ways you can change acceleration?
Acceleration is when objects change in speed (speed up, slow down),
or change direction.
or change direction.
18
New cards
Joanne was riding her bike down a steep hill. As she rides down the hill, what happens to the amount of potential energy and what happens to the amount of kinetic energy?
**The potential energy turns into kinetic energy!**
19
New cards
Examples Of Conduction
Example 1: heat from mug of hot chocolate warming your hands
Example 2: a pan on the stove gets warm from the heat coils
Example 2: a pan on the stove gets warm from the heat coils
20
New cards
**Examples of Convection**
Example 1: warm air rising and cool air sinking in your home.
Example 2: water boiling, steam rising, etc..
Example 2: water boiling, steam rising, etc..
21
New cards
**Examples of Radiation**
Example 1:Sun melting popsicle
Example 2: a campfire or a lit candle
Example 2: a campfire or a lit candle
22
New cards
How has human activity impacted air quality?
More carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gasses create lower quality air. These are created by an increase of the human population. Humans use cars and other conveniences (air conditioning, other means of transportation) that create smog & poor air quality.
23
New cards
How does density play a role in the atmosphere?
Density is responsible for convection, which is a mechanism for warming the atmosphere and cooling the earth. Convection is the transfer of heat through movement and circulation of mass in a fluid. Warmer air rises, which makes cooler air sink. As the air sinks closer to the Earth's surface, the air warms up.
24
New cards
How is ozone (O3) created?
Ozone is created when the kind of oxygen we breathe is split apart by sunlight into single oxygen atoms.
25
New cards
What is the process by which O3 destroyed?
Ozone layer depletion is the thinning of the ozone layer present in the upper atmosphere. This happens when the chlorine and bromine atoms in the atmosphere come in contact with ozone and destroy the ozone molecules.
26
New cards
What problem does the destruction of O3 pose?
More heat gets trapped in our atmosphere = melting ice; increased skin cancers and other damages.
27
New cards
latitude Impact
How direct the sun is hitting a place greatly influences the climate. As latitudes increase, the average temperature cools. Conversely, as latitudes decrease, average temperatures increase. This can be understood through our planet's three climatic zones: the tropic zone, temperate zone, and polar zone
28
New cards
altitude impact
Usually as elevation increases the weather gets colder and the climate becomes harsher (more intense weathering: windier and colder). There is also less air as elevation increases. As elevation decreases on land that most live on, the climate gets warmer as well as more humid.
29
New cards
prevailing winds impact
Prevailing winds bring air from one type of climate to another.
30
New cards
distance from large body of water impact
Land masses near large bodies of water, especially oceans, change temperature as the oceans change temperature: slower and with less extreme fluctuations than land masses farther away.
31
New cards
ocean currents impact
Ocean currents act much like a conveyor belt, transporting warm water and precipitation from the equator toward the poles and cold water from the poles back to the tropics.
32
New cards
topography impact
high elevations are cooler than low elevations because they have less atmosphere to trap heat. Higher altitudes are colder than lower latitudes because they receive less solar radiation during the winter months.
33
New cards
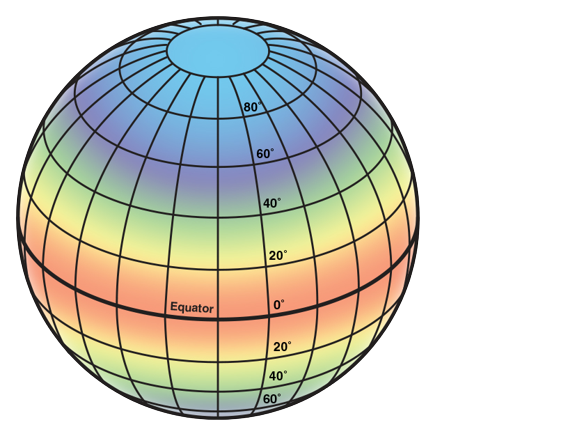
Identify The Polar Zone
The top zone
34
New cards
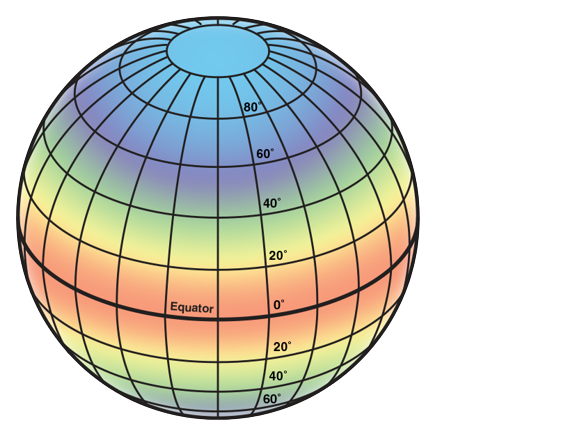
Identify The Temperate zone
Below the continental, at 40 degrees.
35
New cards
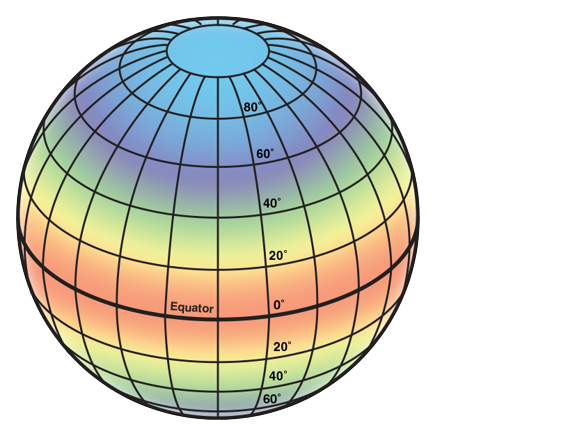
Identify The Tropical zone
Near the equator, 0 degrees.
36
New cards
What causes the uneven heating of the earth?
The earth is tilted on its axis and the rays of the sun are falling directly on the equator which produce heat at the equator more than the other region
37
New cards
How do convection currents create wind?
*Convection(rising air due to heat) lowers surface pressure creating a pressure gradient that tries to correct itself by having air move from higher pressure to the lower pressure area created by the rising air. This correction is wind.*
38
New cards
**Cold Front**
cold air advances towards the warm air lifting the warm air up. Cold air is denser causing it to sink below warm air.
Weather Impact: violent weather
Weather Impact: violent weather
39
New cards
**Occluded Front**
an occluded front is a type of weather front formed during cyclogenesis.
Weather Impact: wide variety
Weather Impact: wide variety
40
New cards
**Stationary Front**
results when neither cold air nor warm air advances.
Weather Impact: same weather
Weather Impact: same weather
41
New cards
Warm front
warm air advances towards the cold air sliding over the cold air forming a gentle slope.
Weather Impact: wet weather
Weather Impact: wet weather
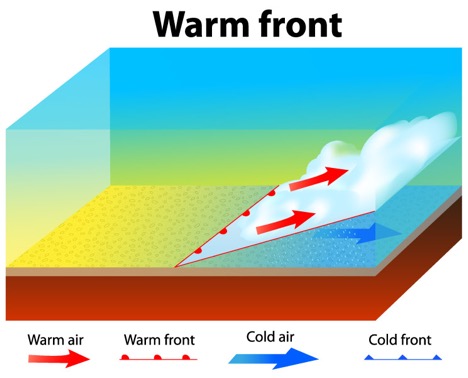
42
New cards
What is needed to form a tornado?
* 3 types of air masses: Warm, humid air rises while cool air falls.
* low pressure systems
* The air masses add more energy to the already existing thunderstorm and create a tornado
* low pressure systems
* The air masses add more energy to the already existing thunderstorm and create a tornado
43
New cards
describe how tornadoes impact ecosystems.
Tornadoes affect the environment by destroying buildings and trees. Tornadoes also kill animals, which effects the food chain and disrupts the whole environment
44
New cards
What is needed to form a hurricane?
* 1-warm ocean water must be present to provide a source of energy;
* 2-moisture from the evaporating ocean must combine with heat energy to move the hurricane;
* 3-wind patterns on the surface of the ocean must spiral inward.
* 2-moisture from the evaporating ocean must combine with heat energy to move the hurricane;
* 3-wind patterns on the surface of the ocean must spiral inward.
45
New cards
Identify the role of the oceans in the formation of hurricanes.
Hurricanes start simply with the evaporation of warm seawater, which pumps water into the lower atmosphere. This humid air is then dragged aloft when converging winds collide and turn upwards.
46
New cards
How much nitrogen is in the Atmosphere?
78%
47
New cards
How much oxygen is in the Atmosphere?
21%
48
New cards
How much Argon is in the Atmosphere?
0\.9%
49
New cards
How much Other gases are in the Atmosphere?
0\.1%
50
New cards
Where does warm air rise in Sea/land breeze?
to the top
51
New cards
Where does cool air sink in sea/land breeze?
to the bottom
52
New cards
When does sea/land breeze occur?
anytime there is cold and warm air in an area
53
New cards
What is responsible for weather moving across the United States?
The jet stream is a narrow band of fast, flowing air currents located near the altitude of the tropopause that flow from west to east. The jet stream flows around the entire earth. They usually have a meandering, snake-like shape.
54
New cards
Gravity
**one of the main unbalanced force acting on things on earth**
55
New cards
Friction
the action of one surface or object rubbing against another, the force of friction depends on the type of surface and how hard they rub together, friction works AGAINST motion
56
New cards
Air resistance
the "friction" experienced by objects falling through the air that works opposite to motion
57
New cards
High Pressure System
Dense air mass that is usually cooler and drier than the surrounding air.
58
New cards
Low Pressure System
less dense air mass that is usually wetter and warmer than the surrounding air.
59
New cards
**What interaction contributes to the formation of hurricanes during late summer?**
**warm ocean water temperatures & warm air masses**
60
New cards
**What type of pressure is in a tornado?**
Very low
61
New cards
**How is a Tornado different than a hurricane?**
**Tornadoes are smaller, Tornadoes are short lived, and Tornadoes have stronger winds.**
62
New cards
**A Tornado is most likely to form during a:**
Thunderstorm
63
New cards
**how does tornado form**
**they form with warm and humid air**
64
New cards
**The boundary where two air masses meet is called a:**
Front
65
New cards
**How do ocean currents affect weather?**
**spreading heat from solar energy**
66
New cards
**Winds generally moves across the United States**
WEST TO EAST
67
New cards
**What is true about hurricanes?**
**Need rotational winds to develop, Need warm water to develop, and Need areas of low pressure to form.**
68
New cards
**Global winds are created by**
**Unequal heating of Earth's surface**
69
New cards
**Low Pressure Systems are often associated with what type of weather?**
**Rain, Snow/ Stormy weather**
70
New cards
**Low pressure systems usually bring**
**clouds, wind, & precipitation**
71
New cards
**Where do the warm water currents start?**
**At the equator**
72
New cards
**How does conduction heat transfer?**
**Through touch/contact**
73
New cards
**How does radiation heat transfer?**
**Through rays**
74
New cards
**How does convection heat transfer?**
**Through air and water**
75
New cards
**Type of heat transfer that drives wind?**
Convection
76
New cards
**Kinetic energy depends on**
mass and speed
77
New cards
**potential energy is...**
**energy that is stored in an object**
78
New cards
**Velocity is**
**An object’s speed AND direction at a given time**
79
New cards
**How do you get speed**
**Distance divided by time**