Den 7101 Davenport Bone Resorption/Formation
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
In resorption calcium and phosphate
must be removed and pumped against a concentration gradient
The body has the ability to regulate the formation of bone with
inhibitors and accelerators
Mineral is the last thing in so the first thing you remove is
the mineral
What do we know about the precipitation process?
alkaline phosphatase is the marker
works at about 7.4 pH
body fluids are slightly basic/acidic. Why?
basic, because other wise our bones would dissolve
alkaline environment for ____________, acidic environment for _________________
precipitation, dissolution
If you bring in something across the concentration gradient, what does that require?
energy
osteoprogenitor cells
resting cell that can transform into and osteoblast and secrete bone matrix
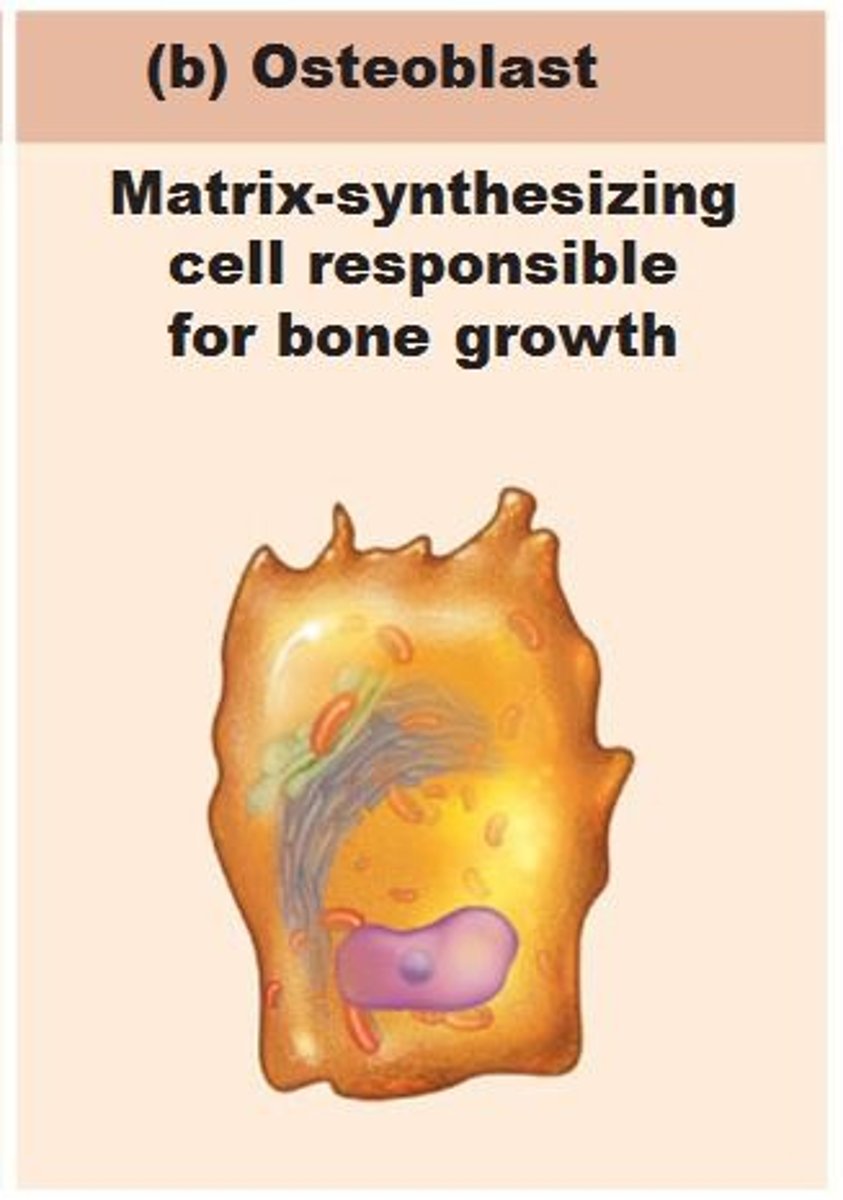
Osteoblast
a differentiated bone forming cell that secretes bone matrix
osteoblast processes communicate with other osteoblasts and osteocytes by gap junctions
Ob
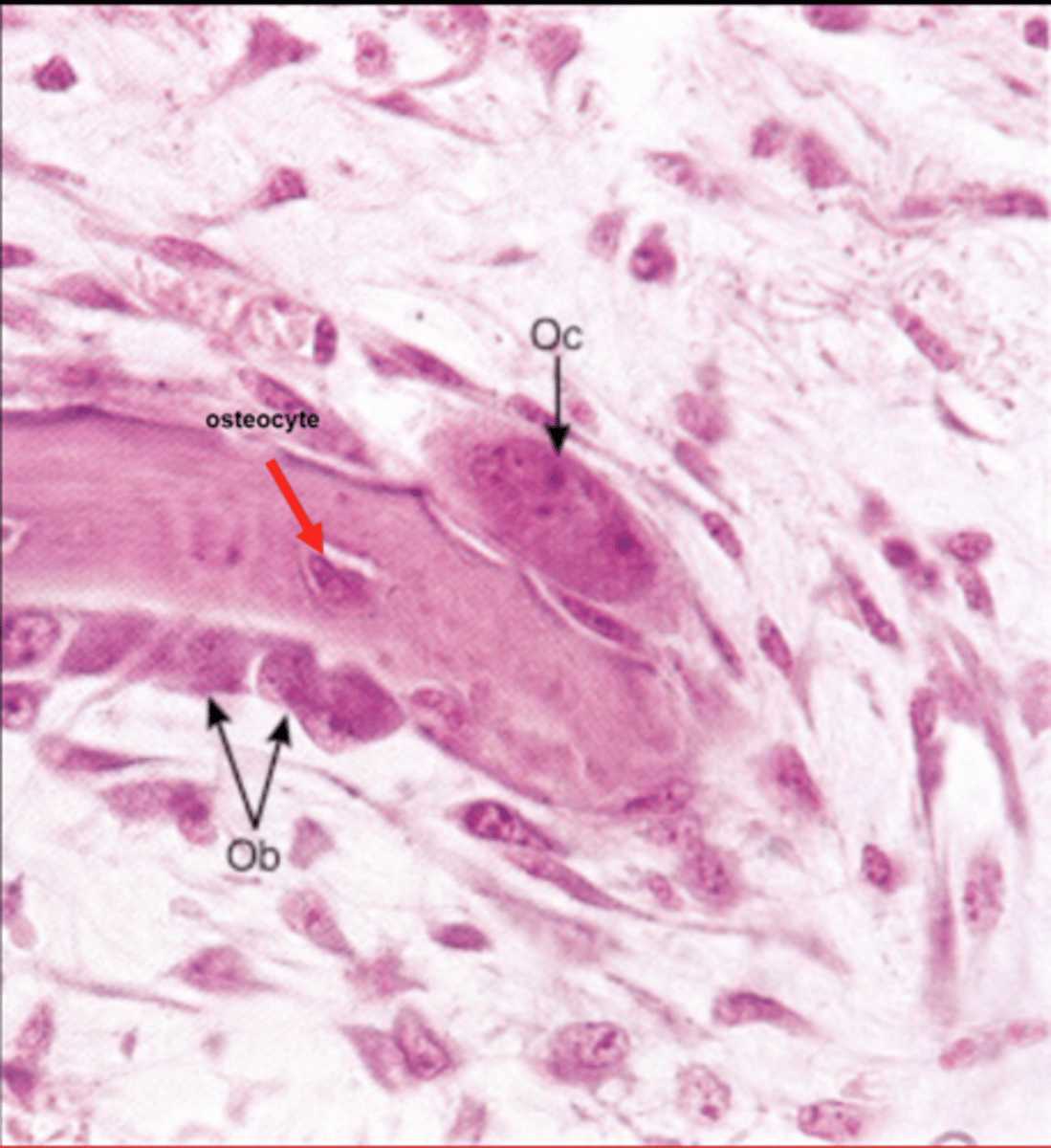
What is the difference between and osteoblast and an osteocyte?
osteocyte it resides in the lacuna
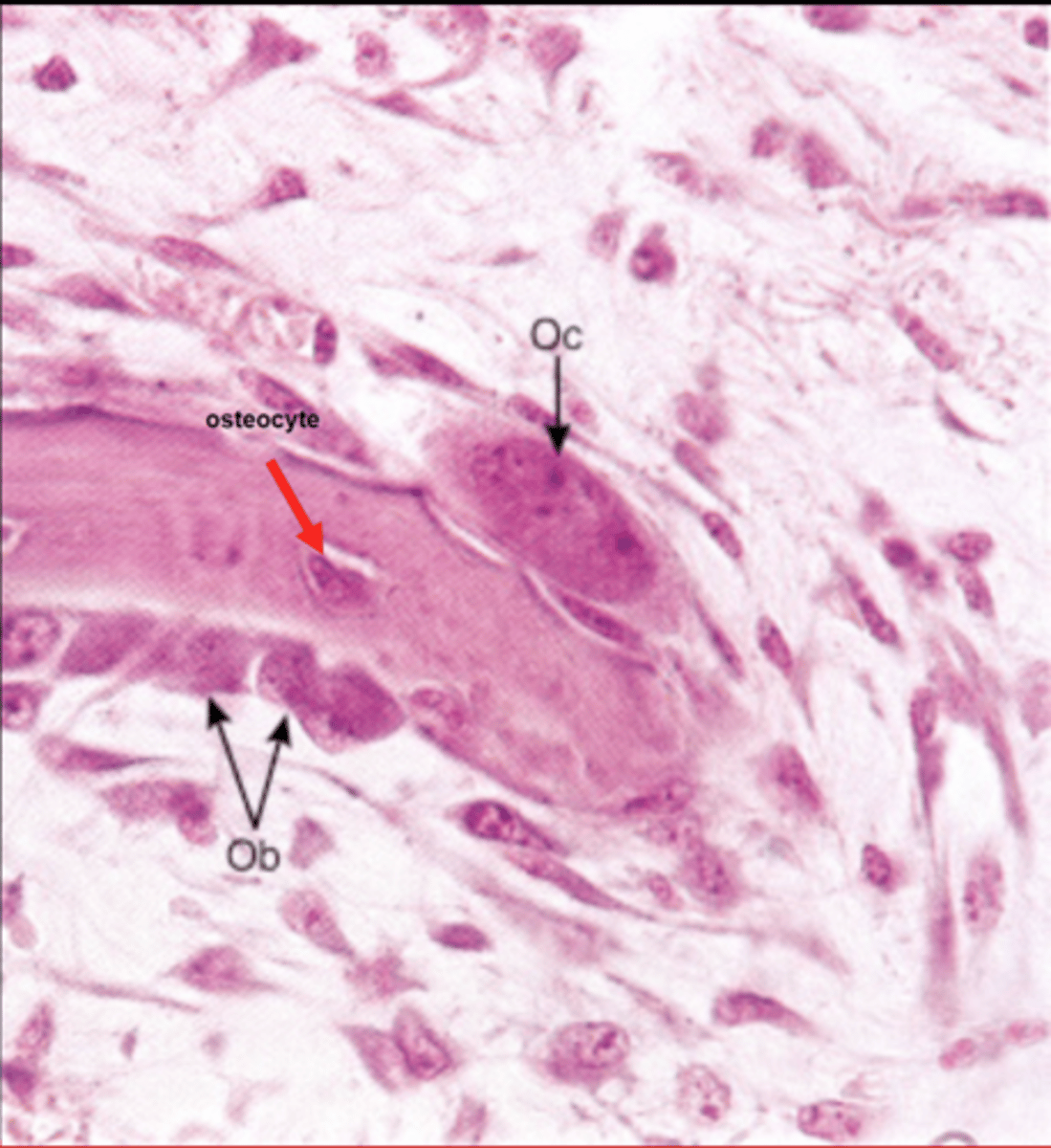
Osteoclast
-large multinucleated bone cell that absorbs and removes unwanted bony tissue
-releases lysosomes into the extracellular space
-are phagocytic
Oc
Osteoclast contain low levels of
isocitric dehydrogenase-minor contributor to the acidic environment in the cell
Osteoclasts demonstrate high
carbonic anhydrase activity-major contributor to the acidic environment in the cell
Citrate and carbonic acid levels are high in the ____________ regions of the osteoclast
border
________________ is probably responsible for the low pH necessary for mineral dissolution by osteoclasts
Carbonic acid
Collagenase activity is seen in
active bone resorption
Acid phosphatase activity is also a marker for
active bone resorption
4 regions of the active osteoclast
Basal zone (outer edge)
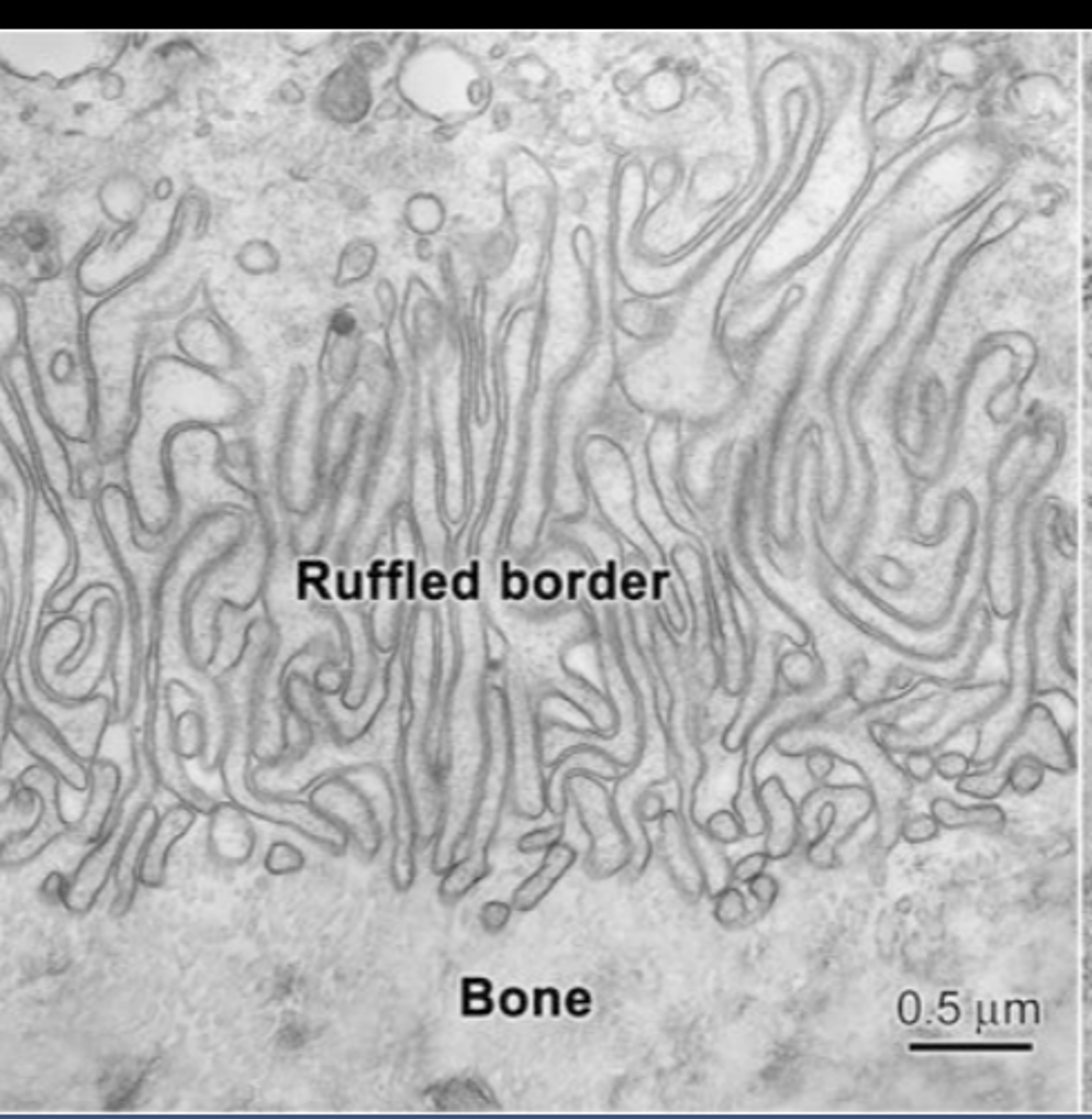
Ruffled border
Clear zone
Vesicular zone (business area of the cell, mitochondria, nucleus, golgi, etc.)
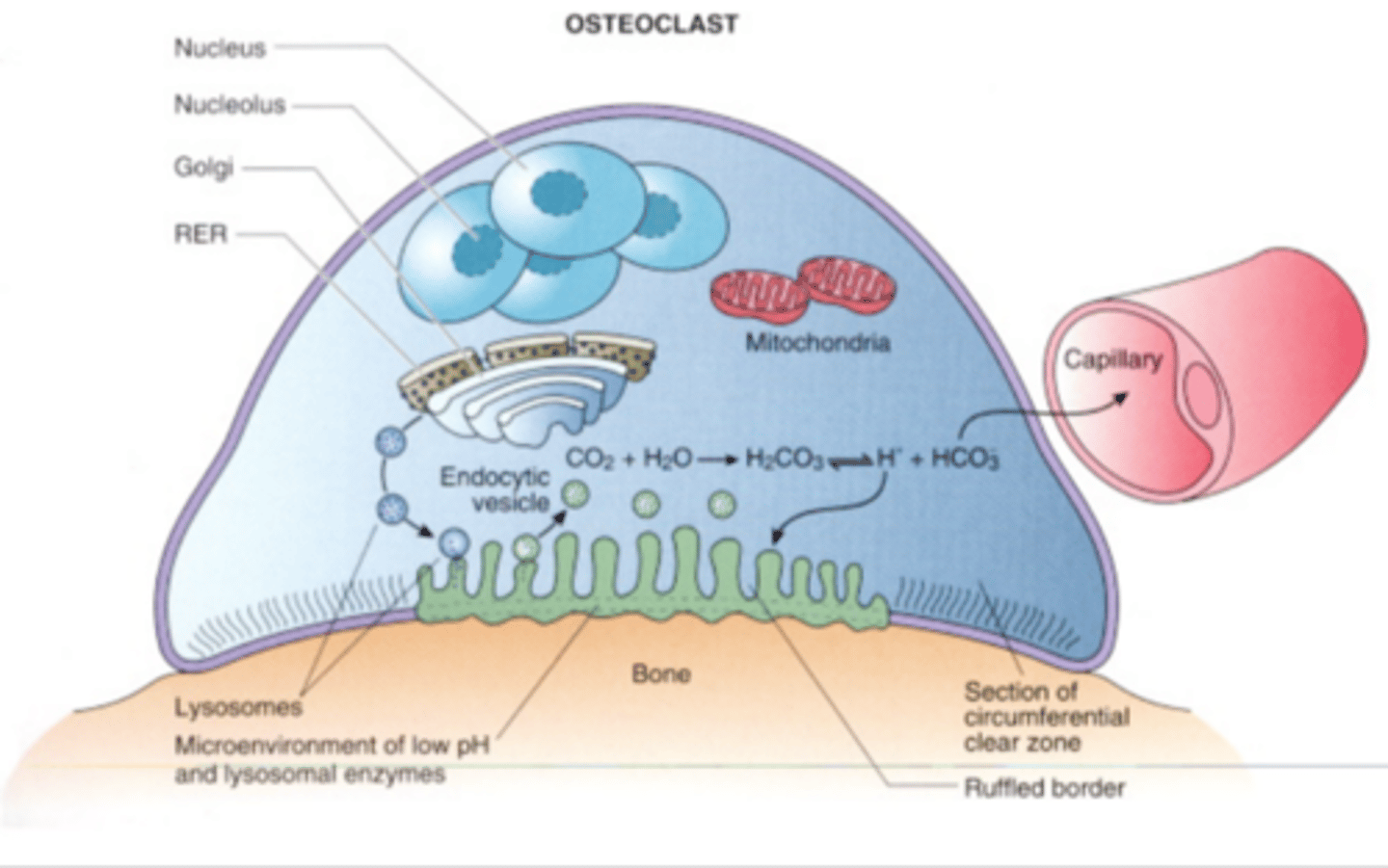
Ruffled border
where cell membrane borders bone and resorption is taking place
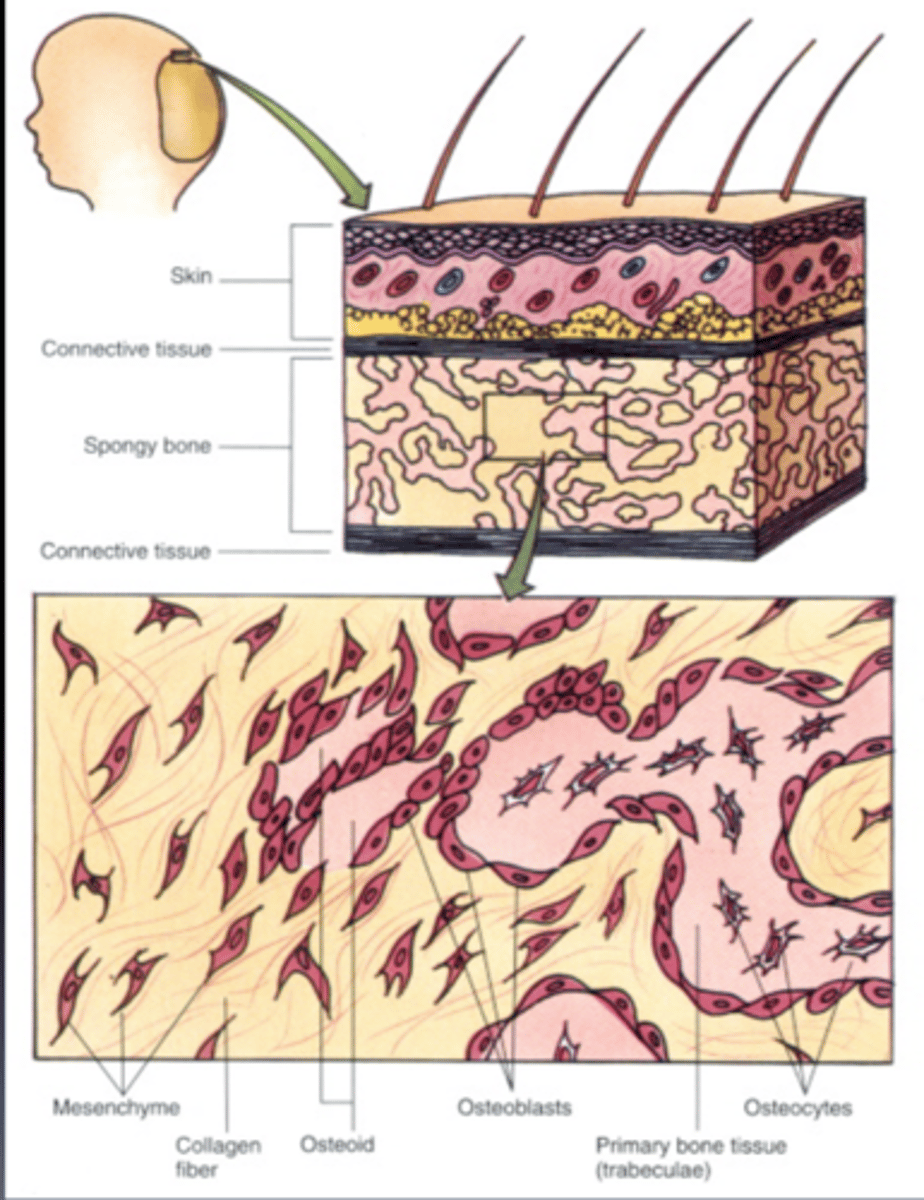
intramembranous ossification
bone develops from a fibrous membrane, (bone forms around blood vessels)
endochondral ossification
a cartilage template is replaced by bone, involved intramembranous formation in long bones
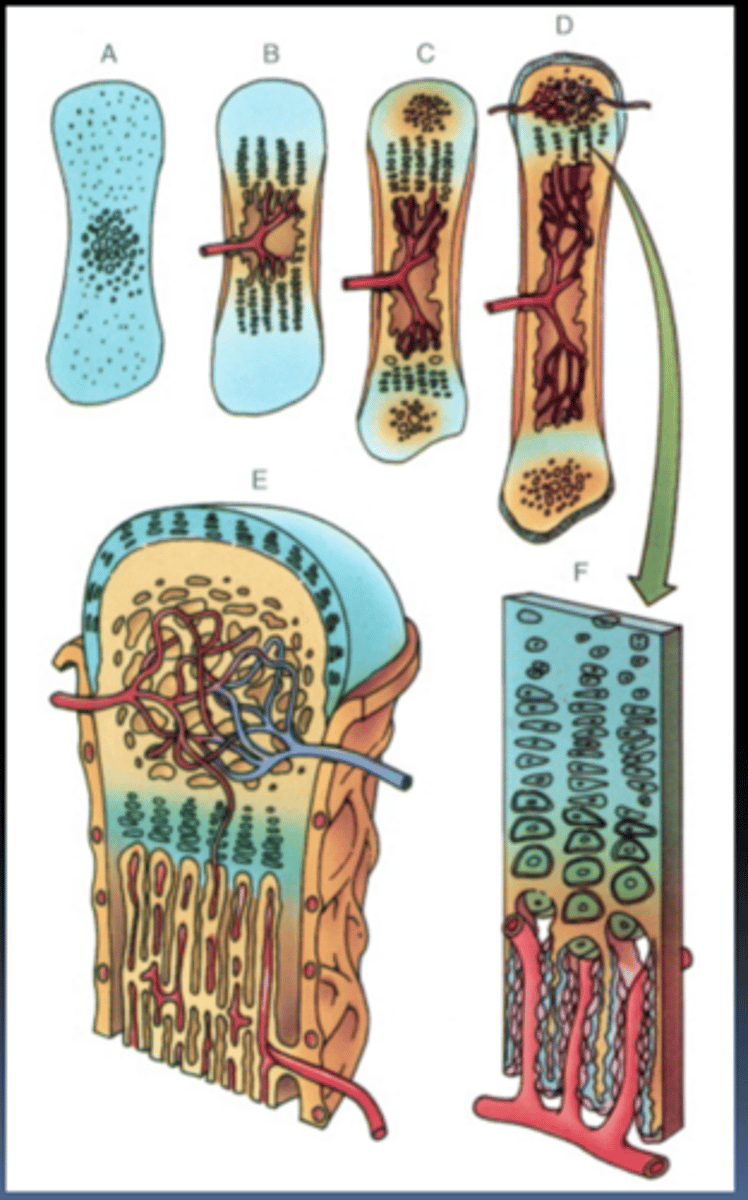
When cartilage gets innervated by a blood vessel it begins to_____________
die, and becomes calcified (replaced by bone)
during bone formation chondroblasts become____________
osteoblasts and form a subperiosteal bone collar (intramembranous bone formation)
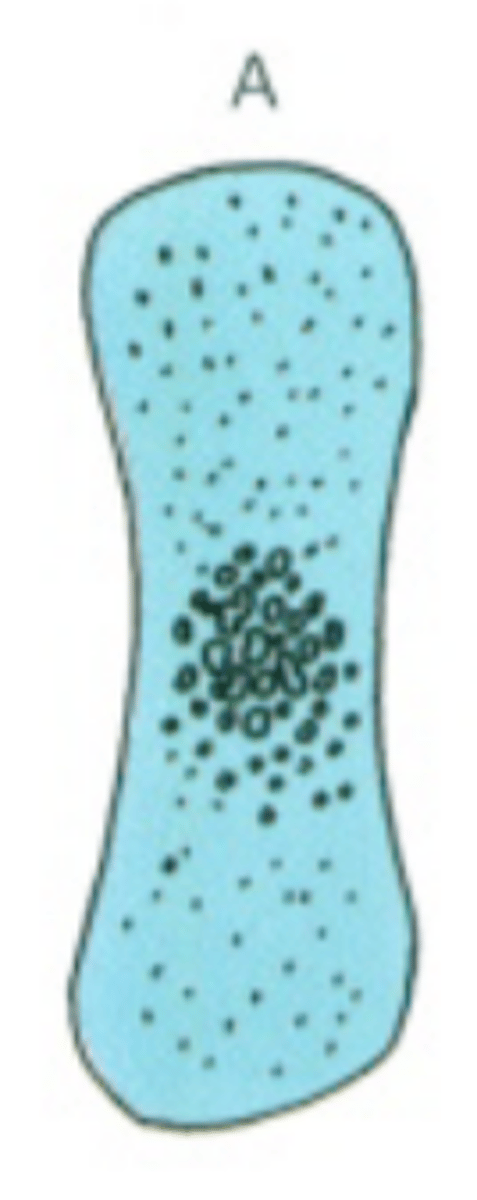
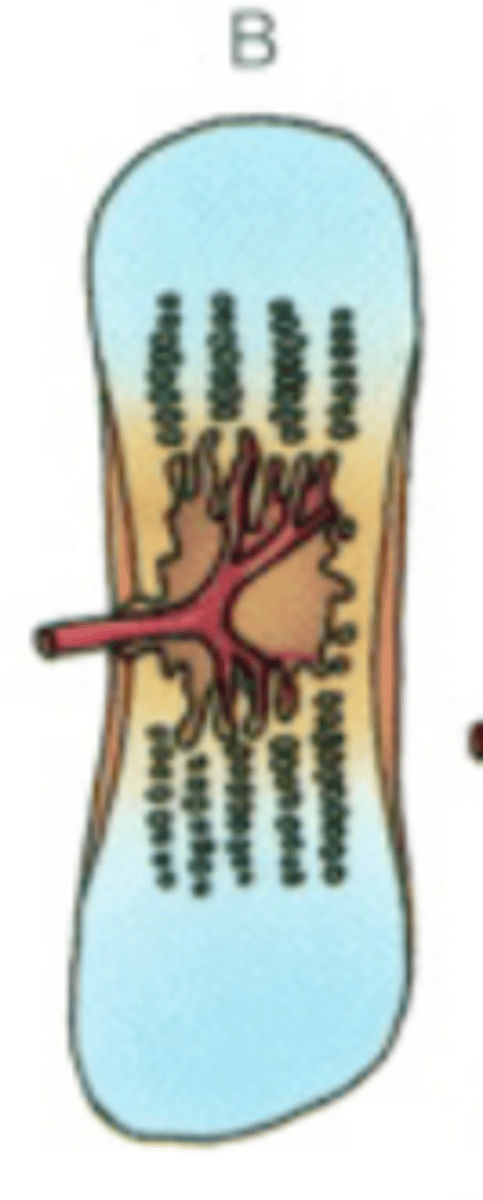

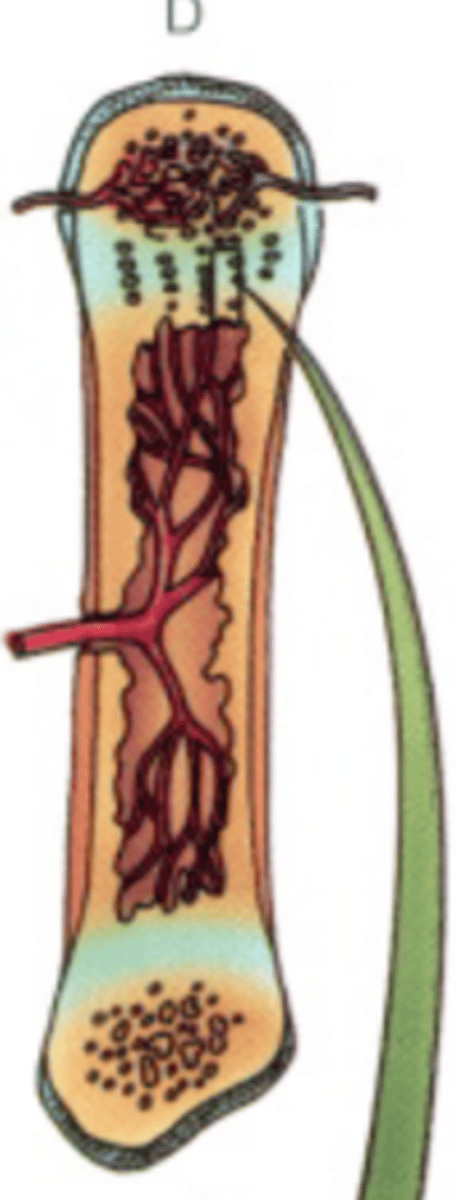
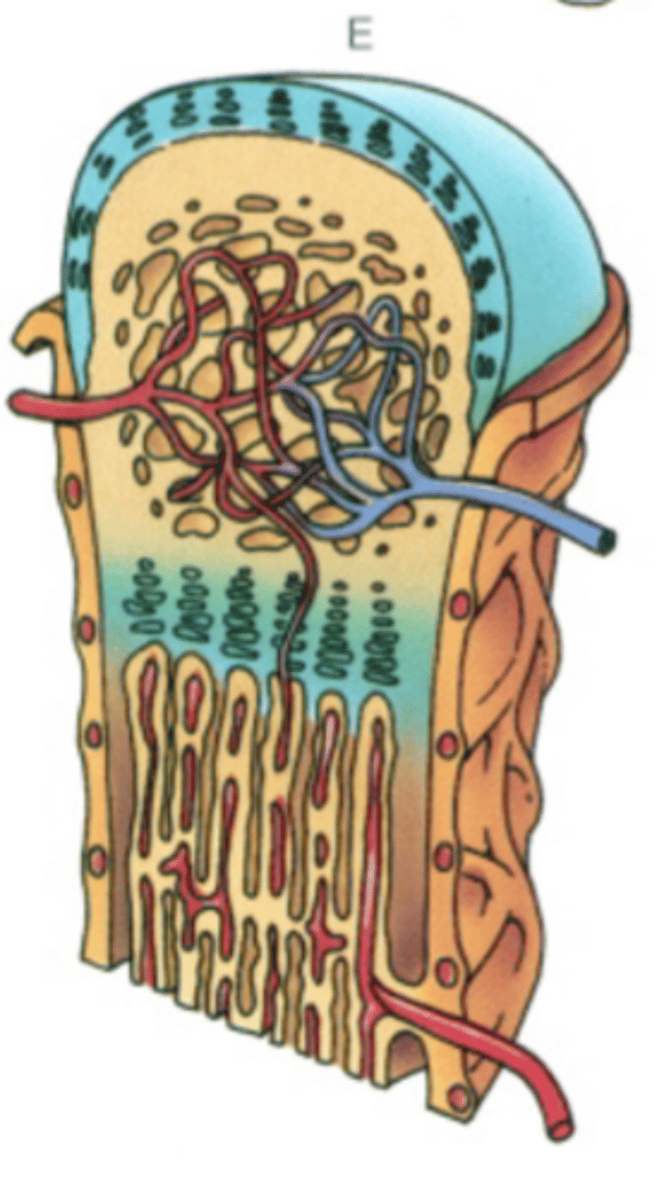
Endochondral bone formation 6 stages, 4 zones
Reserve cartilage (zone 1)
Proliferation (zone 2)
Cell maturation and hypertrophy (zone 3)
last three happen in zone 4
Cartilage calcification
Cartilage removal
Bone deposition
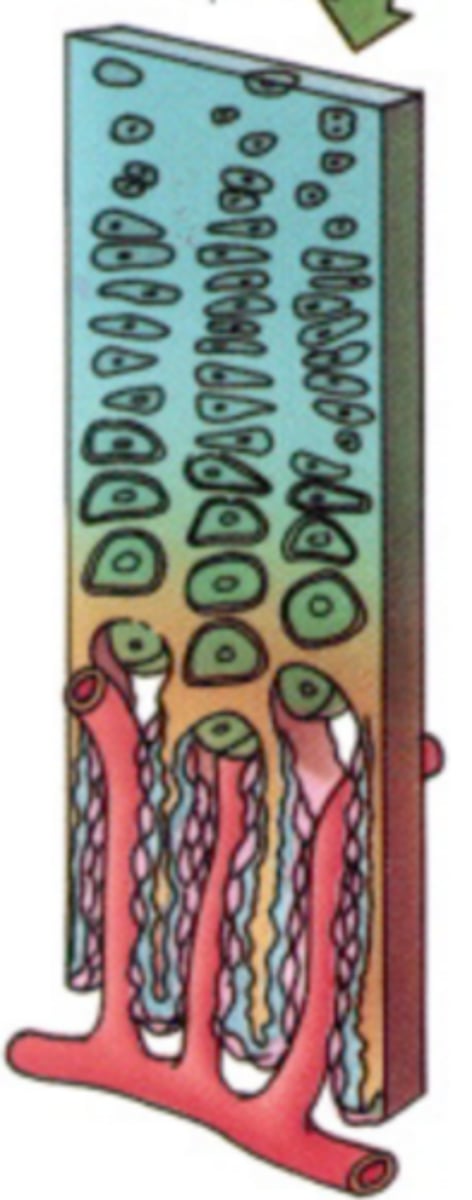

bone itself only grows by _______________ it does not grow__________________
appositionally, interstitially
parathyroid hormone
A hormone of the parathyroid gland that regulates the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in the body.
parathyroid hormone (definition from slide)
activates receptors on osteoblasts, suppressing matrix formation and initiating manufacture and secretion of osteoprotegerin ligand and osteoclast-stimulating factor by the osteoblasts. These factors induce osteoclast formation and stimulate quiescent osteoclasts to become active, leading to bone resorption and the release of calcium ions.
Calcitonin
decreases blood calcium levels
Calcitonin (def from slide)
Parafollicular cells of the thyroid secrete calcitonin, a polypeptide hormone that activates receptors on osteoclasts, inhibiting them from resorbing bone.
somatotropin
growth hormone
somatotrophin (def from slide)
secreted by cells in the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland, influences bone development via somatomedins (insulin-like growth factors), especially stimulating growth of the epiphyseal plates.
Children deficient in this hormone exhibit dwarfism, whereas persons with an excess of somatotropin in their growing years display pituitary gigantism.
Thyroid hormone (def from slide)
hyposecretion in infancy and childhood results in cretinism (failure of bone growth and dwarfism)
Acromegaly
abnormal enlargement of the extremities
Osteoporosis
A condition in which the body's bones become weak and break easily.
osteogenesis imperfecta
inherited condition of deformed and abnormally brittle bones
Rickets
Vitamin D deficiency in children, causes bone deformation
osteomalacia
"adult rickets" disease marked by softening of the bone caused by calcium and vitamin D deficiency