The Reactions of Alkenes: The Stereochemistry of Addition Reactions
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This set of flashcards covers key concepts from the lecture on the reactions of alkenes and their stereochemistry.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
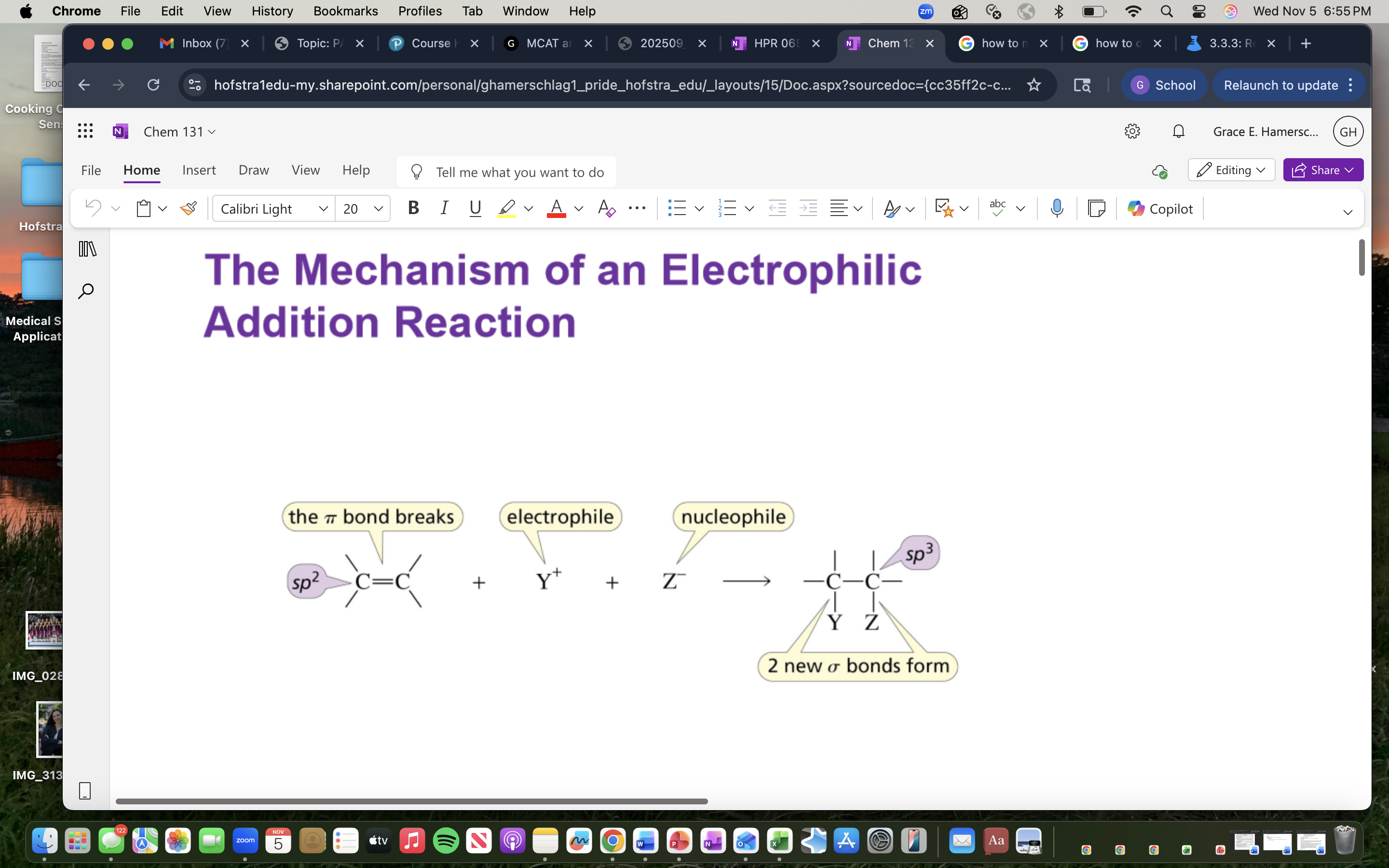
Electrophilic Addition Reaction
A reaction where an electrophile reacts with a nucleophile to form a product, typically involving the addition of a hydrogen halide.
reagent will often com in the form of a HCl or acid that ionizes easily
Carbocation
An organic ion with a positive charge on a carbon atom, often formed as an intermediate in reaction mechanisms.
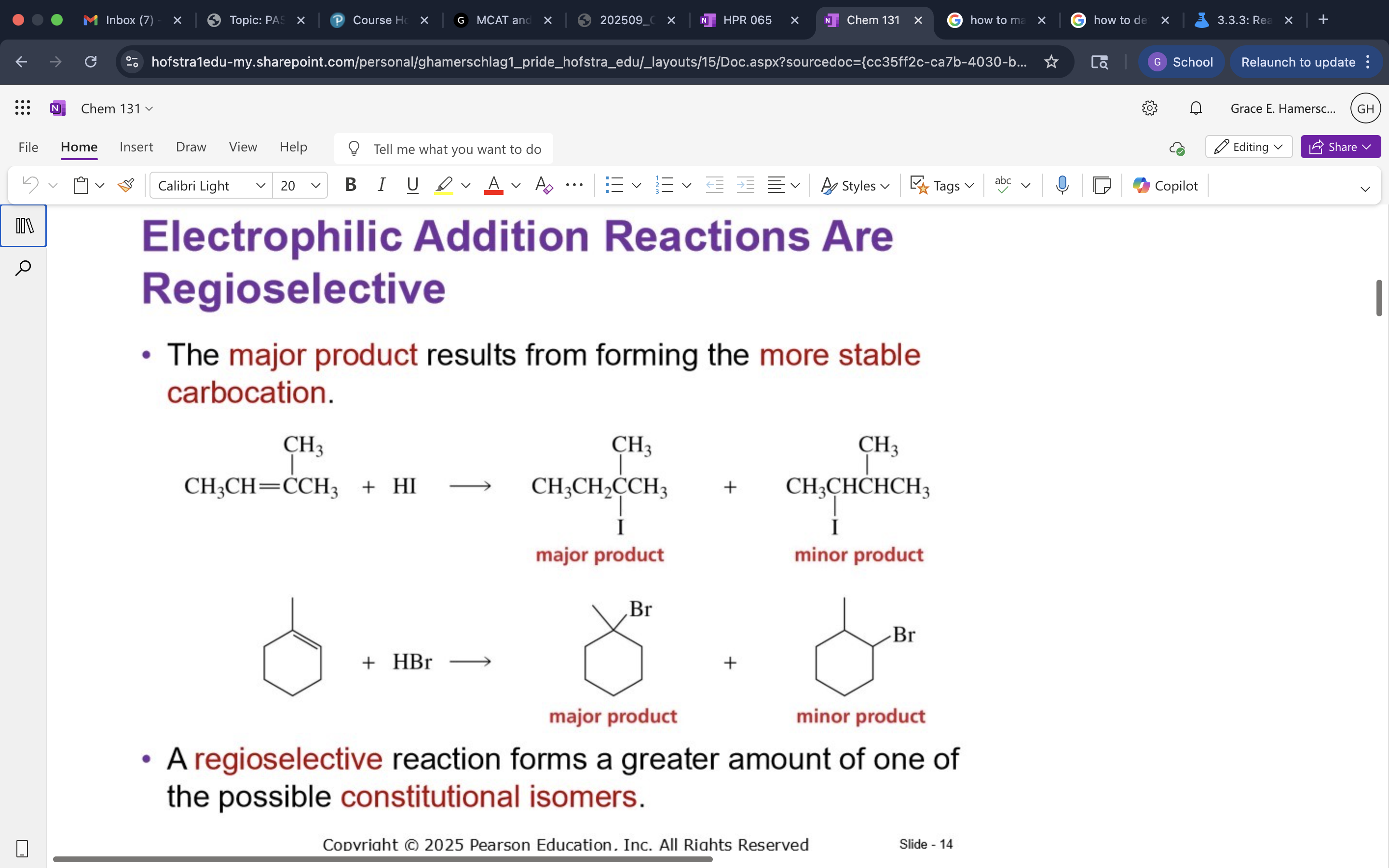
Regioselective Reaction
A reaction that produces a greater amount of one constitutional isomer over others.
good for synthesis
Stability of Carbocations
The stability of carbocations increases with the number of alkyl substituents; tertiary > secondary > primary.
Hyperconjugation
A stabilizing interaction that occurs when the σ bonds of adjacent alkyl groups overlap with an empty p orbital on a carbocation.
hydride shift and carbonyl shift related
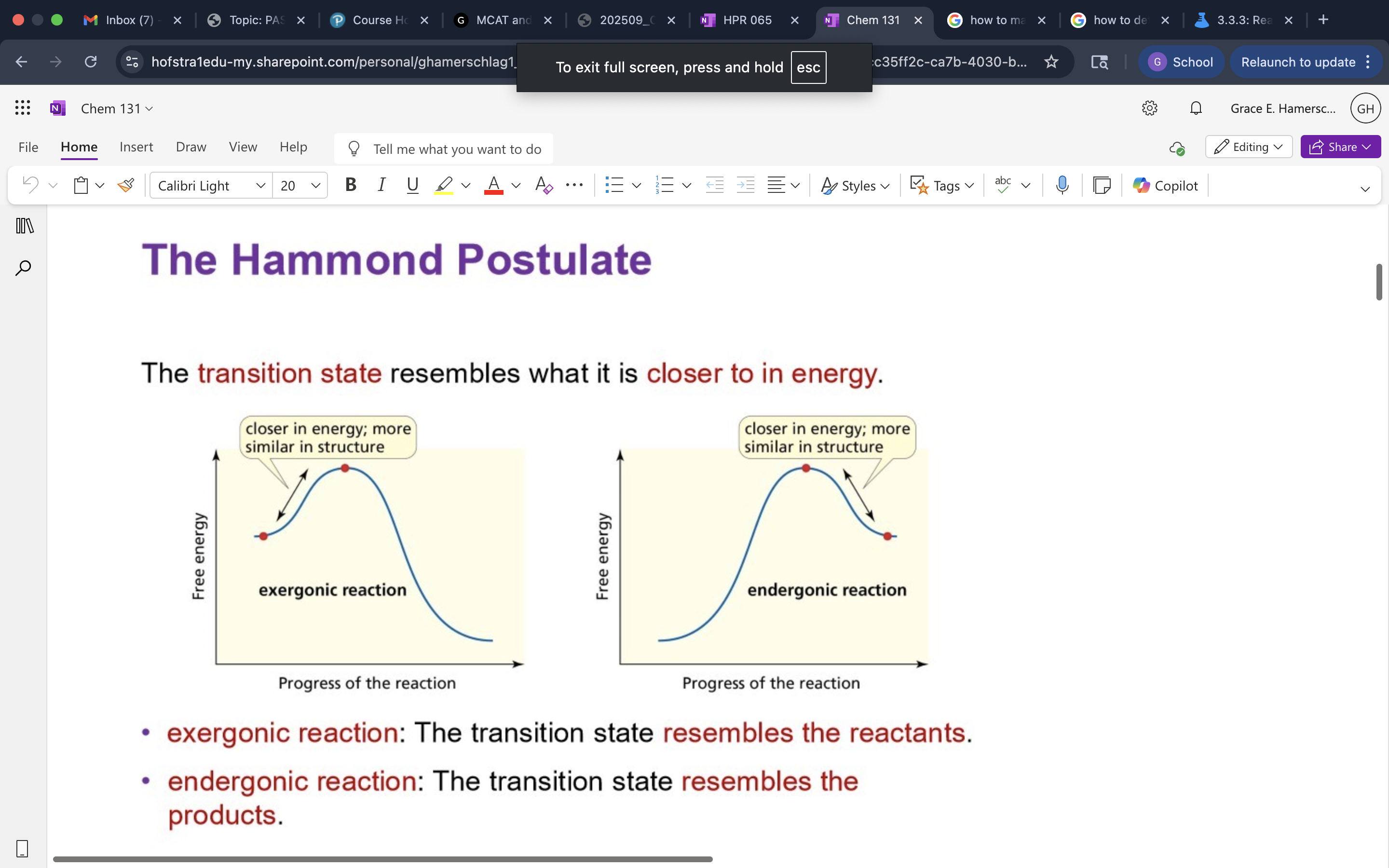
Hammond Postulate
The principle that the transition state of a reaction resembles the structure of the species (reactants or products) to which it is closer in energy. (easiest to determine on an energy diagram)
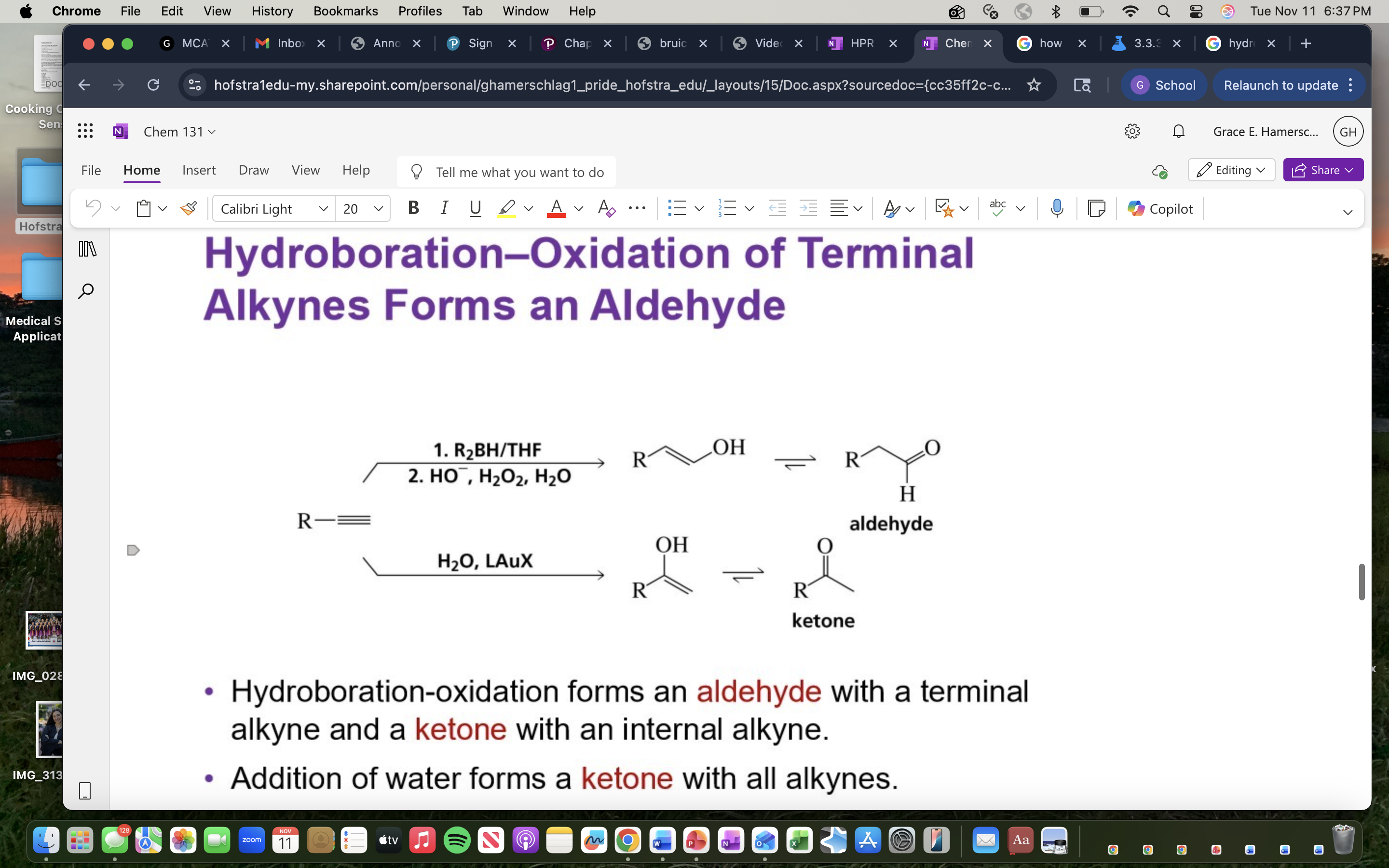
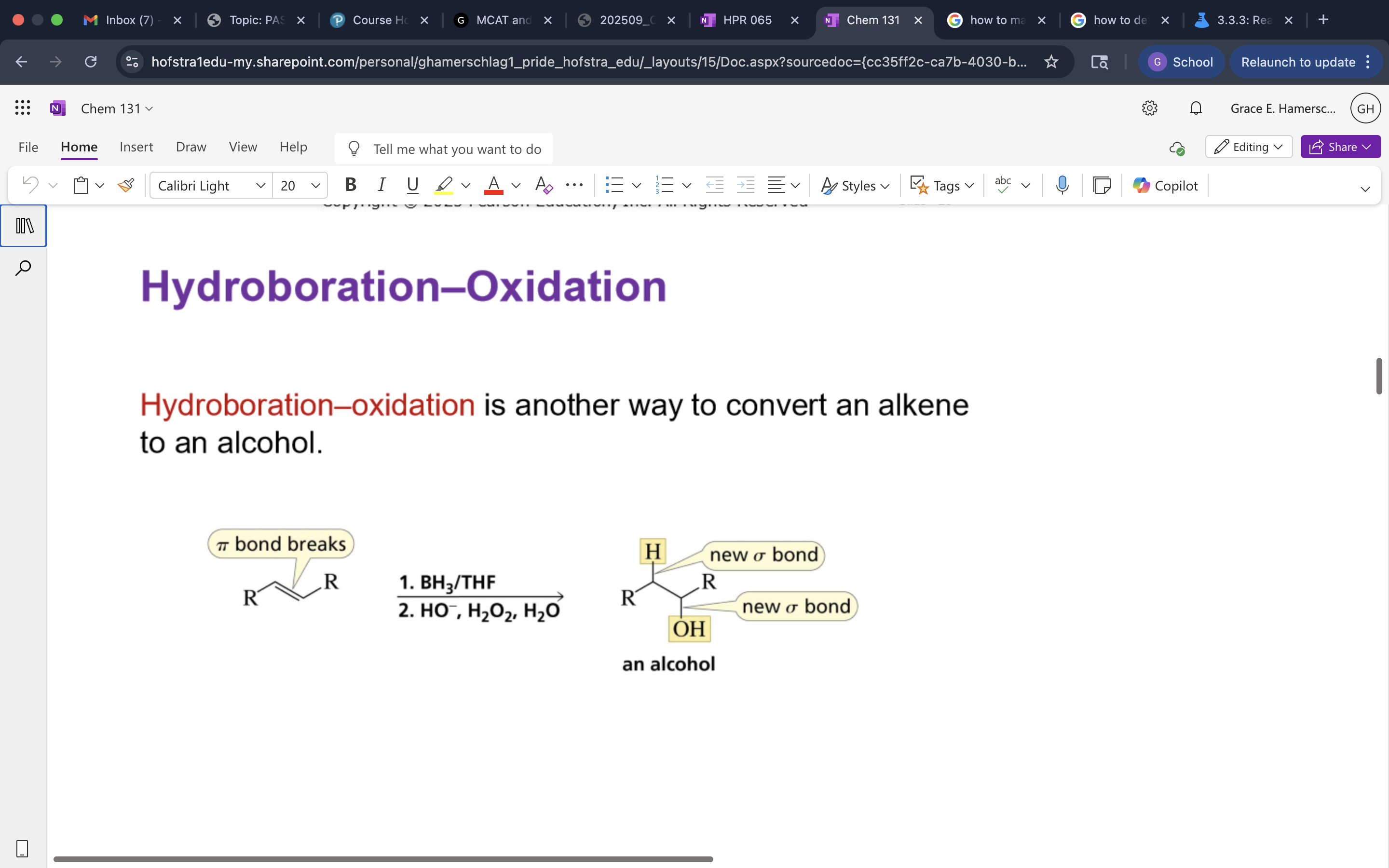
Hydroboration-Oxidation
A two-step reaction that converts alkenes to alcohols through the addition of borane followed by oxidation.
Ozonolysis
A reaction where an alkene is cleaved by ozone to form carbonyl compounds (ketones or aldehydes).
Stereospecific Reaction
A reaction where different stereoisomers react to form different products.
Enantiomers
Stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other.
Meso Compound
A compound that has multiple chiral centers but is not optically active due to an internal plane of symmetry.
Reaction kinetics of electrophilic addiction of halogen
carbocation formed
carbocation is rate limiting step
order of the reaction will be determined experimentally and based off of the reactants

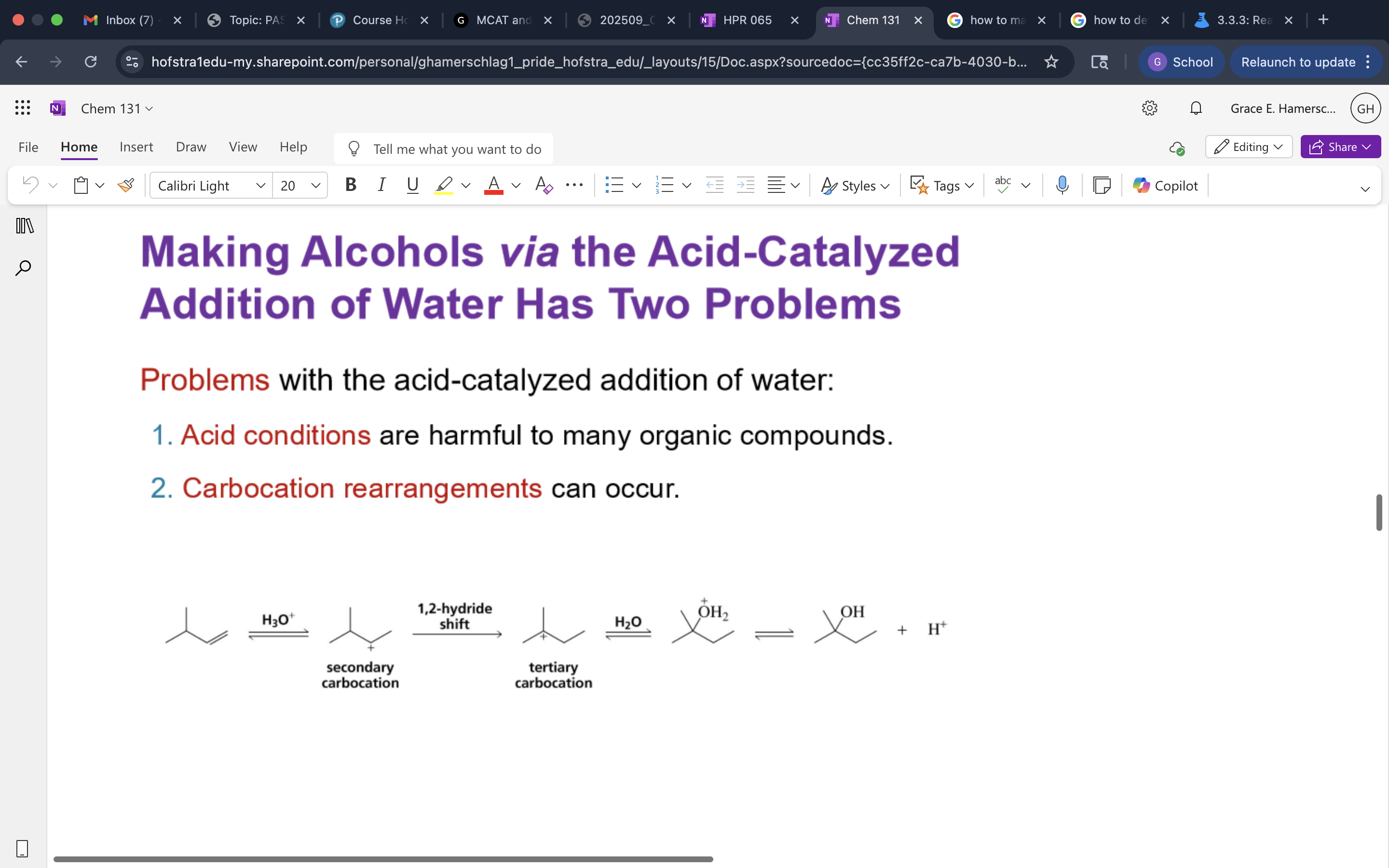
Acid Catalyzed Addition of Water and mechanism
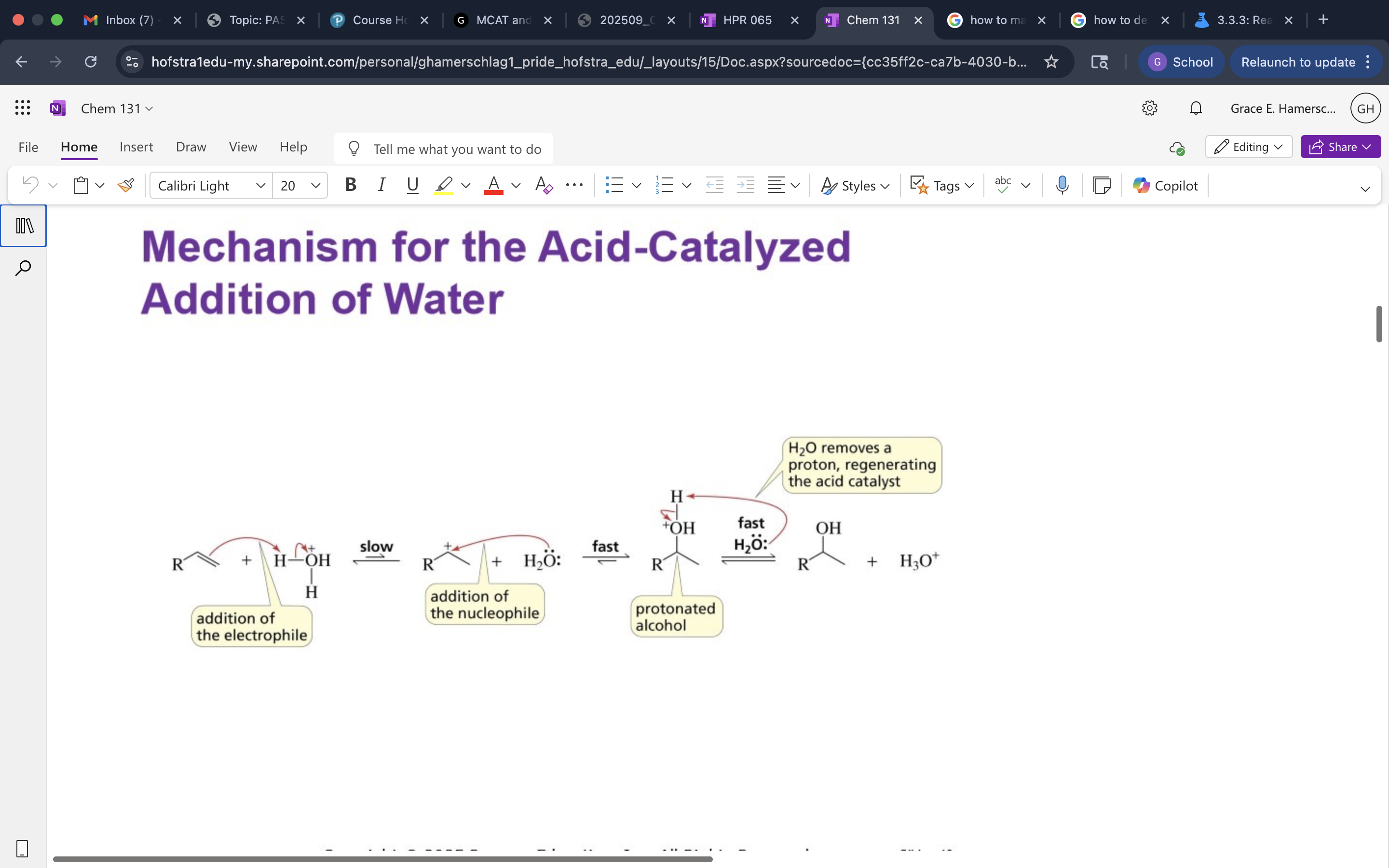
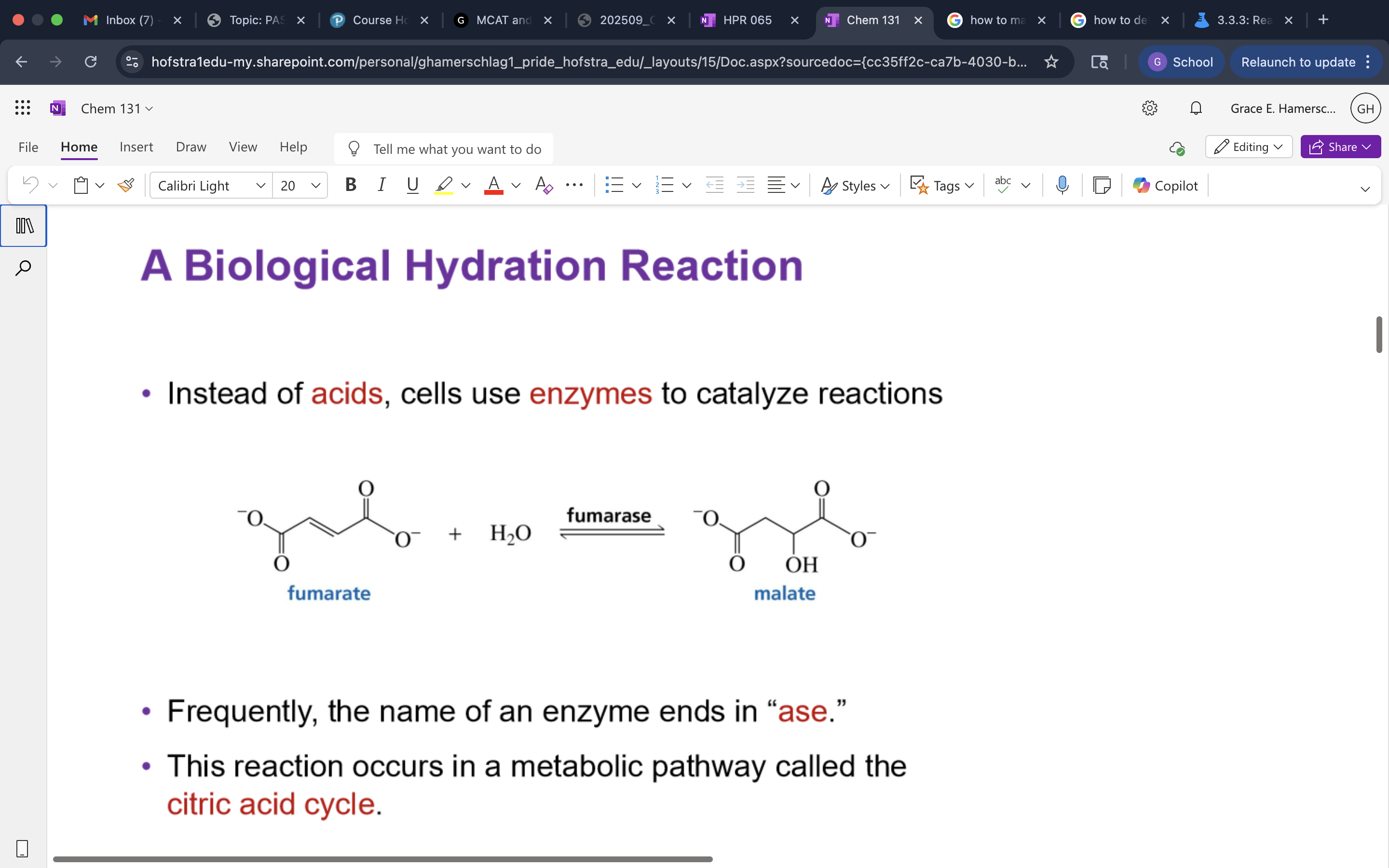
Glycolysis Hydration Reaction
alkene opens up to mark. addition to add OH
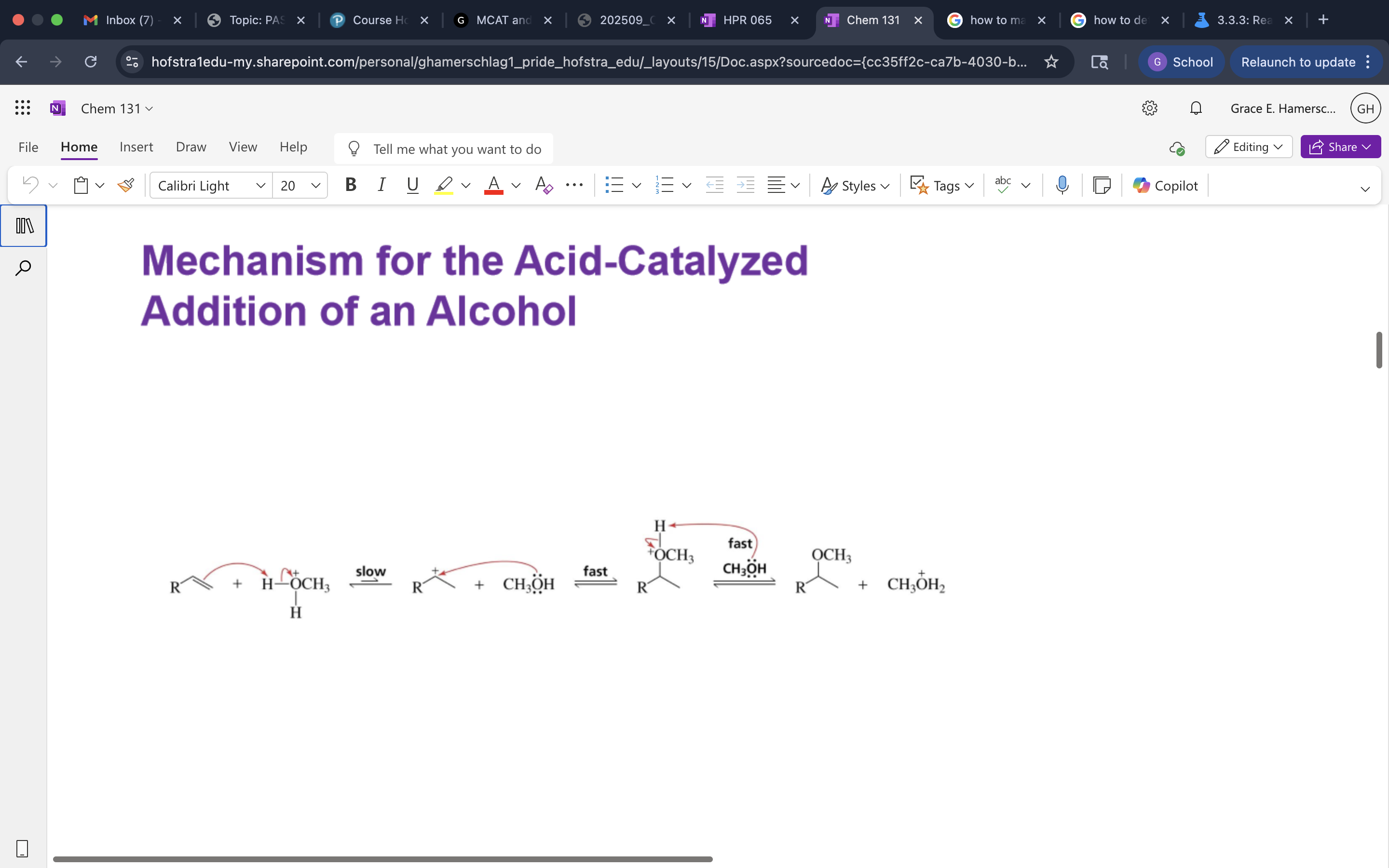
Acid catalyzed Addition of an Alcohol
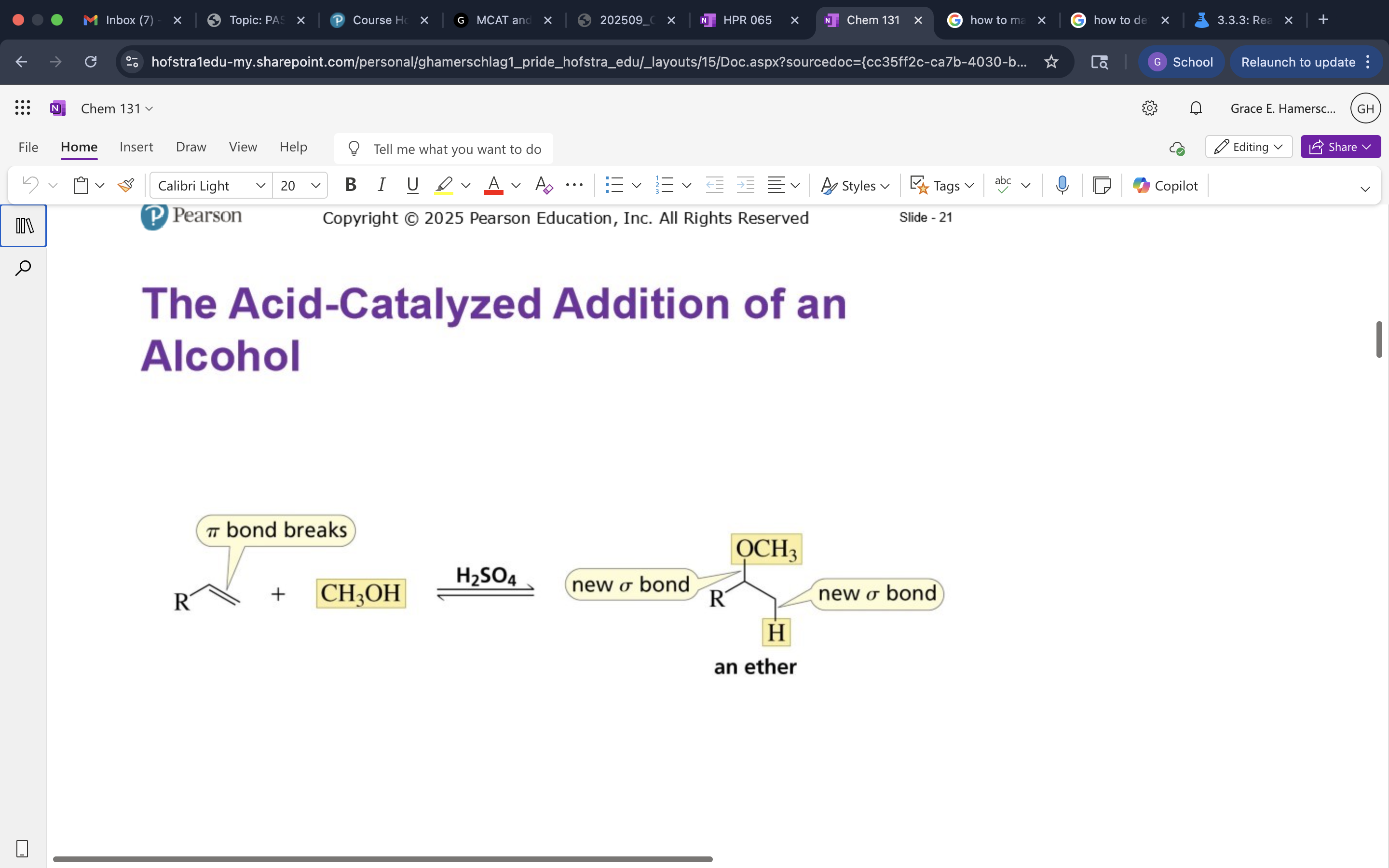
mechanism of Acid catalyzed Addition of an Alcohol
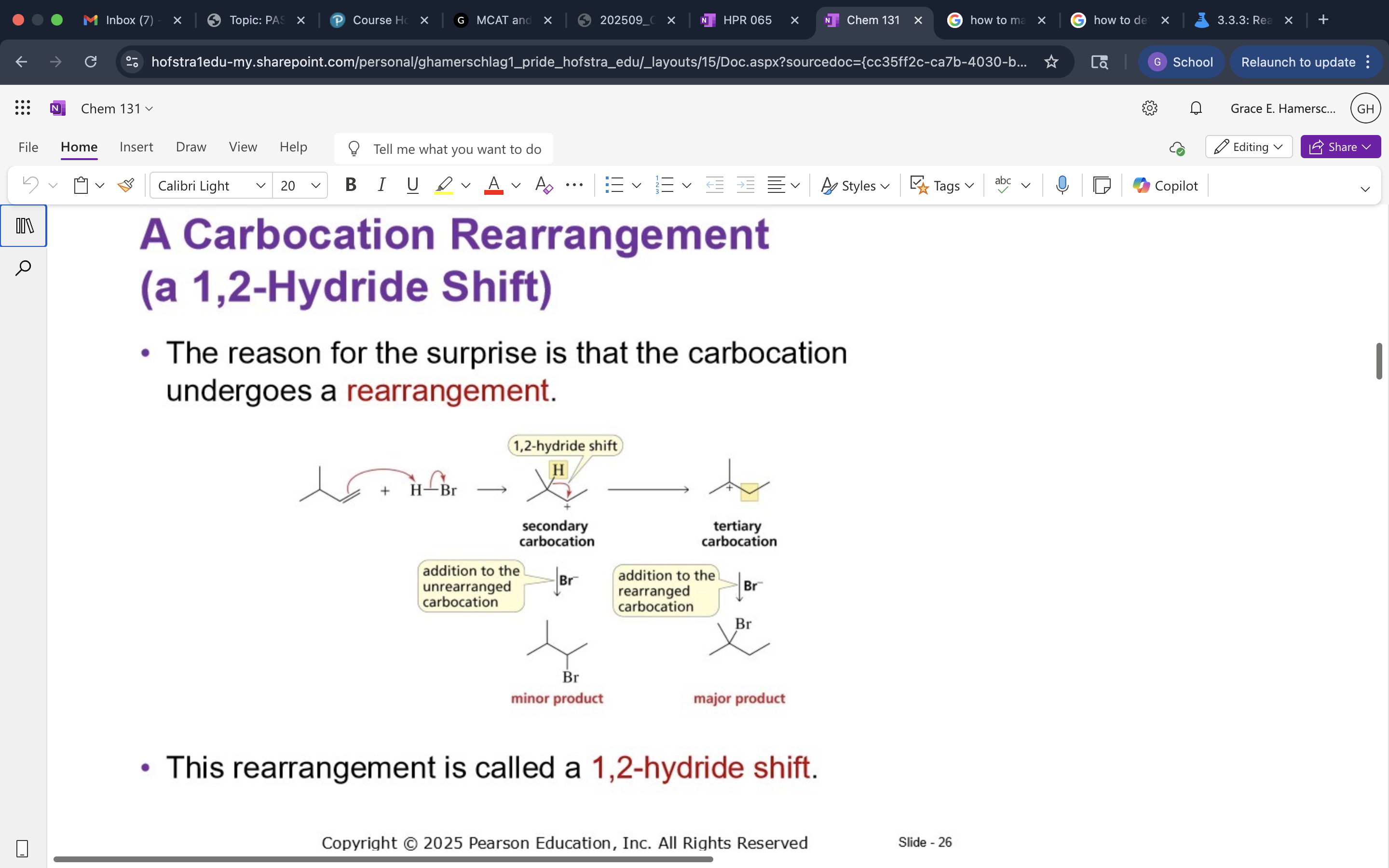
Carbocation Rearrangement
Mechanism of Hydroboration Oxidation B Specific
followed Markov. Addition
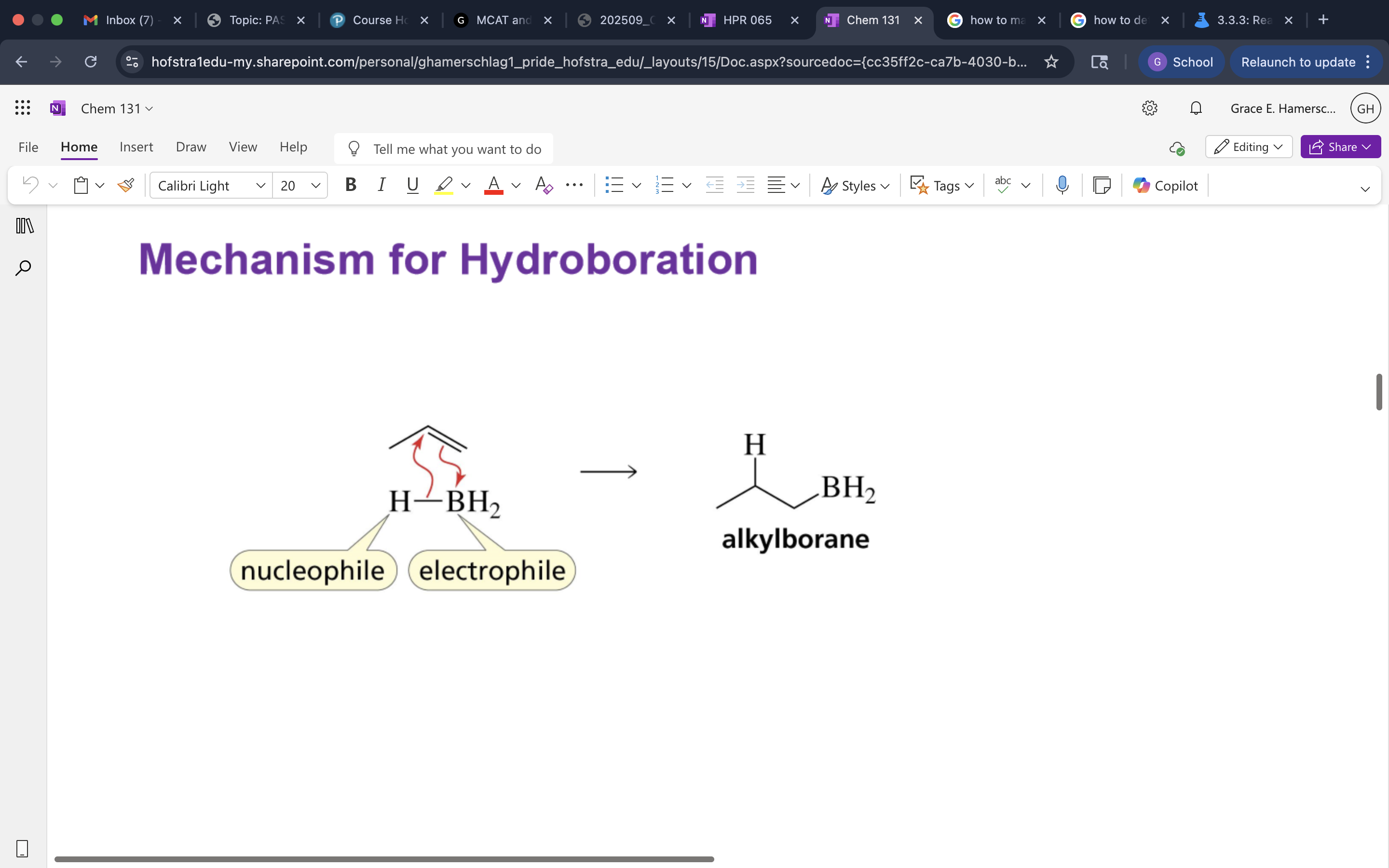
Step 2 of Hydroboration Oxidation Mech.
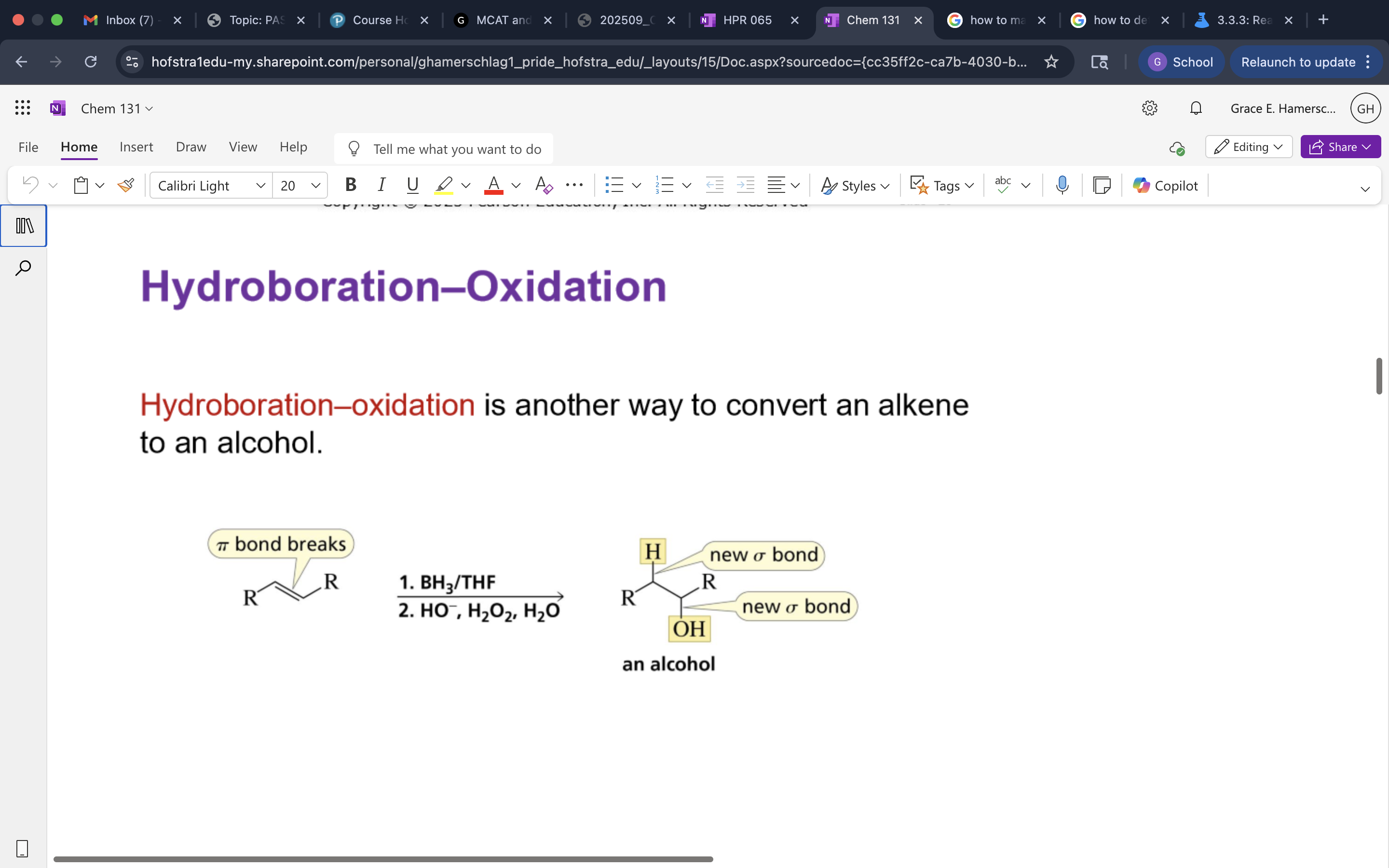
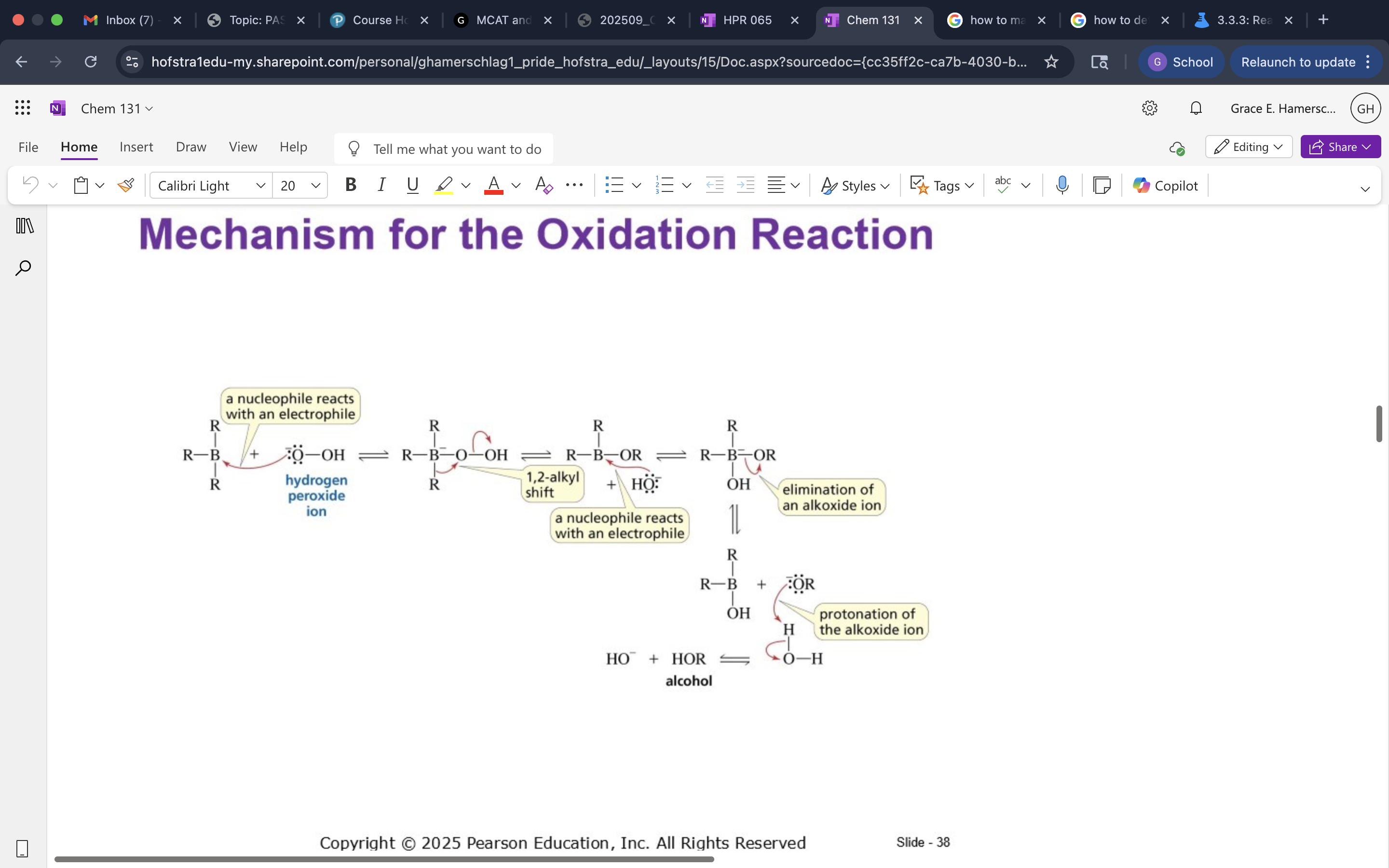
Oxidation Mech.
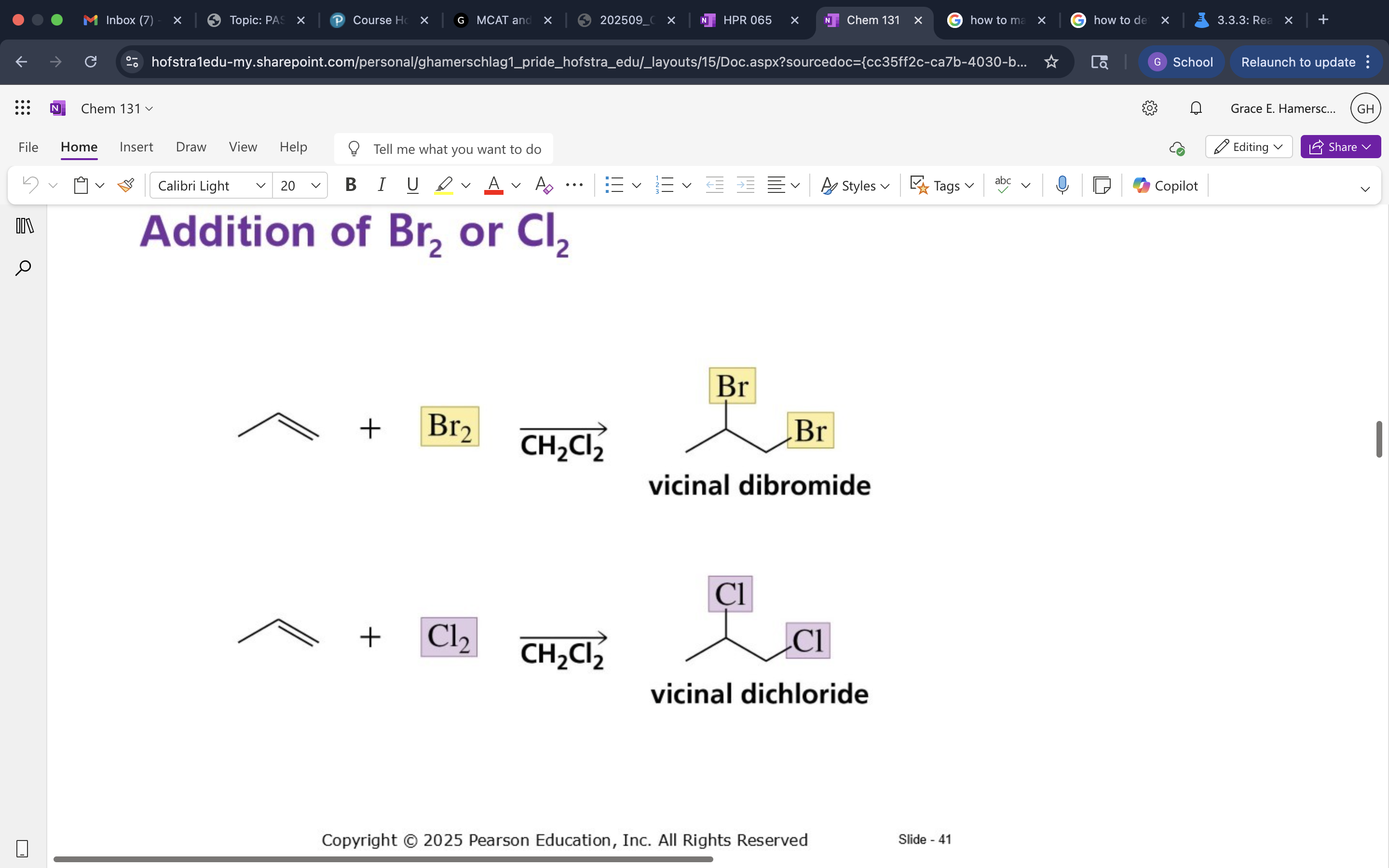
X2 Addition
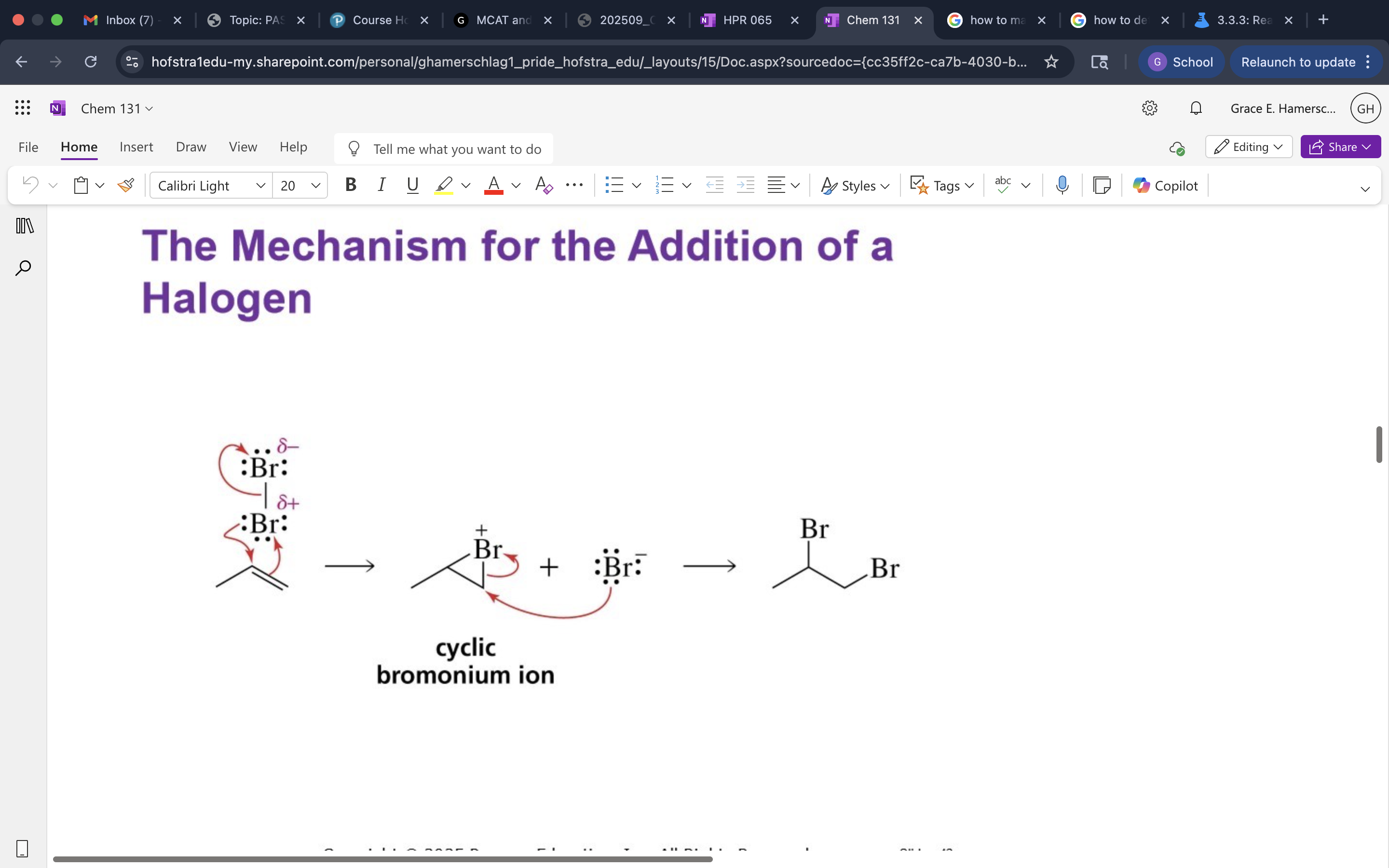
X2 addition mech.
anti addition
Make carbon- Carbon Bond
deprotonate alkyne with NaNH2 and treat with Alkyl halide
What halide is too unstable to add as X2?
I2, with iodine
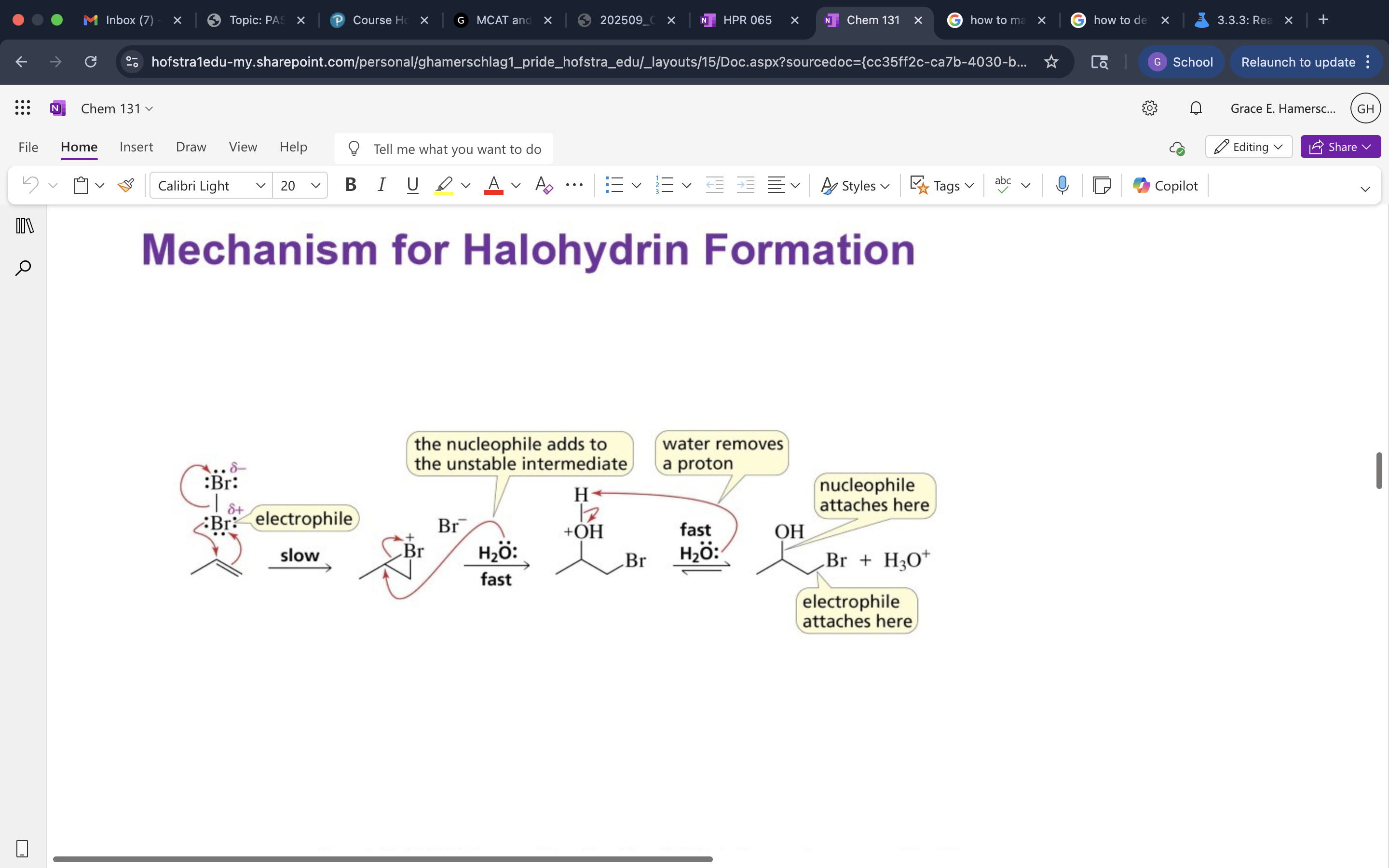
Formation of Halohydrins
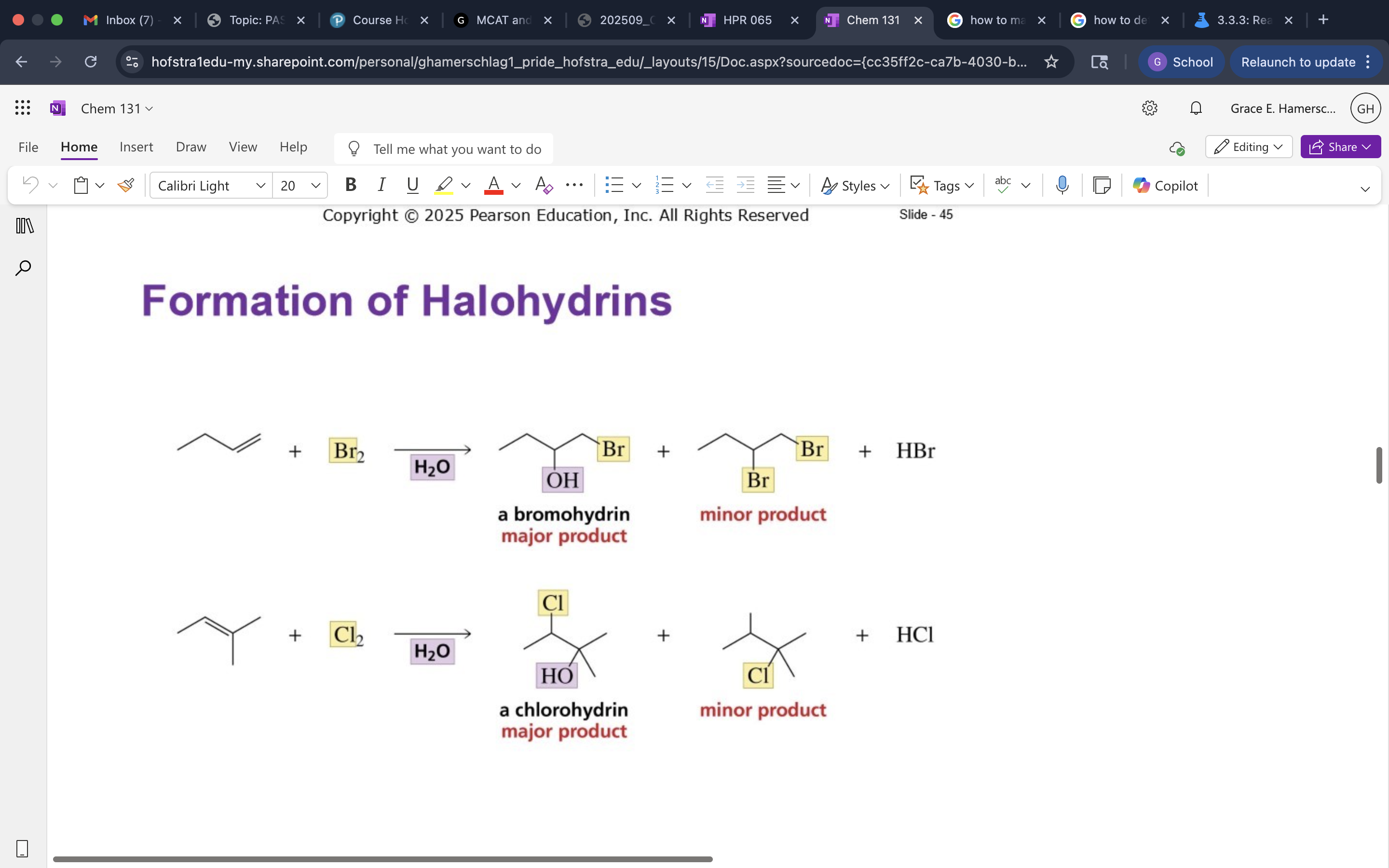
Mechanis mof Halohydrin Formation
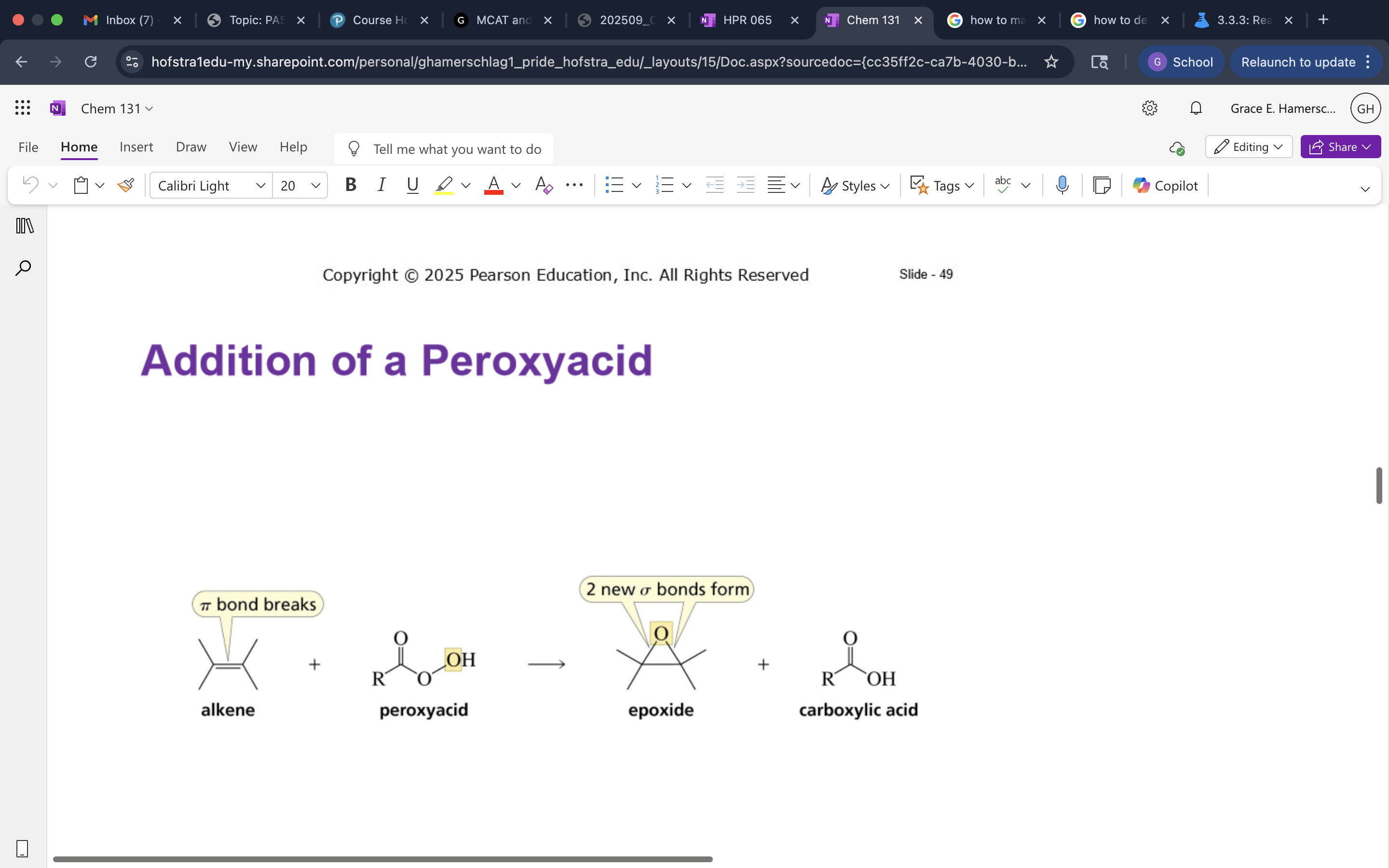
Addition of a Peroxyacid
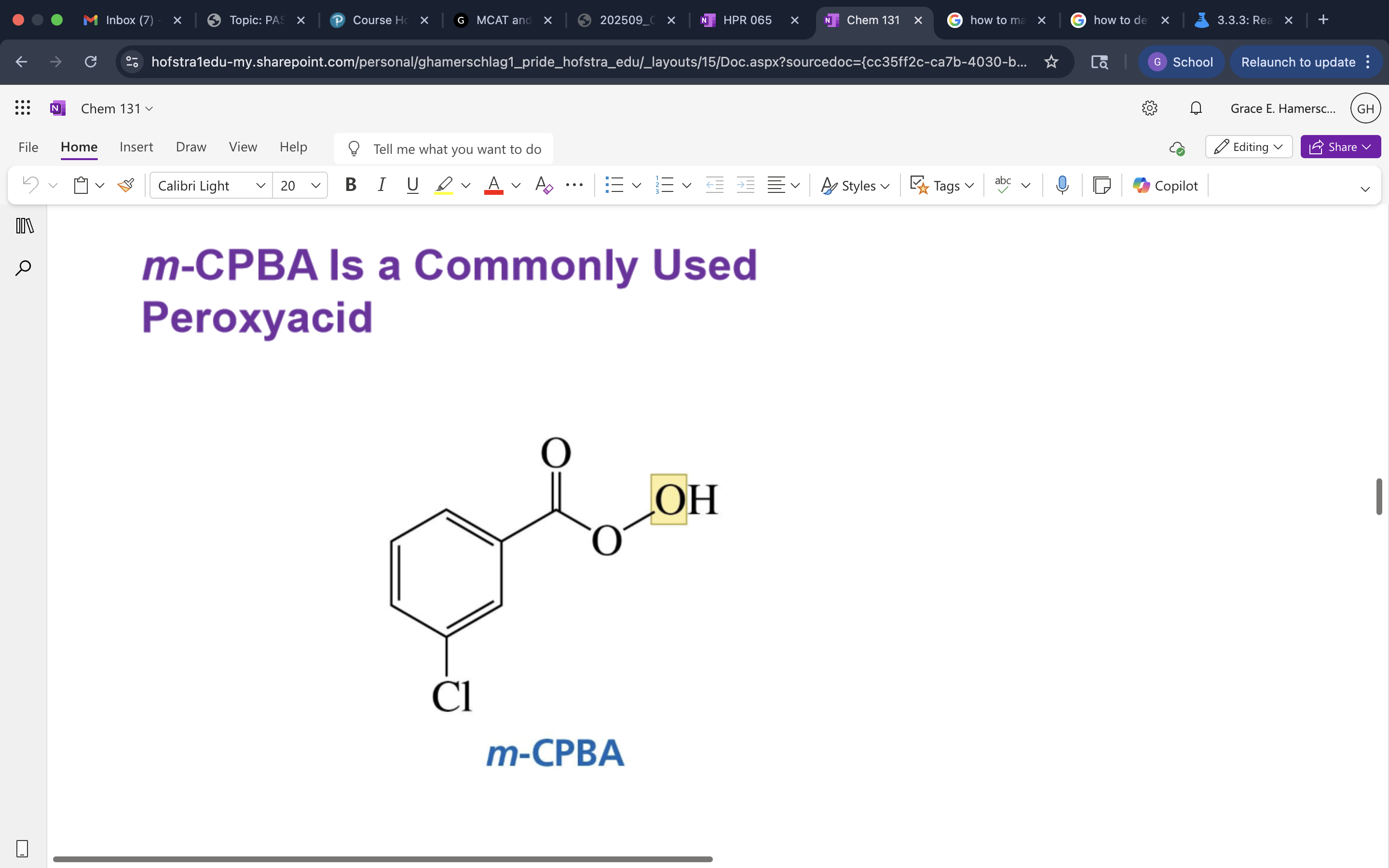
function of m-CPBA
Mechanism of Epoxidation

Alcohol Sythesis with Shift
Hydration with metal (Pd)
syn addition
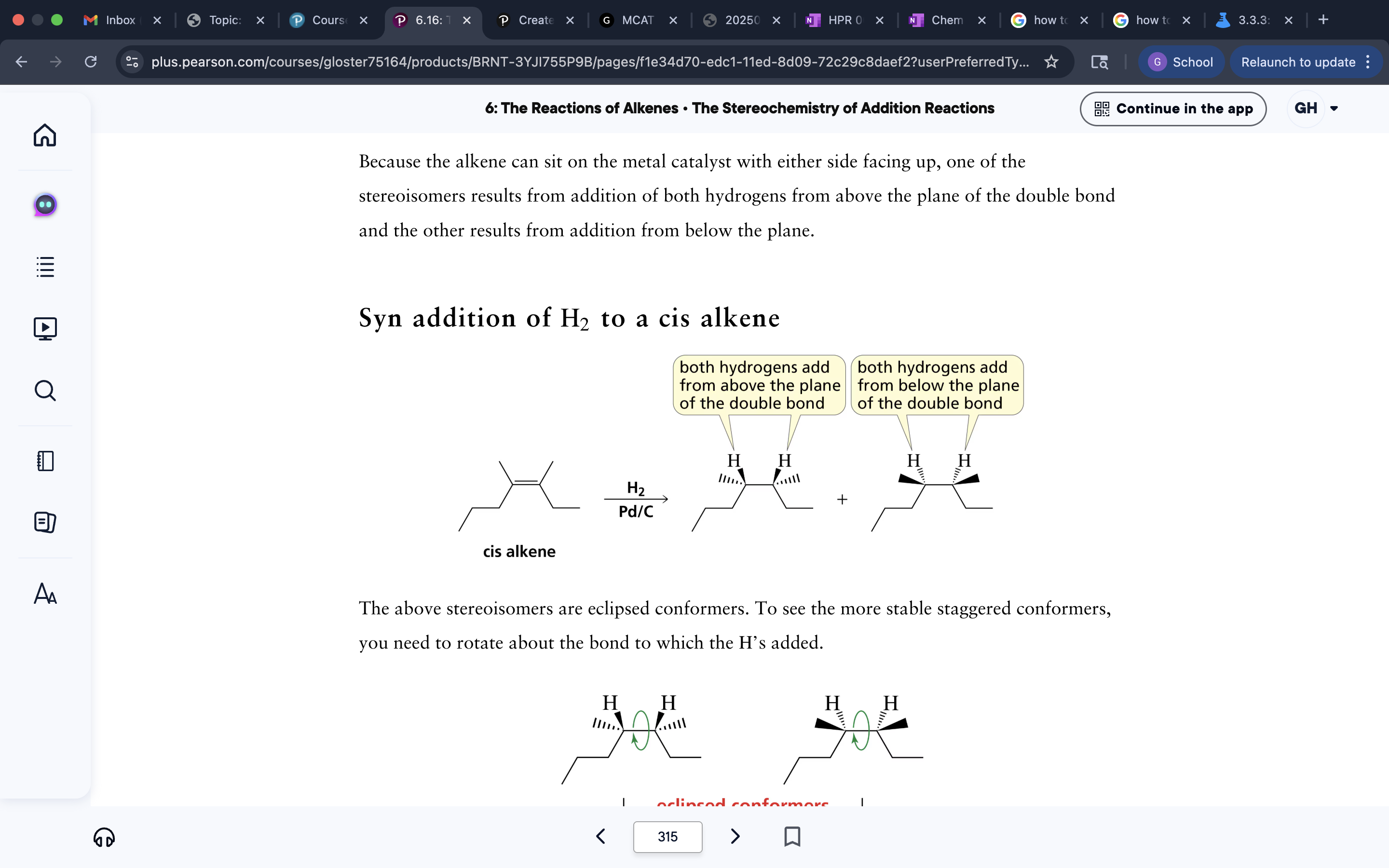
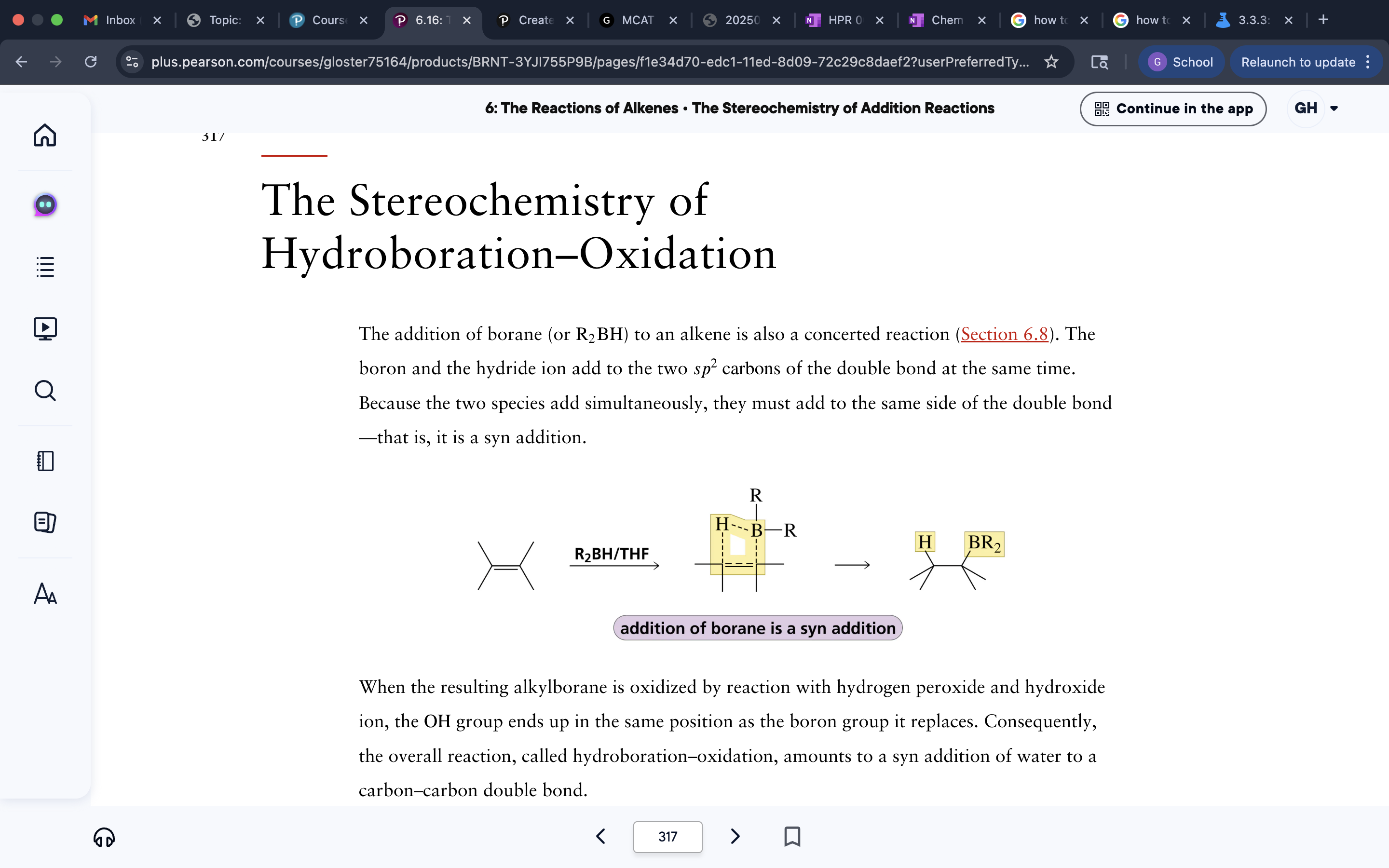
Hydroboration Oxidation Stereochemistry
H-B bridge
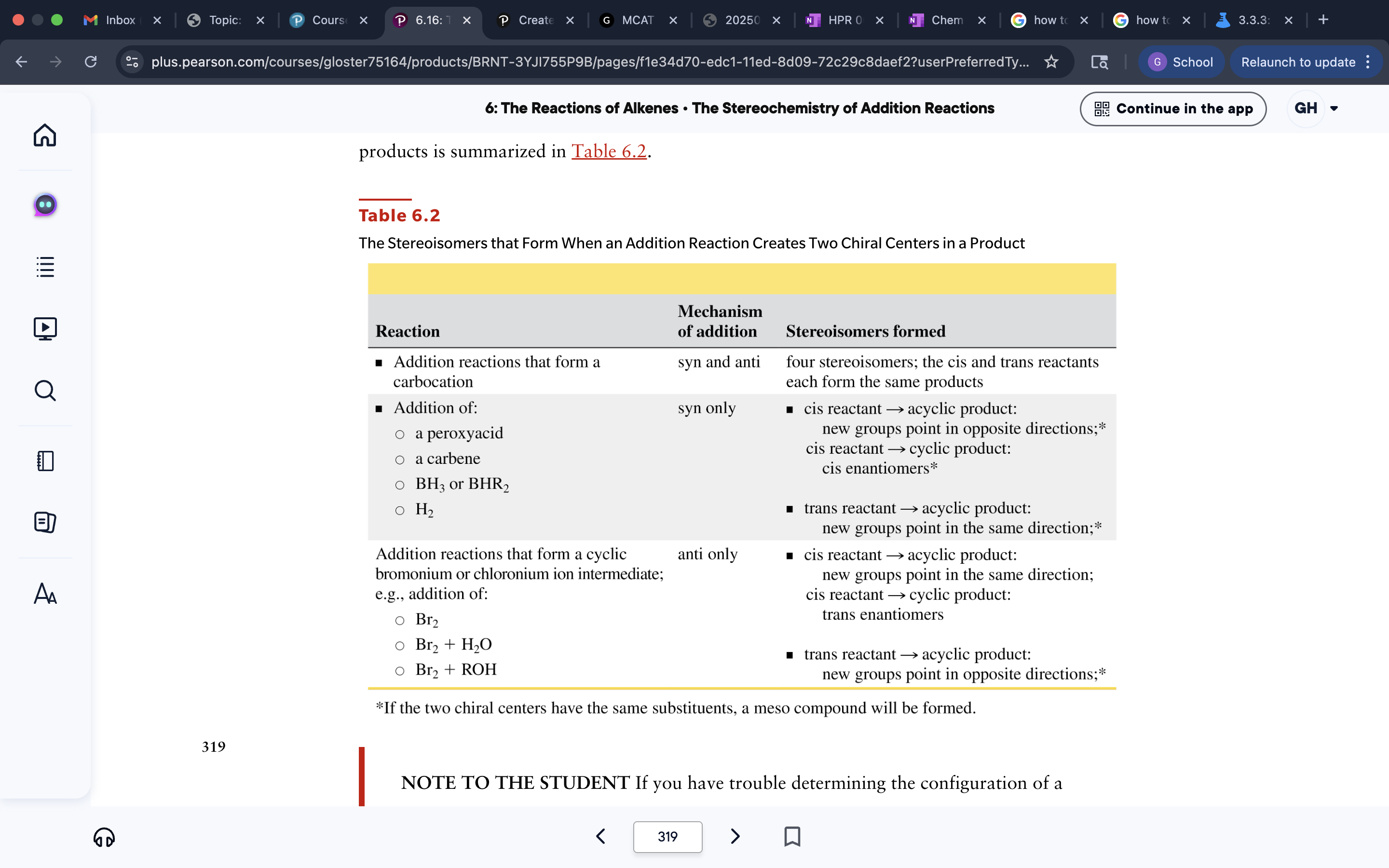
Stereoisomer Forms from Reactions
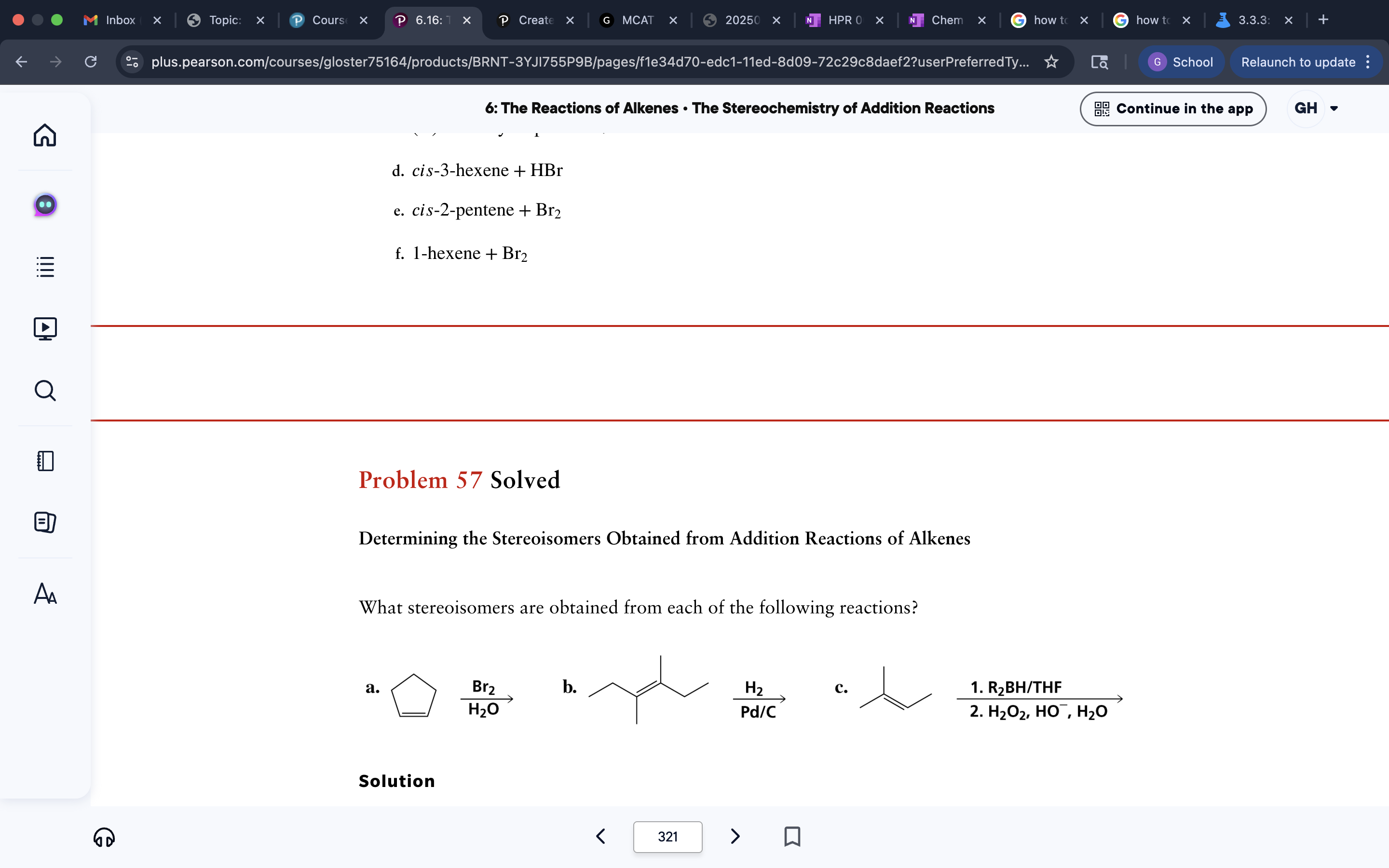
Reaction Product Problems
Reaction Product Problems Part 2
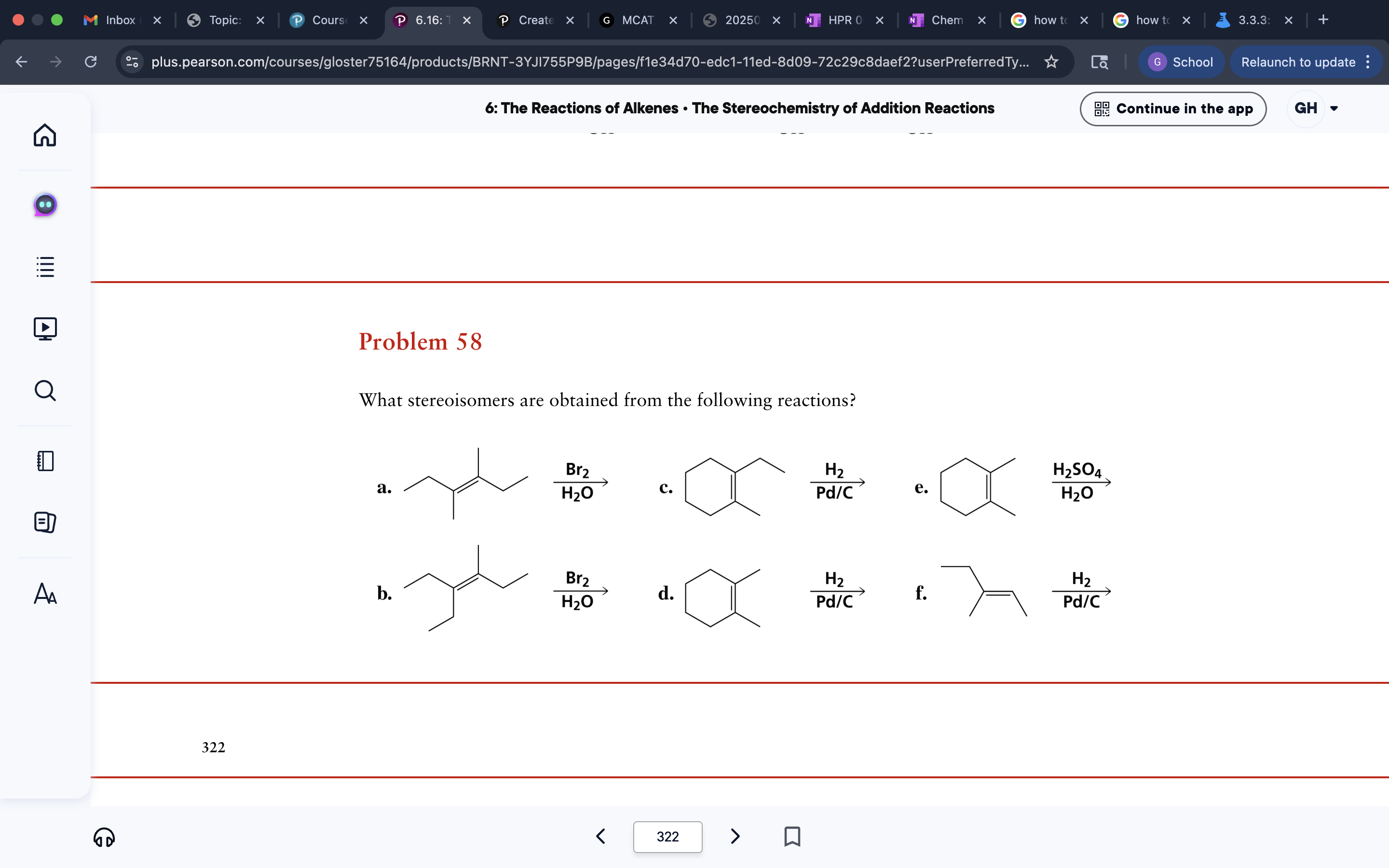
cyclohexene reactions
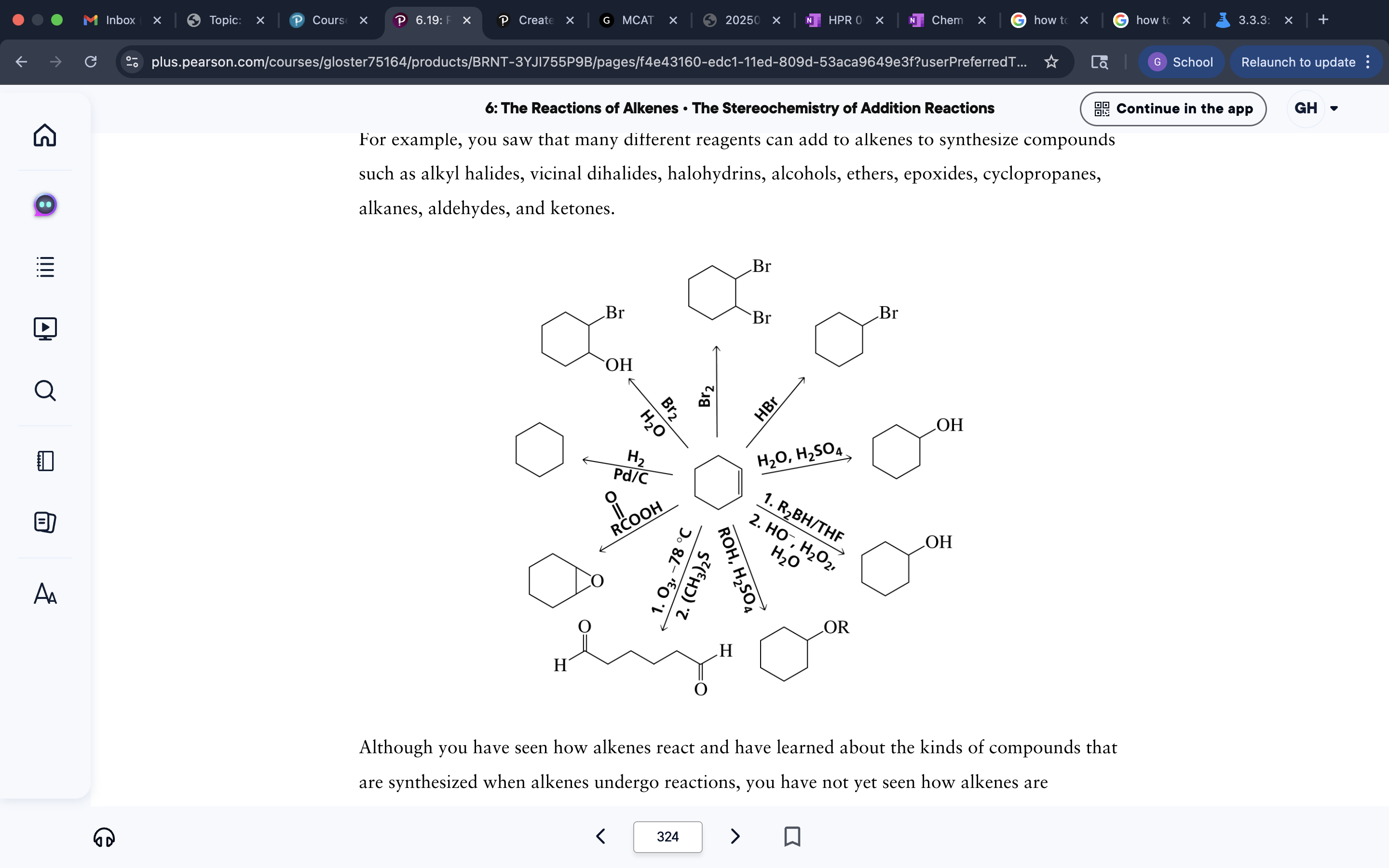
Synthesis problems
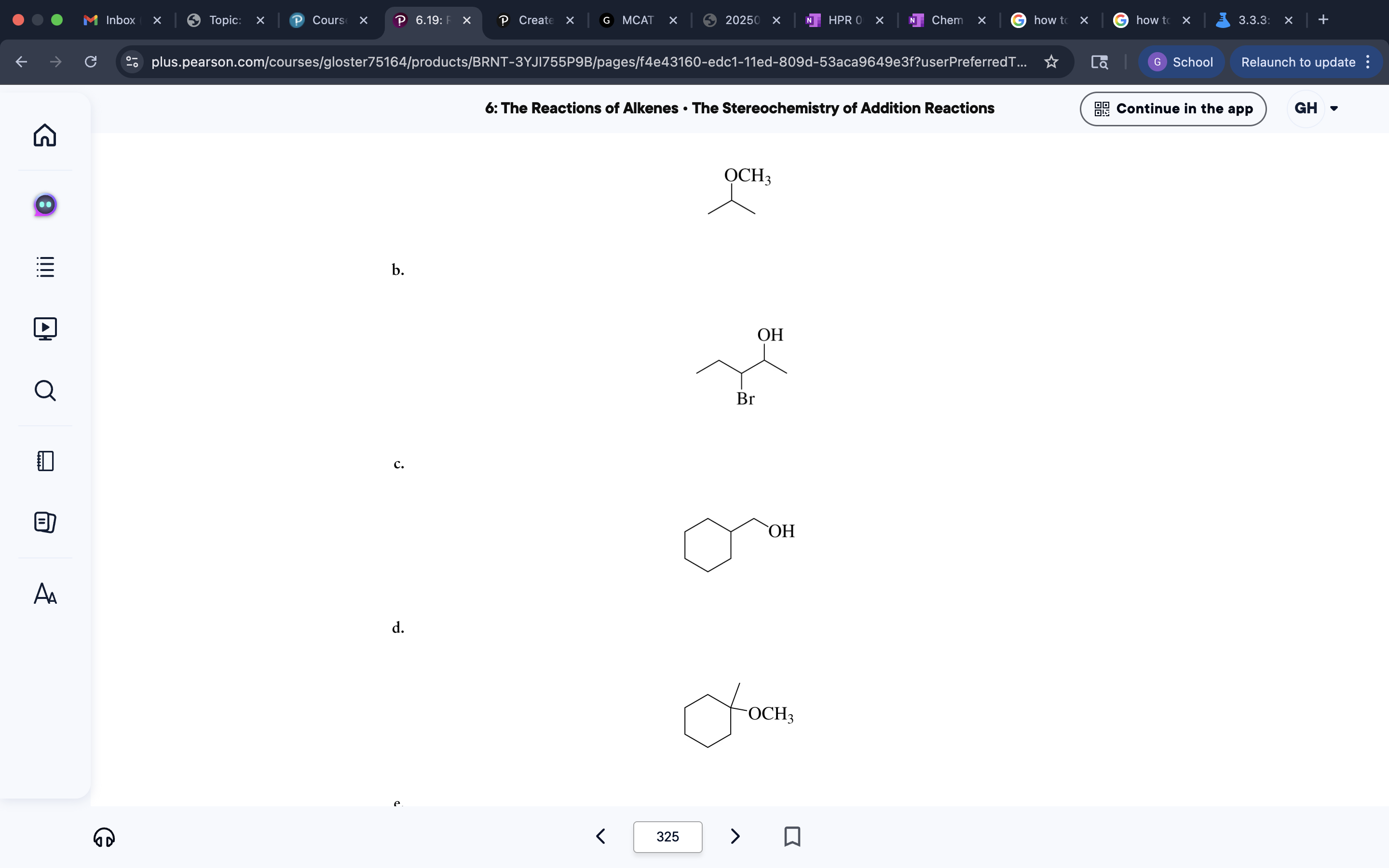
Differences in OH or ketone/alyl addition position depending on reagent