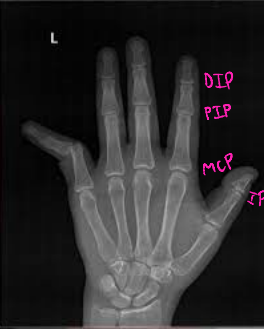
Imaging Modalities: Upper Extremities
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
bone/joint, dental, procedures, available, low, soft tissue, two, radiation, pregnancy
X-Rays: Indications, Benefits, Limitations, and Contraindications
-Indications:
_____/_____ pain or injuries, lung/digestive/_____ issues, screenings, guiding medical ____________
-Benefits:
Quick, readily __________, small radiation dose, and ___ cost
-Limitations:
Does not reveal ____ ______ abnormalities (directly), ___ dimensional only, and _________ exposure
-Consider Risks vs Benefit:
______________ → avoid abdomen/pelvis
Children
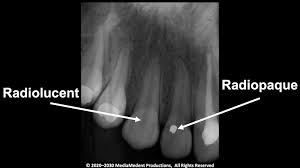
Radiolucent
a substance/area that allows x-rays or other radiation to pass through relatively easily, appearing dark or black on the resulting image
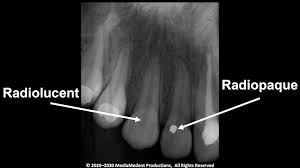
Radiopaque
a material’s ability to block or absorb radiation, particularly X-rays, making it appear white or bright on imaging
side, osteoarthritis, joint, 2-4, above, below, individual, alignment, swelling
Ordering and Reading X-Rays
-Ordering:
Note which _____ you are interested in → left, right, or both. Imaging both sides for comparison is good in kids or for evaluation of ___________.
Note if you want images of the ____ or long bone
Number of views → _-_ views typically
Consider joint _____ and/or ______ depending on findings
-Reading:
Check each __________ bone → look for fractures, bony lesions, or tumors
Assess _____________ of joints
Look for soft tissue ___________
location, alignment, articulation, closed
Descriptive Terminology for Fractures
-__________ → what bone, which side
-Plane → transverse, oblique, spiral, vertical
-_______________ → displaced or non-displaced
-Angulation
-Comminution
-_____________ → intraarticular or extraarticular
-Open vs ______
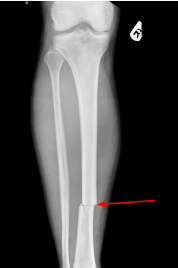
Transverse
What is the plane of this fracture?
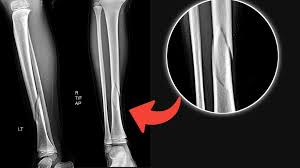
Oblique
What is the plane of this fracture?
Spiral
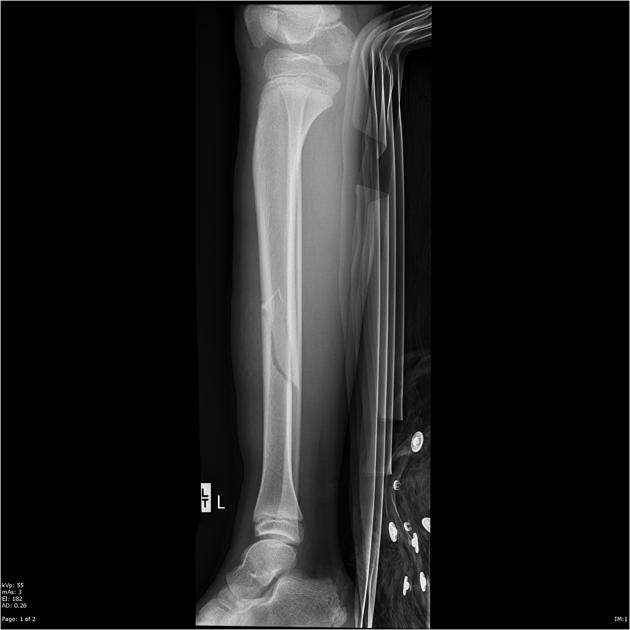
What plane is this fracture in?
Vertical
What plane is this fracture in?
-This type of fracture is really only seen in the patella
Non-displaced
Describe the alignment of this fracture
Displaced (dorsal)
Describe the alignment of this fracture
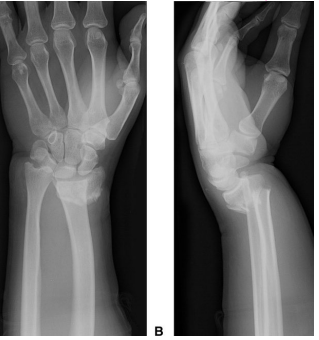
dorsal, volar
When describing a displaced fracture, you should state whether the distal piece is displaced towards the back of the hand (________) or the palm (_______)
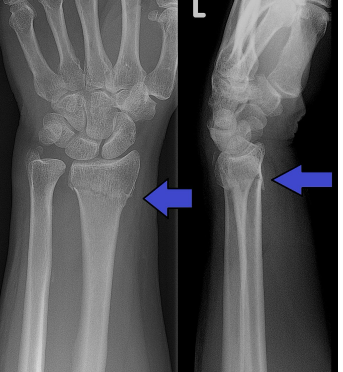
No angulation
What angulation can be seen here?
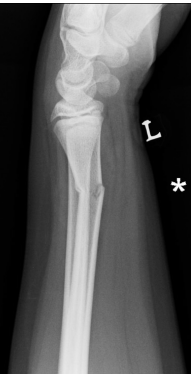
Dorsal angulation
What angulation can be seen here?
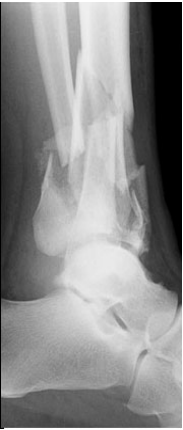
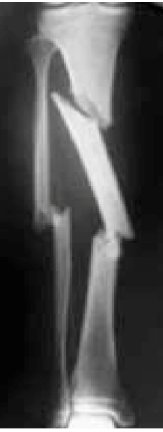
Comminuted
Would you describe this fracture as comminuted or segmental?
Segmental
Would this fracture be described as comminuted or segmental?
joint, cartilage
Intra-Articular Fractures
-When the fracture enters the _____ space
-Can do damage to the articular _______ and cause downstream issues
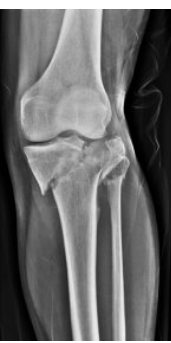
Open
When there is an open wound over a fracture, the fracture is also described as _____.
quick, 3D, tumors, radiation, cost, kidney function, detail, surgical, complex, head, trauma, masses
CT Scans: Benefits, Limitations, and Indications
-Benefits:
_____, gives complete circumference of bone, __ images help with surgical planning of complex fractures, and good for evaluation of ____
-Limitations:
__________ exposure (more than x-ray), ____ ($1,000-2,000), contrast agents can lead to ________ _________ issues, and availability
-Indications:
Evaluate for fracture → gives more ______ of the fracture and helps with _______ planning if needed
Evaluate more _______ fractures → tibial plateau, calcaneal, spine, scaphoid, pelvis/acetabular, and comminuted
Imaging modality of choice for ____/spine/abdominal/chest ______
Evaluates _______/bony lesions
axial, coronal, sagittal, white, gray, black
Interpreting a CT
-Know your anatomy
-Identify the plane:
____ → looking through the body from the inferior aspect to the superior (horizontal slice)
_______ → looking across the body from front to back
_________ → looking across the body from right to left or left to right
-Shades of white, gray, and black
Dense structures (bone) = _____
Fat/fluid = varying levels of ____
Air = _____
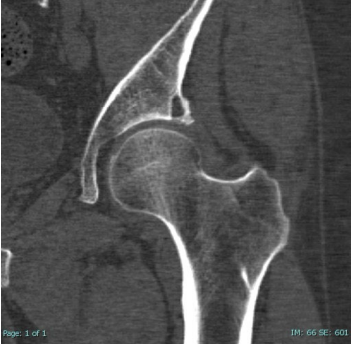
T1
What type of MRI is best for seeing occult fractures? It highlights fat (white) and fluid (dark)
T2
What type of MRI is better for identifying tears? It highlights water/fluid (white) and fat (intermediate)
soft, marrow, radiation, metal, claustrophobia, soft tissue, occult, failed, compression
MRI: Benefits, Limitations, and Indications
-Benefits:
Best modality for ____ tissue, excellent for bone _______ changes/occult fracture, and no __________ exposure
-Limitations:
Cost/insurance approval, not as widely available, time consuming (30-60+ minutes)
Safety concerns → ____ objects in the body or room, pt ____________
-Indications:
Positive exam findings after an acute injury concerning for ____ ______ injuries, evaluate for stress/_______ fractures, when conservative treatment has ________ and surgery is being considered, assessing for nerve ____________, and suspect osteomyelitis
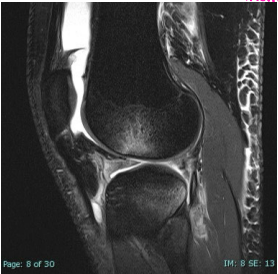
Bone bruising
What does this show?
-Hint: a classic sign of ACL tear
injections, tendon, no, low, penetrate, destruction, metastasis, non-specific
Ultrasound and Bone Scans
-Ultrasound
Common uses → needle guided ____________, evaluate vascular flow, ______ injuries, synovitis/bursitis
Benefits → __ radiation, portable, dynamic (can have them move)
Negatives → ___ image quality, operator dependent, doesn’t _________ bone
-Bone Scan
Indications → bone healing/fracture follow up, bone _____________, and evaluate for bone _________
Limitations → ___-________ cause, time consuming
AP, axillary, scapular Y, Grashey
What 4 views can you order for a shoulder?
-__, _________, __________ _, _________
AP
What view is this?
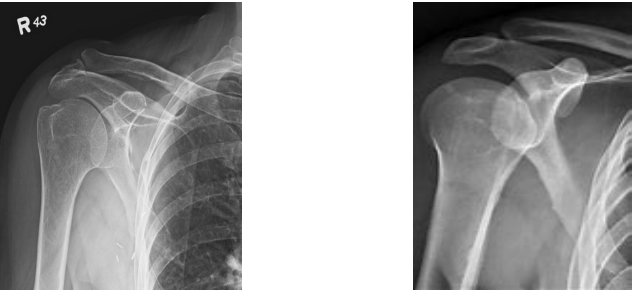
Axillary
What view is this?
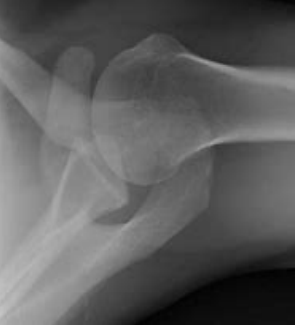
humeral, middle
Scapular Y View
-__________ head should sit in the _______ of the Y
-Shows the profile of the acromion, as well as dislocations
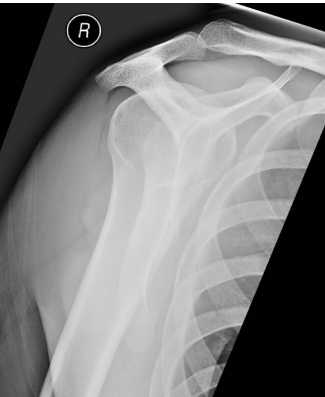
GH, internal, external
Grashey View
-Not part of the standard shoulder films, more of an ortho thing
-Called the “true AP” view
-Provides a better view of the __ joint
-Can be taken with the humerus in ________ or _________ rotation
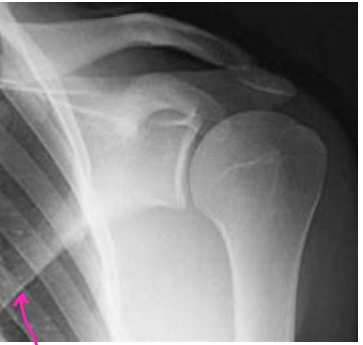
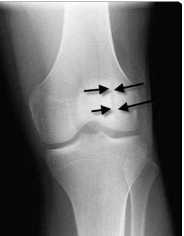
Glenohumeral Osteoarthritis
What can be seen on this image?
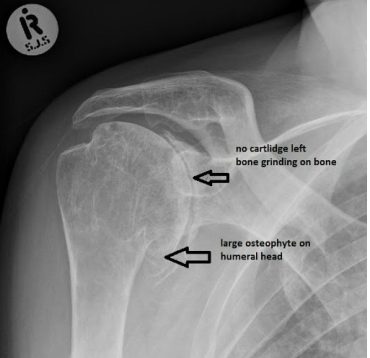
Rotator cuff (RTC)
Having an elevated humeral head can be indicative of an injury to what group of muscles?
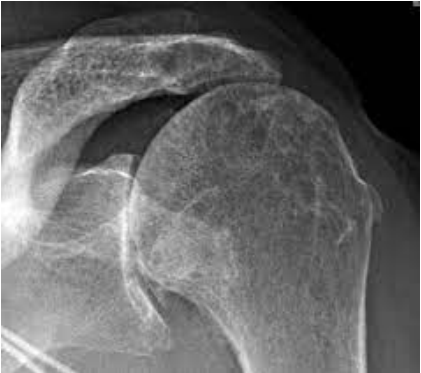
Proximal humerus
This image shows a __________ _________ fracture
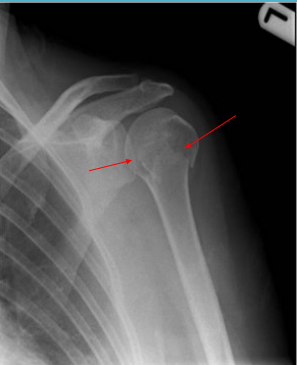
Greater tuberosity
What part of the humerus is fractured here? This type of fracture can result in issues with the rotator cuff muscles
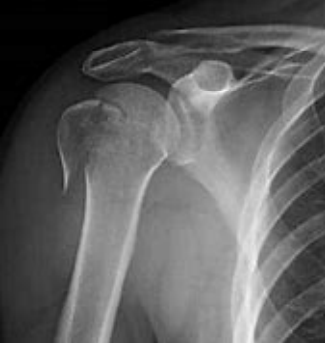
Glenoid
Where is the fracture?
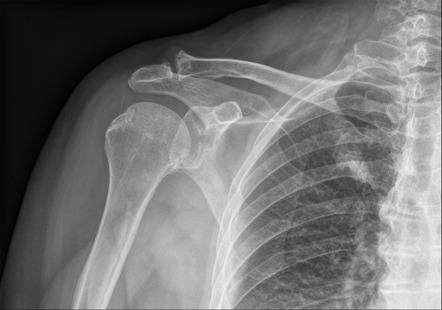
2, thirds
Clavicle Fractures
-Image with _ views
-Divided into ______ → distal, midshaft, and proximal
-MC in kids and young adults
-MOI → FOOSH or direct blow
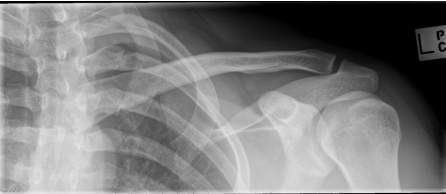
Anterior
What type of shoulder dislocation can be seen here?
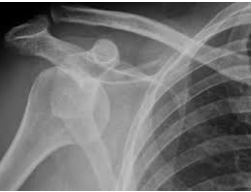
Hillsach’s
What kind of deformity can be seen here?
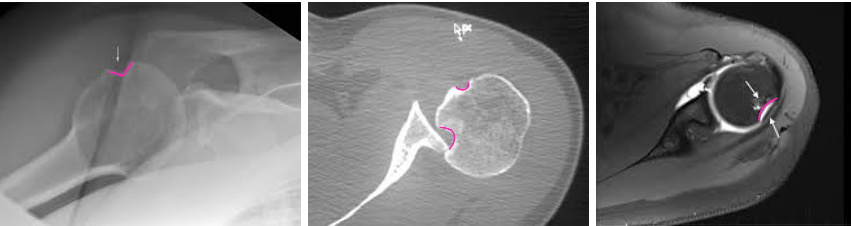
Bony Bankart
What type of lesion can be seen here?
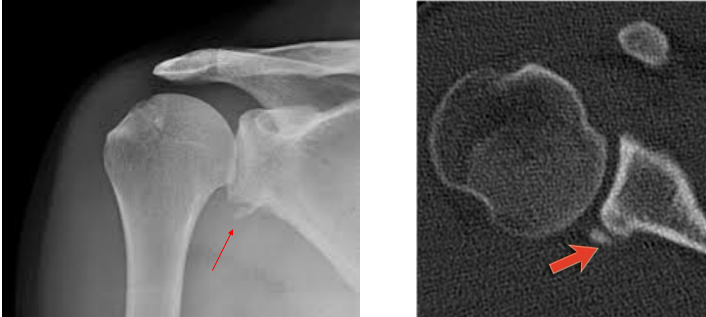
Posterior
What type of shoulder dislocation can be seen here?
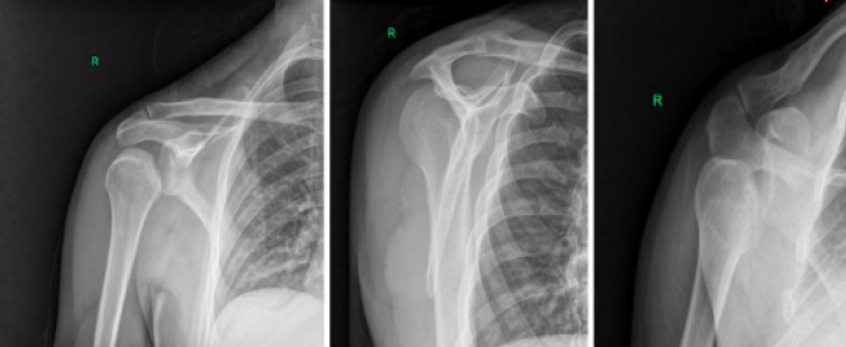
AC joint separation
What abnormality can be seen on this imaging?
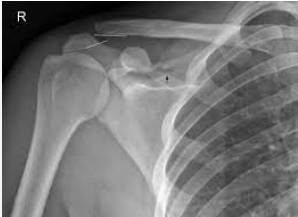
AP, middle, capitellum, middle
Interpreting Elbow X-Rays
-Order __ and lateral films
-Anterior Humeral Line → should pass through the ______ of the _________
If it doesn’t, then there is a supracondylar fracture present
-Radio-capitellar line → should pass through the ______ of the capitellum
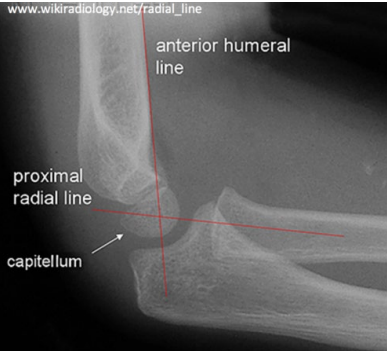
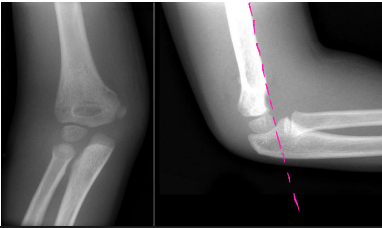
Supracondylar
What type of humerus fracture am I describing?
-Fracture of distal humerus just above the epicondyles
-Check nerve function during examination → radial, ulnar, and median nerves can be damaged
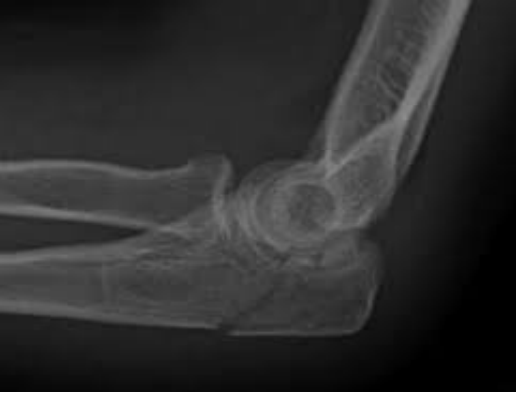
Olecranon fracture
What can be seen here?
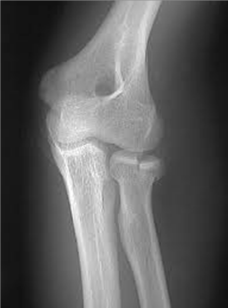
Radial head fracture (intraarticular)
Describe the fracture
head, humerus
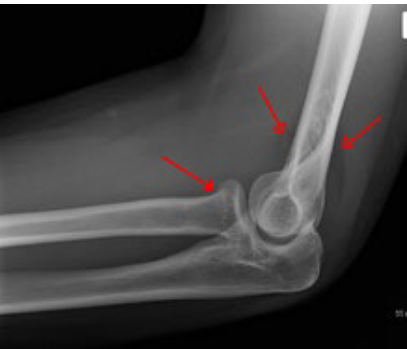
Fat Pad Sign
-Anterior → “Sail sign”, usually indicates a radial ____ or distal __________ fracture
-Posterior
AP, lateral, wrist, elbow
Forearm X-Rays
-Two views → __ and _______
-Should include the _____ and _____ joints
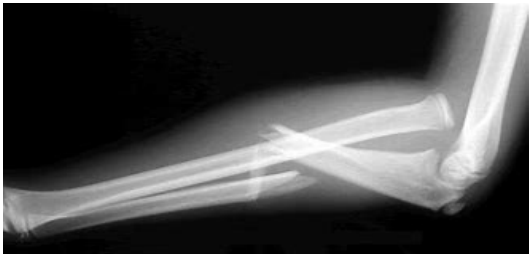
Monteggia Fracture
What type of fracture is shown here?
-An ulnar shaft fracture with radial head dislocation, may need true elbow and wrist films
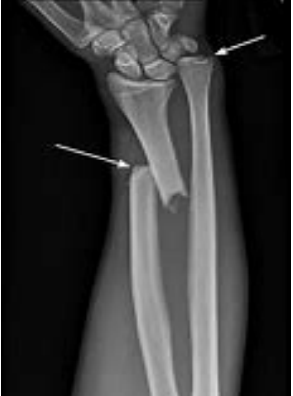
Galeazzi Fracture
What type of fracture is shown here?
-Distal radius fracture with radioulnar joint dislocation
AP, lateral, oblique
What views do you need for a wrist x-ray?
-__ → radial inclination of 20-25 degrees, should intersect with the ulna. Carpal arcs
-______ → distal radius, lunate, and capitate. Should be in a straight line
-_______
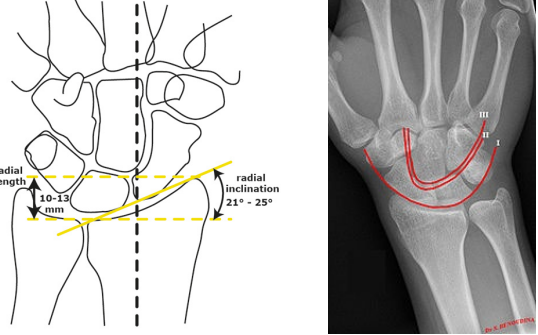
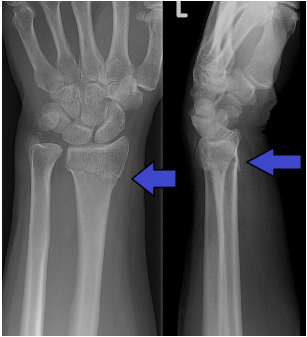
Scaphoid
What carpal bone is fractured?
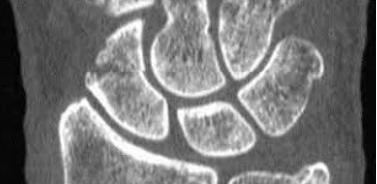
base, shaft, neck
Metacarpal fractures can be described as ____ (proximal), _____ (middle), or ____ (distal)
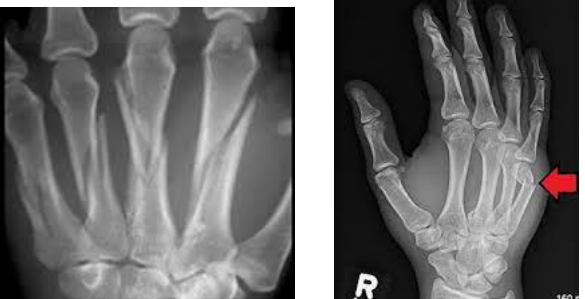
Phalanx (first, proximal)
What bone is fractured here?
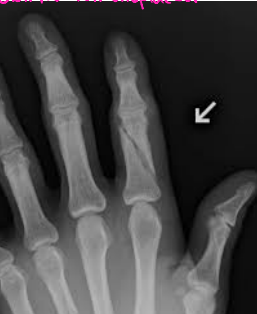
Mallet Fracture
What type of fracture is shown here?
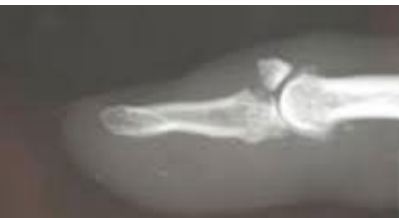
Tuft
What type of fracture is shown here?
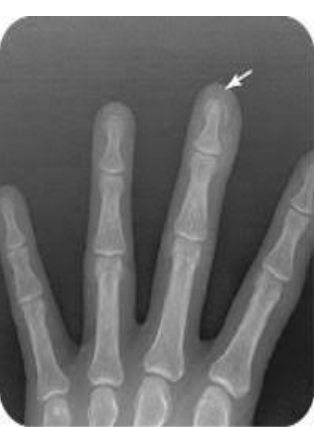
PIP, distal, volar
Finger Dislocations
-Types
MCP, ___, DIP
-Classification → based on the location of the ______ bone in relationship to the proximal
Dorsal, _____, lateral