Cell Structure and Function
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
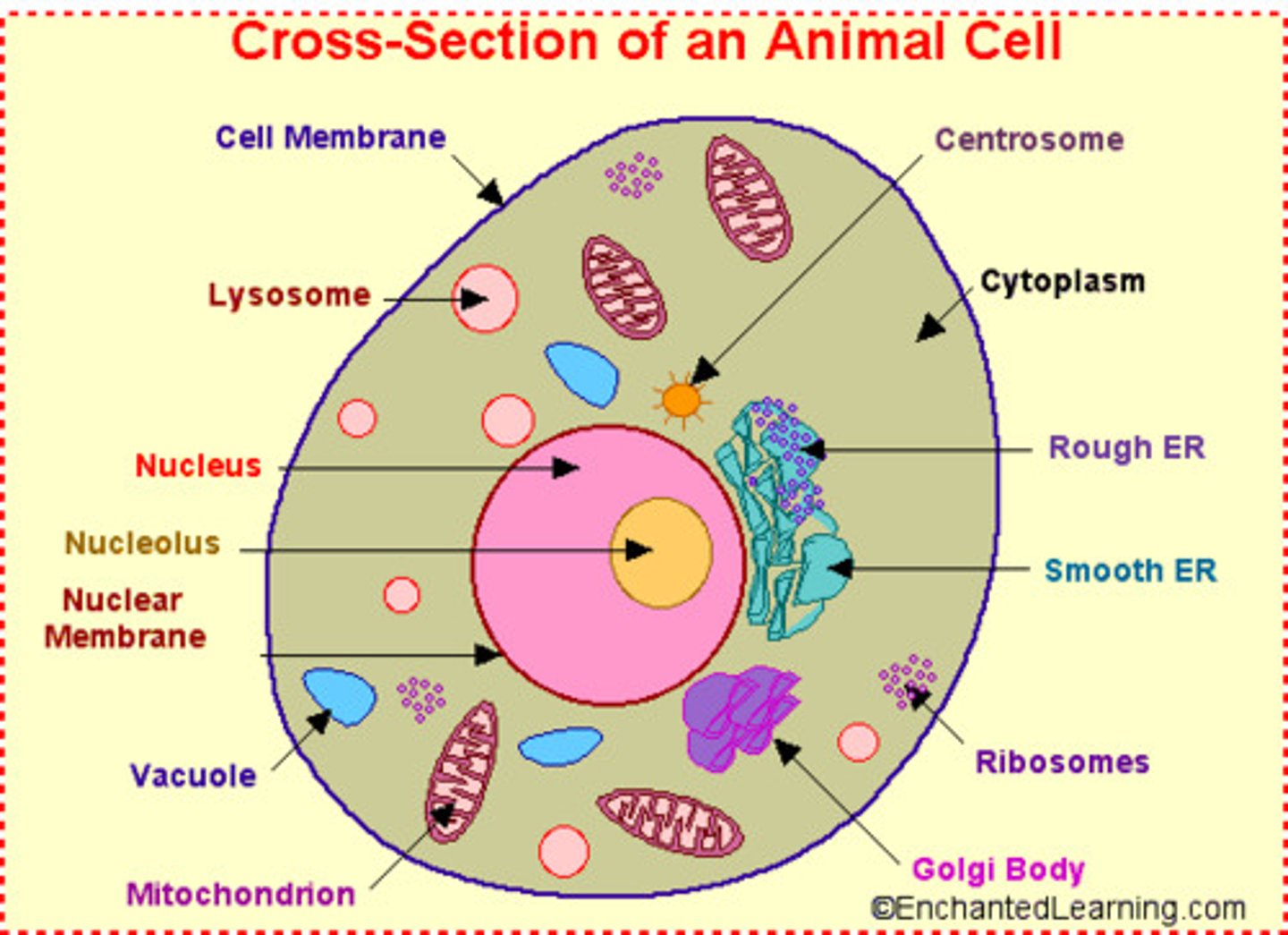
Cell
basic unit of all living things
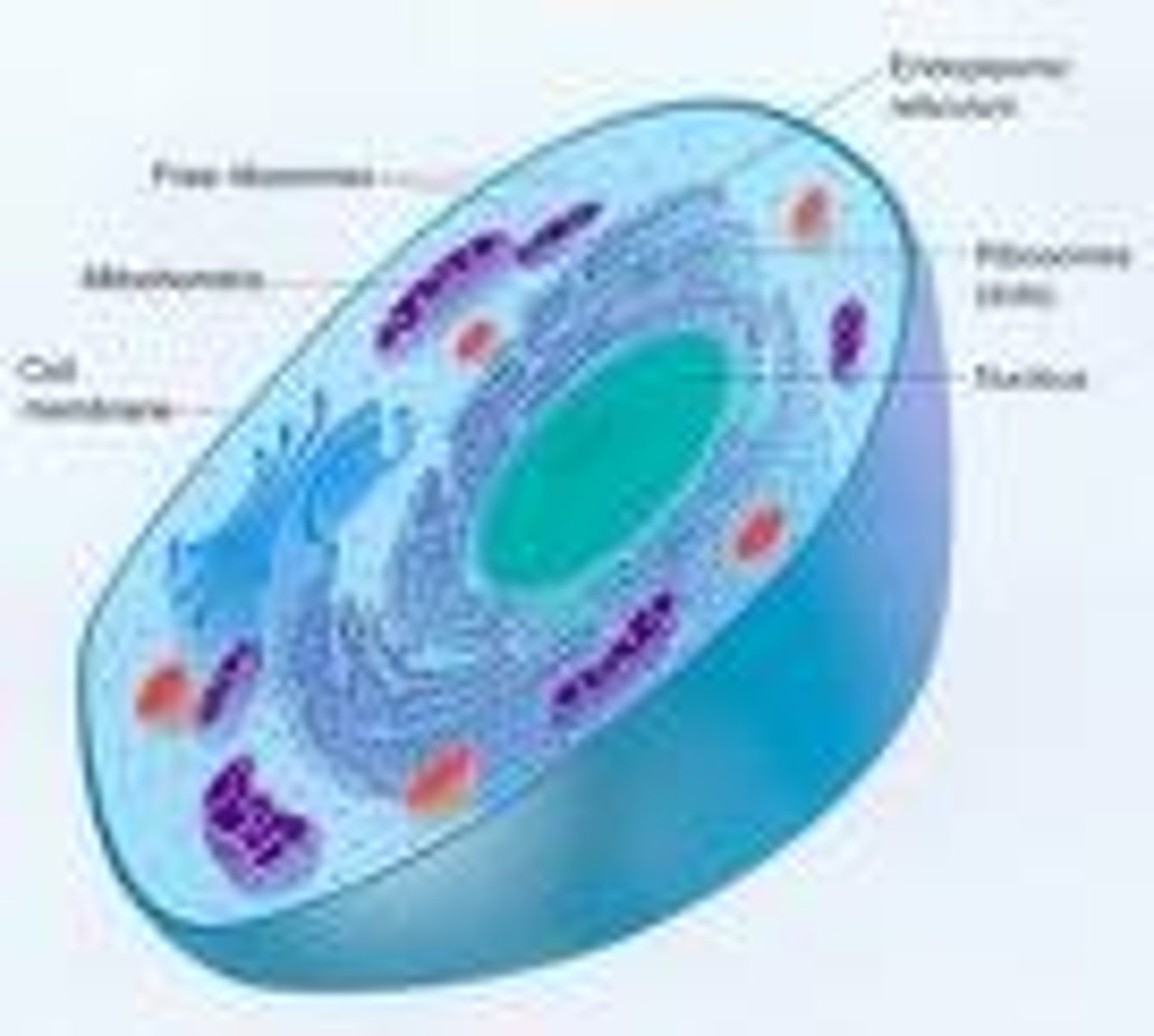
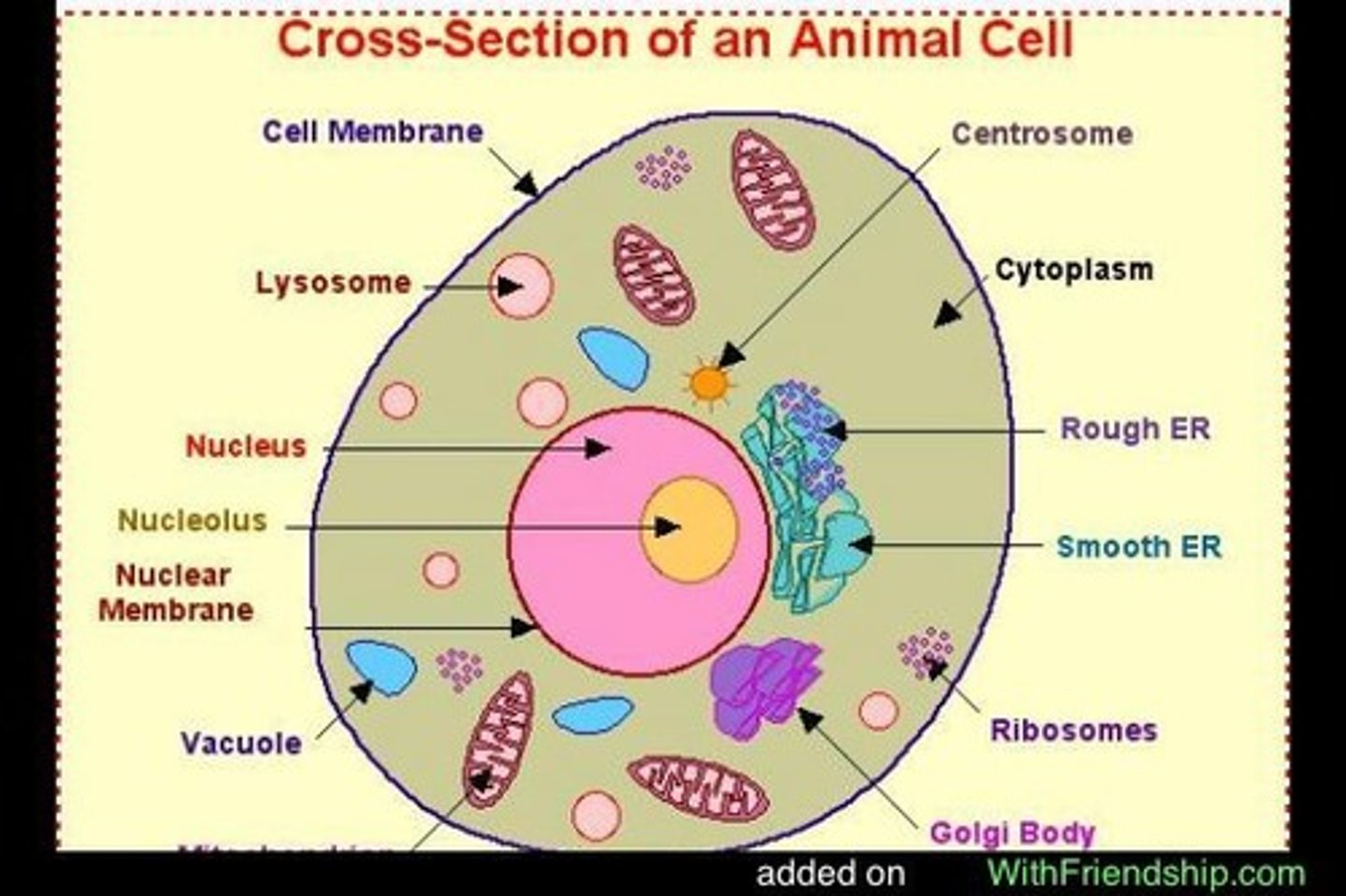
Cell membrane
thin, flexible barrier around a cell; regulates what enters and leaves the cell
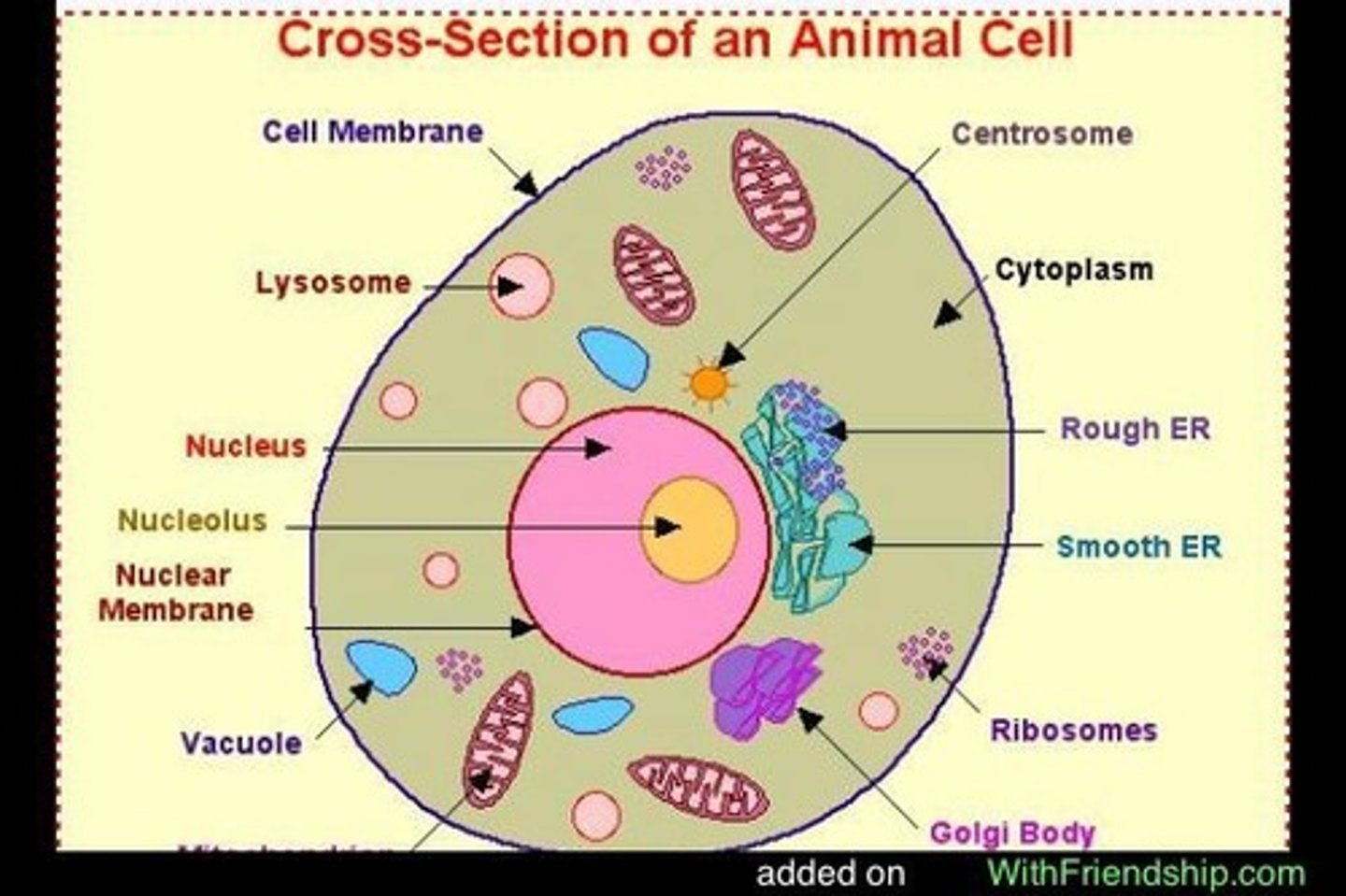
Cytoplasm
a jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
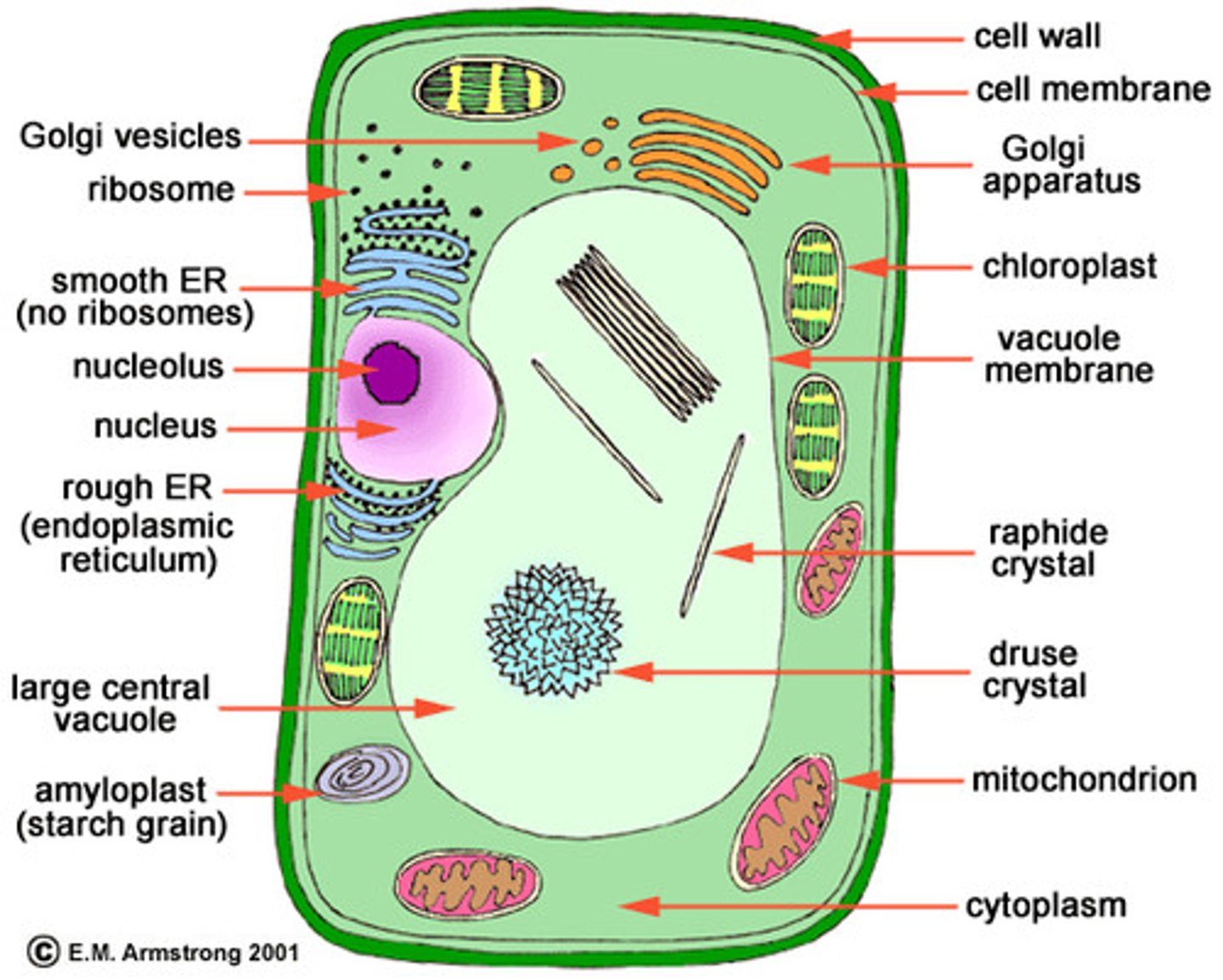
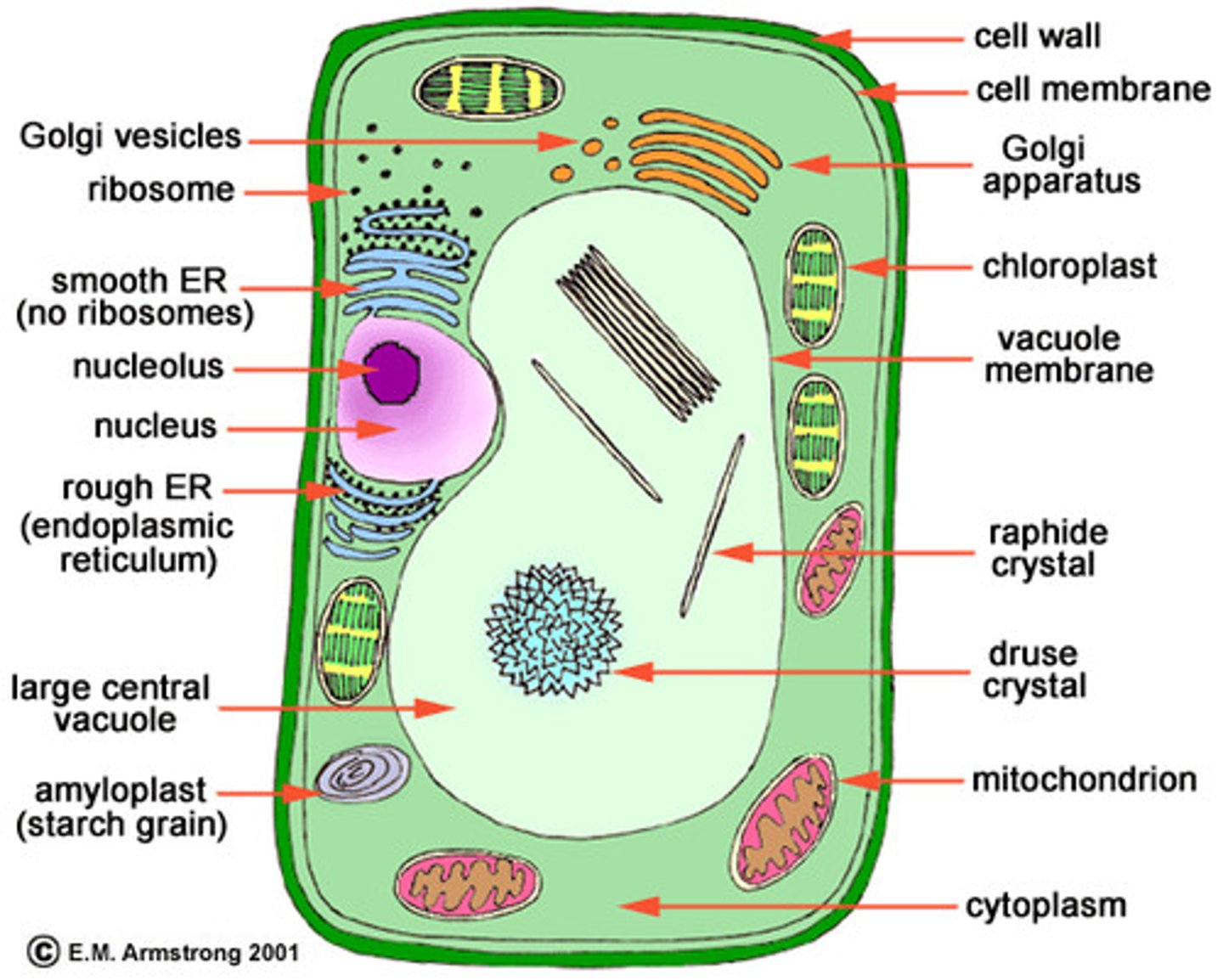
Cell wall
strong wall outside a plant cell's cell membrane that protects the cell and maintains its shape
Organelle
a tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell
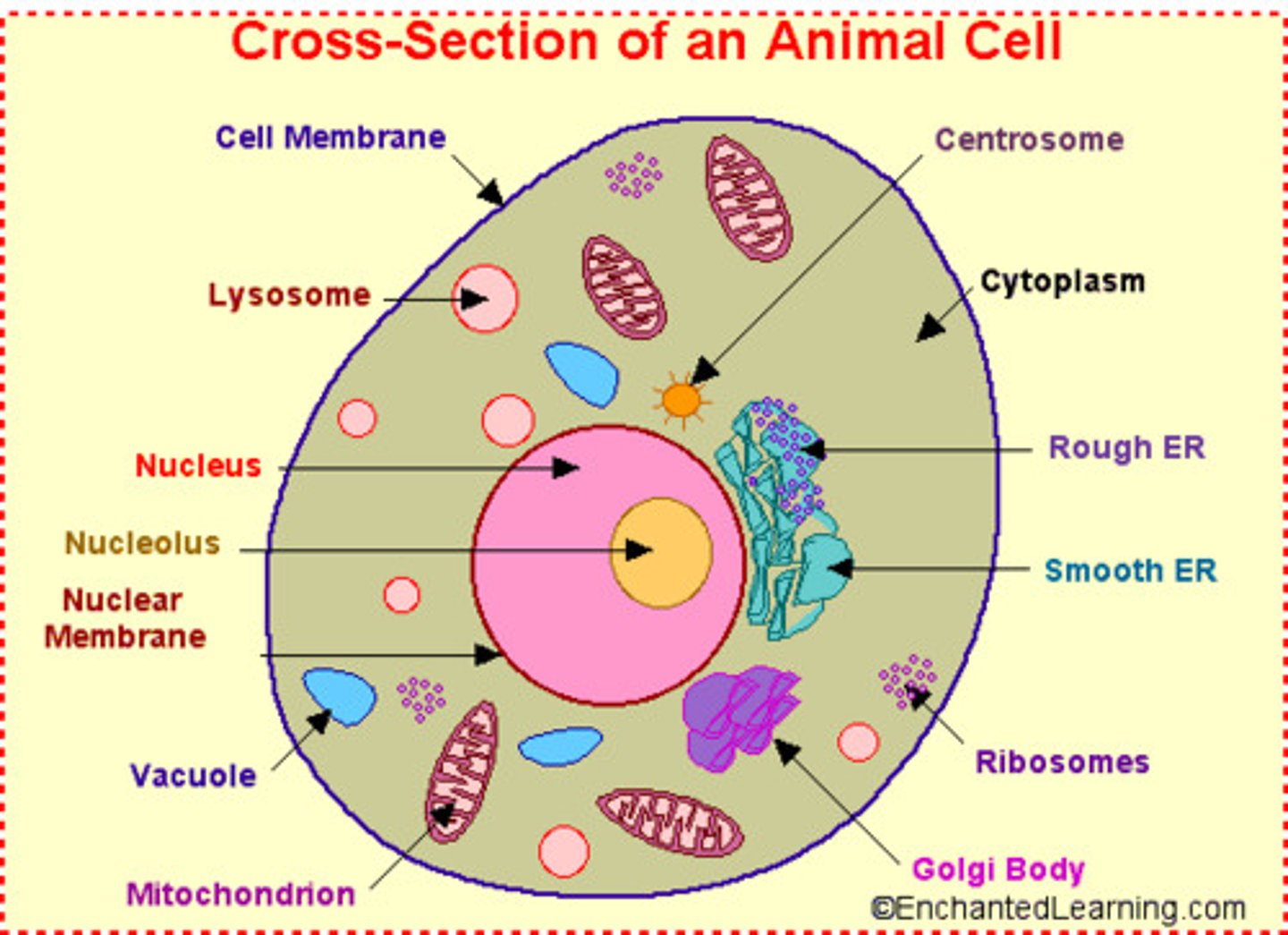
Nucleus
organelle that controls all the activities of a cell and contains hereditary material made of proteins and DNA
Chloroplast
a structure in the cells of plants and some other organisms that captures energy from sunlight and uses it to produce food
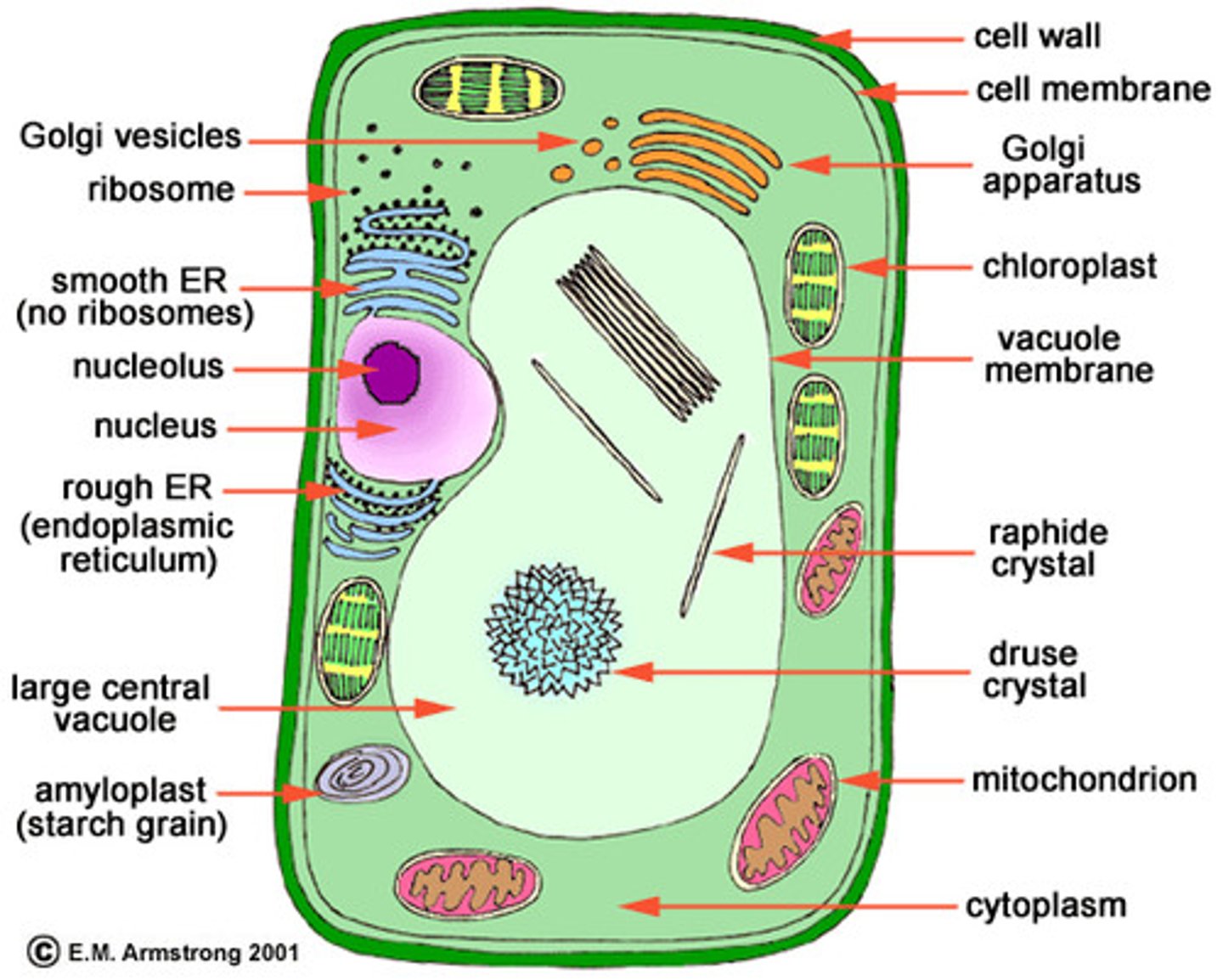
Mitochondrion
bean shaped organelle that releases energy from stored food molecules which supplies energy for the cell
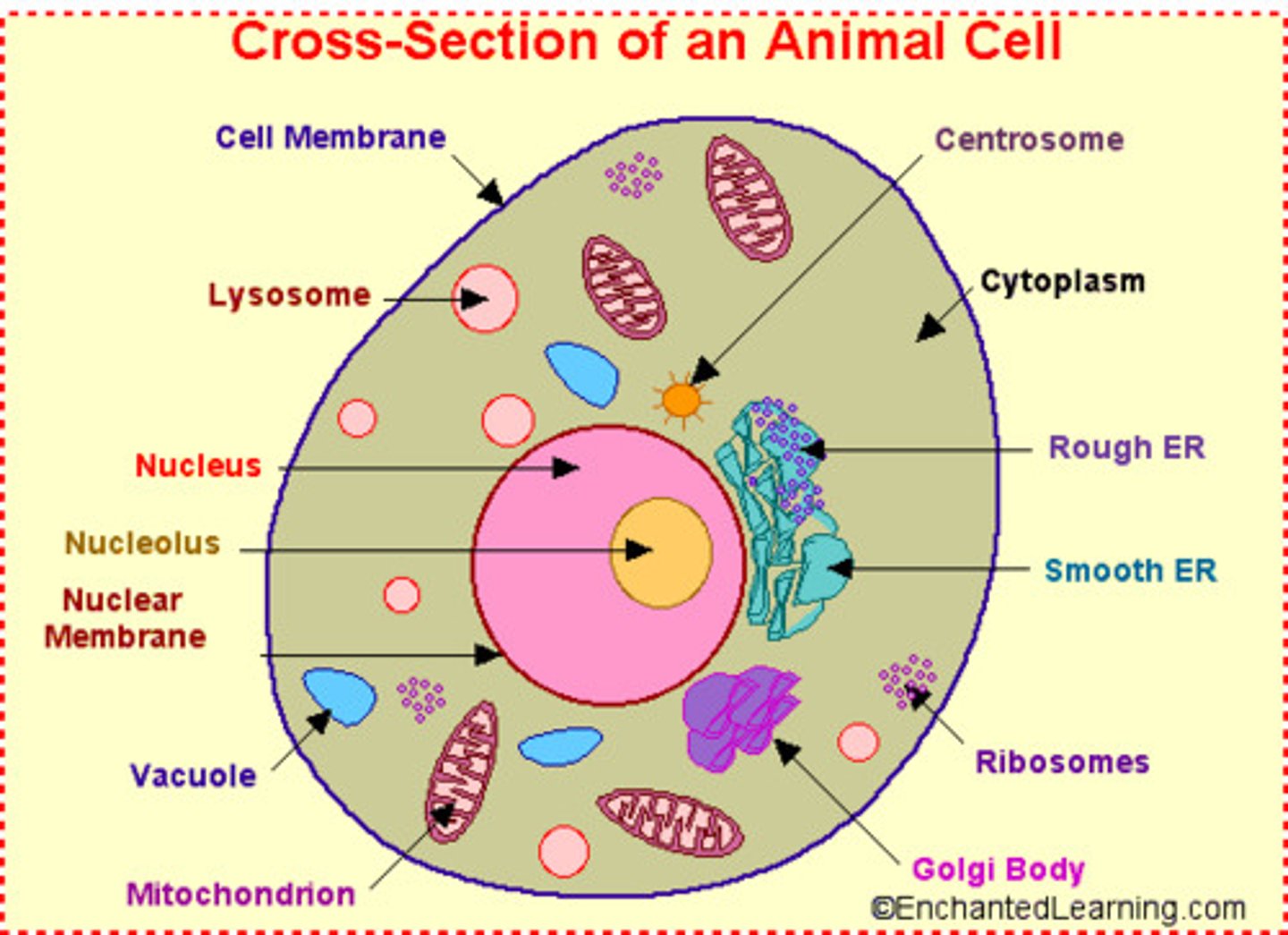
Ribosome
an organelle that is resposible for making proteins.
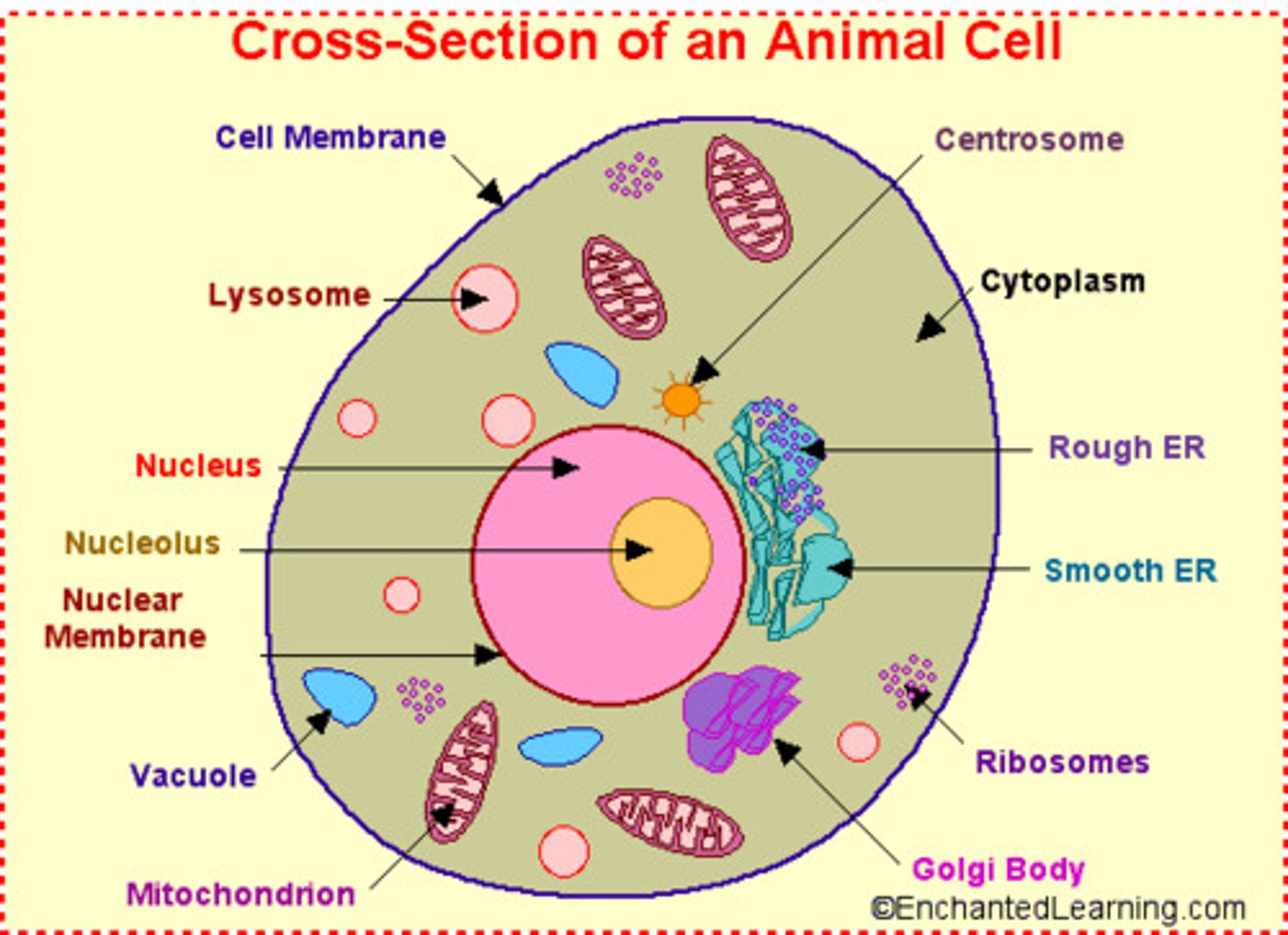
Endoplasmic reticulum
a cell structure that forms a maze of passageways in which proteins and other materials are carried from one part of the cell to another.
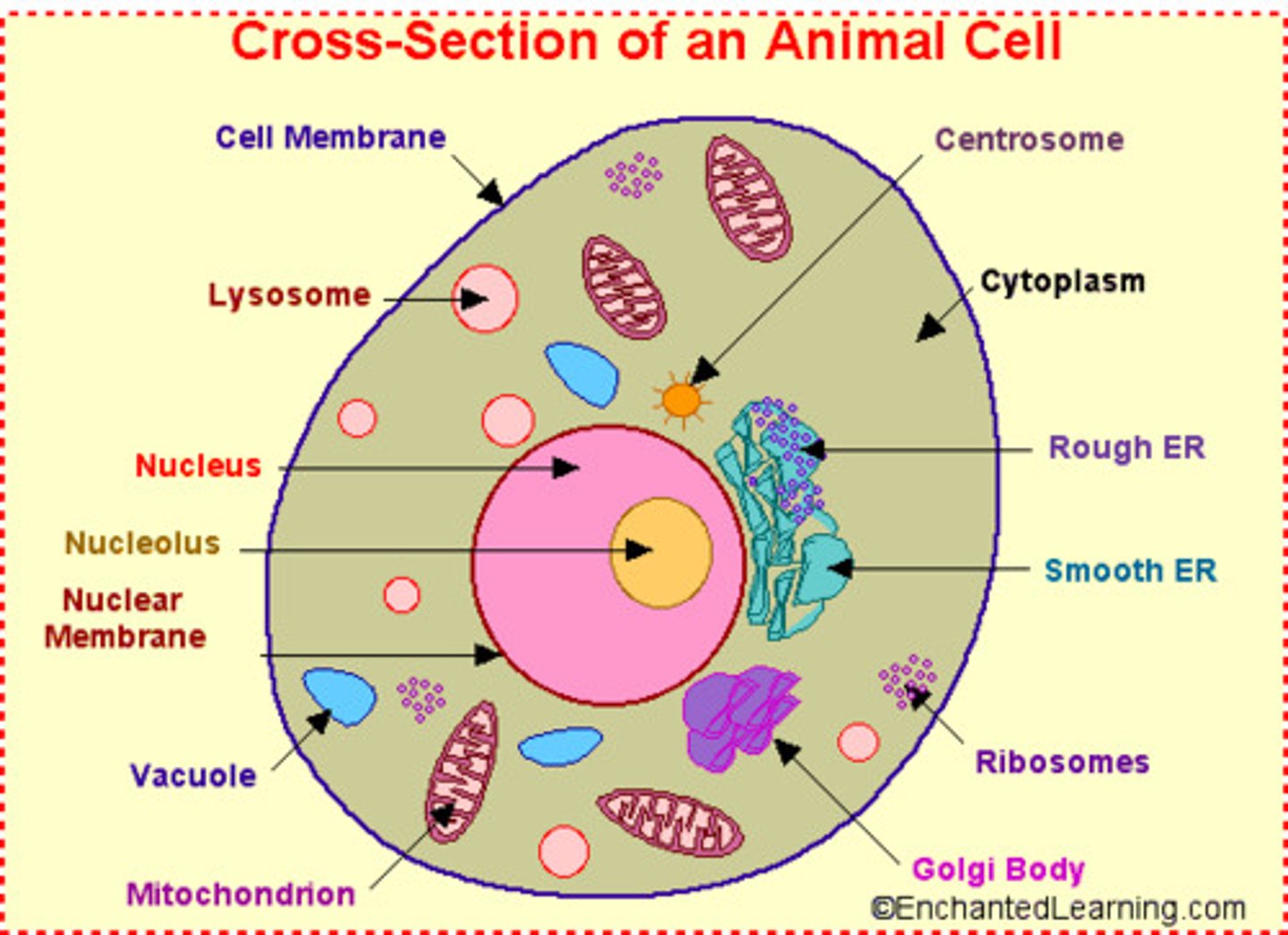
Golgi body
A structure in a cell that receives proteins and other newly formed materials from the endoplasmic reticulum, packages them, and distributes them to other parts of the cell.
Tissue
group of similar cells that perform a particular function
Organ
a collection of tissues that carry out a specialized function of the body
Organ system
group of organs that work together to perform a specific function
Organism
Any living thing

Mitosis
cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes
Meiosis
A process in cell division during which the number of chromosomes decreases to half the original number by two divisions of the nucleus, which results in the production of sex cells
Chromosome
a structure in the nucleus that contains hereditary material
Vacuole
an organelle that stores food, water, and other materials needed by the cell
Multicellular
organisms composed of many cells

Unicellular
a type of organism that is made up of a single cell

cytoskeleton
reinforces cell shape, functions in movement
components are made of protein
microtubules
forms mitotic spindle and maintains cell shape
microfilaments
fibrous proteins; forms cellular cortex
intermediate filaments
provide structural support and tensile strength, anchoring organelles in place.
centrosome
microtubule organizing center
peroxisome
an organelle involved in the breakdown of fatty acids and detoxification of hydrogen peroxide
metabolizes waste
nuclear envelope
a double membrane that surrounds the nucleus, protecting its contents. protein-lined pores allow material to move in and out
nucleolus
structure where ribosomes are formed