Test 3: Cells and Membranes
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Receptor mediated endocytosis
cells engulf target substances (ligands) from external environment; these substances bind to receptors on the cell membrane which cause a coated pit/ vesicle to form
highly selective
most signal receptors are…
plasma membrane proteins
most abundant organic compound on Earth
cellulose (plant cell walls)
Purines (structure and N bases)
AG, 5 membered ring + 6 membered ring
function of protein kinases
transfer phosphates from ATP to protein (aka “phosphorylation”)
function of protein phosphatases
remove phosphates from proteins (aka “dephosphorylation”)
turn off signal transduction pathway → making protein kinases available for reuse (cell can respond to signal again)
who discovered how epinephrine (hormone) acts on cells (cell signaling)
Earl W. Sutherland
Adding phosphate groups often changes the form of a protein from ____ to ____
inactive to active
Cell Signaling: reception
binding of signaling mQ to receptor protein in membrane (ligand)
^^highly specific based on shape
can happen inside the cell too though
ligand binding makes receptor protein change shape (most receptors directly activated by this shape change)
What kinds of molecules pass through a cell membrane most easily
small hydrophobic (nonpolar)
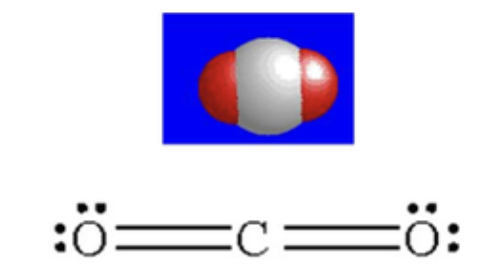
is CO2 polar or nonpolar
nonpolar
True or false? The water-soluble portion of a phospholipid is the polar head, which generally consists of a glycerol molecule linked to a phosphate group.
true!
nonpolar covalent bonds present between….
all mQs that are dimers
cotransport (secondary transport)
mechanism where a transport protein couples the movement of one solute down its concentration gradient with the movement of another solute against its gradient. This process is akin to using the energy from water flowing downhill to pump another substance uphill
In plant cells, cotransport often involves hydrogen ions (H+) and nutrients like sucrose.
conditions required for simple diffusion across the cell membrane
small & nonpolar (hydrophobic) mQs
what is a transmembrane protein
A protein that spans the phospholipid bilayer one or more times (perpendicular)
Which molecules are localized on the exterior of a phospholipid bilayer?
phosphate groups (heads of phospholipids)
how do the phospholipids in a plasma membrane stay together
hydrophobic effect / amphipathic nature
what component in cell membrane plays roll in cell-cell recognition
carb chain (attached to glycoprotein)
Ex: A and B antigens on RBCs to tell blood type
Pyramidines (structure and N bases)
CUT; 6 membered ring
Nitrogenous base pairs are joined by _____
hydrogen bonds
What functional feature(s) does the phosphate group contribute to the structure of a phospholipid?
hydrophilic head, negative charge (phosphate group), diversity (phosphate group can be linked to various small, charged, or polar molecules, creating different types of phospholipids → allows for specialized functions in cell membranes)
most abundant organic compound in living things
proteins
glucose + glucose = ____ by ____
maltose; dehydration synthesis
enantiomers
mQs that are mirror images of one another (isomers)
Turgor pressure
force exerted by water inside the cell against the cell wall; crucial for maintaining structure and firmness of plant cells
hypotonic solution → more turgid
hypertonic solution → less turgid
plasmolysis (verb)
plant cells lose water and shrink when placed in a hypertonic solution (plasma membrane retracts from cell wall)
osmoregulation
cells maintain the balance of water and solutes within their environment (crucial for function and survival)
tonicity plays a role
isotonic
solute concentrations inside = outside; no net water movement
Animal cells thrive in isotonic environments unless they have adaptations for osmoregulation
Eukaryotic vs prokaryotic cells
Eukaryotic: have organelles, nucleus, bigger
Prokaryotic: no organelles, nucleoid, smaller
pinocytosis
(type of endocytosis AT): cell “drinking” by engulfing lique environment from extracellular environment; allows cell to get nutrients form the liquid environment
nonselective in the molecules it brings into the cell
phagocytosis
(type of endocytosis AT): cell “eating” by engulfing large solid contents from extracellular environment
primary active transport
protein pump
secondary active transport (cotransport)
uses E stored in an electrochemical gradient created by primary active transport (divided into symporters which move two or more substances in the same direction and antiporters which more two or more substances in opp directions
flaccid (adj)
low turgid pressure
Lyse
cell membrane ruptures
more common in animal cells than plant cells (strong cell walls)
what types of bonds are in fats
ester bonds
makeup of a phospholipid
2 fatty acids (tails) [ester bond] phosphate group attached to glycerol
steroid makeup
lipid with carbon skeleton of 4 fused rings
ex: cholesterol
hydrolytic enzymes
specialized proteins that facilitate the breakdown of macromolecules through hydrolysis (found in lysosomes)
Plasmodesmata
Channels connecting adjacent plant cells for sharing materials (water, nutrients, chemical messages)
Peroxisome
Metabolic compartment (enzymes break down fatty acids for cellular energy)
form H2O2 which then turns to water (helps with detoxification)
Centrosome
Aids in cell division using microtubules to attach to and pull apart chromatids (in animal cells)
spectrin
peripheral protein that forms a lattice around the inner cell membrane for structural support
thylakoids
flat sacs in chloroplasts responsible for photosynthesis
stroma
fluid filled space inside chloroplasts
what mQs can dissolve in the membrane and cross it with ease
Hydrophobic molecules, such as hydrocarbons, carbon dioxide, and oxygen
Submerging a plant cell in distilled water will result in
cell becoming turgid (distilled water has very few solutes)
how is glucose transported into animal cells
facilitated diffusion using protein carriers (passive, doesn’t require E)