Anatomy and Physiology of the Ear: Outer, Middle, and Inner Structures
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
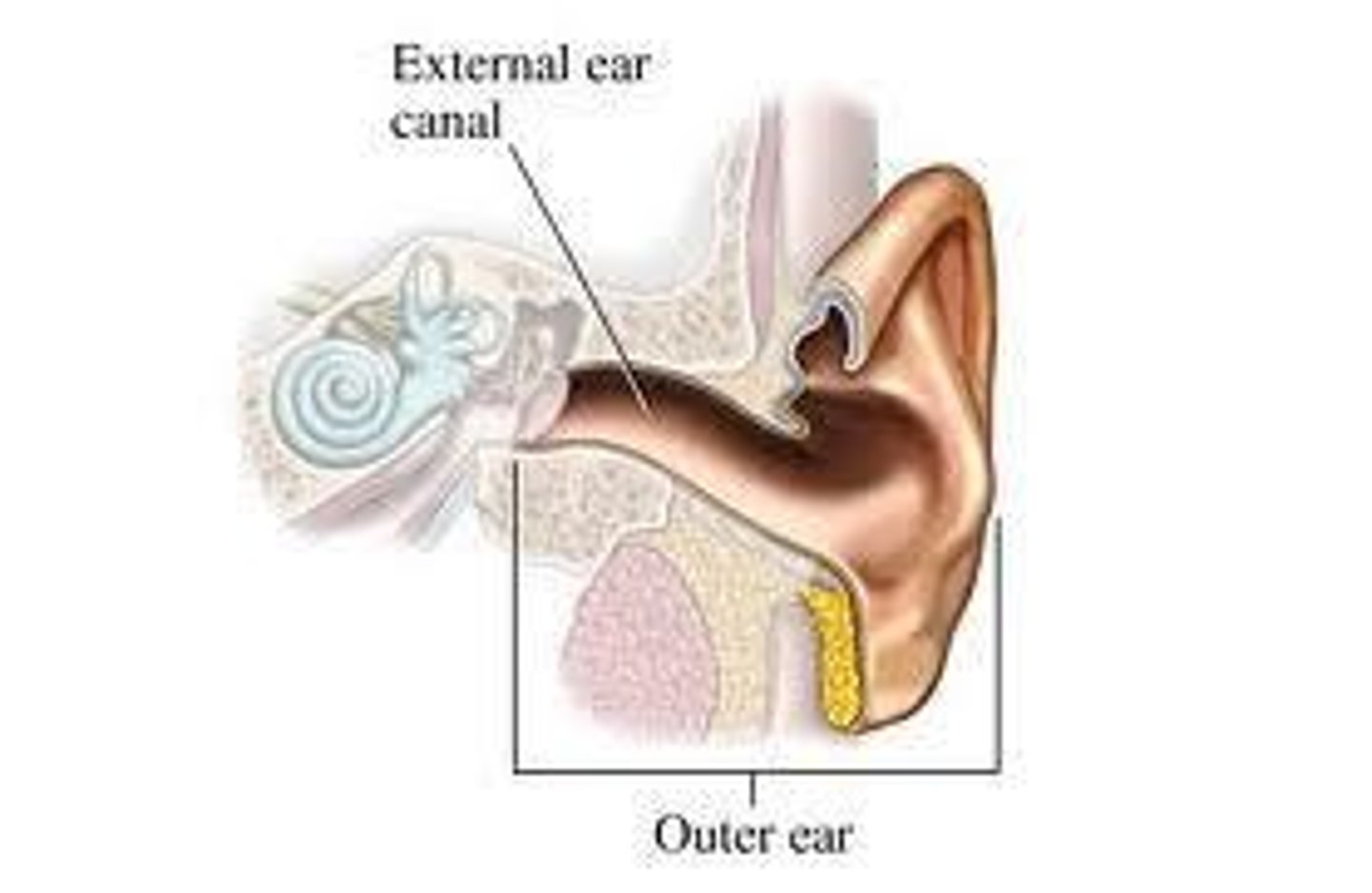
Outer Ear
Two main parts: Auricle and External Auditory Meatus.
Auricle
Also known as Pinna; made of cartilage and skin.
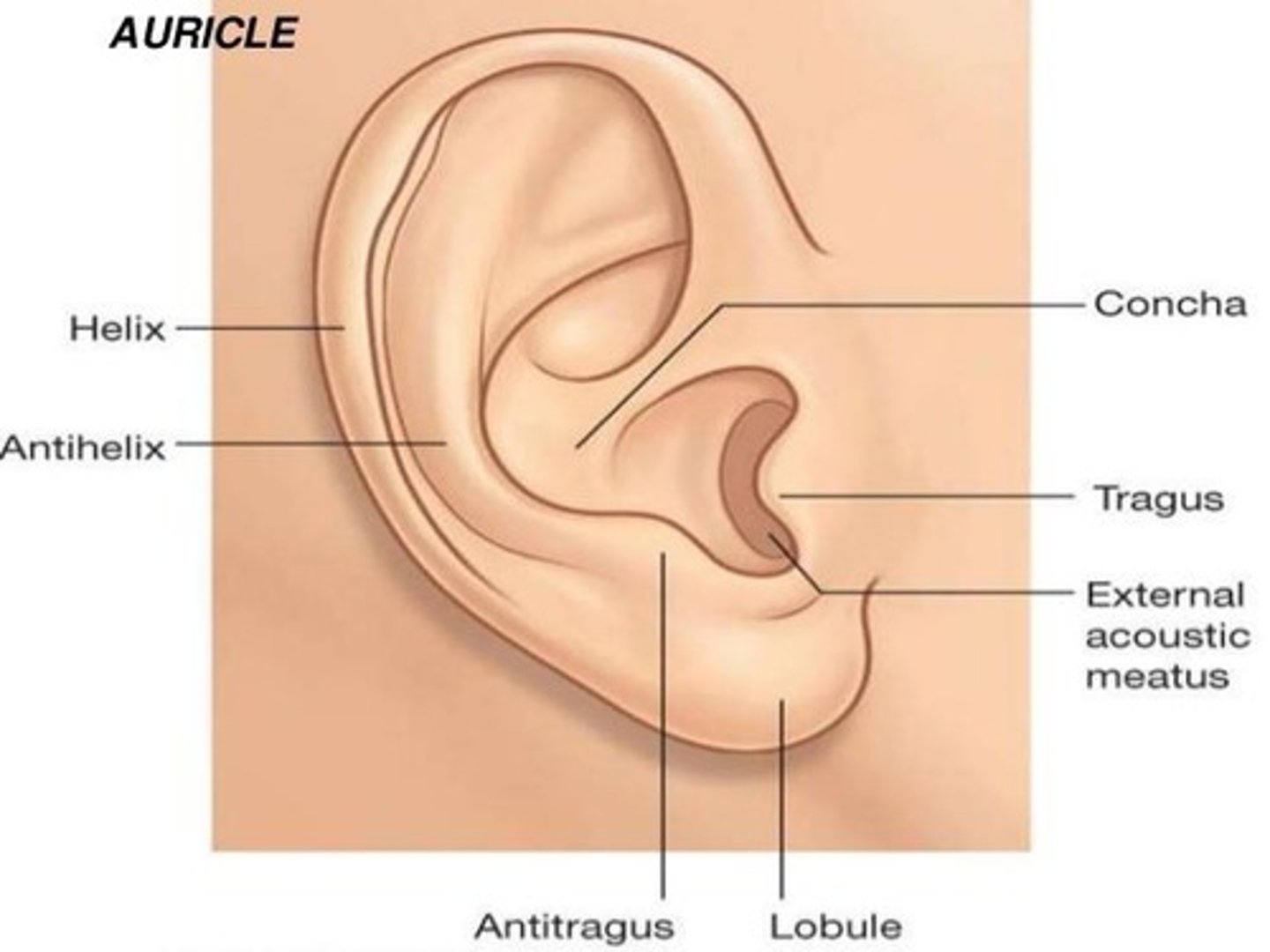
Auricle Landmarks
Lobe, Helix, Antihelix, Tragus, Concha.
Auricle Functions
Collects all sounds, giving an extra boost in intensity to high-frequency sounds and helps to localize sound.
External Auditory Canal
Also known as ear canal; starts at concha and ends at Tympanic Membrane (TM).
External Auditory Canal Sections
Divided into Outer (lateral) with cerumen-producing glands and hair, and Inner (medial) with skin over bone.
External Auditory Canal Functions
Protects TM (ear drum) and transfers all sounds to TM, giving an extra boost to high-frequency sounds.
Resonant Frequency of External Auditory Canal
2000 to 4000 Hz.
Resonant Frequency of Concha
Closer to ~5000 Hz.
Gain in Sound Intensity
Together, they produce a gain in the 1500 - 7000 Hz range.
Tympanic Membrane
Barrier between outer ear and middle ear; concave disk and very thin.
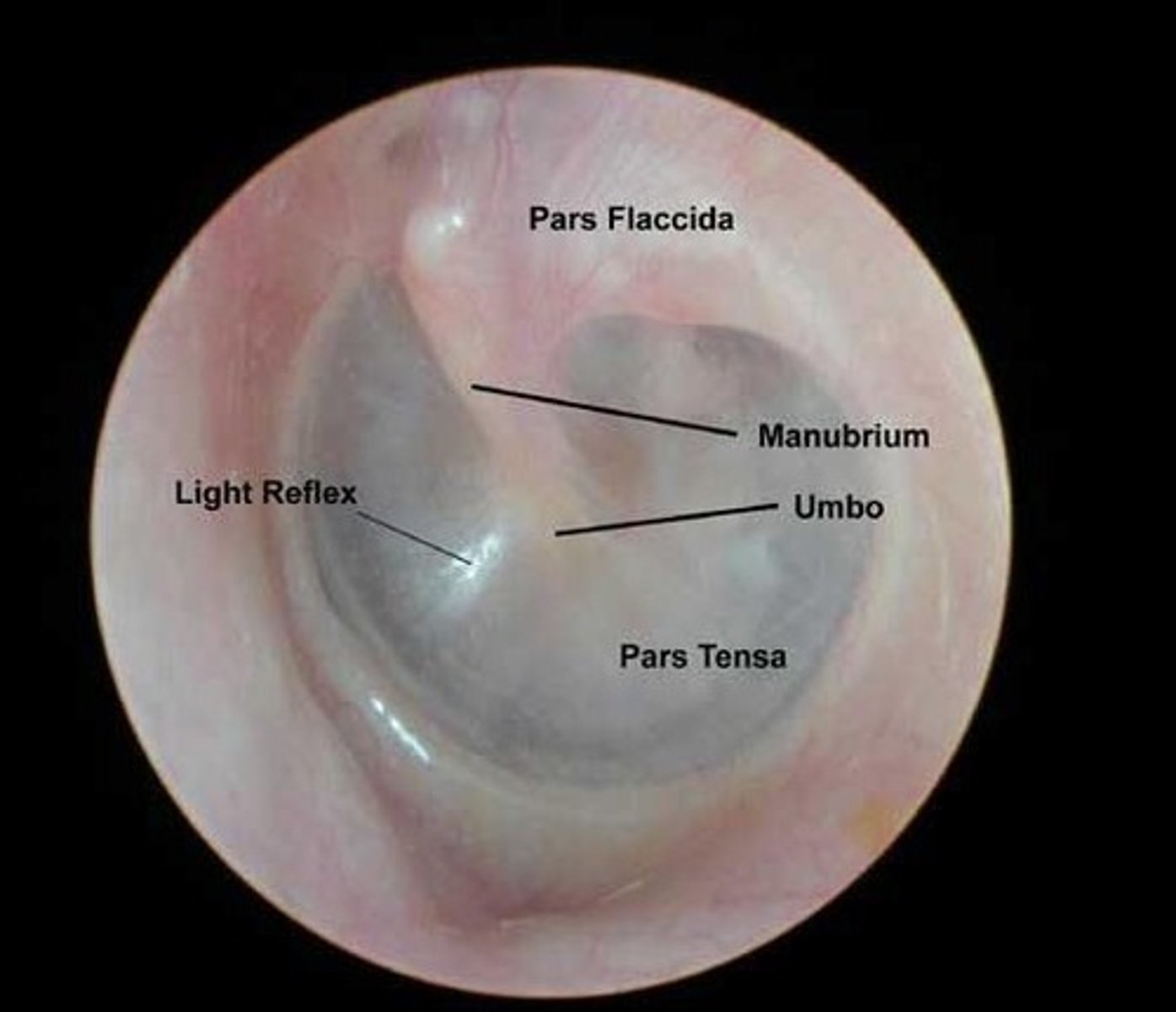
Landmarks of a Healthy Tympanic Membrane
Cone of Light, Handle of the Malleus, Color.
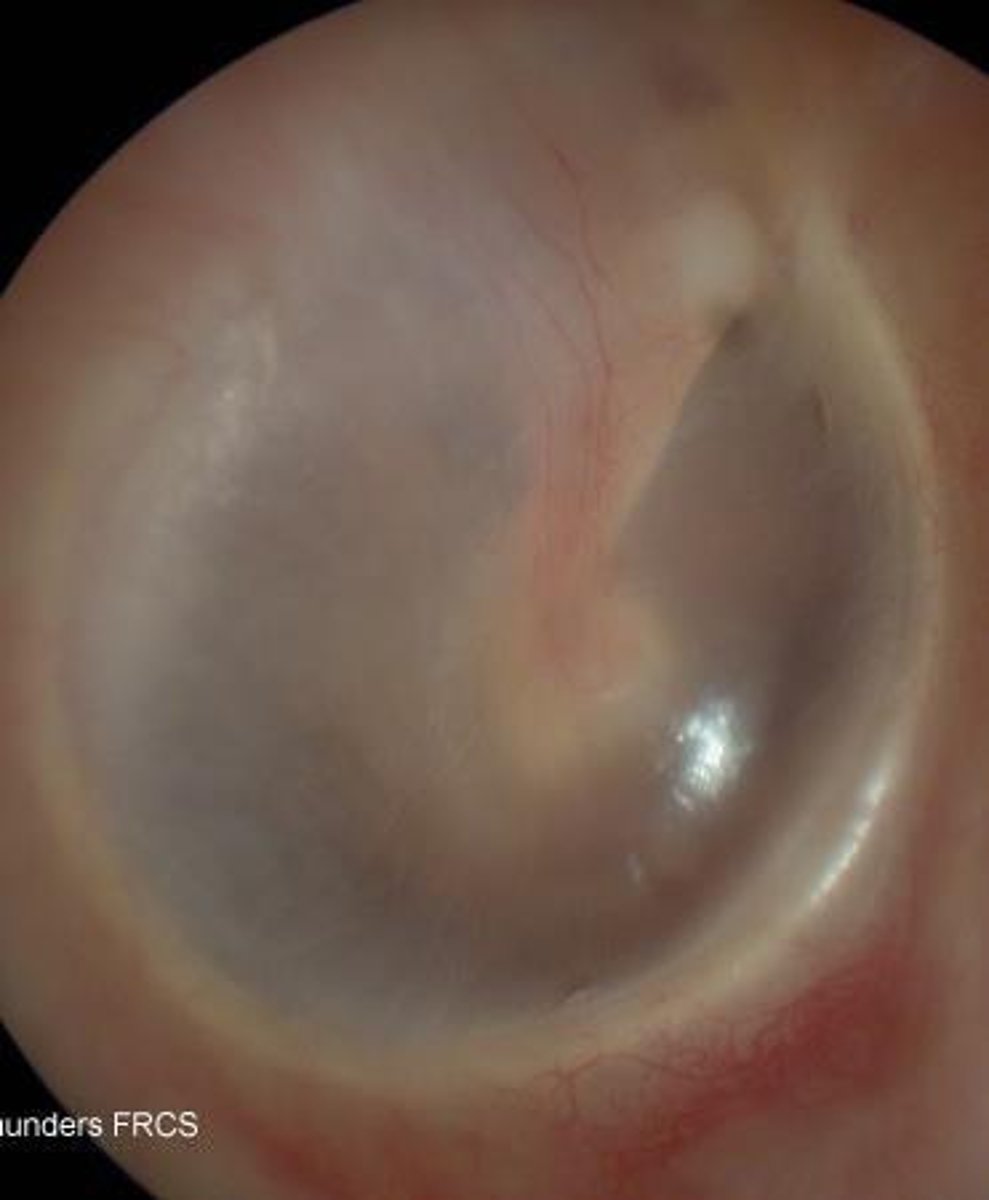
Pars Flaccida
Not as strong (flaccid); part of the Tympanic Membrane.
Pars Tensa
Stronger (more tense/stiff); tubes are often placed here because it is stronger and able to hold the tubes in place.
Eardrum Characteristics
Eardrum is very red, not flat, not shiny; indicates a sick ear.
Middle Ear Functions
Carries sound from outer ear to inner ear and overcomes loss of energy from outer ear to inner ear.
Middle Ear Volume
2 cm3.
Middle Ear Lining
Lined with mucous membrane.
Eustachian Tube
Connects the middle ear to the nasal pharynx.
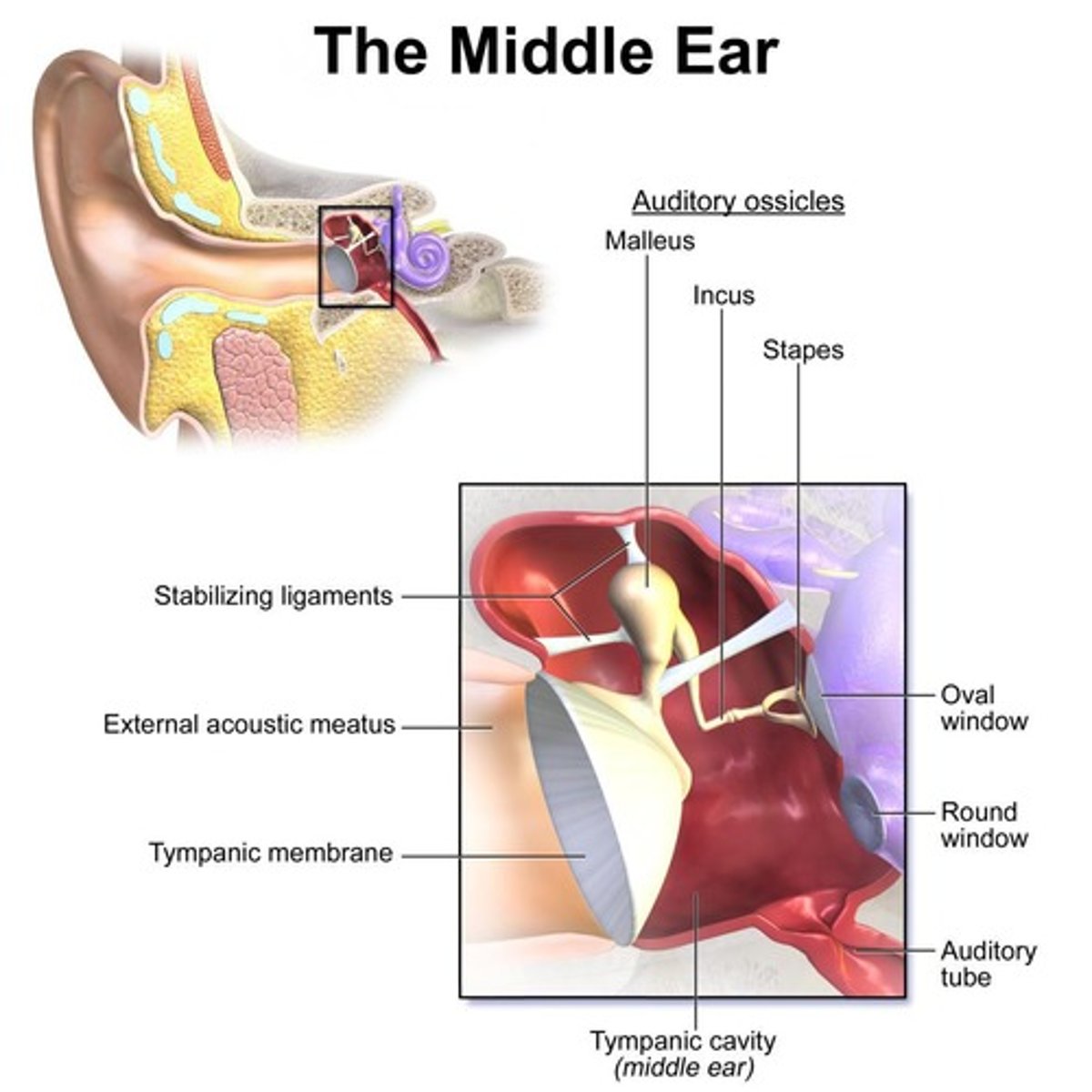
Ossicles
Smallest bones in the body; consists of Malleus, Incus, and Stapes.
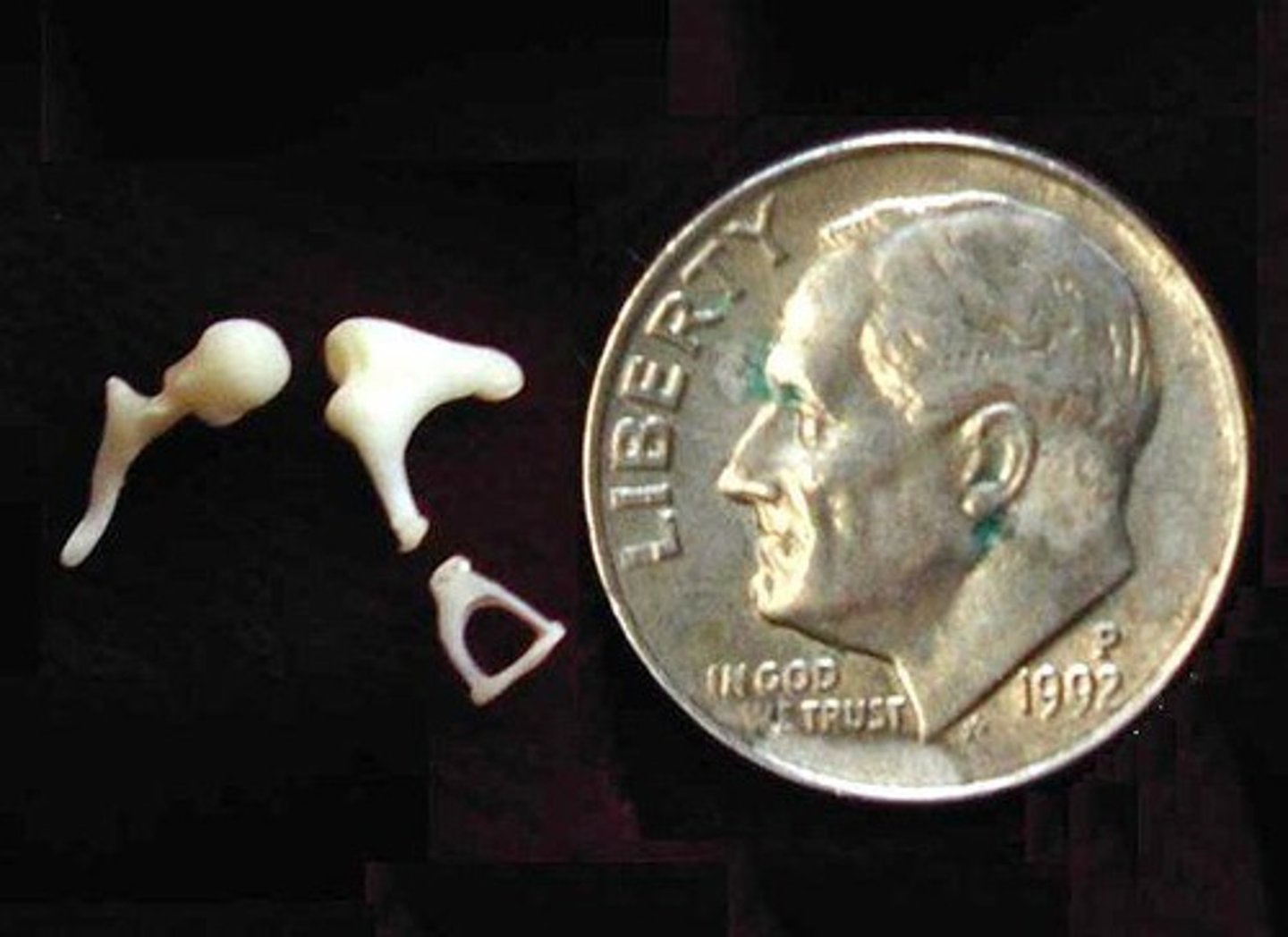
Ossicular Chain
All three ossicles together.
Stapes
Connected to ear drum and the next ossicle, the Incus
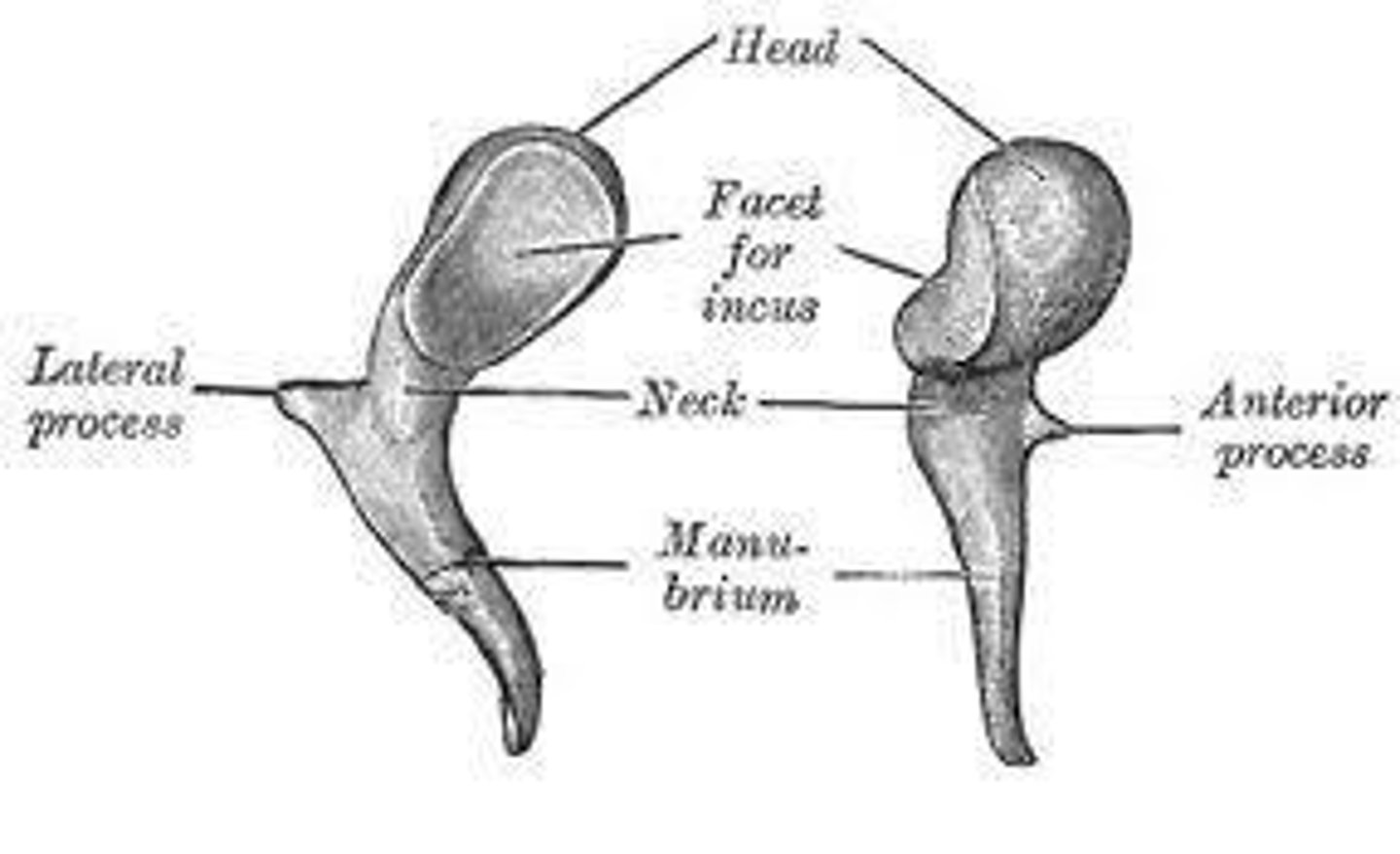
Malleus
aka "hammer"
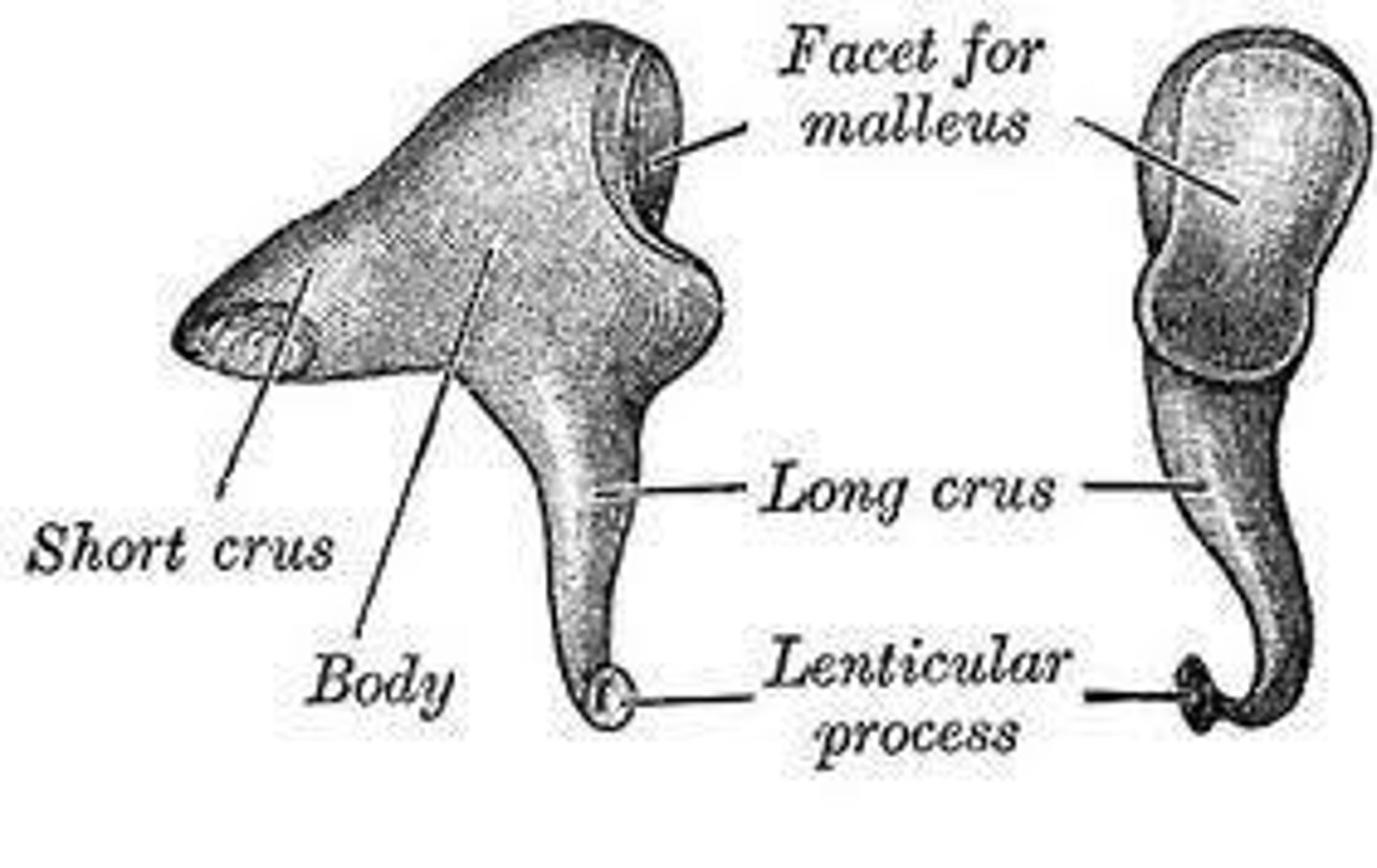
Incus
aka "Anvil"
Sound Transfer through middle ear
Ear drum moves in and out; Rigid connection of Malleus and Incus causes rotation; Force transferred to Stapes; Oval Window moves in and out
Impedance Mismatch
Air and fluid have difference impedances; Cochlear (inner ear) fluids are less compressible than air; Cochlear fluids have more density, therefore more impedance to the transmission of sound than when it travels through air
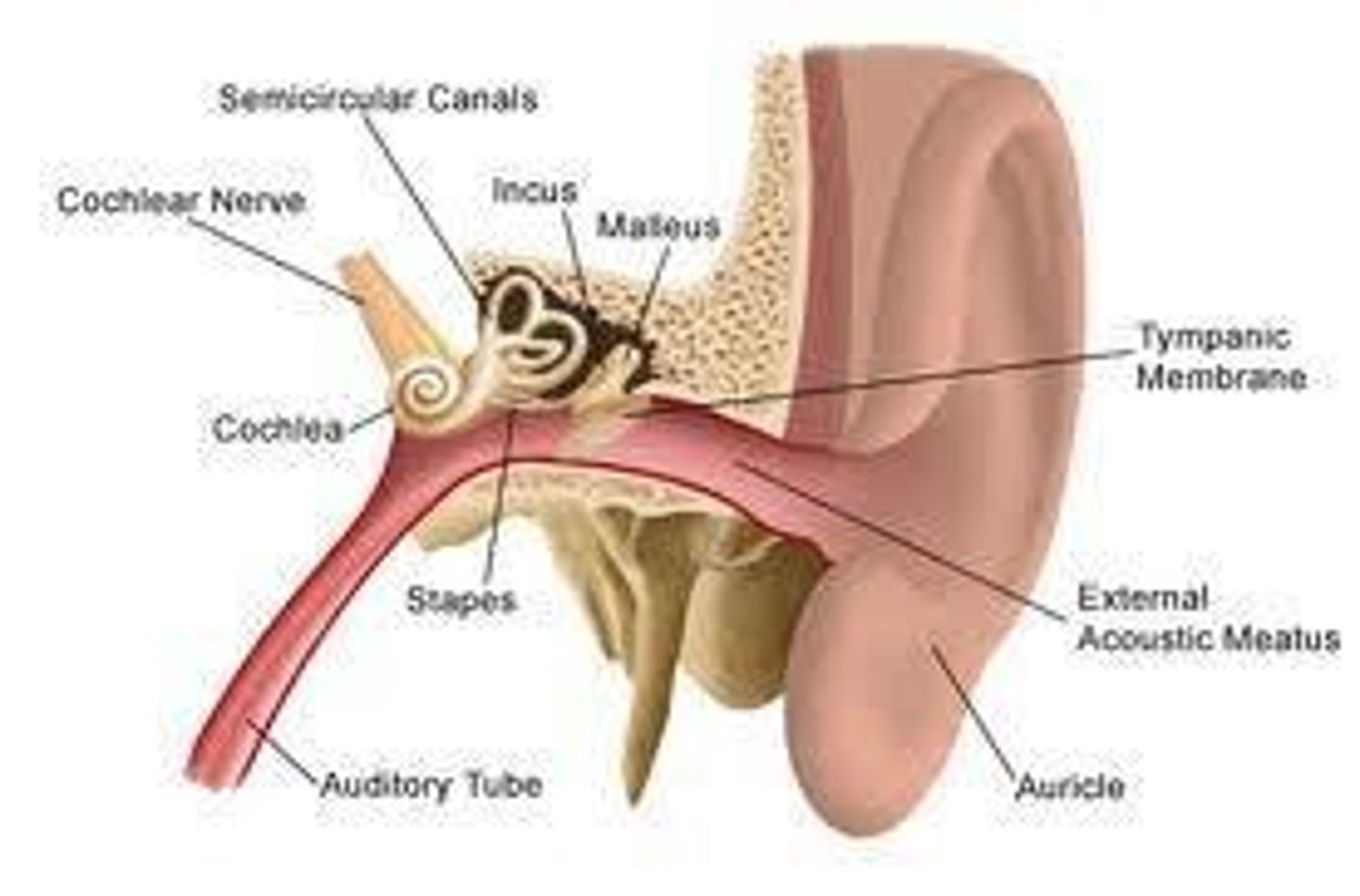
Otoscopy
First part of ear exam; Visual inspection; Equipment used: Otoscope; Observe the state of the canal and ear drum
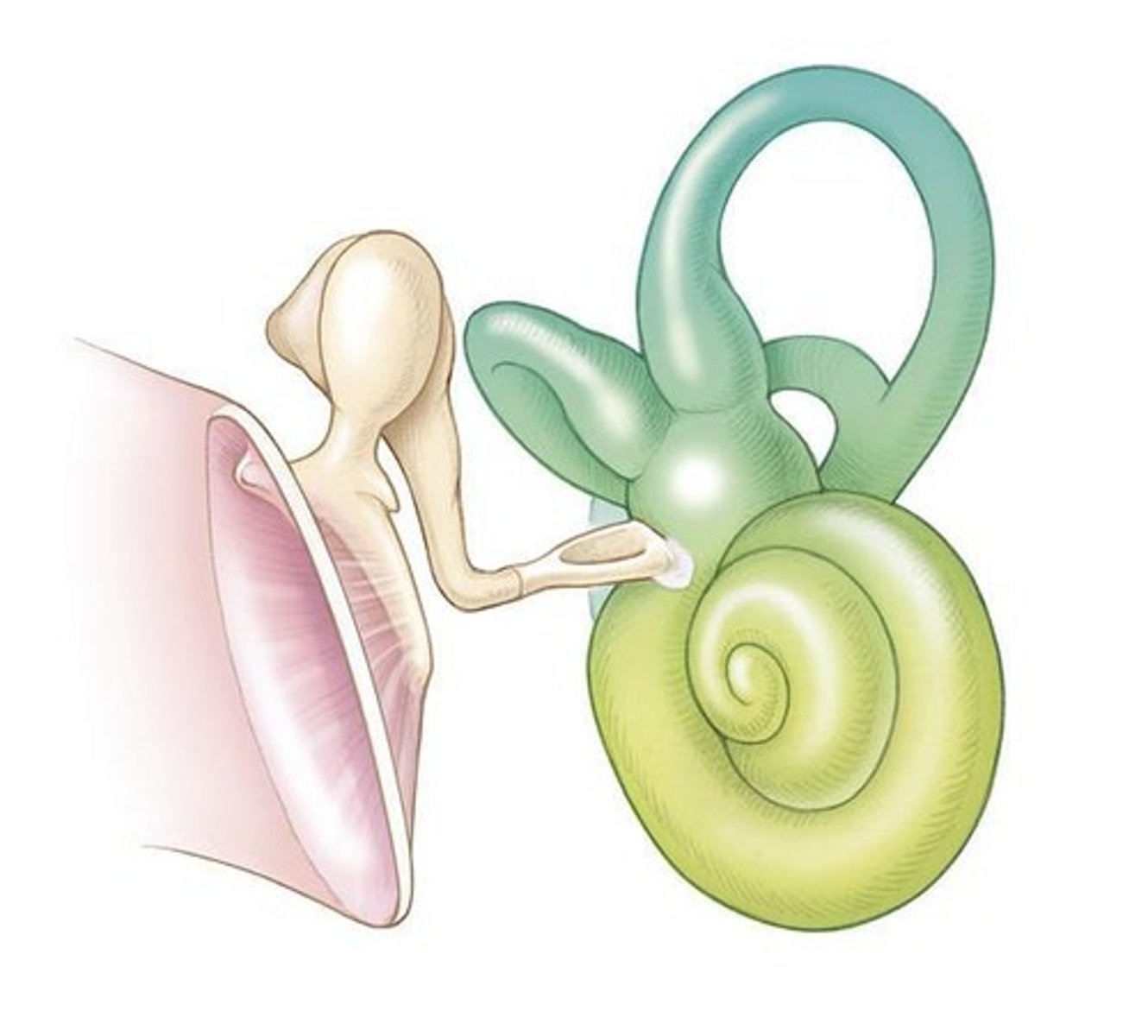
Cochlear Anatomy
The Cochlea is very small, but very complex; Long tube coiled into a spiral; 2 ¾ turns
Cochlear Fluids
Perilymph found in Scala Vestibuli and Scala Tympani; Endolymph found in Scala Media
Scala Media
Completely closed; Triangular shape; Contains the Organ of Corti
Labyrinth
Includes Bony Labyrinth and Membranous Labyrinth
Cochlea - Scala Media
Borders include Reissner's Membrane and Basilar Membrane
Cochlear Anatomy - Reciprocal relationship
Reciprocal relationship between the oval window and round window
Cochlear Fluids - Composition
Perilymph composed primarily of Sodium; Endolymph composed primarily of Potassium
Inner Ear
Housed in the petrous part of the temporal bone; Consists of Cochlear (hearing) components and Vestibular (balance) components
Function of Inner Ear
Main function: transducer of energy; Hearing: changes the mechanical energy from middle ear into a form of information that the brain can interpret; Balance: changes body/head movements into a form of information that the brain can interpret
Middle Ear Ligaments
Malleus Ligament and Incus Ligament; Function: suspensory ligaments
Middle Ear Muscles
Tensor tympani and Stapedius; Function: contract in response to loud sounds
Stria Vascularis
A structure in the cochlea that plays a crucial role in the production of endolymph.
Organ of Corti
Sits on the basilar membrane and is the site of transduction of energy, containing sensory cells.
Hair Cells
Sensory cells in the cochlea that detect sound; includes inner hair cells (1 row) and outer hair cells (3 rows).
Cochlear Physiology
The study of how sound waves are transformed into neural signals in the cochlea.
Sound Wave Movement
Vibration transferred from stapes to scala vestibuli through the oval window, causing a traveling wave.
Tonotopic Organization
The arrangement of the cochlea and auditory pathways where different frequencies are processed in specific locations.
Depolarization of Hair Cells
The process that occurs when hair cells detect sound, leading to the generation of nerve impulses.
Inner Hair Cells
Hair cells that function as sound detectors.
Outer Hair Cells
Hair cells that act as amplifiers in the cochlea.
Afferent Fibers
Nerve fibers that carry signals from the ear to the brain.
Efferent Fibers
Nerve fibers that carry signals from the brain to the ear, regulating cochlear sensitivity.
VIIIth Cranial Nerve
Also known as the vestibulocochlear nerve, it forms when the auditory and vestibular nerve fibers converge.
Internal Auditory Canal (IAC)
A passage in the temporal bone that carries the auditory and vestibular nerves.
Retrocochlear Pathway
The auditory pathway that extends beyond the cochlea to the central auditory system.
Crossover
The process by which most structures in the central auditory system receive input from both ears.
Auditory Cortex
Located in the temporal lobes, it is responsible for the reception of auditory signals.
Central Auditory System
The part of the auditory system that processes sound information after it leaves the cochlea.
Asymmetries of Cerebral Auditory Areas
Differences in the physical and functional characteristics of auditory processing areas in the brain.
Pathway of Sound
The route sound travels from the outer ear through the auditory nerve to the auditory cortex.
Cochlear Portion
The part of the VIIIth cranial nerve that is specifically responsible for carrying auditory information.
Basilar Membrane Vibration
The movement of the basilar membrane that leads to the activation of hair cells.
Shearing of Hair Cell Stereocilia
The bending of the stereocilia on hair cells that occurs due to basilar membrane movement.
Cerumen Production
Location in the external auditory canal where cerumen is produced.
Main Job of the Outer Ear
The primary function and acoustic purposes served by the outer ear.
Sound Transduction in Outer Ear
Description of how sound is transduced through the outer ear.
Middle Ear Structures
Structures that make up the middle ear and their functions.
Purpose of the Middle Ear
Functions served by the middle ear.
Sound Transduction in Middle Ear
Description of how sound is transduced through the middle ear.
Cochlea Arrangement
Description of the cochlea's arrangement, including compartments and barriers, and the type of fluid in each.
Tonotopic
Meaning of the term 'tonotopic' in reference to the cochlea.
Sound Waves in Cochlea
How sound waves travel through the cochlea and how the inner ear creates interpretable sound signals.
Innervation of Hair Cells
Description of how nerves are attached to inner hair cells versus outer hair cells.
Roles of Hair Cells
Difference in the roles of inner hair cells and outer hair cells.
Sound Transduction in Inner Ear
Description of sound transduction from the inner ear to the auditory nerve.
Auditory Nerve Fiber Arrangement
Arrangement of nerve fibers in the auditory nerve and distinction from the Internal Auditory Canal.
Internal Auditory Canal Structures
Anatomical structures contained in the Internal Auditory Canal (IAC).