OCTH 246 - Therapeutic Exercises
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Training
One type of intervention to support occupations. Facilitation of acquisition of concrete skills for meeting specific goals in a real-life, applied situation. Usually in clinical or simulated setting.
Examples: Resistive bands, active stretching for ROM, opening/closing jars, dexterity activities
Modalities, devices, and techniques
Types of intervention to support occupations. Prepares client for performance. Client typically passive, not active.
Examples: Physical agent modalities, continuous passive motion machine, TENS, manual techniques (e.g., joint mobilization, PROM)
Therapeutic activity
Remediates sensory-motor dysfunction, augments occupation. Intervention: Simulated activities, fine motor practice, components of activities
Therapeutic exercise
Systematic, planned performance of physical movements, postures, or activities to:
1) remediate or prevent impairments of body functions and structures
2) Improve, restore, or enhance activities and participation
3) Prevent or reduce health-related risk factors
4) Optimize overall health, fitness or sense of well-being.
Remediates sensory-motor dysfunction, augments purposeful activity. Interventions: exercise, ROM, endurance, flexibility
Similarities between therapeutic exercise and therapeutic activity
Develop/restore movement patterns
Improve voluntary motor responses
Improve coordination
Increase muscle power
Increase endurance
Remediate ROM deficits
Increase work tolerance
Prevent/eliminate contractures
Concentric contractions
Muscle fibers generate force, shortening the muscles and creating joint motion
Eccentric contractions
Muscle fibers generate force that changes joint angle; muscle is elongating instead of shortening
Isometric contractions
Muscle fibers contract but no joint motion occurs, muscle length remains the same
Contraindications of therapeutic exercises
Unstable medical state; recent joint surgery; tendon or nerve repair; inflamed joints; some cardiopulmonary diagnoses/surgical interventions. For all diagnoses, you don't want to do concentric/eccentric exercises. For some, you can do isometric exercises.
Eccentric vs. concentric exercise
Eccentric exercise appears to be superior in helping increase muscle strength and mass. Eccentric exercise may also place muscle at greater risk for injury. Further research needs to be done.
Open chain exercises
Distal segment moves in space. Independent joint movement. Non-weight bearing position. Resistance applied to the moving distal segments.
Examples: Biceps curl, raising arm overhead.
Better at isolating a specific muscle
Closed chain exercises
Distal surface fixed on stationary support. Interdependent joint movements; movement of body segment distal and/or proximal to the moving joint. Muscle activation of multiple joint muscles’.
Examples: Lunges, squats, pull-up, push up
Manual resistance exercise
Can't be measured quantitatively, but might be useful in early training; resistance limited by therapist strength
Mechanical resistance
Use of machines like in gym - can be measured quantitatively and increased progressively
Progressive Resistance Exercise (PRE)
Dynamic exercise in which constant external load is applied to a contracting muscle and incrementally increased. Exercises graded by increasing the maximum amount of resistance as strength improves. Repetitions remain the same - weight/resistance increases. High load, low repetitions. In contrast, training for endurance: Low-load, high repetitions
Oxford Method
One method of PRE. Progressively lighter. 10 repetitions, 100% max -> 75% max -> 50% max. Maximum weight should increase every 4-7 sessions. Both methods are effective.
DeLorme Method
One method of PRE. Progressively heavier. 10 repetitions, 50% max -> 75% max -> 100% max. Maximum weight should increase every 4-7 sessions. Both methods are effective.
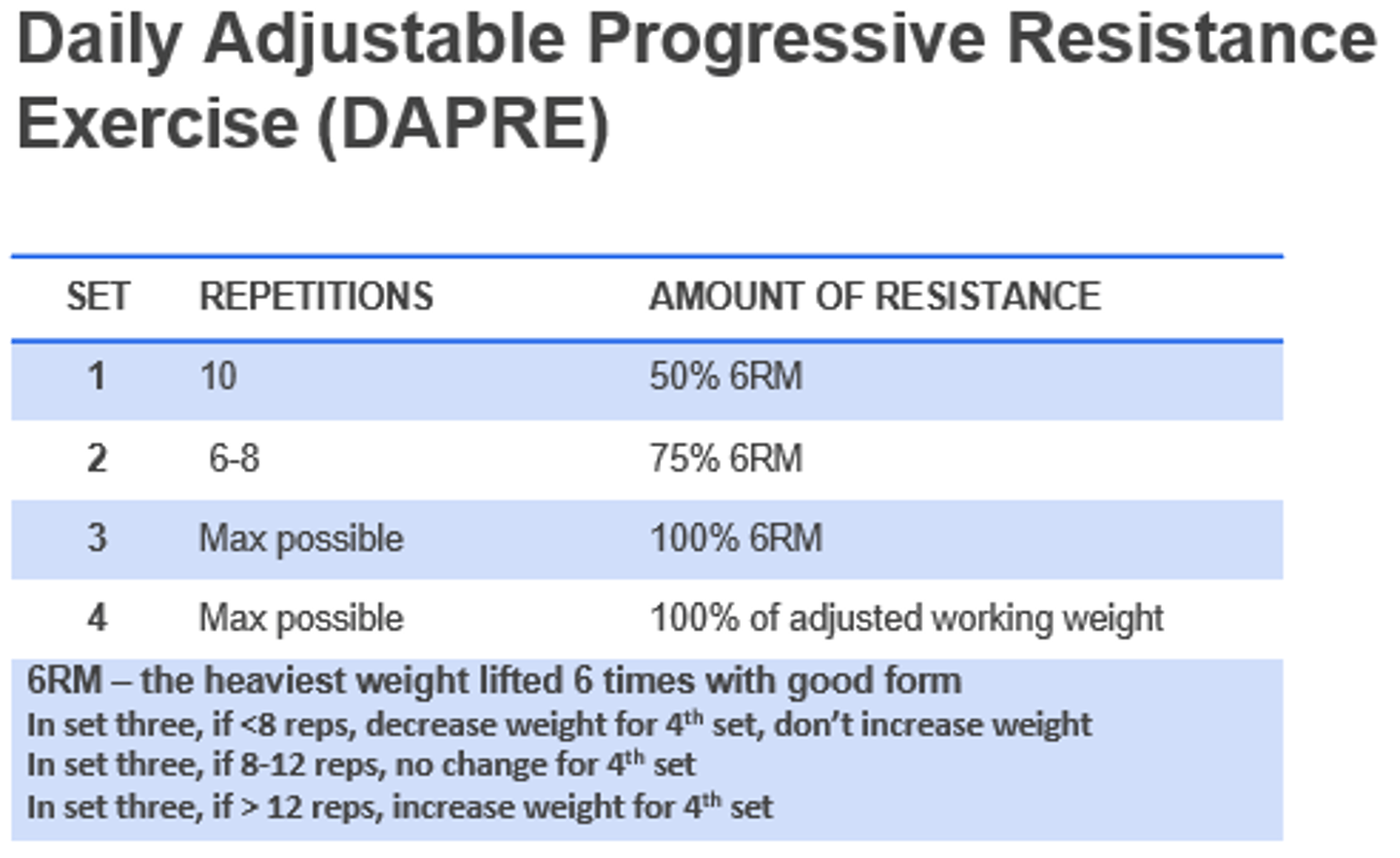
Daily Adjustable Progressive Resistance Exercise (DAPRE)
Muscle grade and type of exercise
5 - Do not need to see patient for strengthening
3+/5 or 4/5 - against gravity + resistance*
3 - AROM, isometric, active-assisted
Isometric to build muscle strength
2 - gravity neutral, active-assisted
1 - e-stim; biofeedback
No muscle movement
*Note: This is for isotonic (concentric and eccentric) exercise. Sometimes isometric exercises are indicated (pain, fractures, tendon repair)