Skull, TMJ and Cervical Spine
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
212 Terms
What does the skull house?
Houses the brain, organs of special sense, upper part of respiratory & gastrointestinal system
The structure of the skull doesn't leave any room for...
The brain to grow
Oedema in the skull can cause
Raised intra-cranial pressure once the sutures in the skull have fused
What is the function of the skull?
• Protects the brain, brainstem, cranial nerves & vasculature
• Provides attachment for muscles
• Provides a framework for the head
• Gives us our identity as individuals
What types of bones are found in the skull?
Flat & irregular bones
Pneumatised bones
What are pneumatised bones?
Bones with air spaces (air cells or sinuses) such as the frontal, temporal, sphenoid & ethmoid
What is the function of pneumatised bones in the skull
Serve 2 functions in the skull; to reduce weight & add resonance to our voice
How do flat bones form
intramembranous ossification
How do pneumatised bones form
endochondral ossification
How many divisions does the skull have?
2
What are the divisions of the skull
Neurocranium and viscerocranium
How many bones are present in the skull?
22 bones in the adult excluding the ossicles of the ear (28 with ossicles)
What is the neurocranium?
Bony case of the brain including cranial meninges with a dome-like roof (calvaria/skullcap) & a floor (cranial base/basicranium)
What is the viscerocranium?
Anterior part of cranium that consists of bones surrounding the oral cavity, nasal cavity & most of the orbit
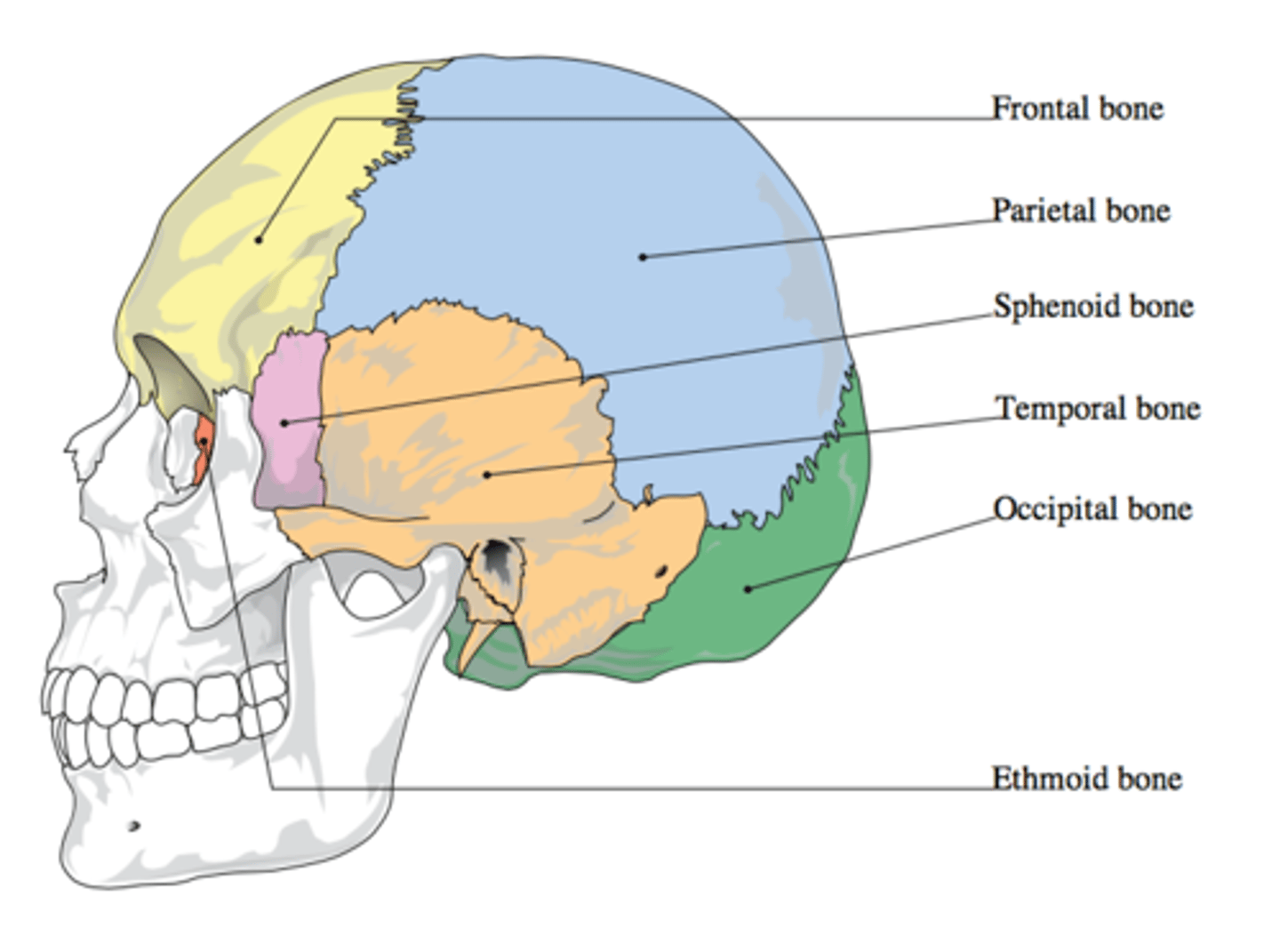
What bones make up the neurocranium
Frontal
Parietal x2
Occipital
Sphenoid
Temporal x2
Ethmoid
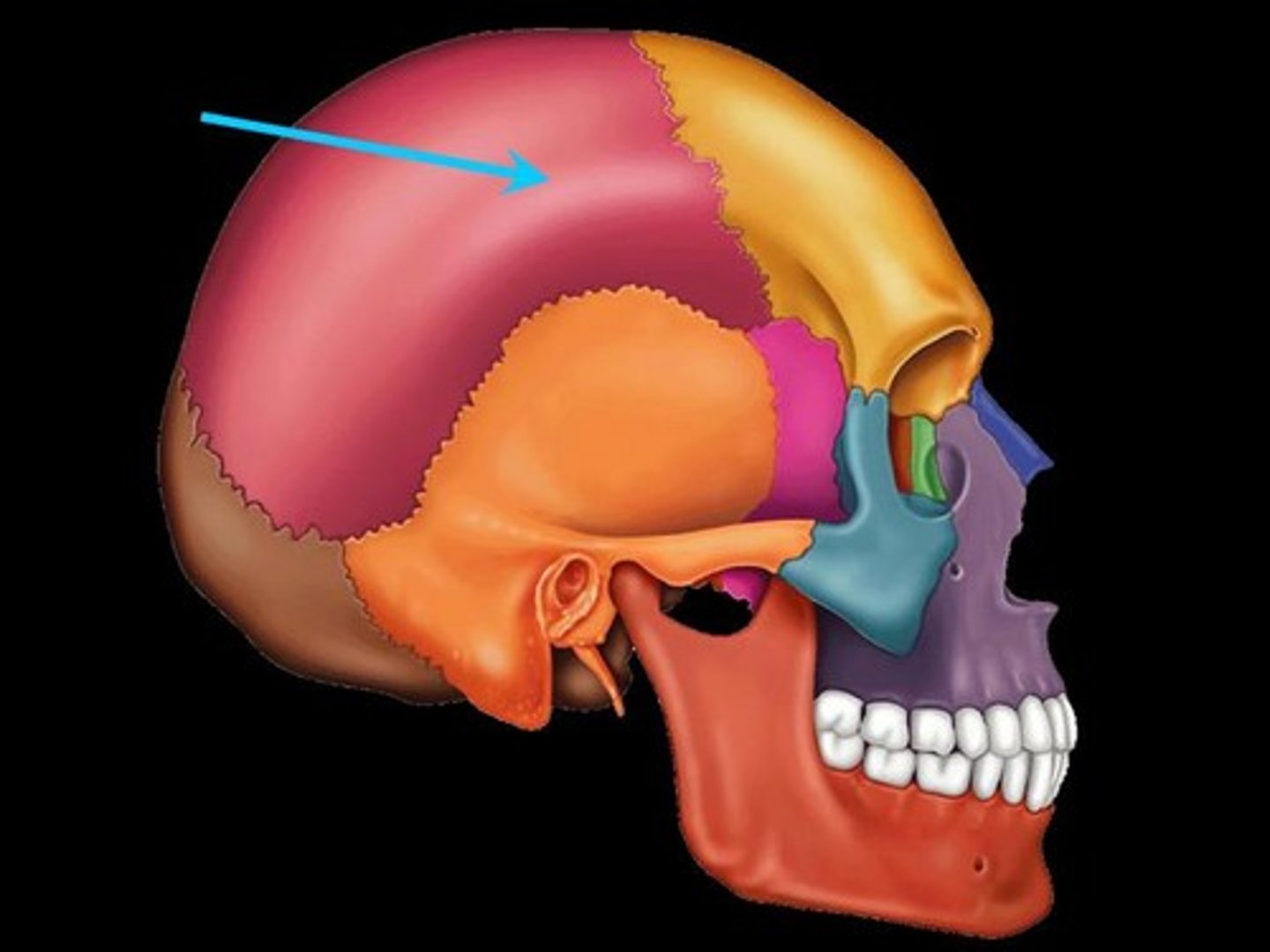
Frontal bone
bone that forms the forehead
Parietal bone
either of two skull bones between the frontal and occipital bones and forming the top and sides of the cranium
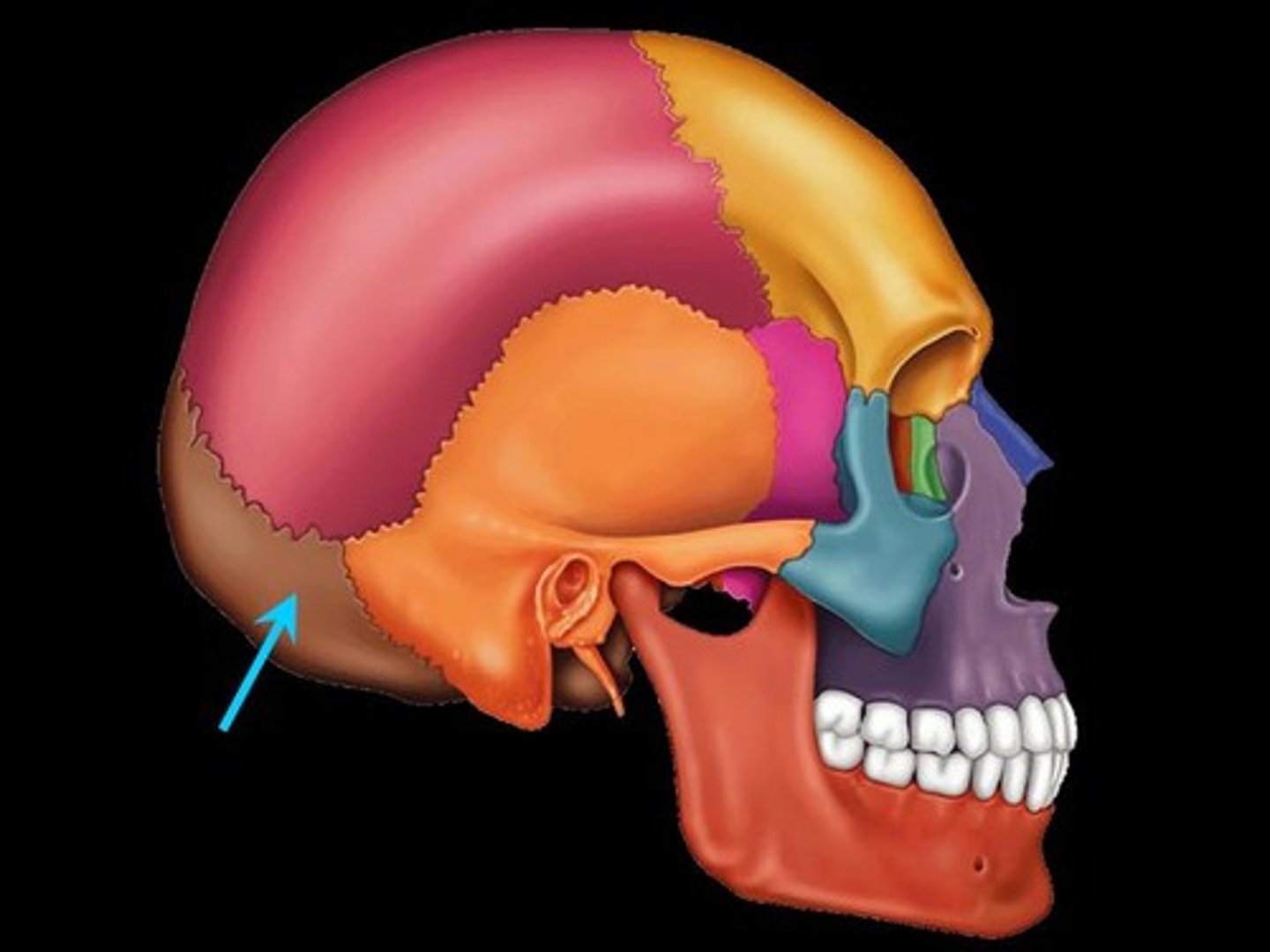
Occipital bone
Bone that protrudes at the base of the skull
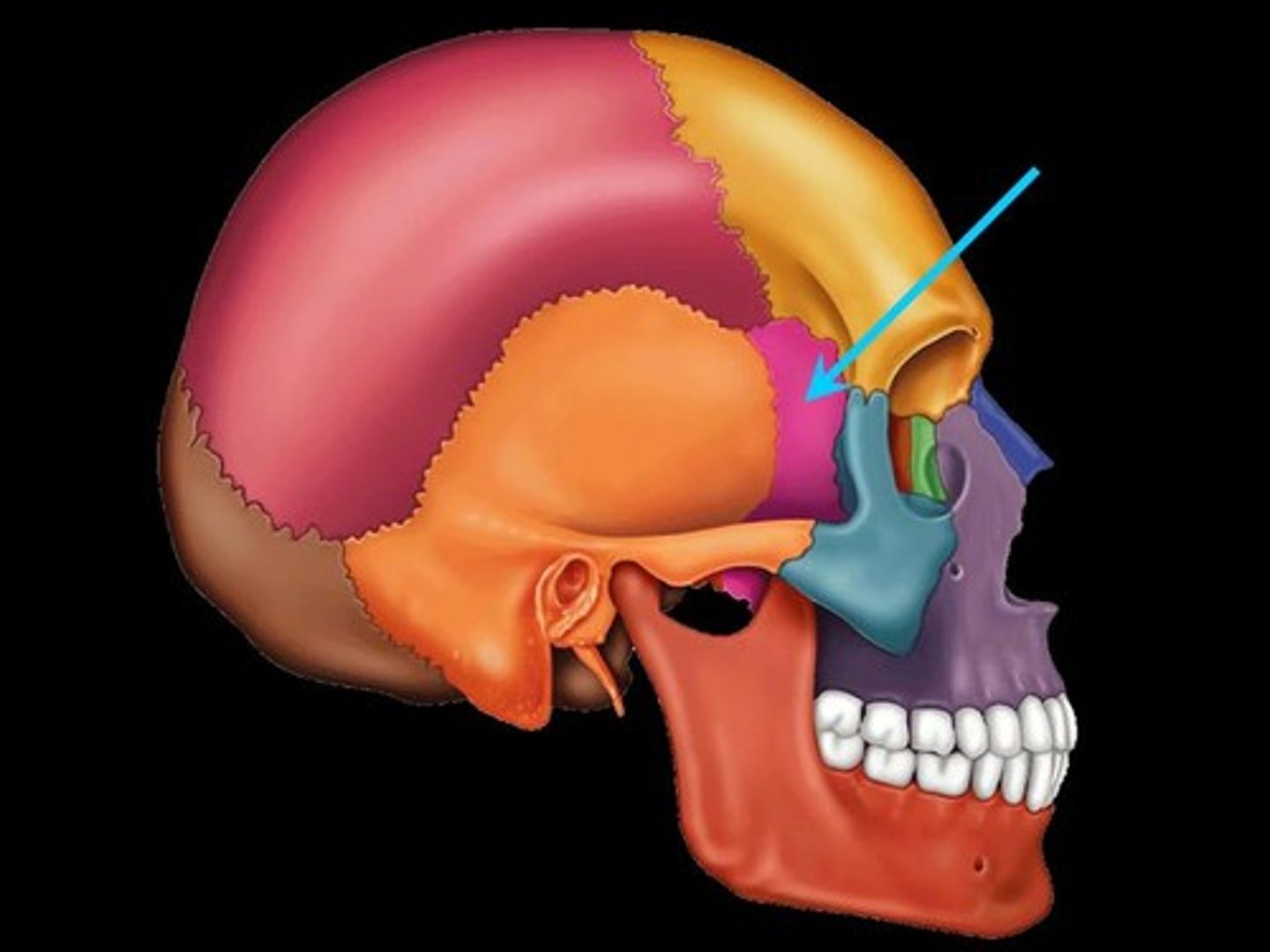
Sphenoid bone
forms part of the base of the skull and parts of the floor and sides of the orbit
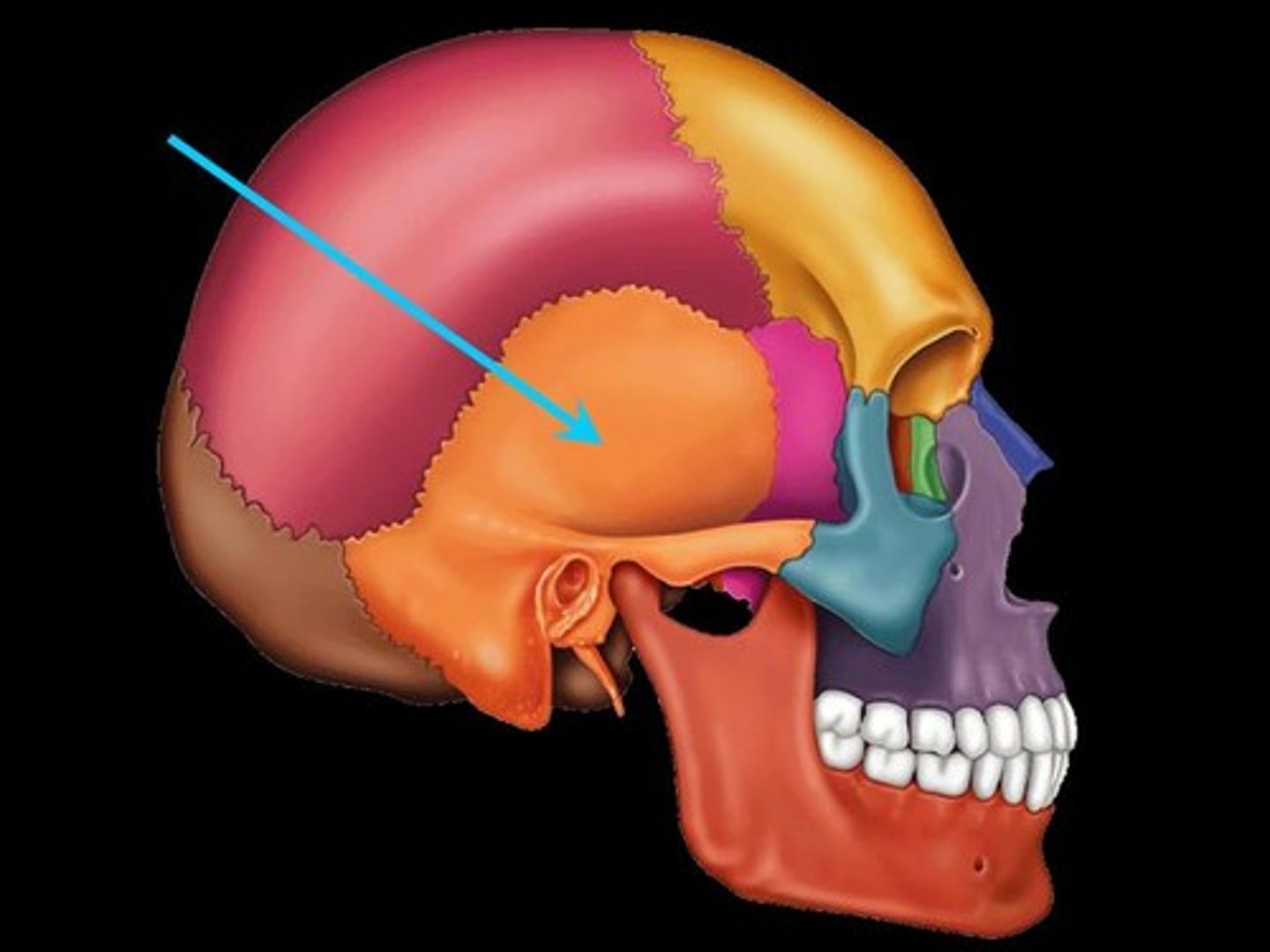
Temporal bone
bone that forms parts of the side of the skull and floor of the cranial activity. There is a right and left temporal bone.
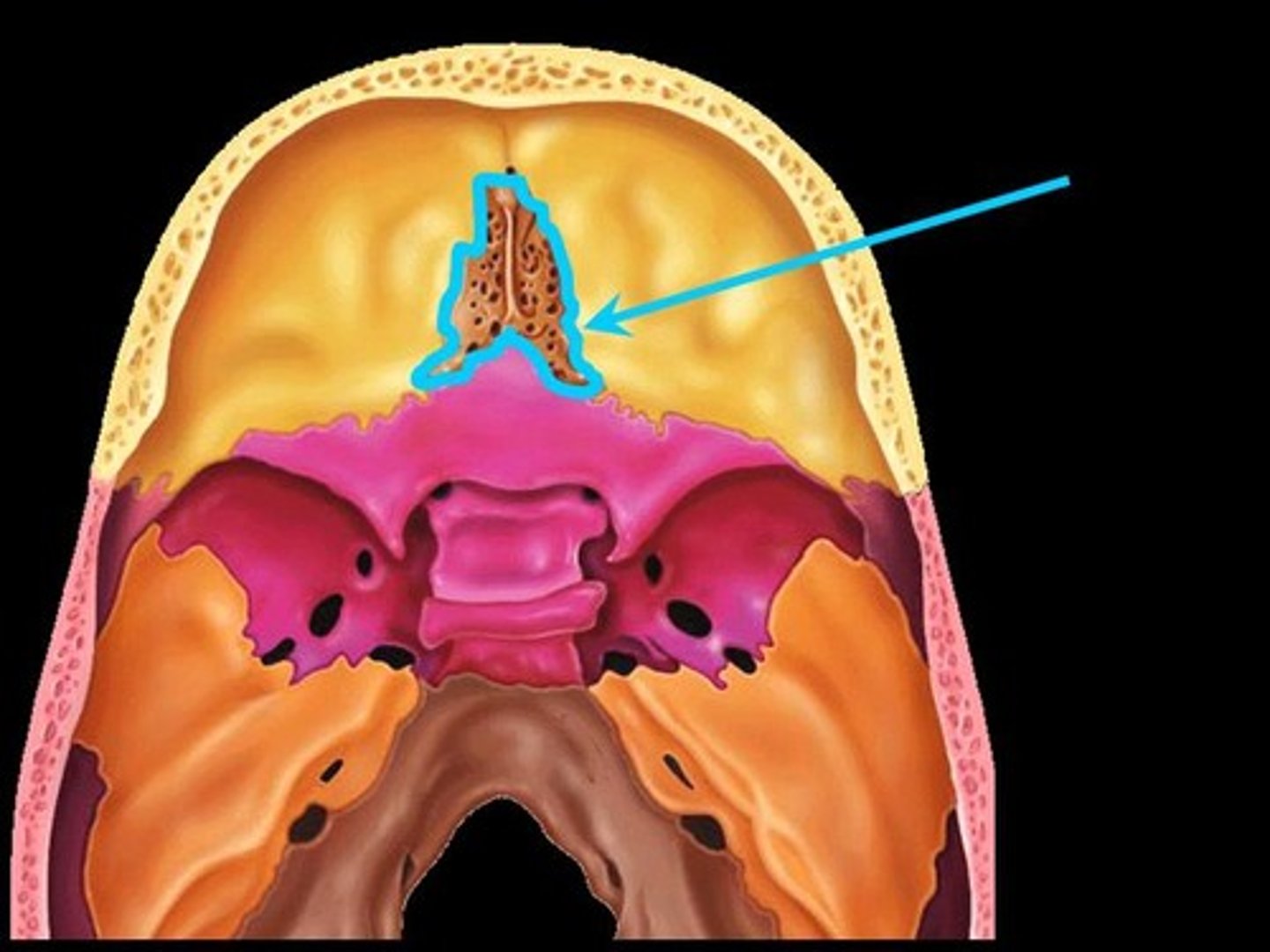
Ethmoid bone
forms part of the posterior portion of the nose, the orbit, and the floor of the cranium
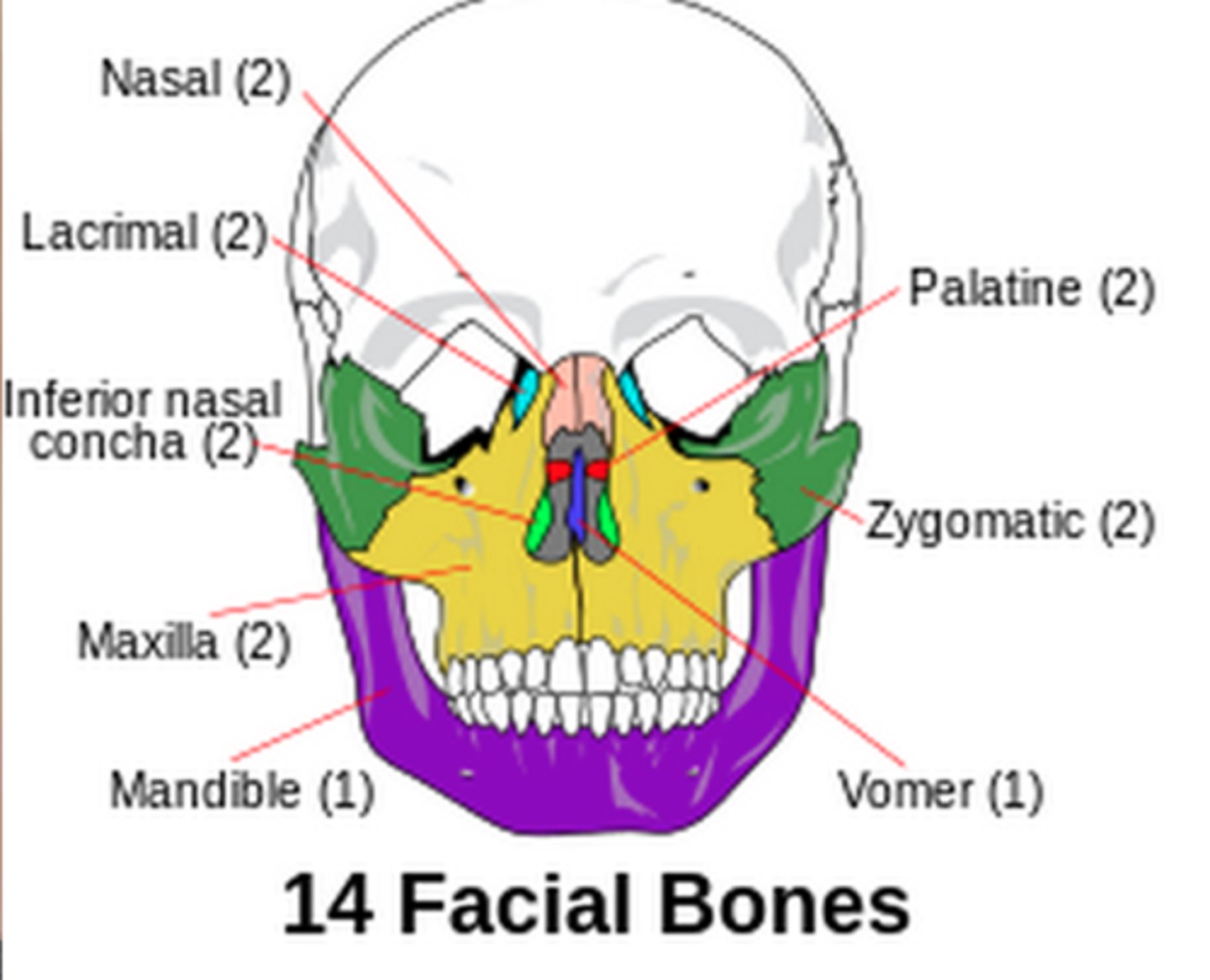
How many bones make up the viscerocranium?
15 irregular bones
What bones make up the viscerocranium
Ethmoid
Palatine x2
Lacrimal x2
Nasal x2
Zygomatic x2
Vomer
Inferior nasal concha x2
Maxilla x2
Mandible
What bone is in both the neuro and viscerocranium
Ethmoid
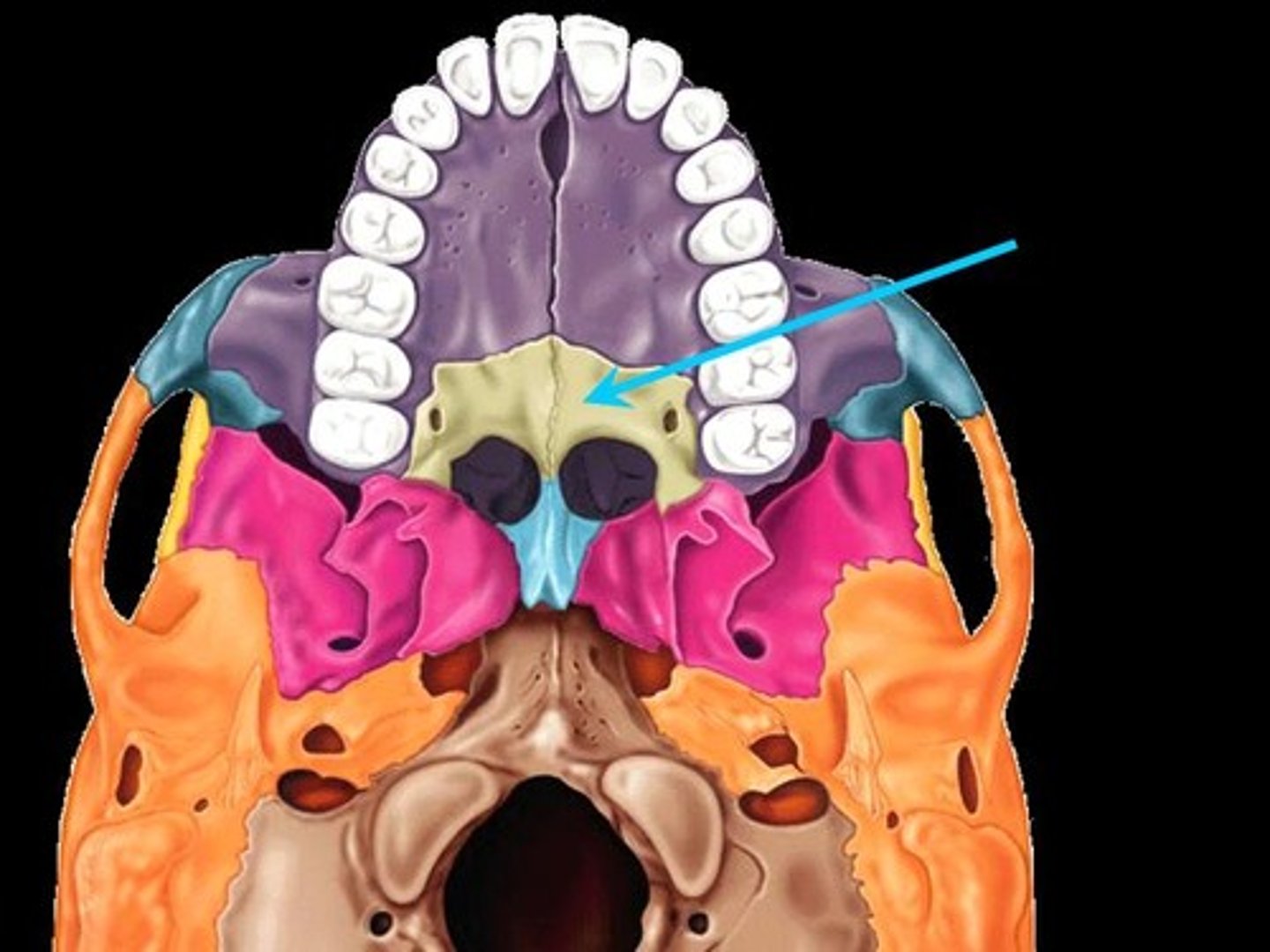
Palatine bone
either of two irregularly shaped bones that form the back of the hard palate and helps to form the nasal cavity and the floor of the orbits
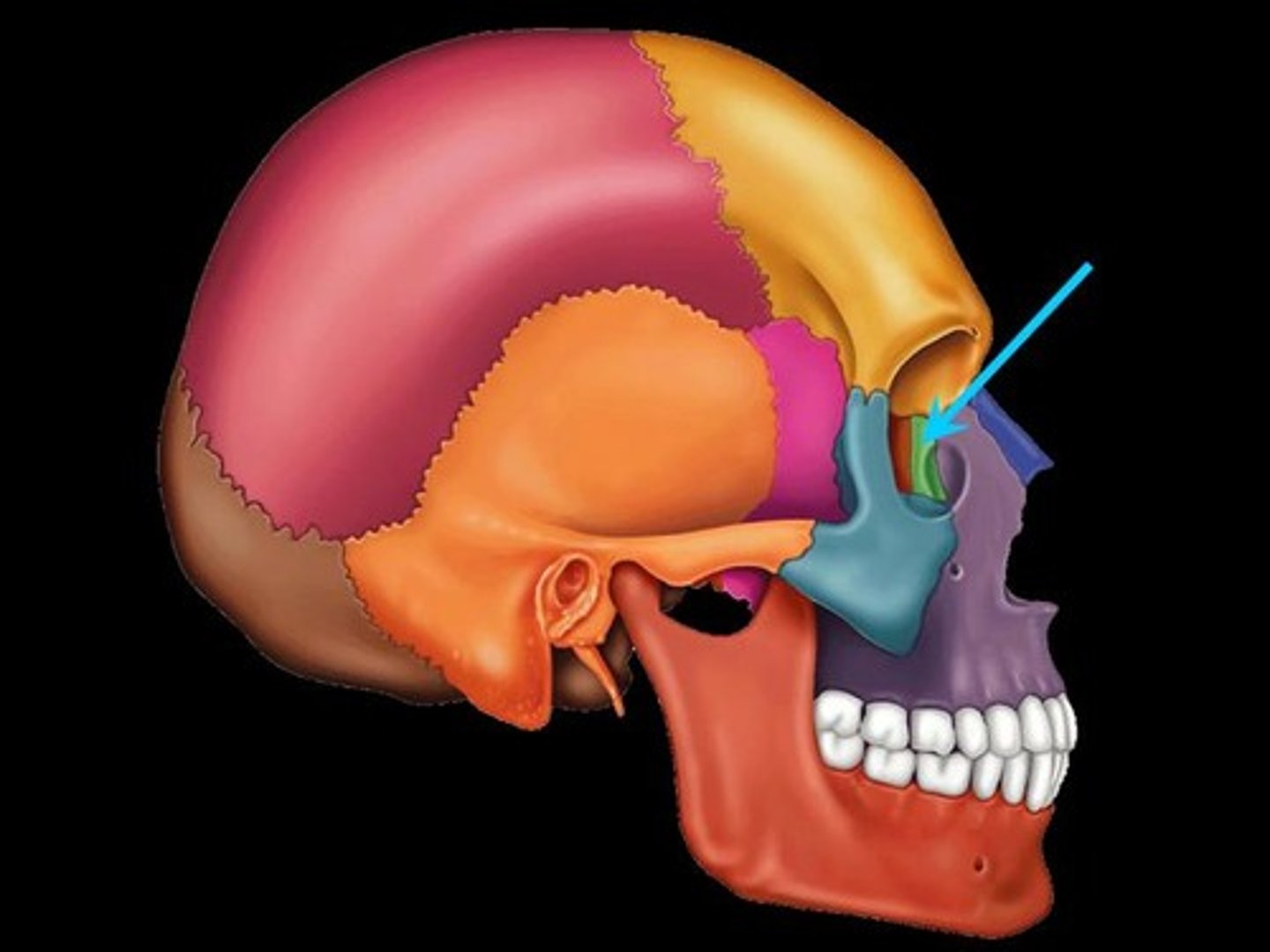
Lacrimal bone
small fragile bone making up part of the front inner walls of each eye socket and providing room for the passage of the lacrimal ducts
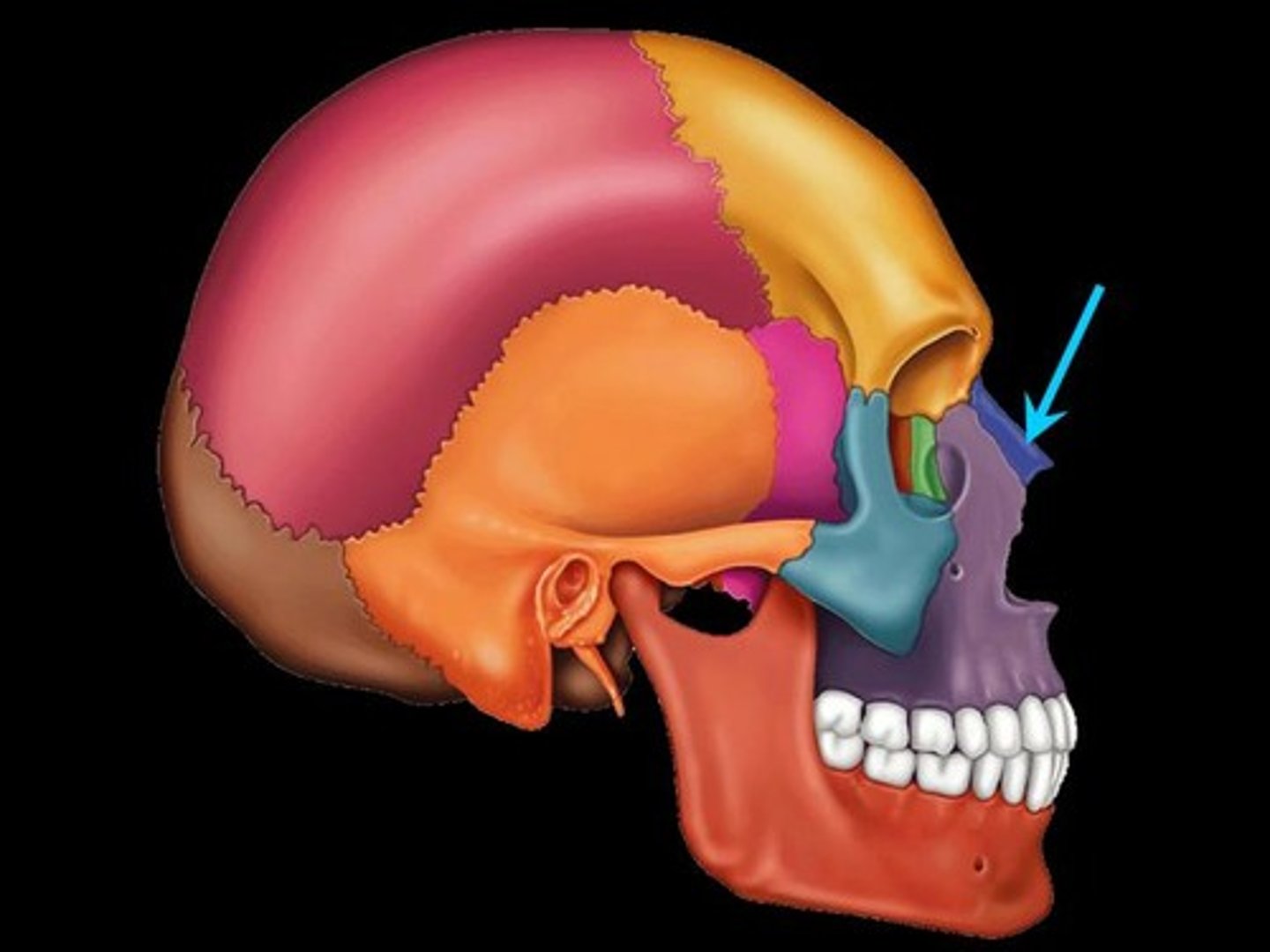
Nasal bone
forms the bridge of the nose
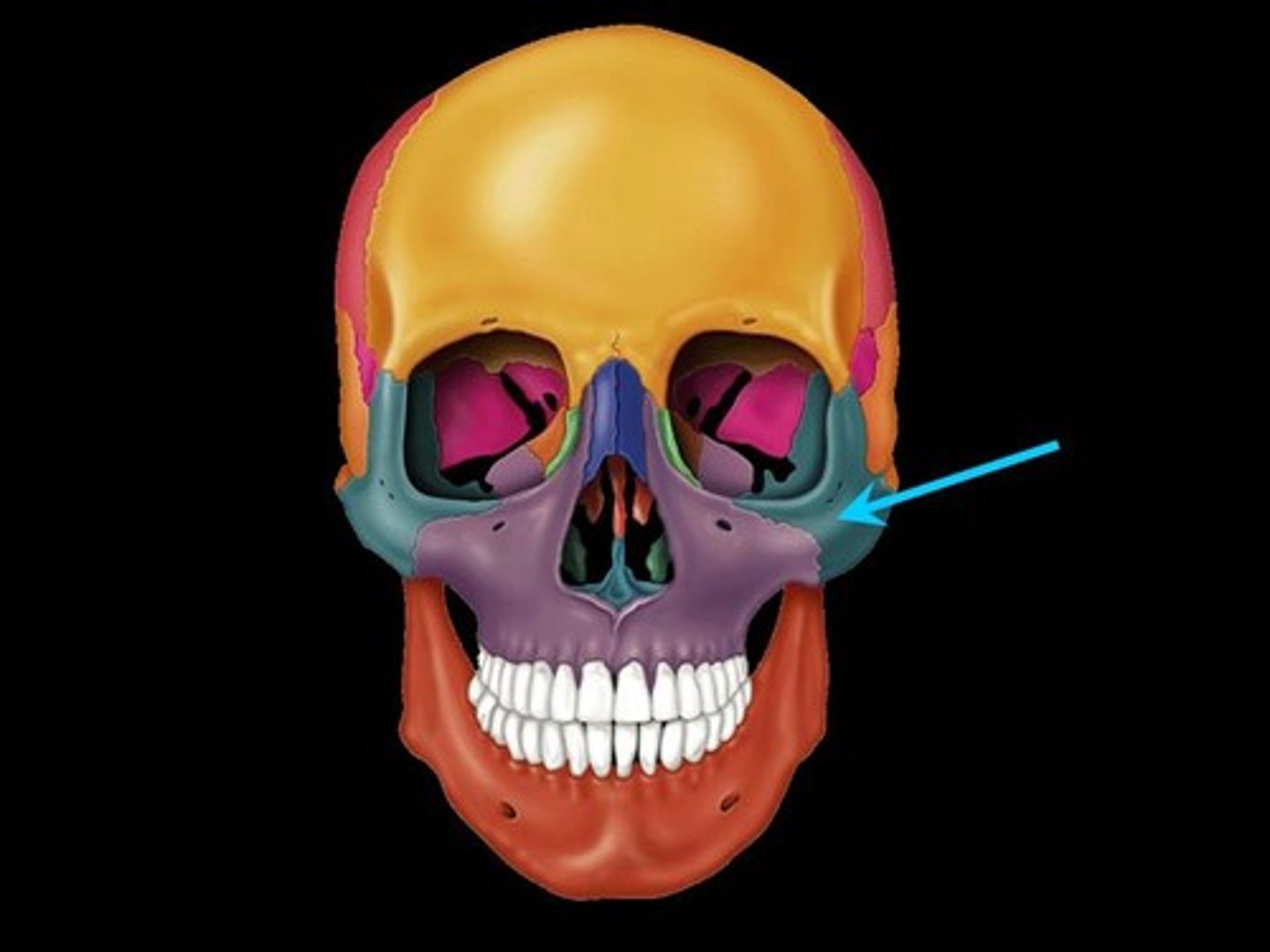
Zygomatic bone
the arch of bone beneath the eye that forms the prominence of the cheek
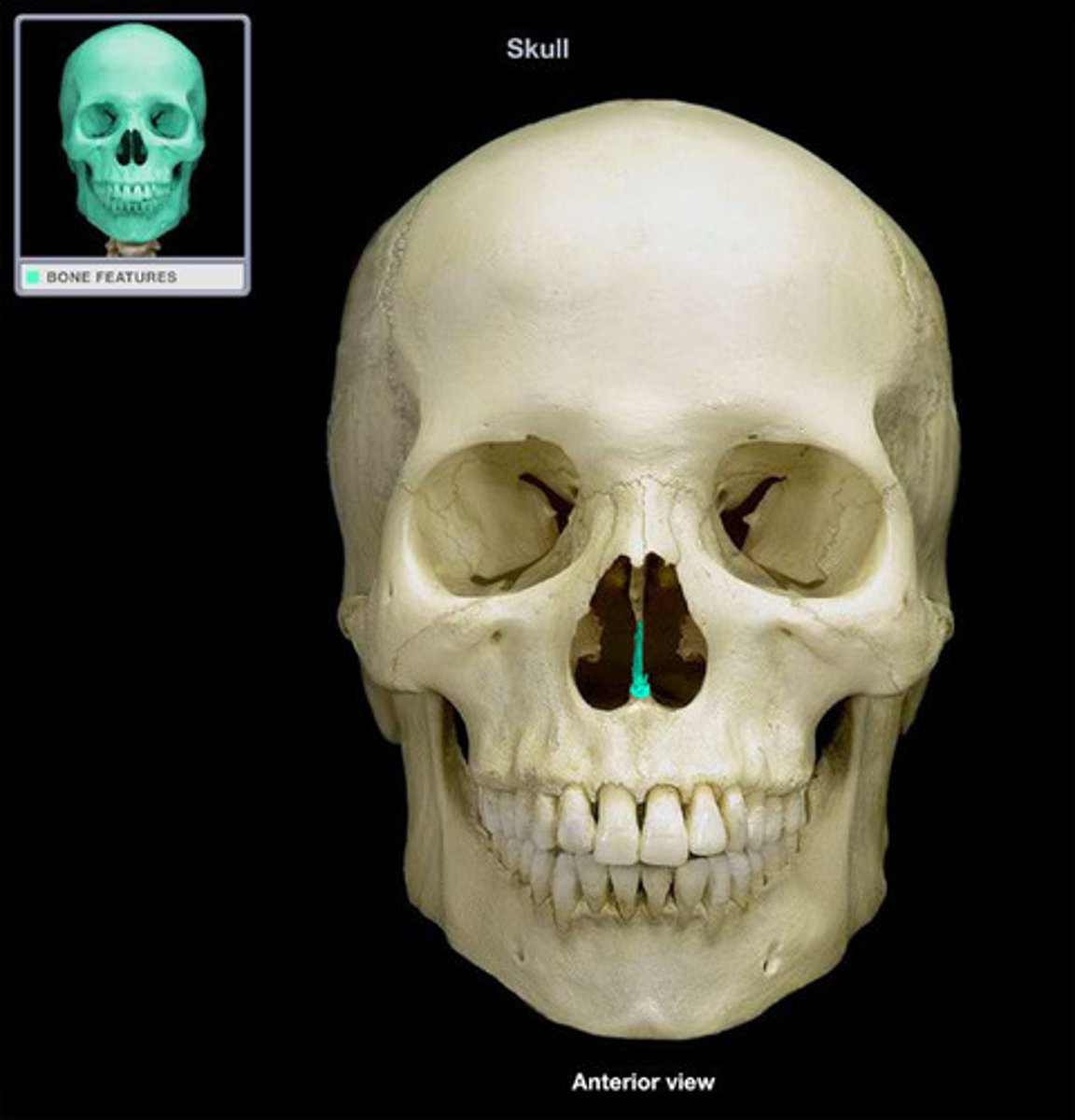
Vomer bone
Flat, thin bone that forms part of the nasal septum
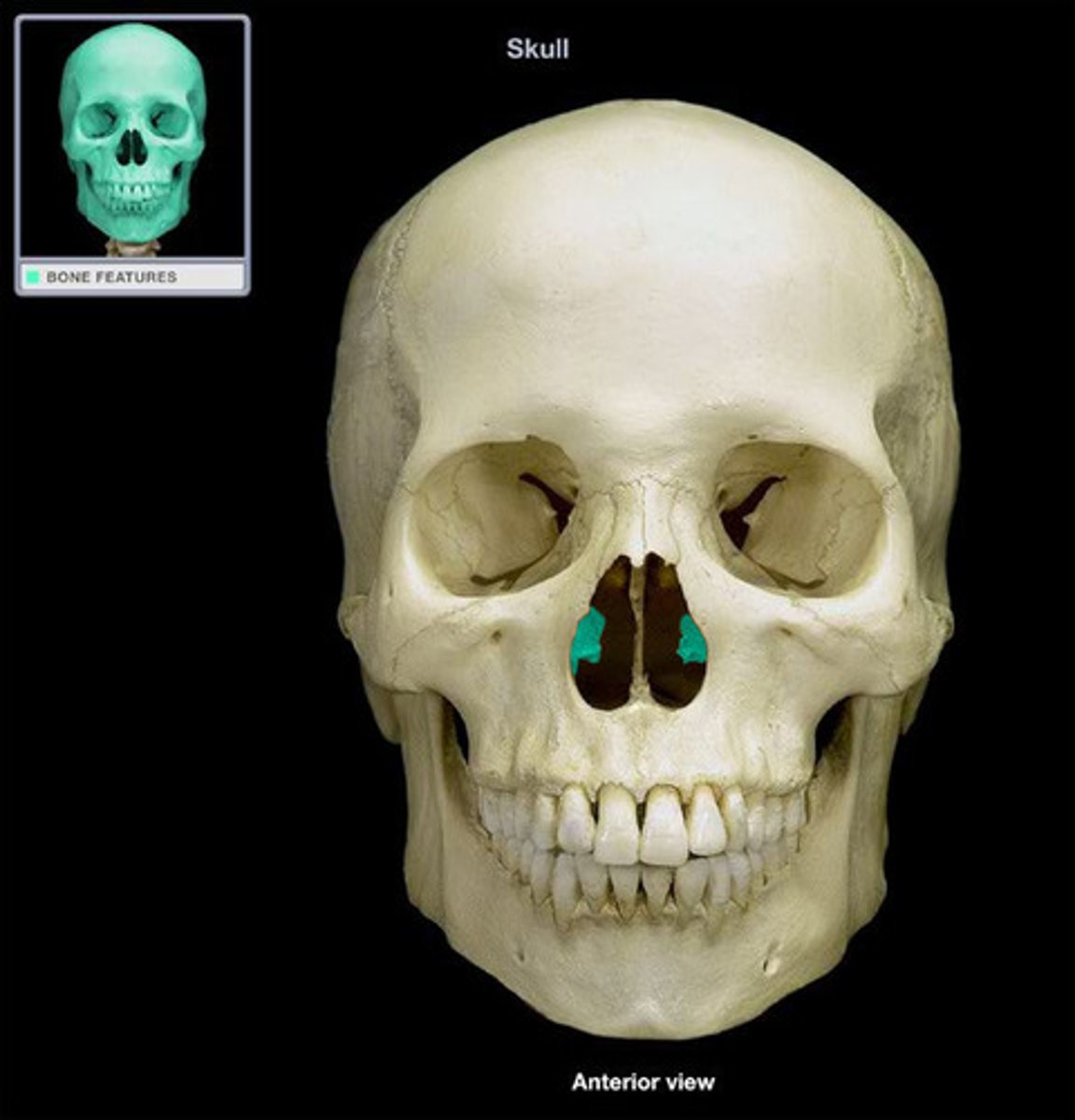
Inferior nasal conchae
The lowermost scroll-shaped bones on the sidewalls of the nasal cavity.
Maxilla
upper jaw bone
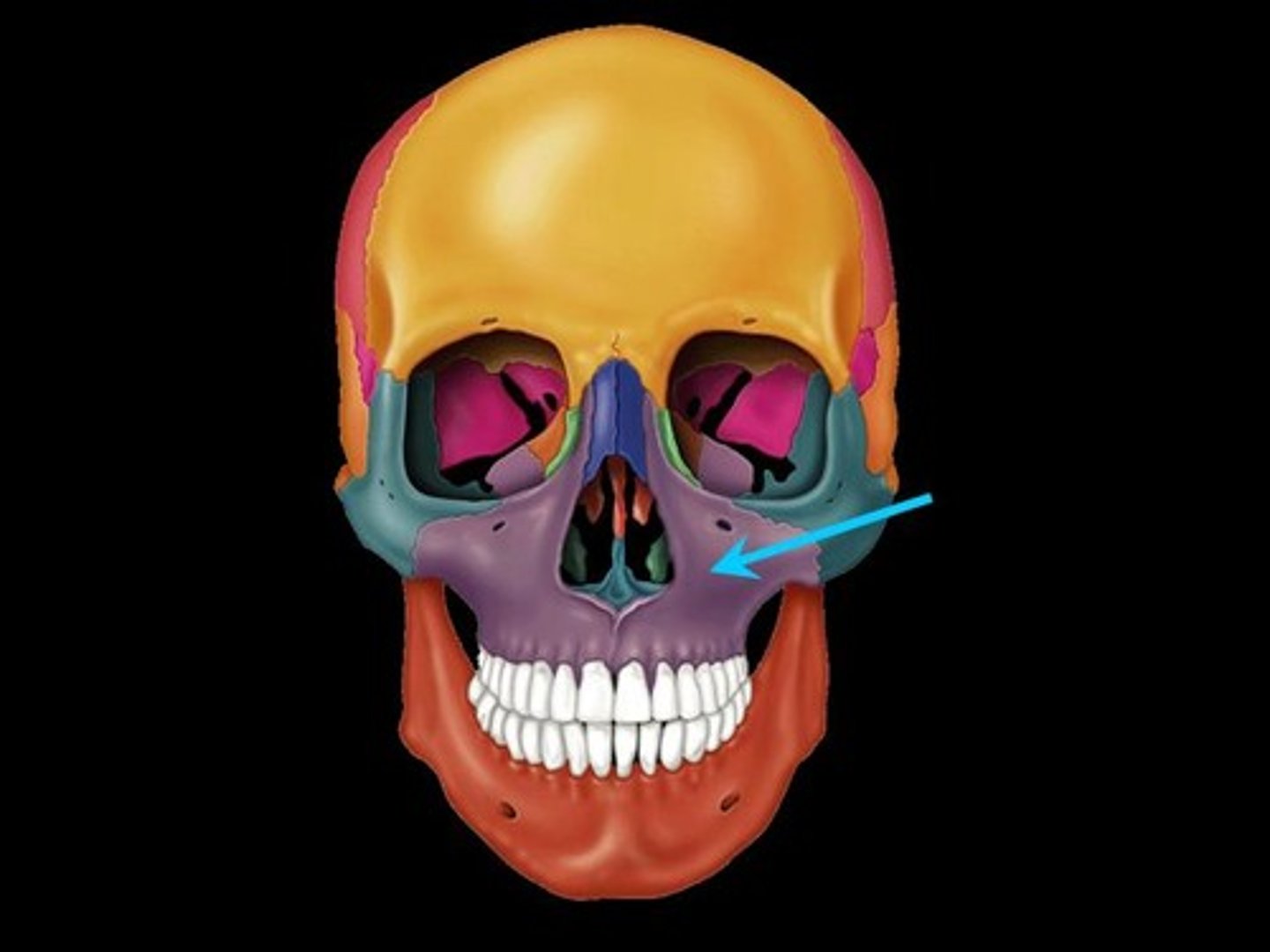
Mandible
lower jaw bone
Which bones of the viscerocranium are singular, midline bones
Ethmoid, vomer and mandible
Which bones of the viscerocranium are paired bones
Palatine
Lacrimal
Nasal
Zygomatic
Inferior nasal concha
Maxilla
On a lateral view, what are the main features of the viscerocranium
Zygomatic arch
Mandible
What forms the zygomatic arch?
temporal process of zygomatic bone and zygomatic process of temporal bone
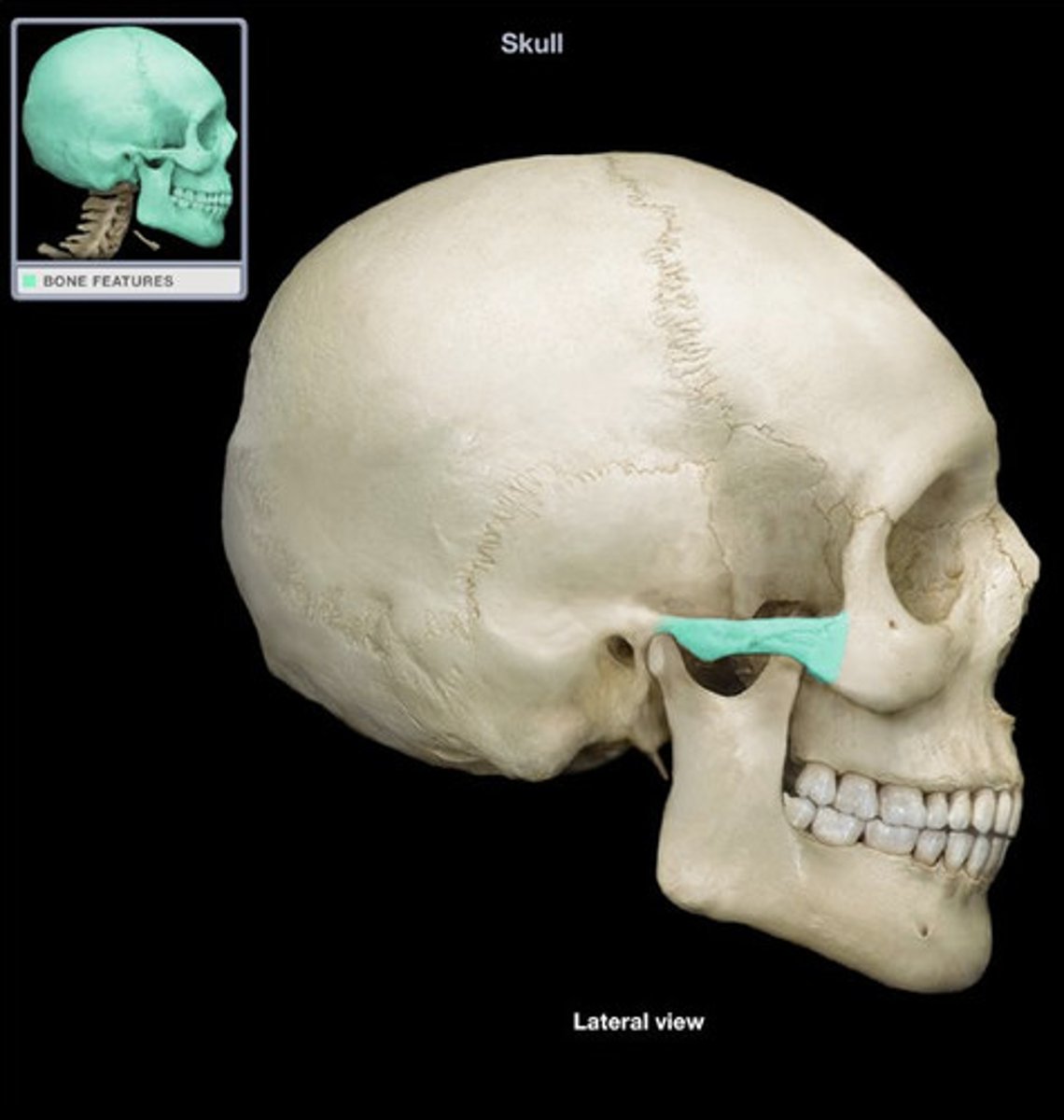
What is found deep to the mandible
Infratemporal fossa
infratemporal fossa
On a lateral view, what are the main features of the neurocranium
Temporal fossa
External acoustic meatus
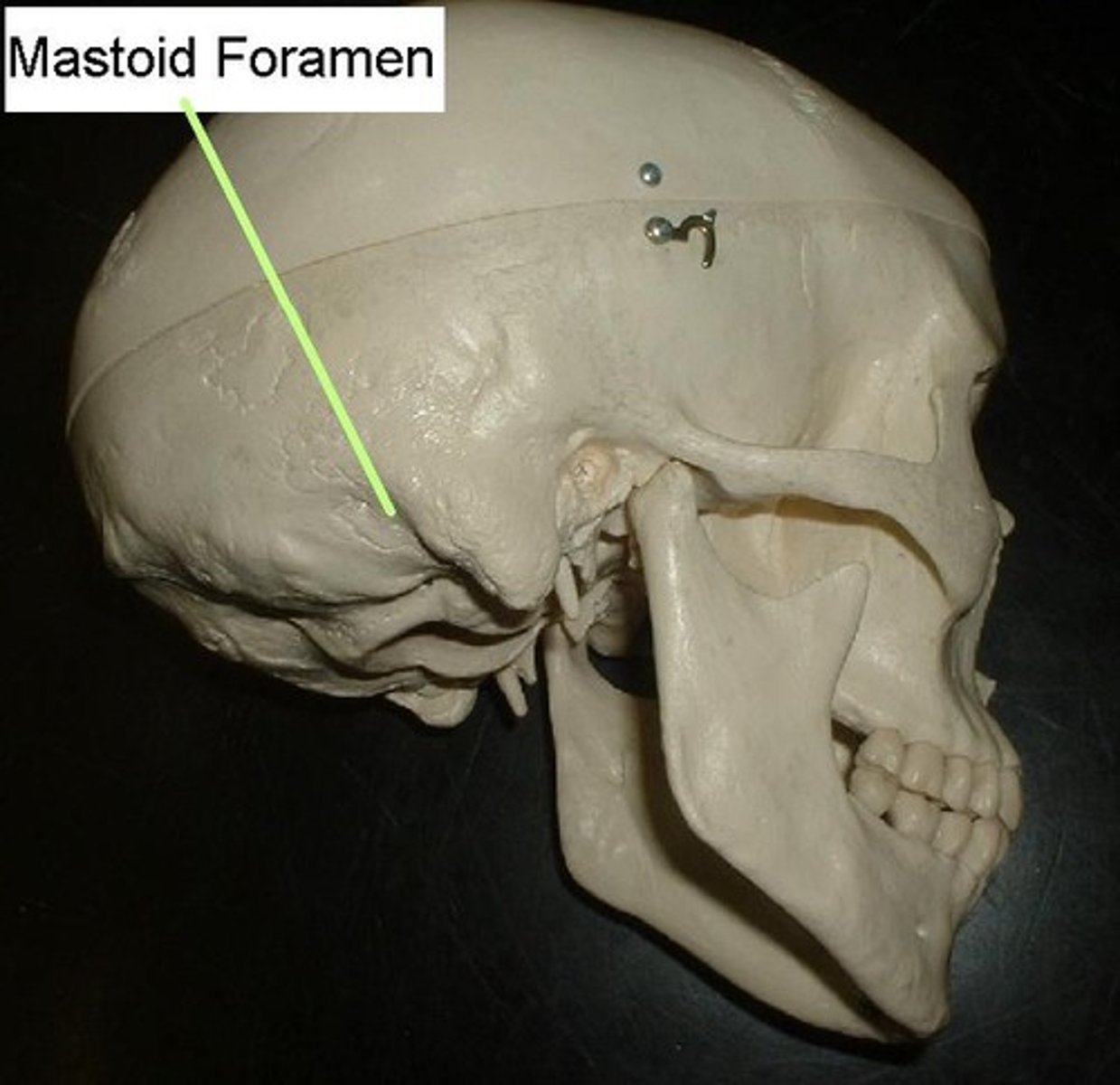
Mastoid foramen
Styloid foramen
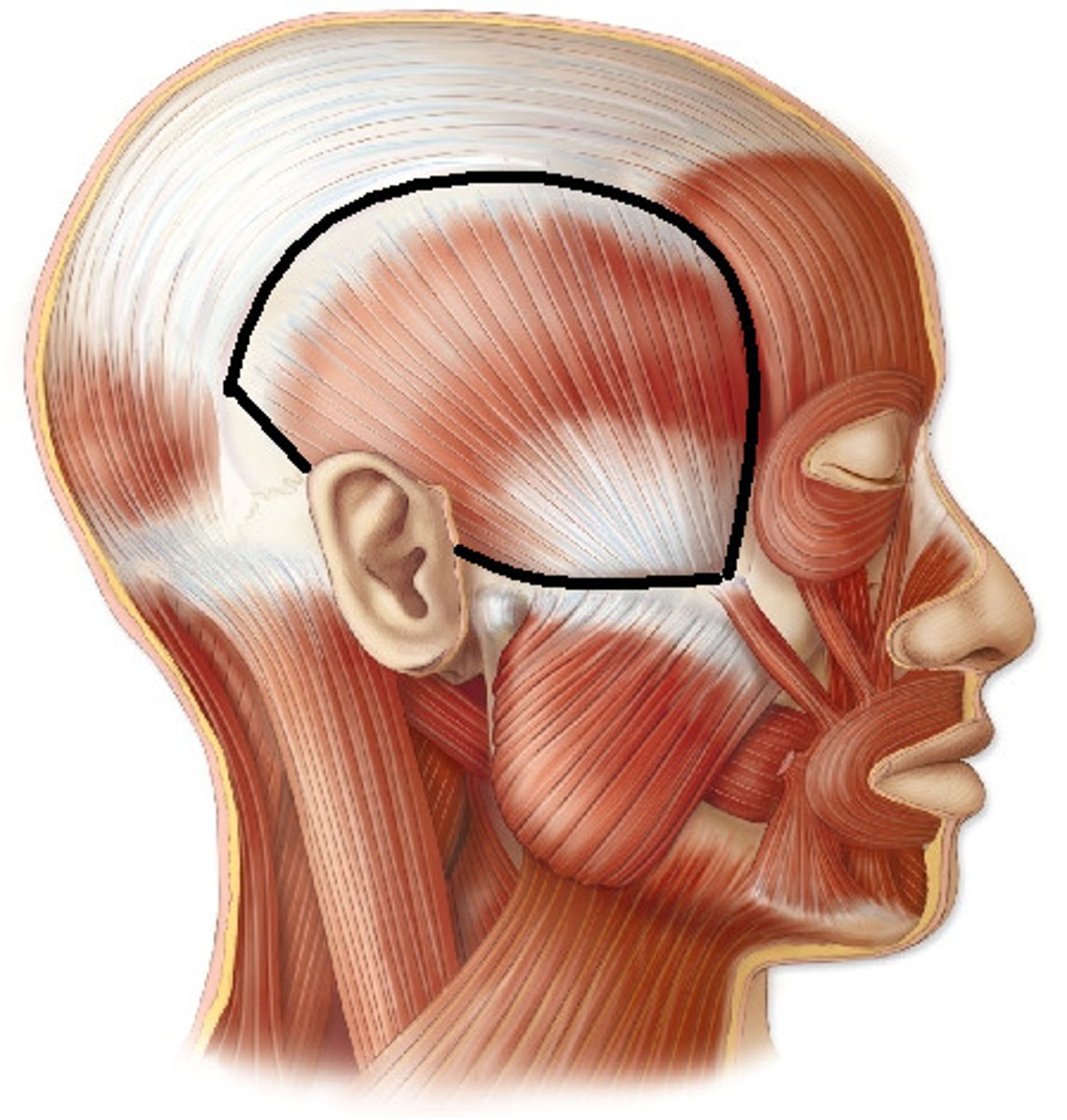
What is the temporal fossa
The temporal fossa is a depression on the temporal region and one of the largest landmarks on the skull. The temporal bone, the sphenoid bone, the parietal bone and the frontal bone contribute to its concave wall. It is superior to the infratemporal fossa which lies beneath the zygomatic arch.
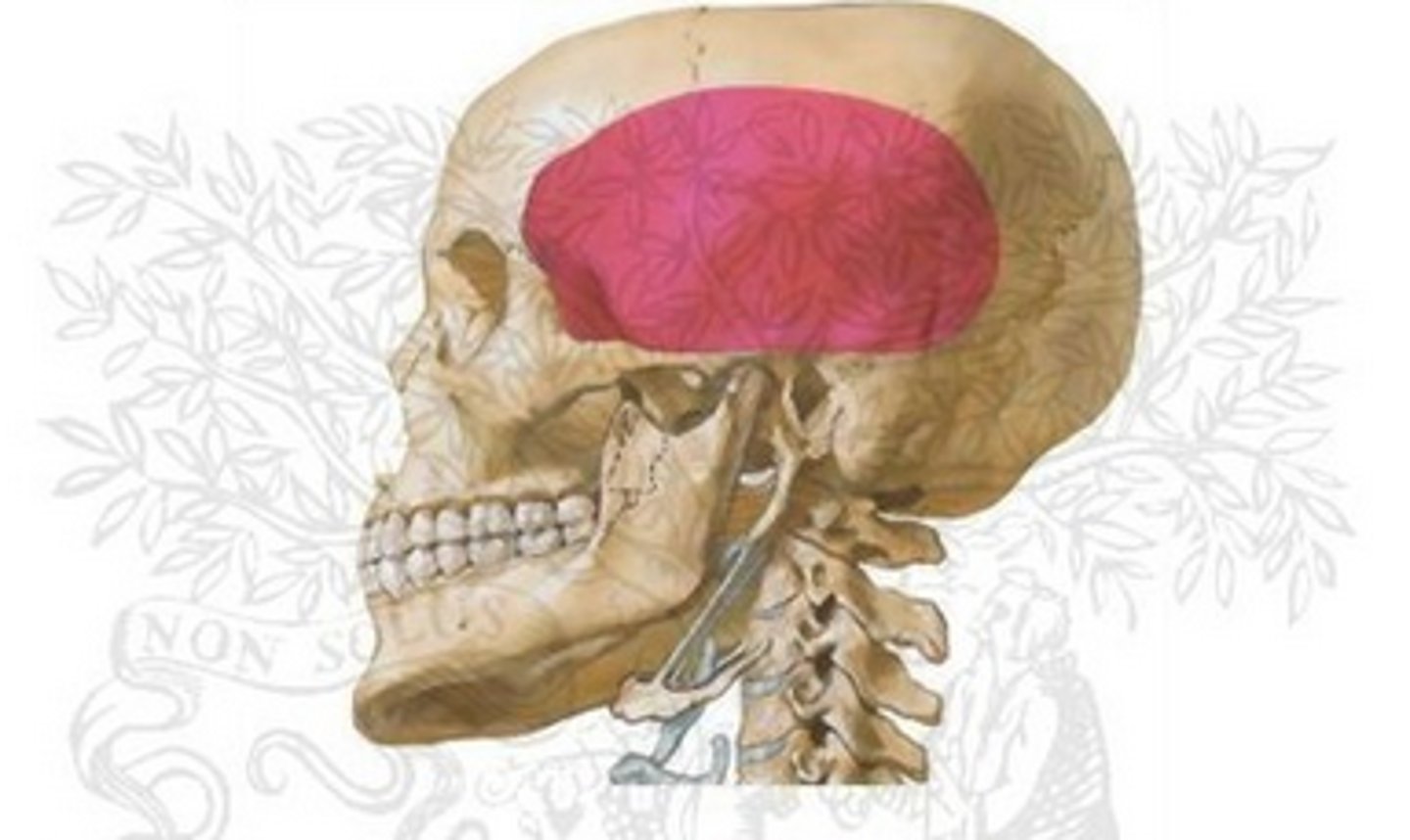
What is the temporal fossa bound by
Superior and inferior temporal lines superiorly and posteriorly, the zygomatic arch, supramastoid crest, the frontal process of the zygomatic bone and the zygomatic process of the frontal bone
External acoustic meatus
Canal leading to eardrum and middle ear
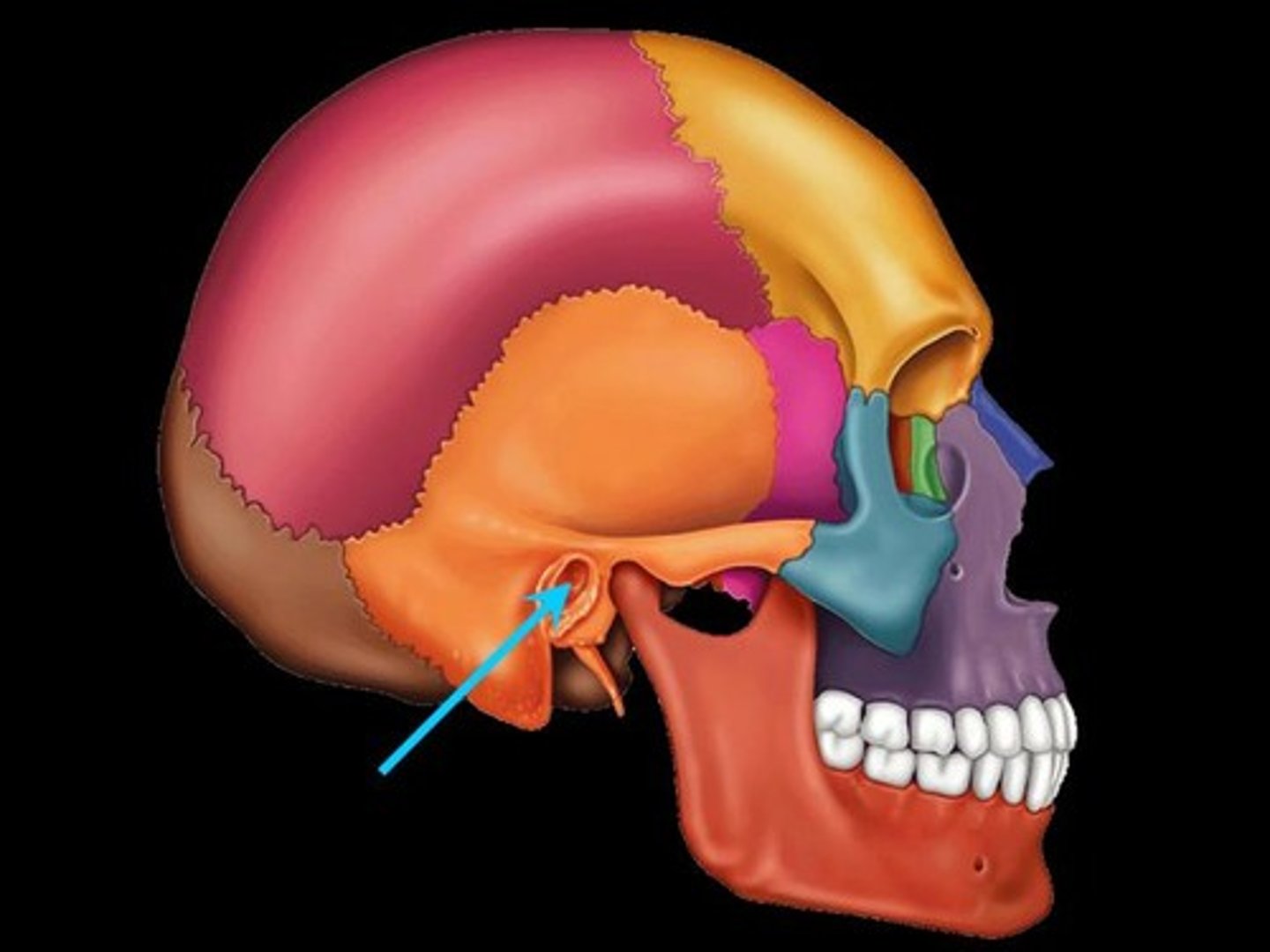
Mastoid foramen
Styloid foramen
What attaches to the inferior temporal line
temporalis muscle
What attaches to the superior temporal line
temporal fascia
What is the function of the temporalis muscle
Muscle of mastication
Origin and insertion of temporalis muscle
Originates from the temporal fossa. It condenses into a tendon, which inserts onto the coronoid process of the mandible.
What is the pterion?
Junction of frontal, parietal, sphenoid, and temporal bones. H shaped
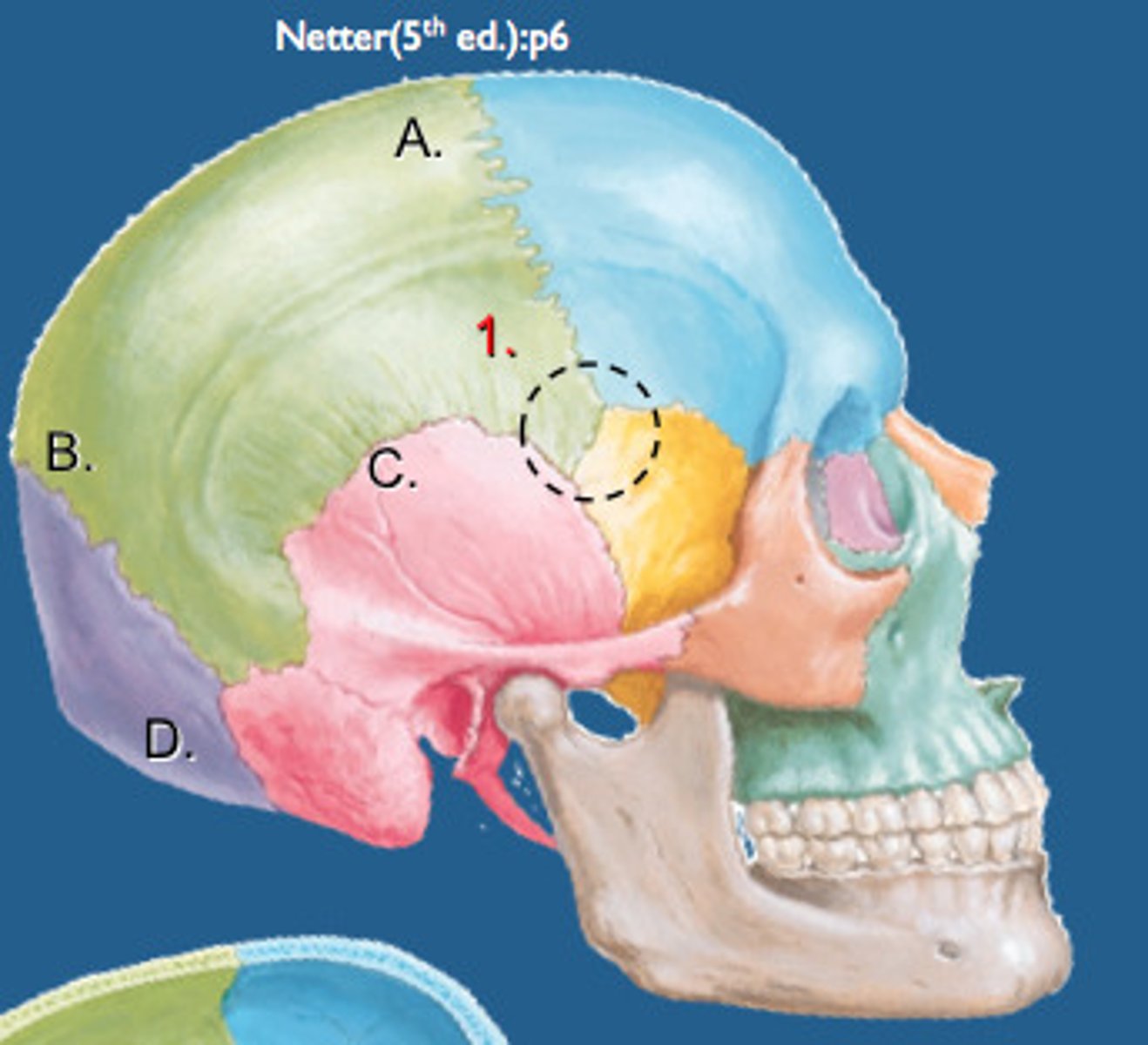
What artery runs directly behind the pterion?
anterior branch of the middle meningeal artery,
What is significant about the pterion
It is a structurally weak area because the bones are very thin meaning the anterior branch of the middle meningeal artery, that runs directly behind it, is very susceptible to injury if trauma occurs to this area
What can trauma to the anterior branch of the middle meningeal artery cause
An extradural or epidural haematoma
What is the surface landmark of the pterion
4cm superior to midpoint of zygomatic arch & 3cm posterior to frontal process of zygomatic bone
What is the calvarium
The top of the neurocranium
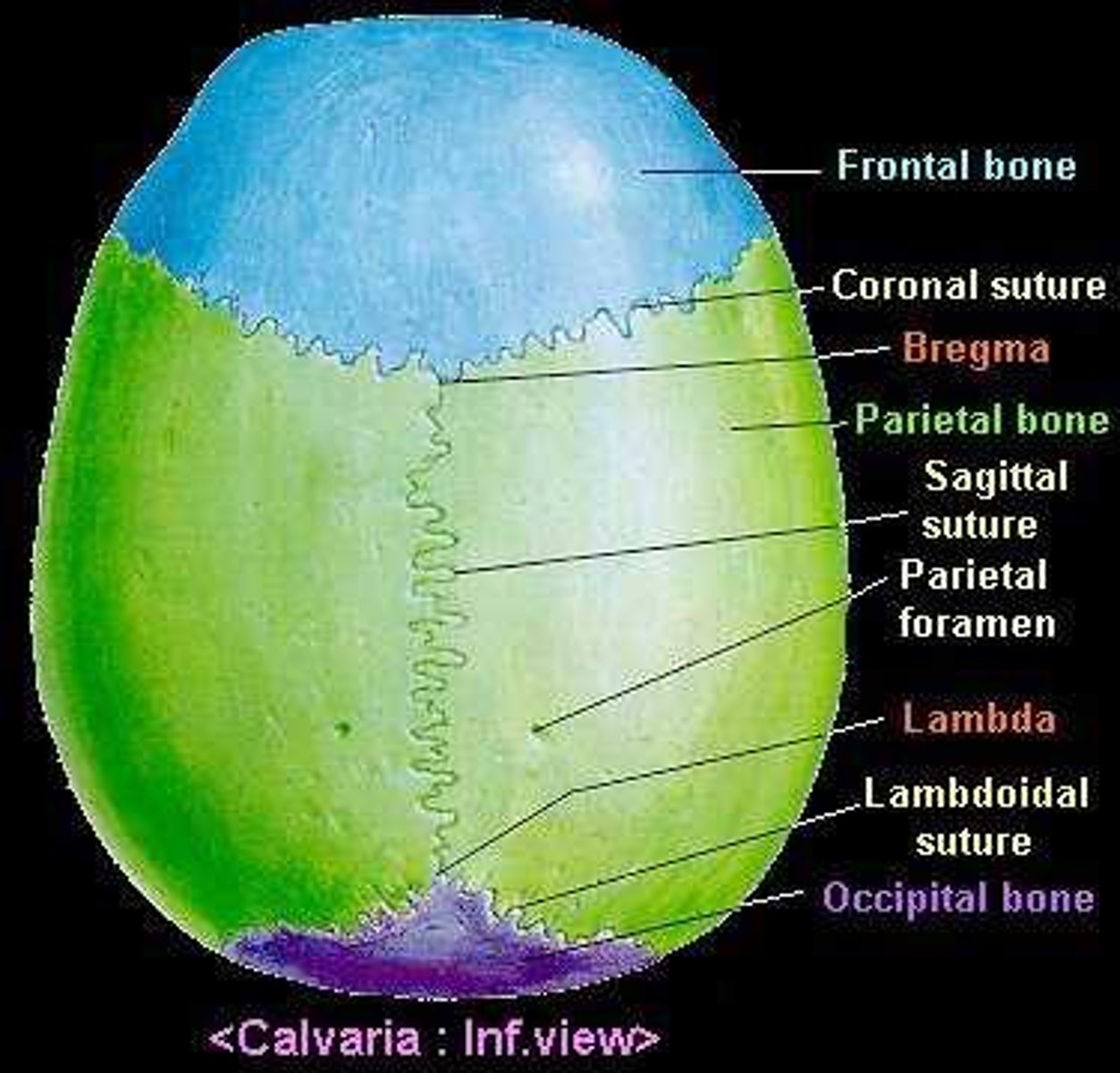
What bones make up the calvaria
frontal, parietal x2, occipital
What sutures fuse the calvarium
Coronal suture
Sagittal suture
Upper part of the lambda suture
What is found in the midline of the calvarium deep to the sagittal suture?
A groove for superior sagittal sinus
What is the superior sagittal sinus?
large vein that carries venous blood to the systemic circulation
What is found on either side of the groove for superior sagittal sinus
Small fossae called granular foveolae
What are granular foveolae?
Arachnoid granulations that return CSF to the venous circulation via the superior sagittal sinus
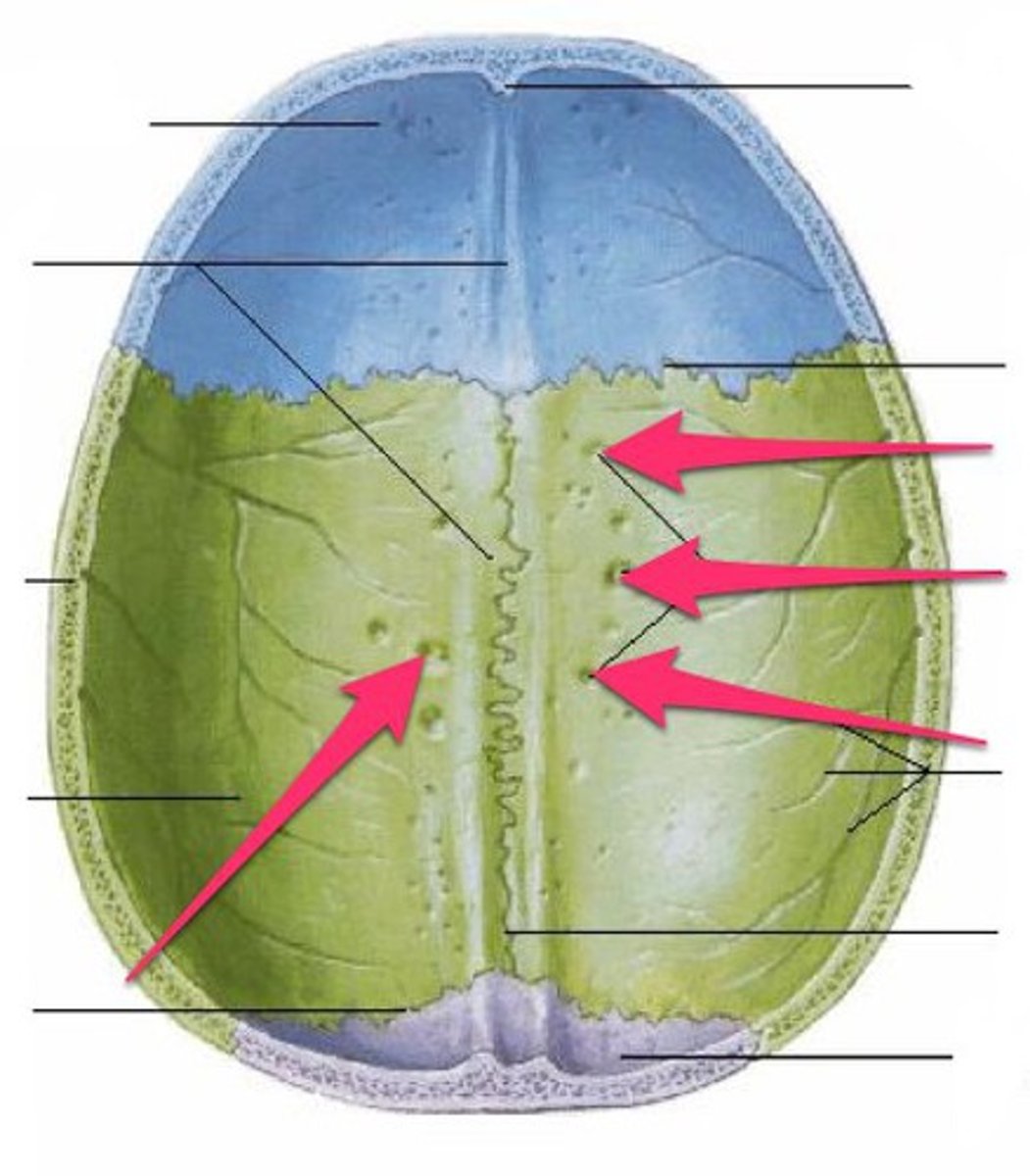
What suture is found between the 2 parietal bones
Sagittal suture
The squamous part of the occipital bone fuses with the parietal bone via what suture?
Lamboid suture
Describe the surface of the occipital bone
Squamous part is smooth and base is rough
What is the base of the occipital bone also known as?
Nuchal region
What attaches to the nuchal region?
Neck and superficial back muscles
What is the boundary between the squamous and nuchal part of the occipital bone called?
Nuchal line
Superior nuchal line
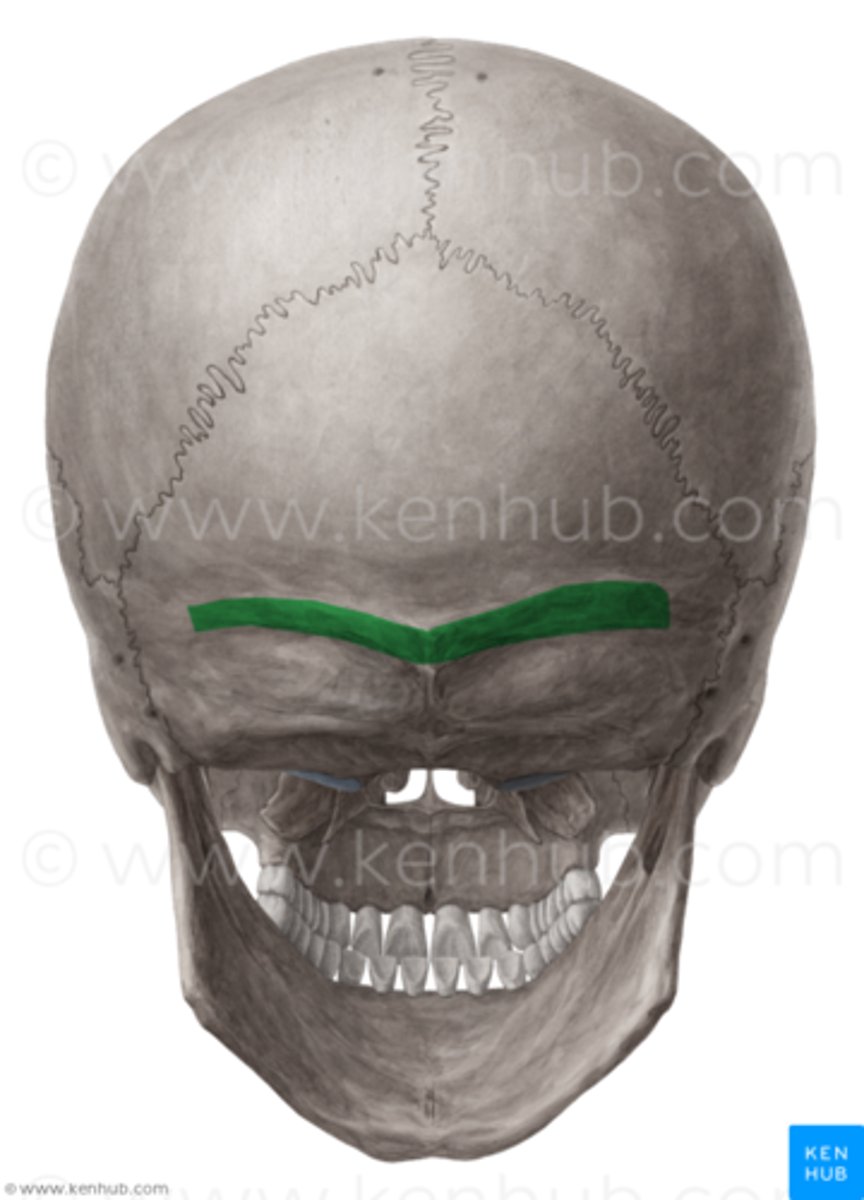
Inferior nuchal line
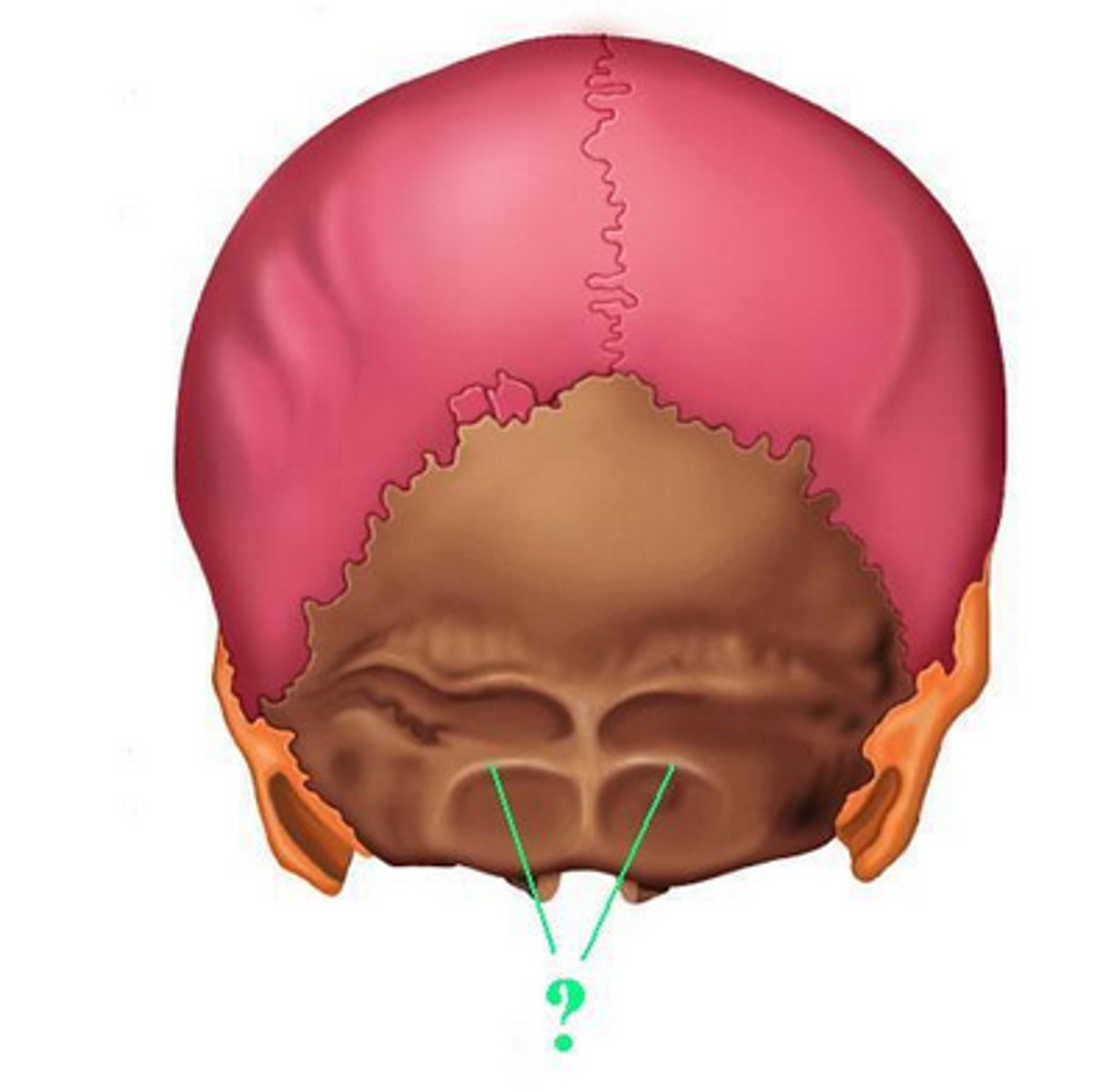
What attaches between the superior and inferior nuchal line
Muscles
Name the sutures of the skull
Coronal suture- separates frontal and parietal
Saggital suture- separates the two parietal bones
Lambdoid suture - separates the Parietal, and occipital
Squamous suture
Why at birth are the sutures not fused?
To allow the brain to develop so the skull can accommodate its growth
What type of joint are the sutures?
Structurally, type of fibrous joint
Functionally, limited or no movement (synarthrosis)
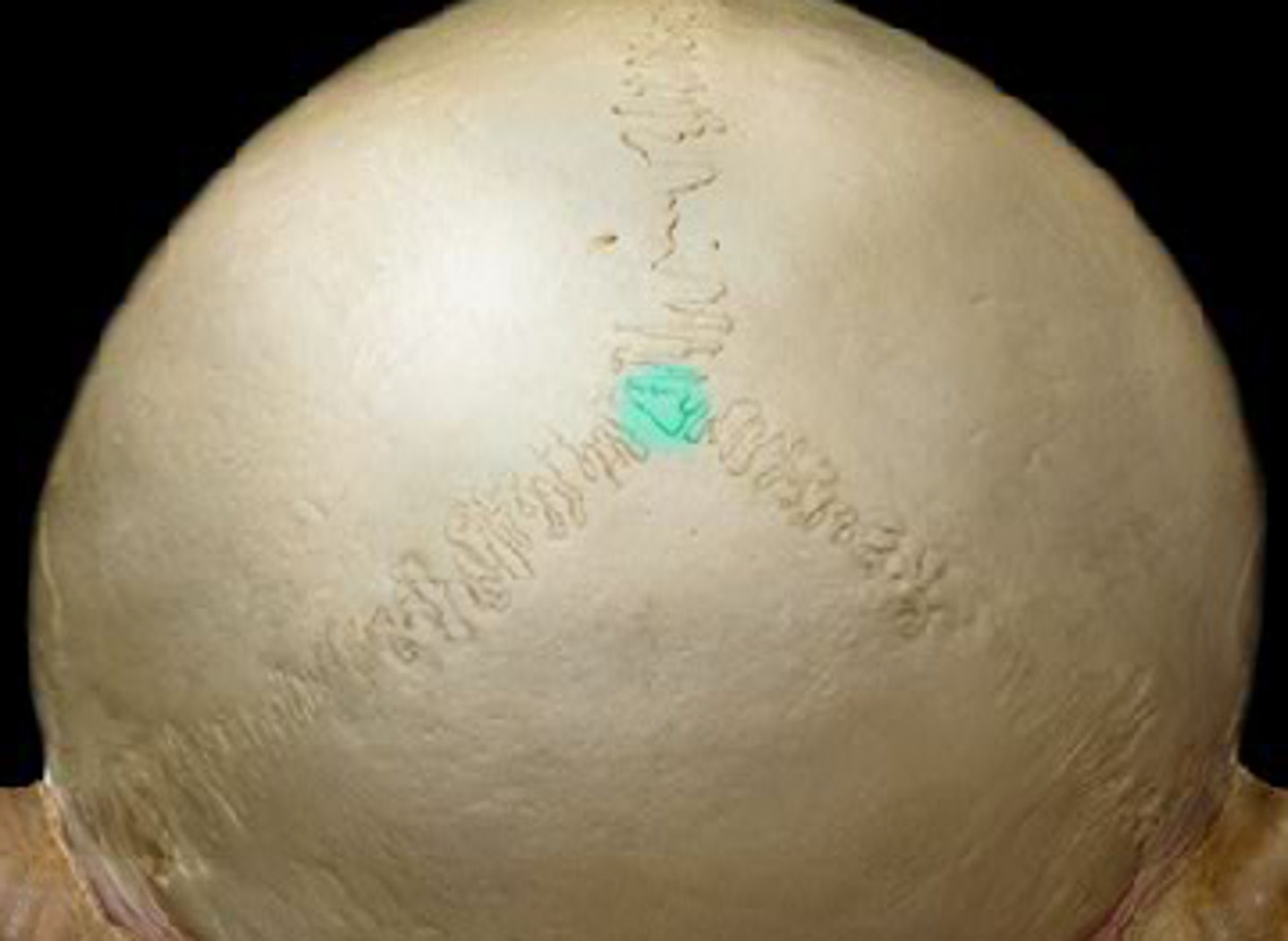
What are fontanelles
Unossified areas between the bones that are found during infancy and early childhood. They allow the moulding of the cranial shape during birth and post natal growth of brain
Where is the anterior fontanelle located?
At the junction of the coronal and sagittal suture
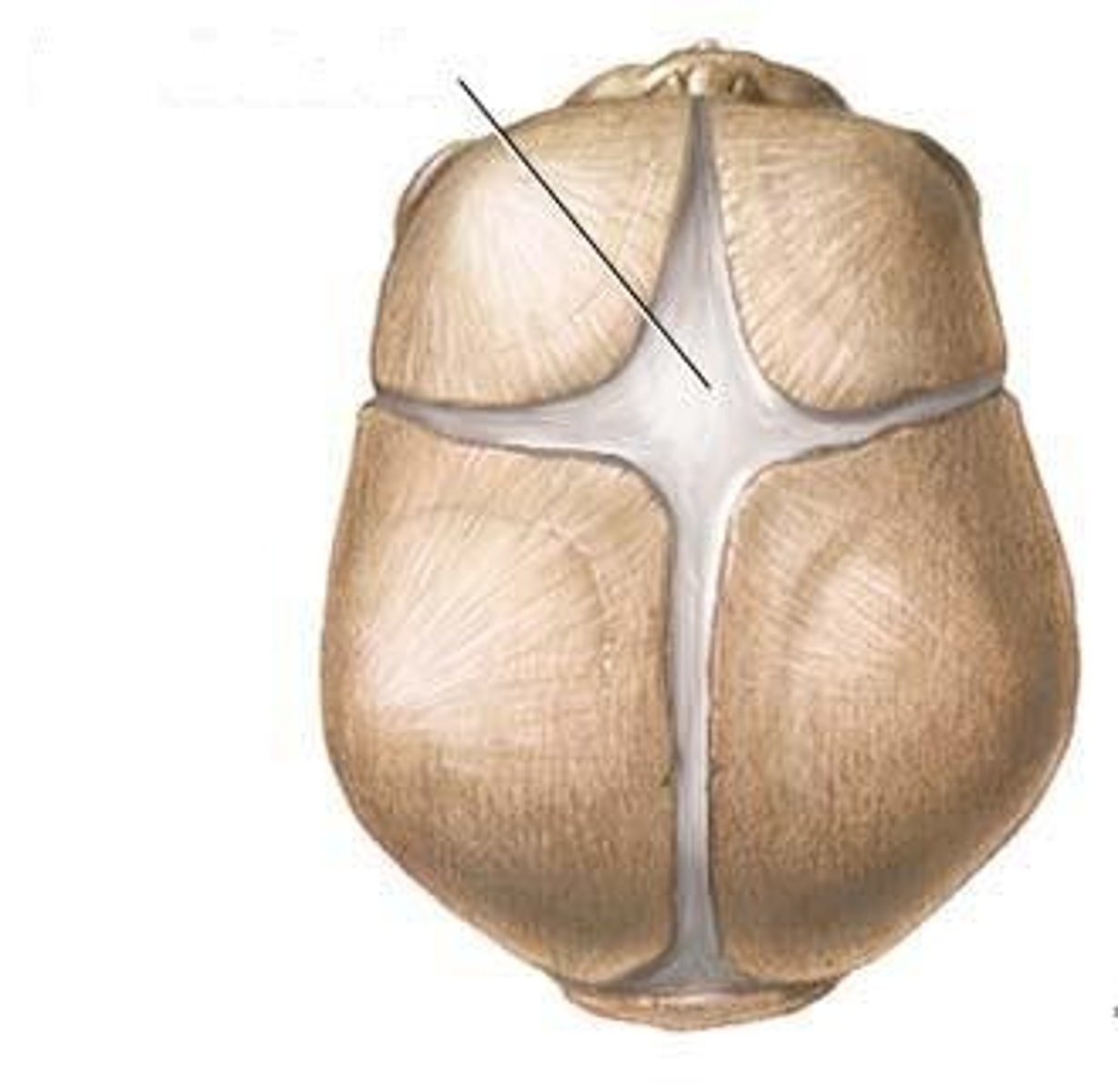
When does the anterior fontanelle usually close?
18 months - sometimes will stay
Where is the posterior fontanelle located
Between the sagittal and lamboid suture
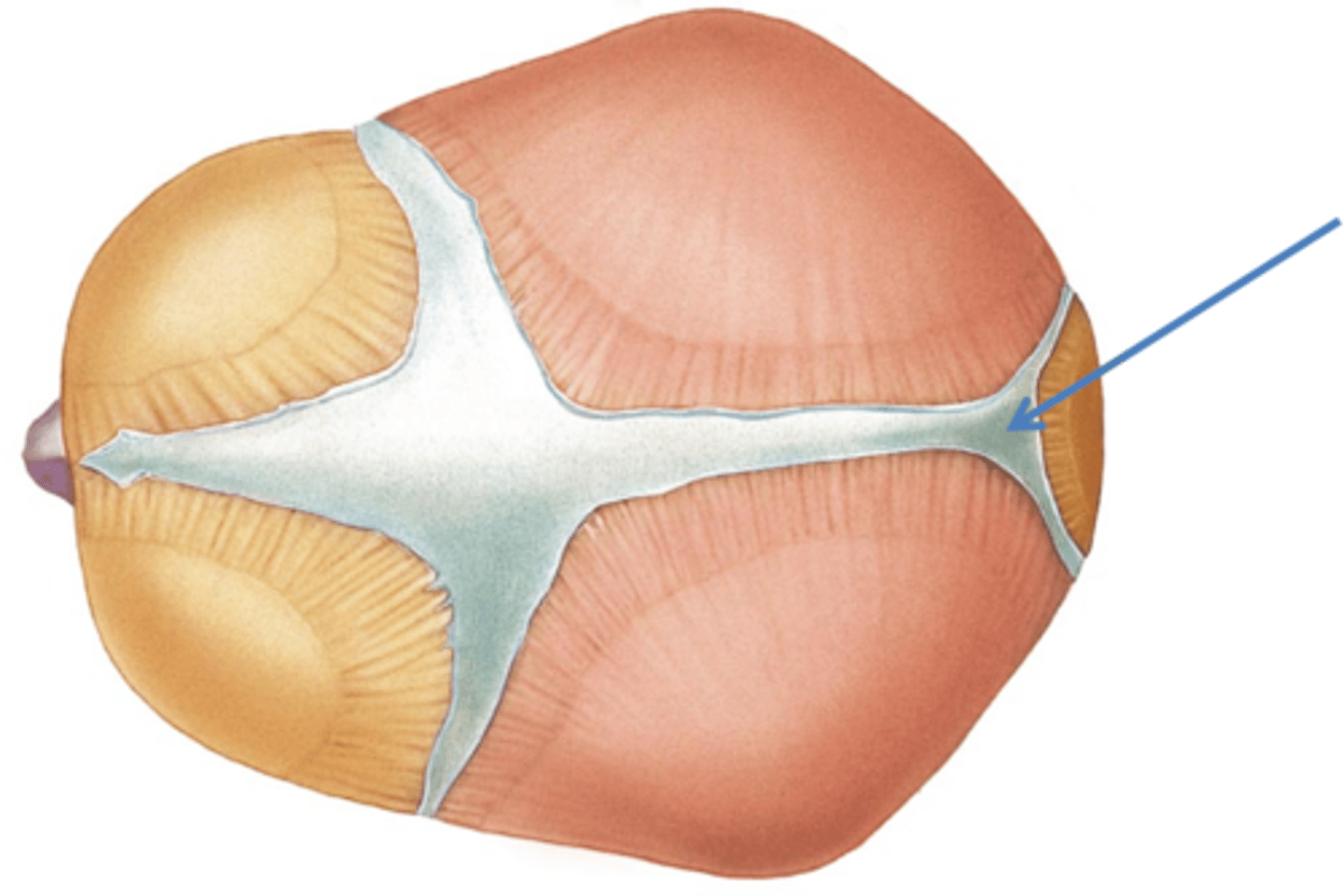
When does the posterior fontanelle usually close
6-9 months
What does it mean if the anterior fontanelle is depressed?
Good indicator that the baby is dehydrated or malnourished
What does it mean if the anterior fontanelle is swollen
Increased intracranial pressure
What does a small pulsation in the fontanelle suggest
This is normal - caused by the pressure gradient in the sagittal sinus
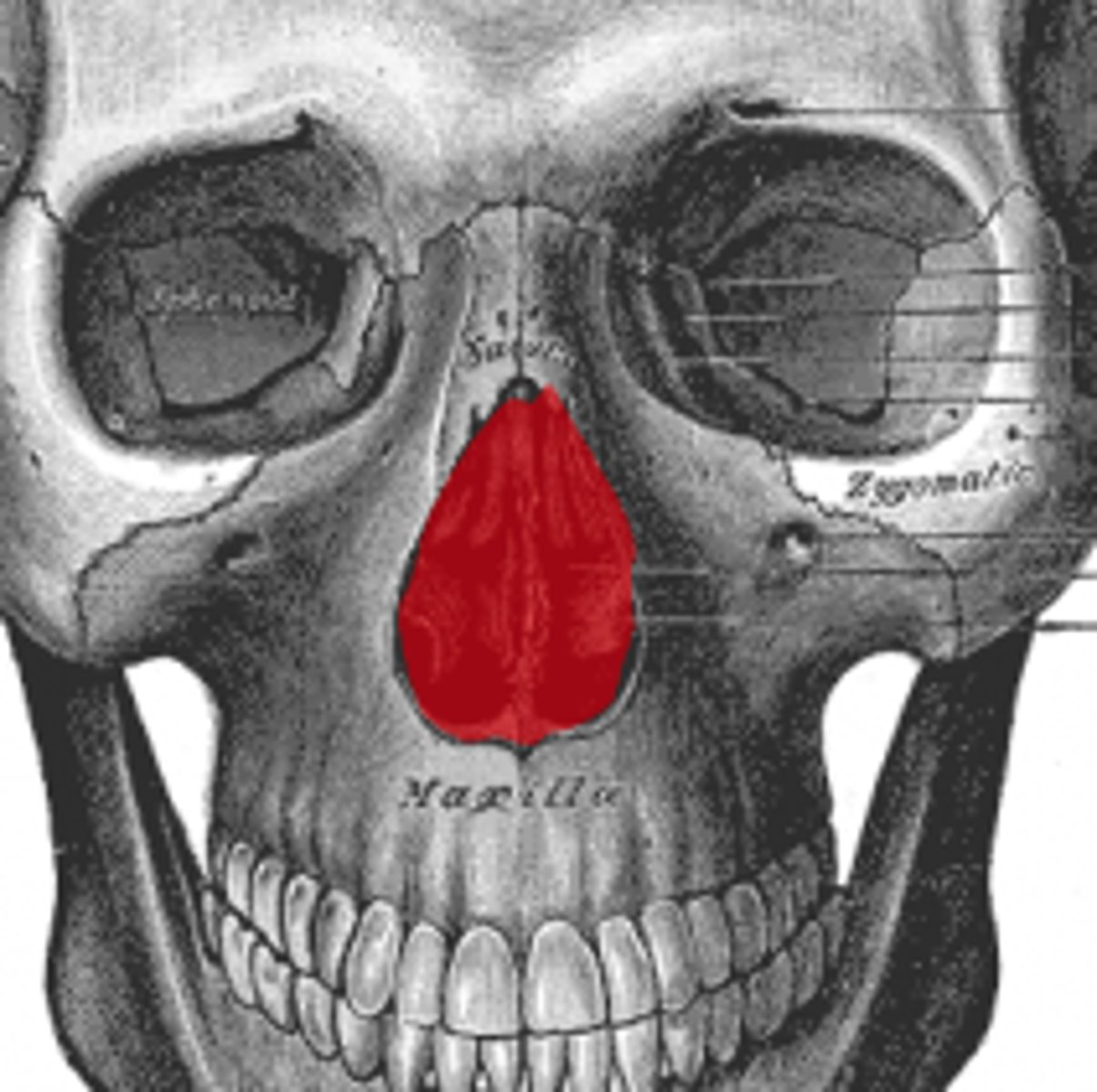
What is the piriform aperture?
The anterior opening of the nasal cavity
How many divisions does the trigeminal nerve have
3
What 3 foramina do the divisions of the trigeminal nerve pass through
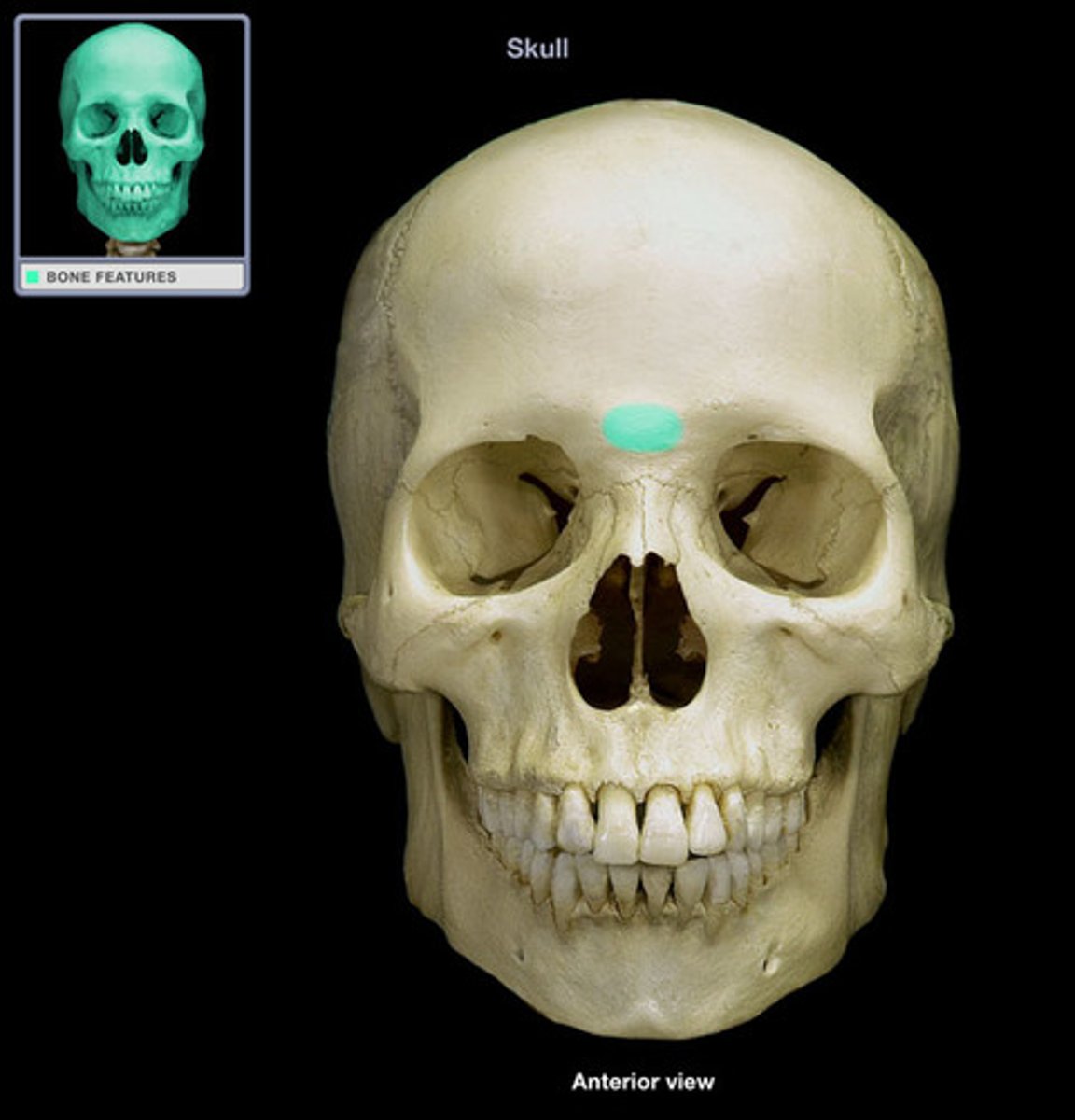
Ophthalmic (V1) - Supraorbital notch
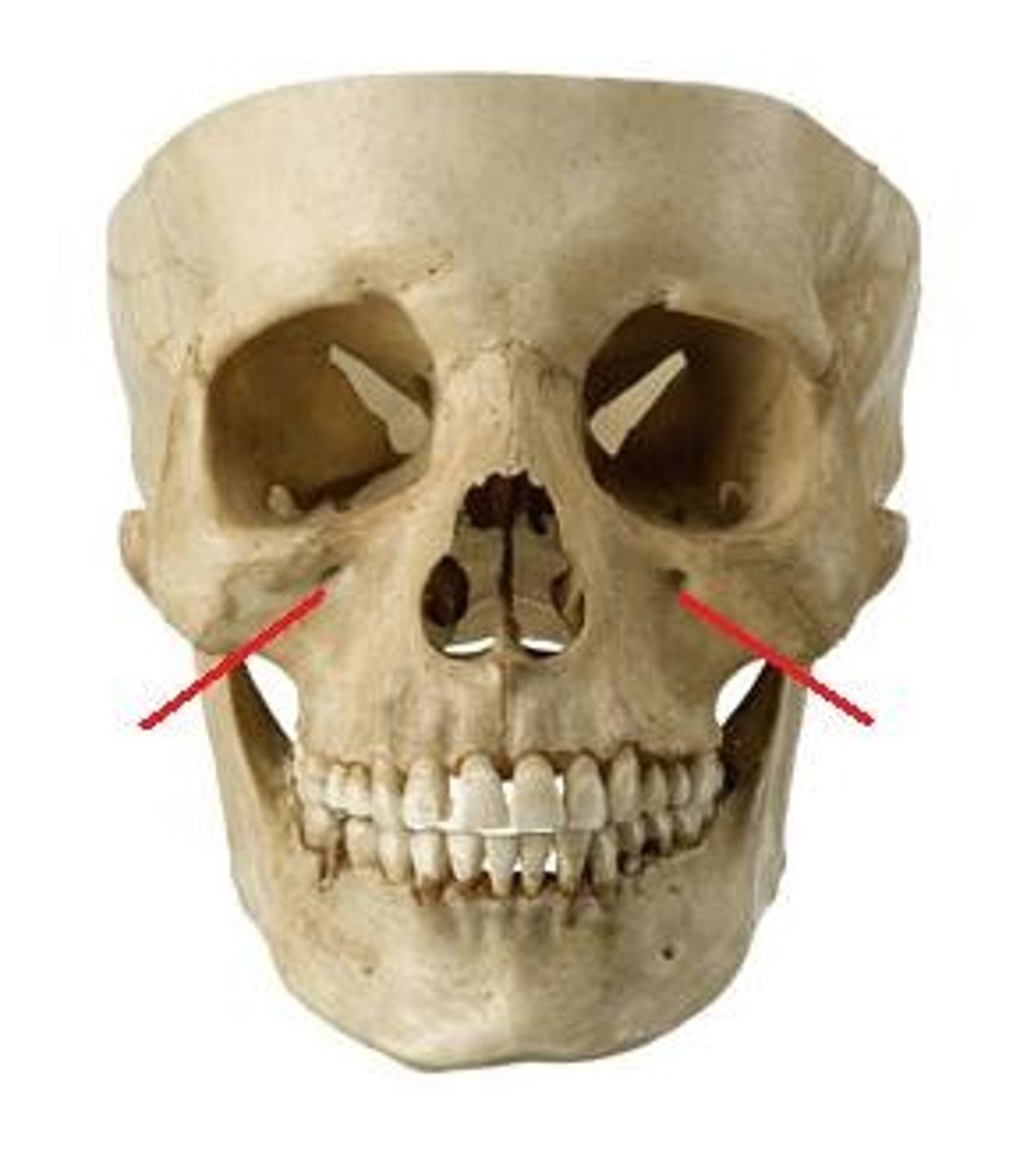
Maxillary (V2) - Infraorbital foramen
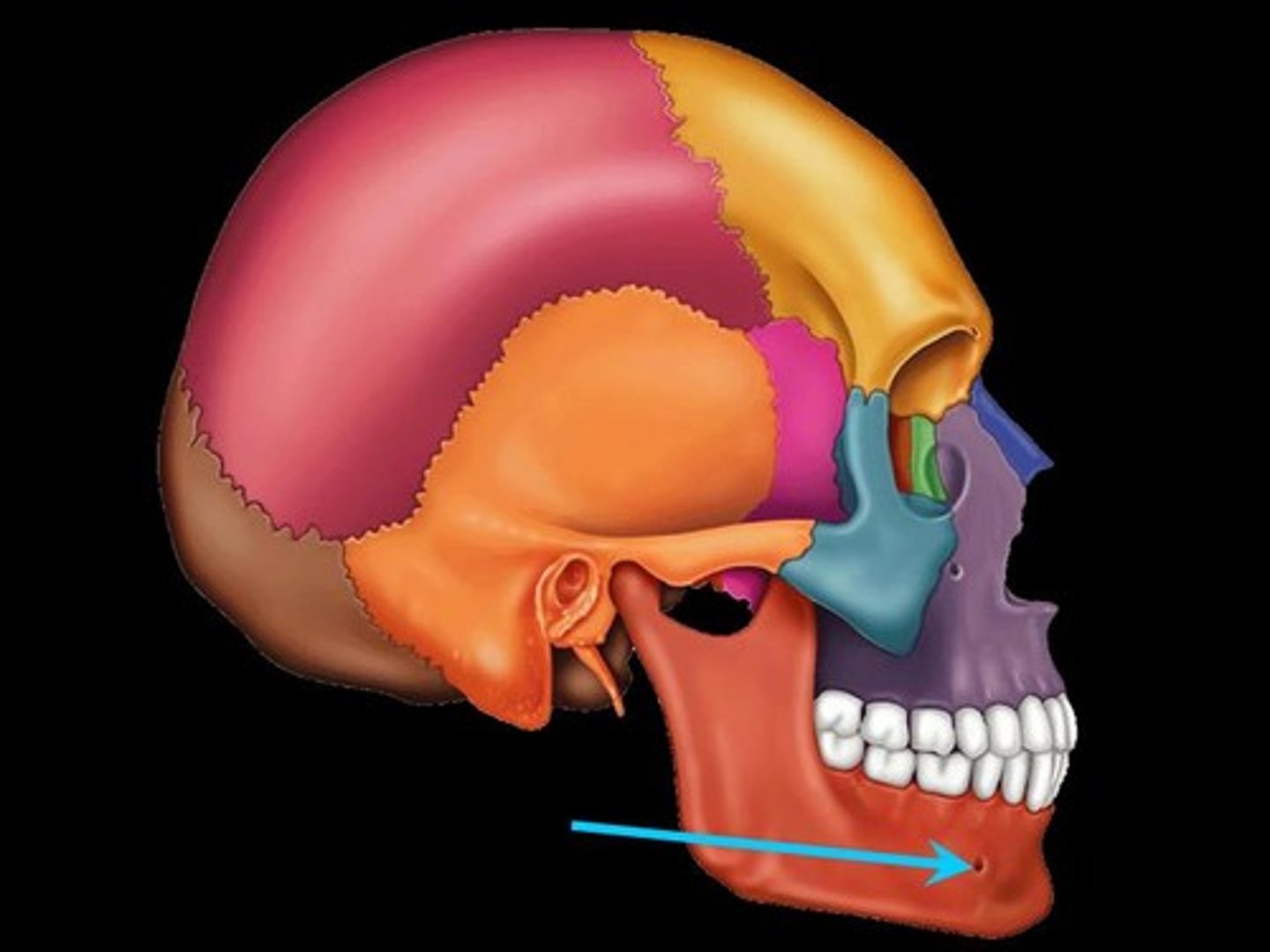
Mandibular (V3) - Mental foramen
Supraorbital notch
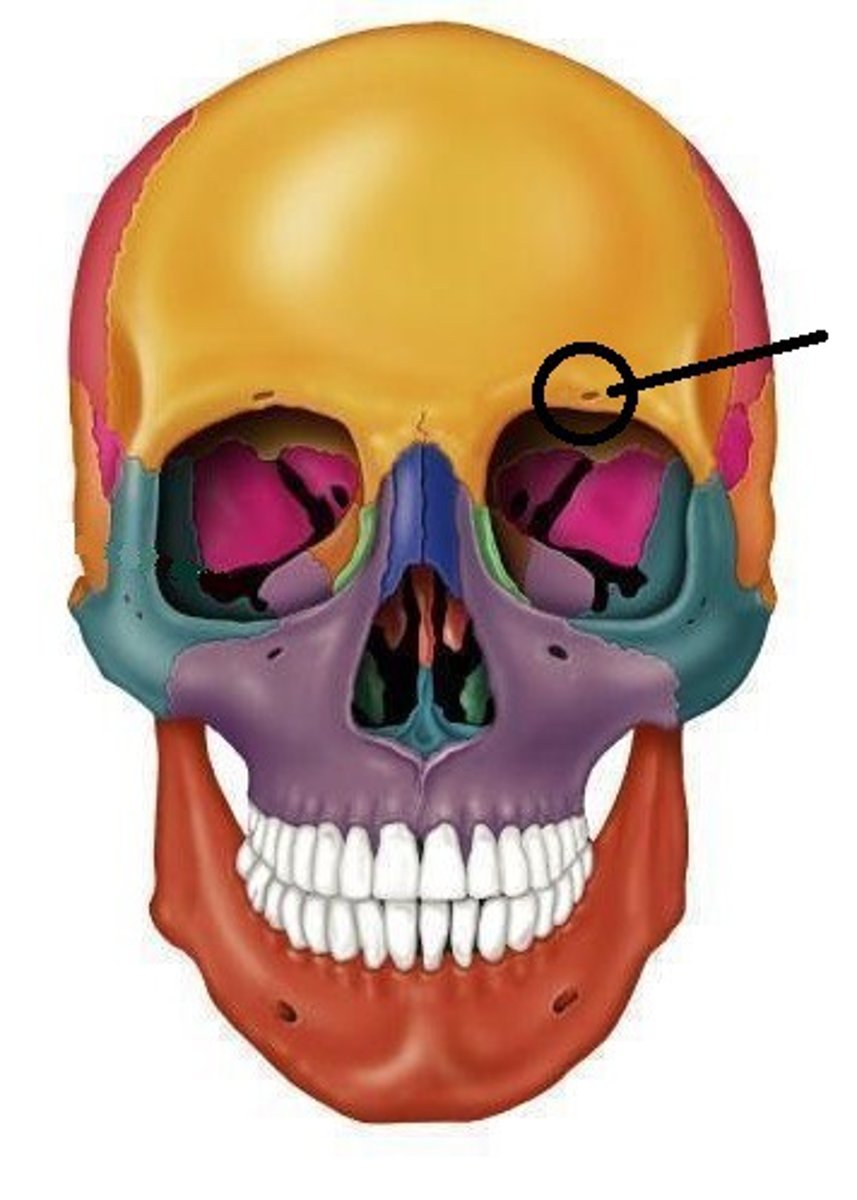
Intraorbital foramen
Mental foramen
What is the glabella?
the smooth, raised prominence between the eyebrows just above the bridge of the nose.
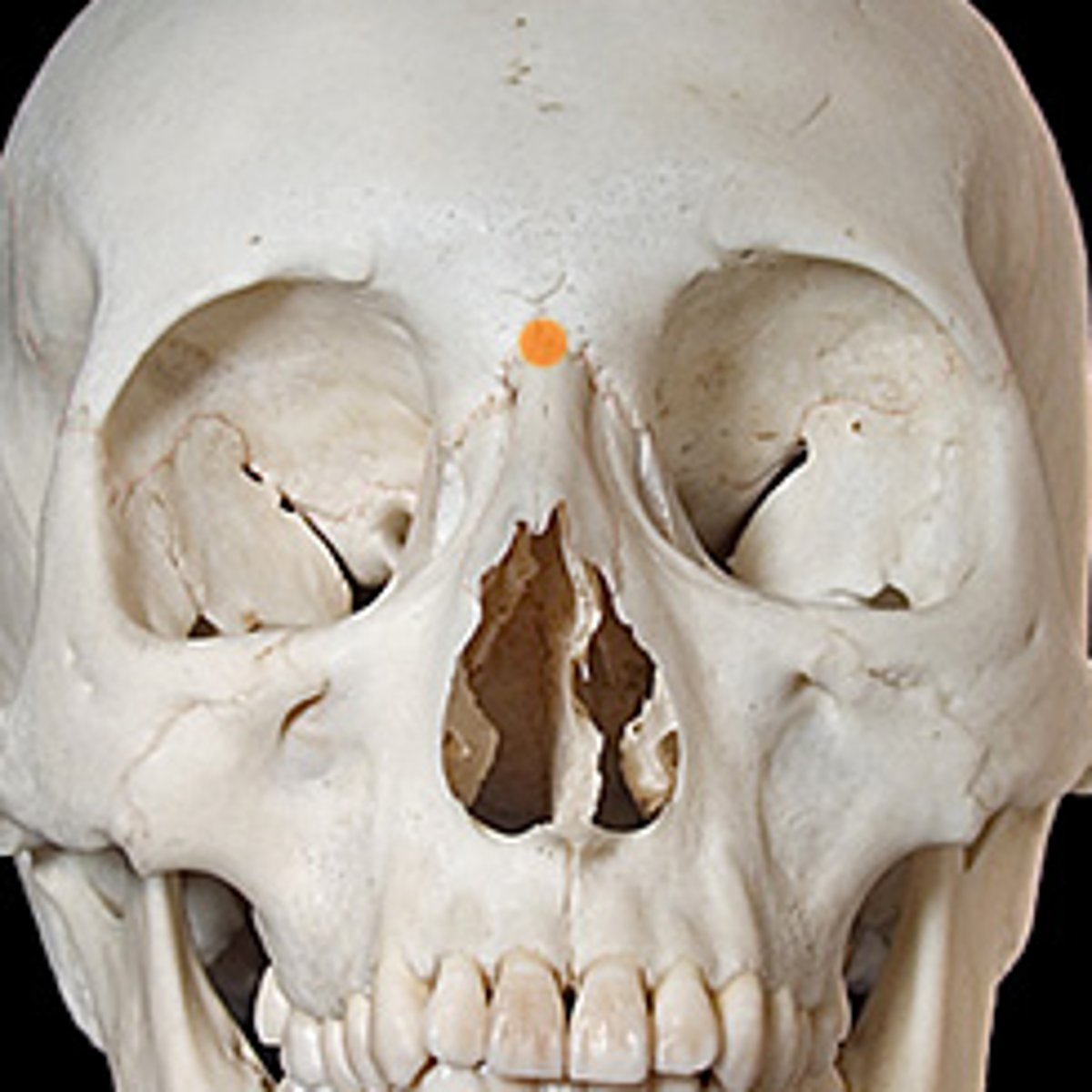
What is the nasion?
Junction between nasal bones & frontal bone
What is the orbit?
The bony cavity containing the eyeball
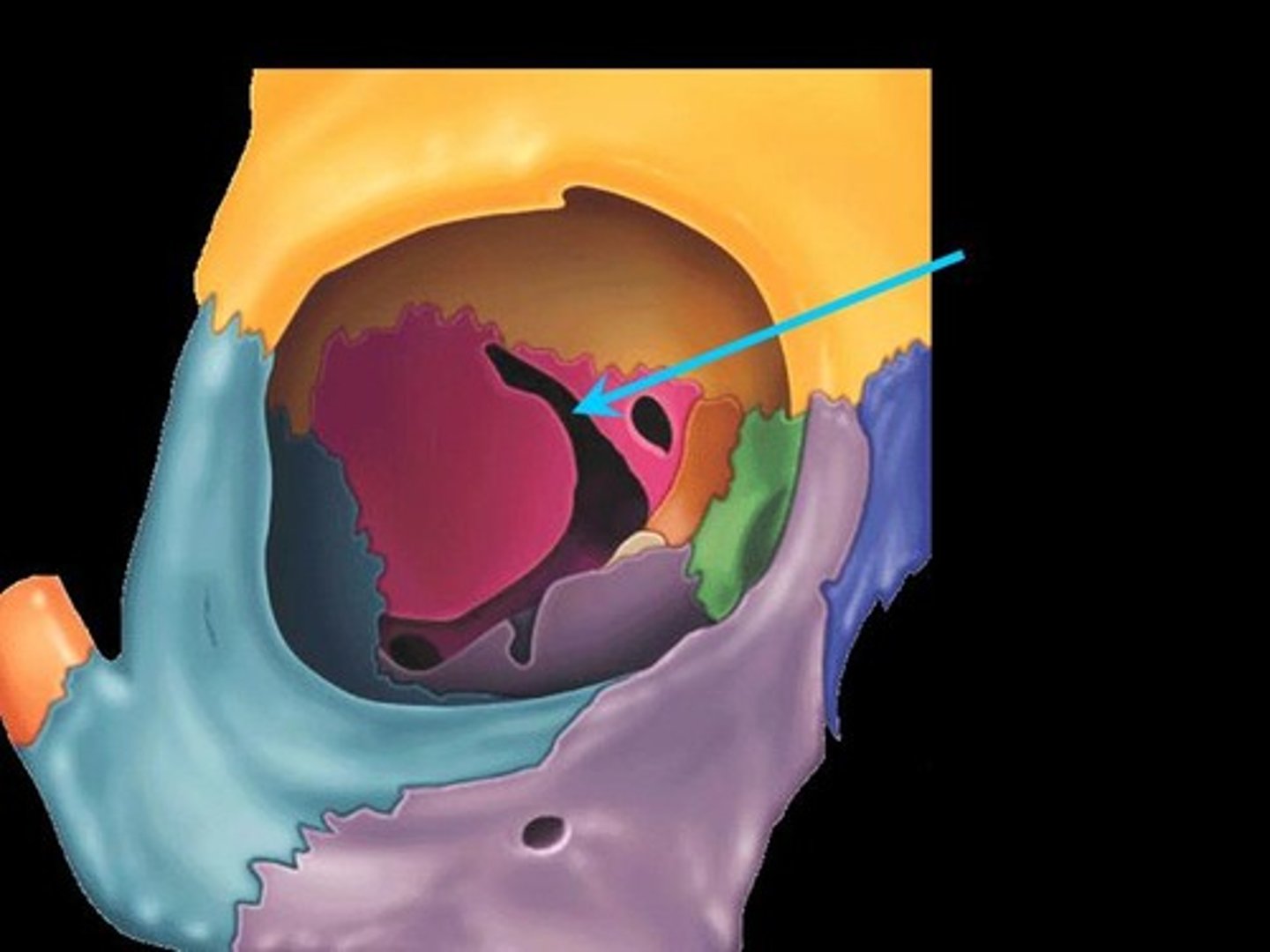
What bones make up the orbit
frontal, sphenoid (greater wing), zygomatic, maxilla, lacrimal, ethmoid, palatine
How does the orbit communicate the rest of the cranial cavity?
Via the superior orbital fissure and the inferior orbital fissure
What is the superior orbital fissure
Connects the orbit to the middle cranial fossa
What does the superior orbital fissure transmit
The nerves supplying the extra ocular muscles - Oculomotor nerve, Abducens nerve and Trochlear nerve - as well as the nerves and vessels supplying structures within the orbit - Lacrimal nerve, Frontal nerve, Nasociliar nerve and Superior ophthalmic vein
What does the inferior orbital fissure transmit
Zygomatic branch of maxillary nerve
Infraorbital nerve
Inferior ophthalmic vein
Sympathetic nerves
What does the inferior orbital fissure connect?
The orbit to the pterygopalatine fossa and from there to the infratemporal fossa
What is a craniometric point?
A landmark on the skull from which craniometric measurements can be taken. An anatomical structure used as a point of origin in locating other anatomical structure (as in surgery) or as a point from which measurements can be taken
Give examples of craniometric points
Pterion
Glabella
Nasion
Bregma
Vertex
Lambda
Inion
Asterion
What is the vertex
highest point of the skull
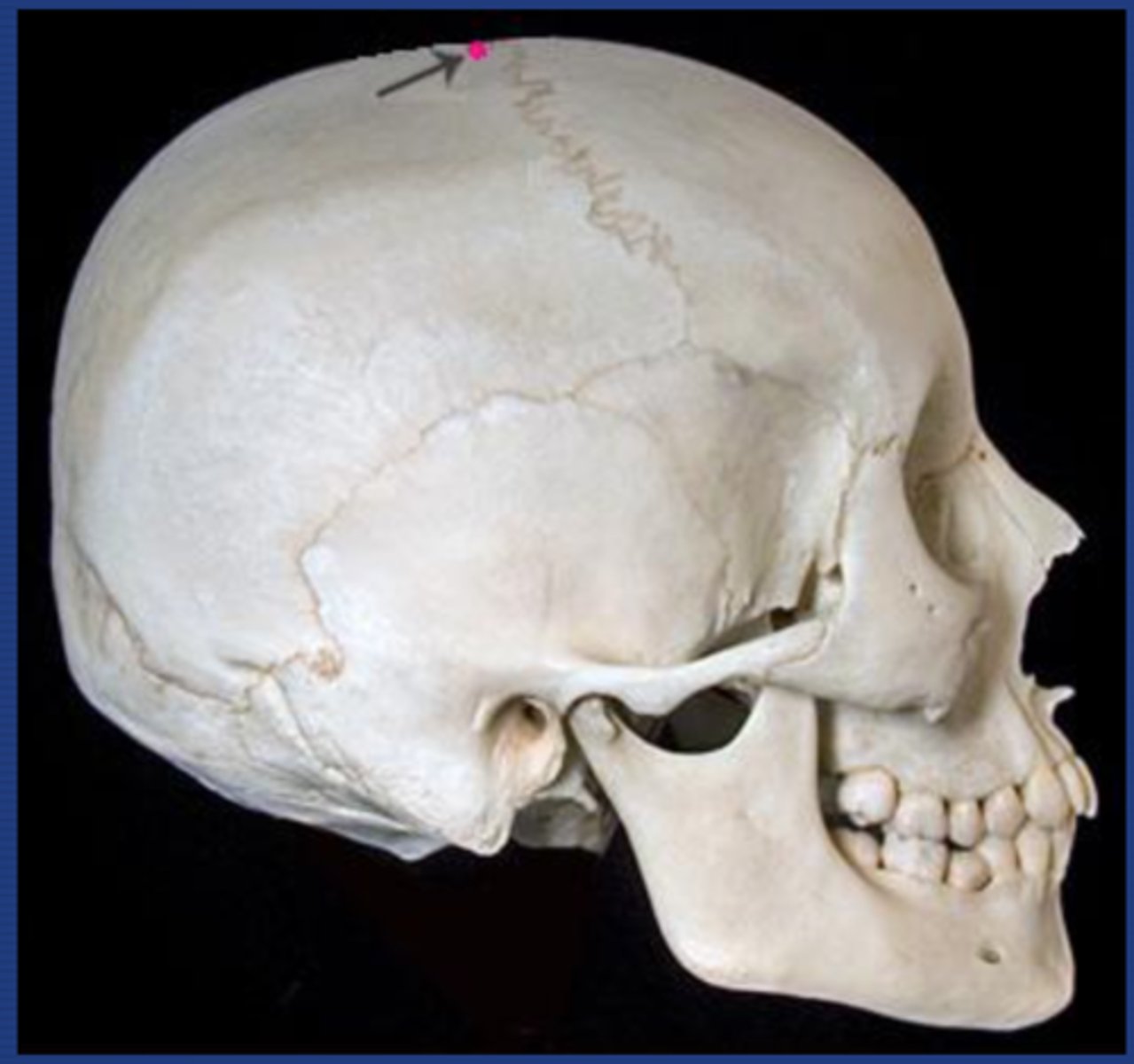
What is the bregma?
The site on the skull where the coronal suture and the sagital sutures meet....site of the anterior fontanelle.
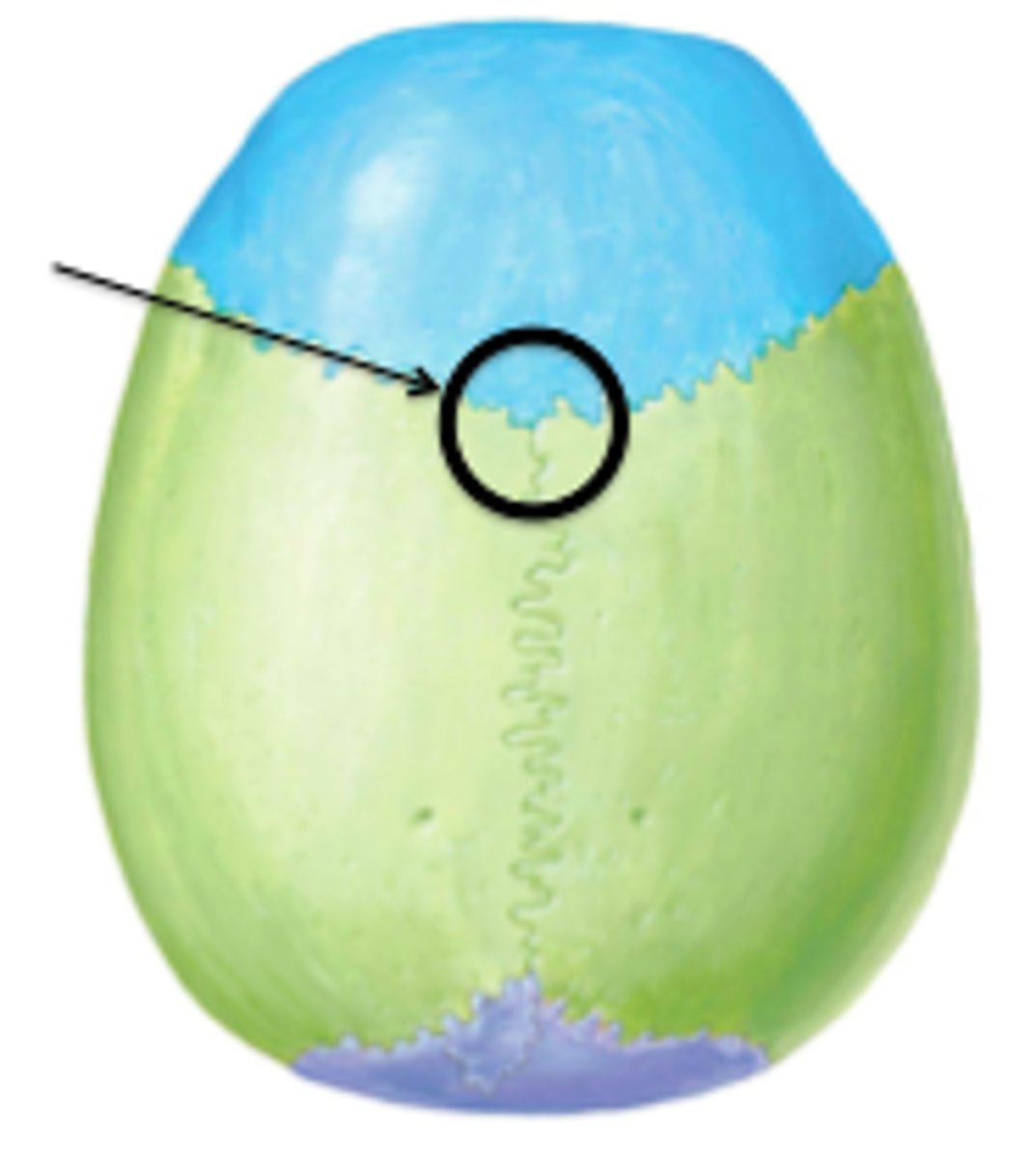

What is the lambda
junction of sagittal and lambdoidal sutures - site of fusion of posterior fontanelle