Comprehensive Study Guide: Ancient Greece Geography, History, Culture, and Legacy
1/137
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 4: Greece
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
What civilization existed in Greece from 2000-1400 BCE?
Minoan Civilization
What major event is believed to have occurred around 1200 BCE?
Trojan War
What period is referred to as the Greek Dark Ages?
1150-750 BCE
When did the first Olympic Games take place?
776 BCE
What significant invasion occurred in 520 BCE?
Persia invaded the Ionian region
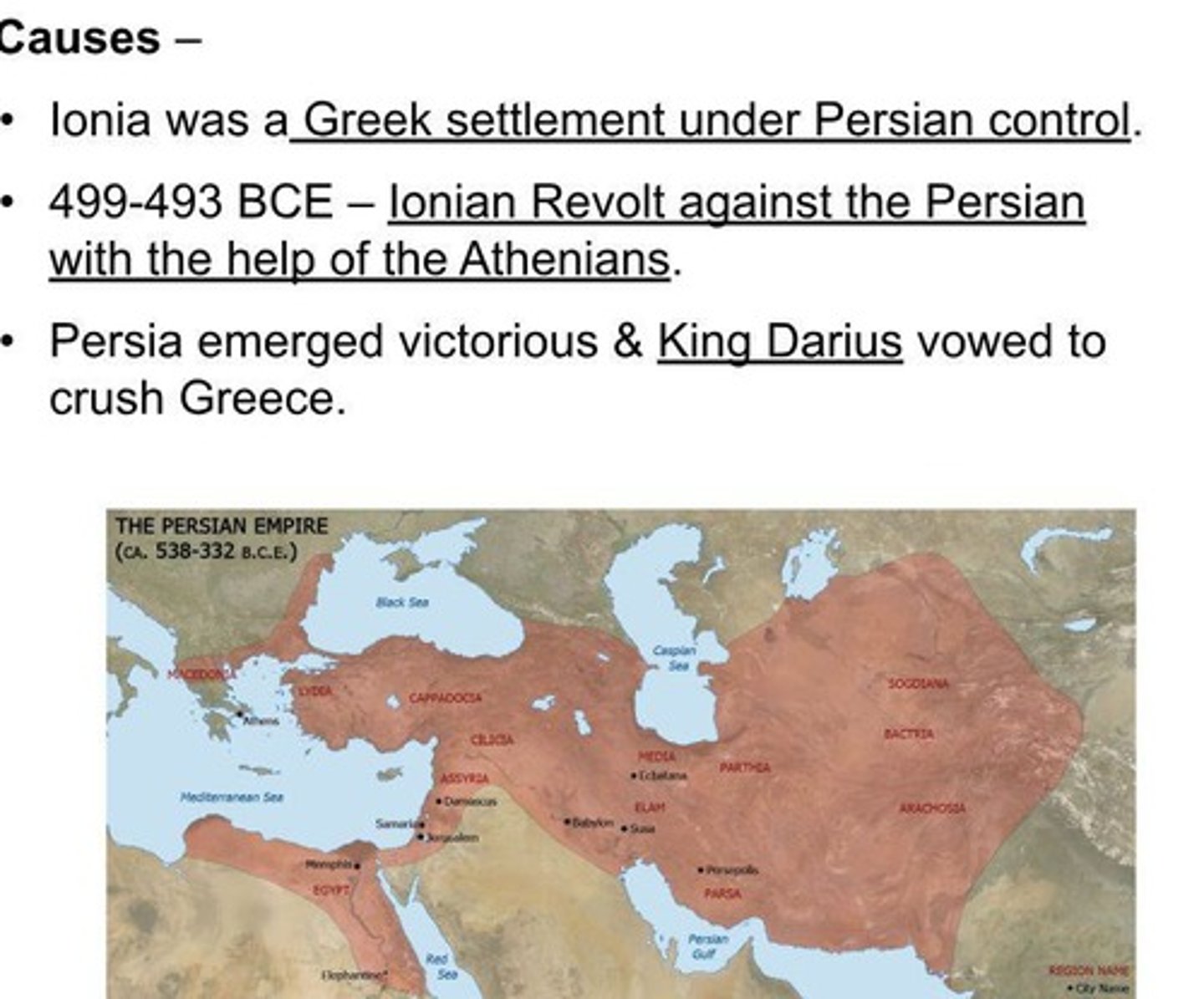
What were the Persian Wars?
Conflicts between Greece and Persia from 490-479 BCE
What is the Age of Pericles?
The Golden Age of Greece from 461-429 BCE
What major conflict occurred between 431-404 BCE?
Peloponnesian War (Sparta vs Athens)

Who invaded and defeated Greece in 338 BCE?
Philip of Macedonia
What geographical feature significantly influenced Greek agriculture?
Extremely mountainous terrain with only 20% usable farmland
Why was sea trade important for ancient Greece?
It facilitated trade and contact with other civilizations, allowing for the export of goods like wine and olive oil.
What civilization did the Mycenaeans invade around 1450 BCE?
The Minoans
What is the significance of Greek mythology?
It is based on a polytheistic religion that explains natural phenomena, human qualities, and life events.
Name two prominent Greek gods.
Zeus and Athena
What is a polis?
A Greek city-state that served as the center of government and citizens' loyalty.
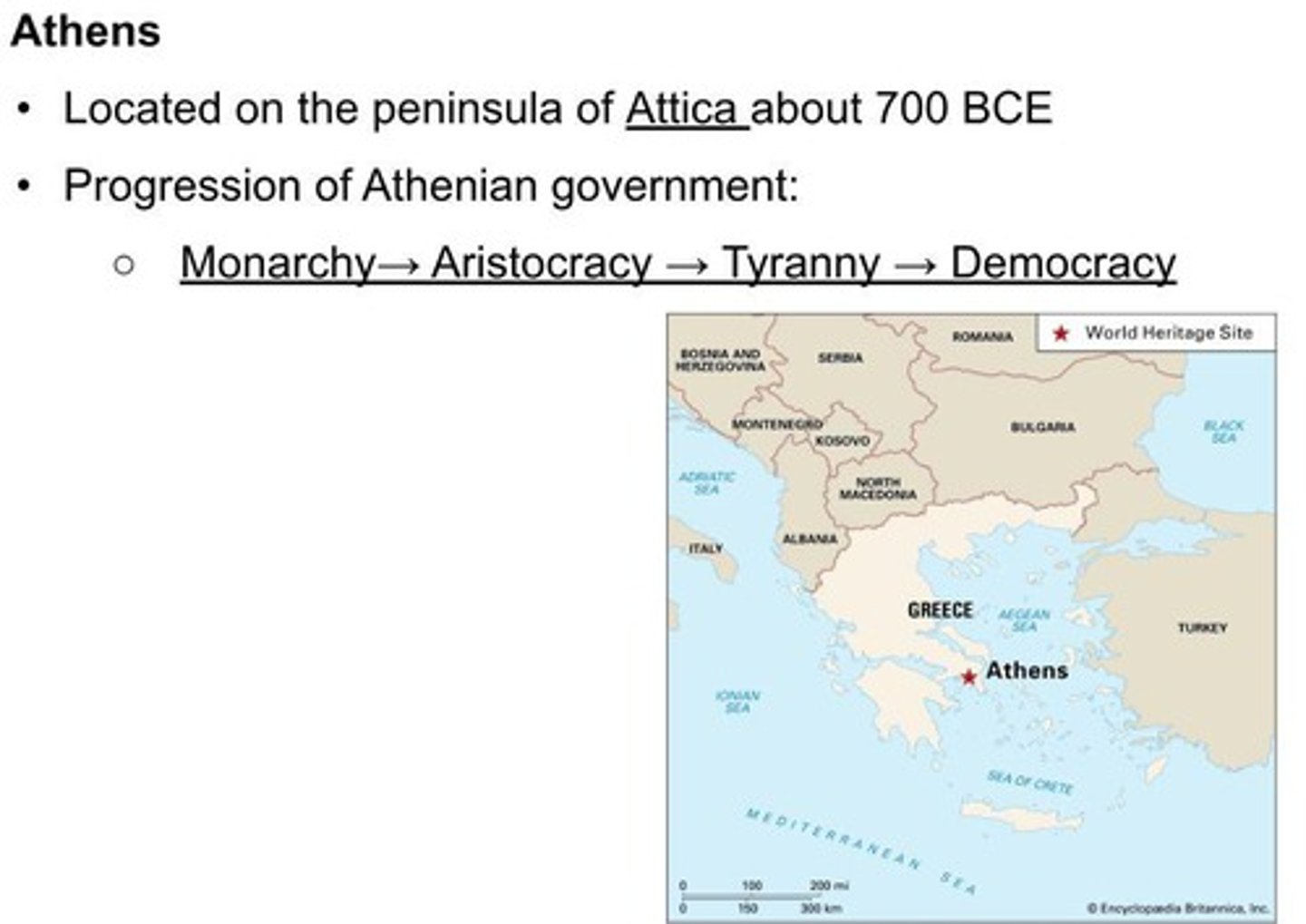
What role did the acropolis play in a polis?
It served as the center of government.
What was Draco's contribution to Athenian law?
He wrote Athens's first law code in 621 BCE.
What reforms did Solon implement in 594 BCE?
He outlawed debt slavery and legalized participation in the assembly by non-aristocrats.
What was the outcome of the growing unrest among common people in Athens?
It led to attempts by aristocrats like Cylon to seize control.
What is the difference between Hellenistic and Hellenic culture?
Hellenic refers to the classical Greek culture, while Hellenistic refers to the culture that emerged after Alexander the Great's conquests.

What are Phalerum and Piraeus known for?
They were important ports in ancient Athens.
What was the significance of the Spartan phalanx?
It was a military formation that contributed to Sparta's military success.
What was the primary reason for cultural diffusion in ancient Greece?
Trade and contact with other civilizations throughout the Mediterranean region.
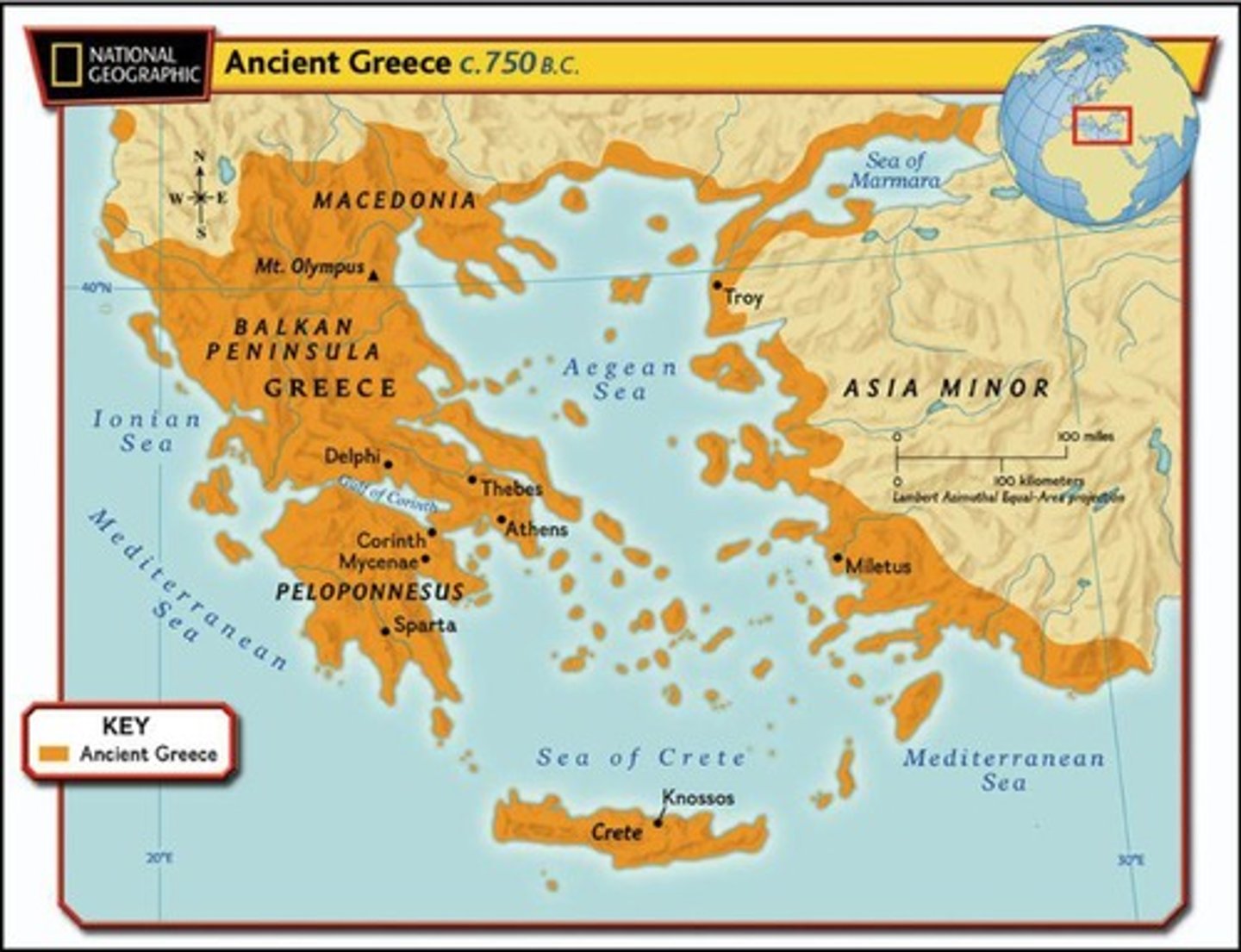
What seas bordered Ancient Greece?
The Aegean, Ionian, and Mediterranean Seas.
How did the geography of Ancient Greece influence its civilization?
The rugged mountains and deep valleys fostered the development of independent city-states (poleis) rather than a unified empire.
What were the major city-states of Ancient Greece?
Athens, Sparta, Corinth, and Thebes.
What role did the sea play in Ancient Greek civilization?
The sea facilitated trade, cultural exchange, and colonization.
What crops did the Greeks cultivate due to limited fertile land?
Wheat, barley, olives, and grapes.
What is the chronological framework of Ancient Greece?
Minoan Civilization, Mycenaean Civilization, Greek Dark Ages, Archaic Period, Classical Period, Hellenistic Period.
What characterized the Minoan Civilization?
Advanced palatial culture, frescoes, and extensive maritime trade networks.
What is the significance of the Lion Gate in Mycenaean architecture?
It symbolizes royal power and possibly religious protection, built around 1250 BCE.
What script did the Mycenaeans use?
Linear B script.
What led to the decline of the Minoan Civilization?
Natural disasters and conquest by Mycenaean Greeks around 1400 BCE.
What was the Dorian migration?
A traditional narrative of Greek-speaking people migrating into the Peloponnese after the fall of Mycenaean palaces.
What was the Greek Dark Ages?
A period from c. 1100 to 800 BCE marked by a decline in literacy, population, and monumental building.
What key reforms did Solon implement in Athens?
He abolished debt slavery and created the Council of 400.

Who reorganized the citizen body in Athens into ten tribes?
Cleisthenes in 508 BCE.
What is the significance of the Archaic Period in Greek history?
It saw the rise of city-states, colonization, and the development of the alphabet.
What major wars occurred during the Classical Period?
The Persian Wars and the Peloponnesian Wars.
What was the Golden Age of Athens?
A period of great achievements in arts and sciences during the Classical Period.

What characterized the Hellenistic Period?
Alexander the Great's conquests and the spread of Greek culture.
What is the significance of the frescoes in Minoan palaces?
They depict religious rituals, nature, and daily life, showcasing artistic sophistication.
What were tholos tombs?
Beehive-shaped burial chambers built by the Mycenaeans.
What was the role of oral tradition during the Greek Dark Ages?
It preserved epic poetry and cultural knowledge despite the decline in literacy.
What was the impact of the natural disasters on the Minoans?
It contributed to the decline of the Minoan civilization.
What was the social structure of Mycenaean society?
A hierarchical system with a warrior aristocracy ruling over farmers and artisans.
What is the significance of the Mask of Agamemnon?
It is a famous gold artifact associated with Mycenaean burial practices.
What were the main features of Minoan architecture?
Multi-storied palaces with elaborate plumbing, storage magazines, and open courtyards.
What was the primary form of government in Athens before democracy?
Monarchy, followed by aristocracy and tyranny.
What was the cultural significance of the Greek city-states?
They were centers of political, social, and cultural development in Ancient Greece.
What epic poems recount the legends of the Trojan War?
Homer's Iliad and Odyssey

What significant event marked the beginning of the Greek Dark Ages?
The destruction or abandonment of Mycenaean palatial centers around 1100 BCE
What are some debated causes for the onset of the Greek Dark Ages?
Internal strife, invasions, and broader regional upheavals
Who are the Dorians and what is their significance in Greek history?
The Dorians were a Greek-speaking people believed to have migrated into the Peloponnese after the fall of Mycenaean palaces; their migration is now considered more myth than fact.
What characterized the Greek Dark Ages (c. 1100 to 800 BCE)?
A decline in literacy, population, and monumental building, but also the development of iron technology and preservation of epic poetry.
What were the key reforms introduced by Solon in Athens?
Abolished debt slavery and created the Council of 400.
Who reorganized the citizen body of Athens into ten tribes?
Cleisthenes in 508 BCE.
What was the role of Pericles in Athenian democracy?
Expanded democratic participation and led Athens during its Golden Age.
How was Athenian society structured?
Divided into citizens (adult males with political rights), metics (resident foreigners), and slaves.
What was the economic foundation of Athens?
Based on agriculture, trade, and craftsmanship, with the port of Piraeus as a major commercial hub.
What subjects were emphasized in Athenian education?
Arts, rhetoric, philosophy, and physical fitness.
What type of government did Sparta have?
A militaristic oligarchy ruled by two kings, a council of elders (Gerousia), and five annually elected ephors.

What were the three classes of Spartan society?
Spartiates (full citizens and soldiers), Perioikoi (free non-citizens), and Helots (state-owned serfs).

What was the agoge in Sparta?
A rigorous military training program that boys entered at age seven.

What was the core military formation of the Spartan army?
The hoplite phalanx.
What were the strengths and weaknesses of Sparta?
Strengths included military prowess and stability; weaknesses included a rigid social structure and neglect of arts.
What are the four main types of government in Ancient Greece?
Monarchy, Oligarchy, Tyranny, and Democracy.

What defines Athenian democracy?
Direct participation of all male citizens over 18 in decision-making through the assembly (Ekklesia).
What was the significance of the Greco-Persian Wars?
Preserved Greek independence and enabled the flourishing of classical culture.
What sparked the Trojan War according to legend?
The abduction of Helen by Paris.
REMOVE
REMOVE
What were the major battles of the Greco-Persian Wars?
Marathon, Thermopylae, Salamis, and Plataea.
What was the outcome of the Peloponnesian War?
Rivalry between Athens and Sparta led to Athens' defeat and the decline of its power.
What was the Peace of Nicias?
A temporary truce during the Peloponnesian War that was soon broken.
What was the Sicilian Expedition?
A disastrous Athenian military campaign during the Peloponnesian War.
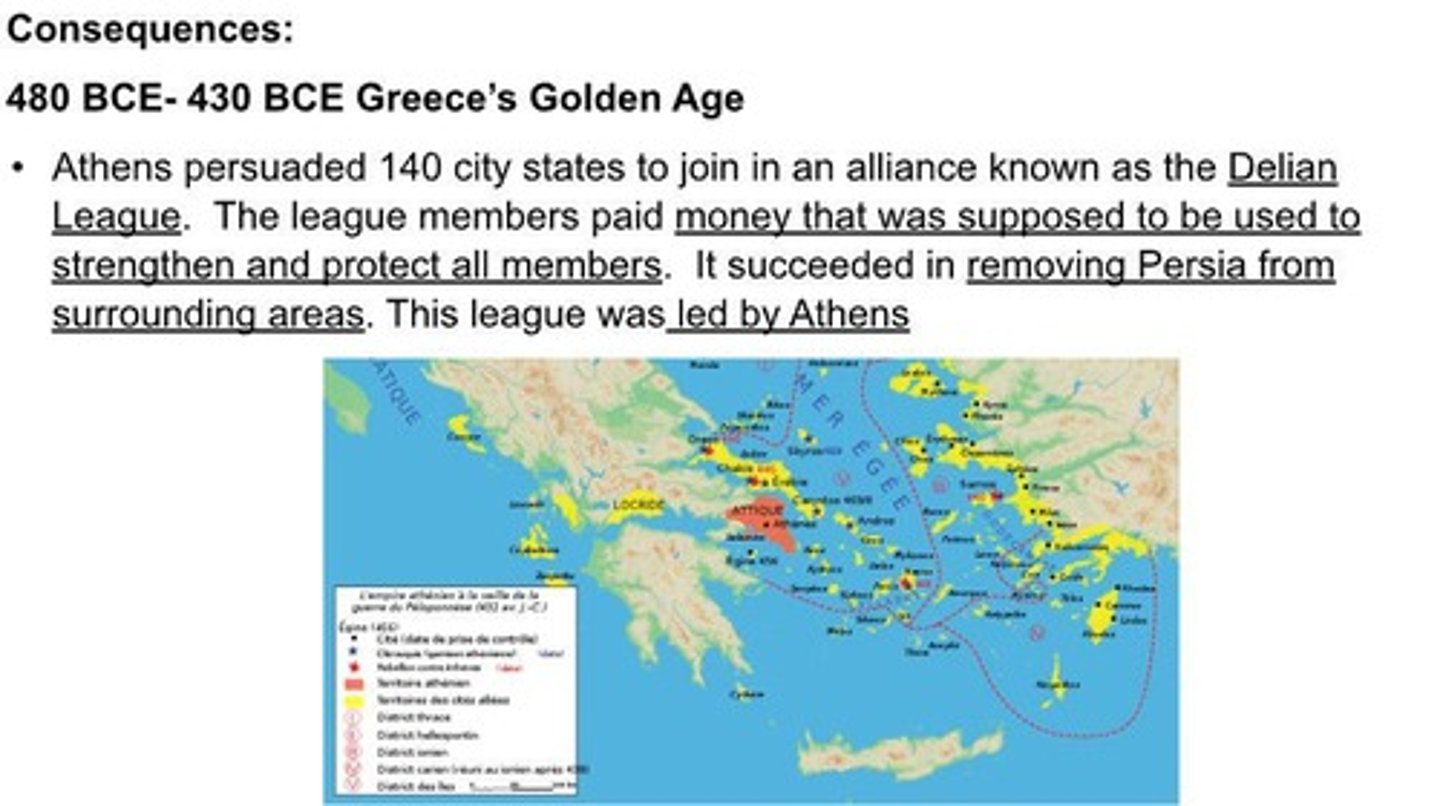
What role did the Delian League play after the Greco-Persian Wars?
It was a defensive alliance led by Athens formed to protect against future Persian threats.
What marked the Ionian/Decelean War?
Persian support for Sparta, Athenian naval defeats, and eventual surrender of Athens from 413 to 404 BCE.
When was the Delian League established?
The Delian League was established in 478 BCE.
What was the primary aim of the Delian League?
To defend against Persian aggression and liberate Greek cities under Persian control.
Where was the Delian League's treasury initially located?
On the sacred island of Delos.
What contributions did member states make to the Delian League?
Member states contributed ships or monetary tribute (phoros).
How did Athens emerge as the dominant power in the Delian League?
Due to its naval supremacy.
What significant military operations did the Delian League achieve under Athenian leadership?
Expulsion of Persian forces from the Aegean, capture of Eion, conquest of Scyros, and victory at the Battle of Eurymedon.
What transformation occurred in the Delian League over time?
Athens centralized control, moved the treasury to Athens, and used League funds for its own projects.
What led to the dissolution of the Delian League?
The League was dissolved after Athens' defeat in 404 BCE.
What was the significance of the Delian League?
It demonstrated the potential and challenges of collective defense and the dangers of hegemonic dominance within alliances.
What were hoplites?
Heavily armed citizen-soldiers in ancient Greece.
What is a phalanx?
A dense, rectangular formation of hoplites with overlapping shields and projecting spears.
What was the Spartan military system known for?
Maintaining a professional standing army with lifelong service and rigorous training.
What is a trireme?
A fast, agile warship with three rows of oars on each side, crucial for naval warfare.
What naval tactics were used in ancient Greek warfare?
Tactics included periplous (flanking) and diekplous (breaking through enemy lines).
Who was Pericles?
A leader during Athens' Golden Age, known for expanding democracy and promoting the arts.
What major architectural achievement is associated with Pericles?
The construction of the Parthenon between 447 and 432 BCE.

What were the three major genres of Greek drama?
Tragedy, comedy, and satyr plays.

Who were the major playwrights of Greek tragedy?
Aeschylus, Sophocles, and Euripides.
What is the Hippocratic Oath?
An ethical standard for physicians established by Hippocrates, emphasizing confidentiality and non-maleficence.
What are the three orders of Greek columns?
Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian.
What characterizes Doric columns?
Simple, sturdy columns without bases and plain capitals.
What distinguishes Ionic columns?
Slender columns with bases and scroll-shaped capitals.
What features define Corinthian columns?
Ornate capitals with acanthus leaves and slender proportions.