2.1 Utility
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is Behavioural Economics
A method of economical analysis the applies psychological insights into human behaviour to explain economic decision-making
What is rationality
A decision making process that is based on making choices that result in the optimal benefit or maximum utility for an individual
What is utility
Satisfaction / Economic welfare that a consumer gains from consuming a good/ service
What are the assumptions of rational behaviour
A consumer has fixed and consistent preferences
Consumers choose independently irrespective of someone else’s preferences
They gather all the information on all alternative choices
Make an optimal choice based off of this
What is bounded rationality
Refers to the idea that people make decisions within the limits of their cognitive abilities (Individuals have limited info and resources to make a decision so they make an educated guess / use heuristics to make a decision
What is bounded self control
Refers to the idea that people posses a limited willpower when making a decision
Resisting temptations for example
Describe the differences between system 1 and system 2 thinking
System 1 is fast and system 2 is slow
System 1 is conscious, 2 is conscious
System 1 is automatic, 2 takes effort
System 1 is everyday decisions, 2 is complex decisions
System 1 is prone to making wrong decisions while 2 reliable
What does marginal mean
What does marginal utility mean
Additional
Additional satisfaction from consuming one more unit
What is the marginal utility theory
The marginal utility theory examines the increase in satisfaction consumers gain from the last unit of a good
What is the point of satiation
When marginal utility = 0 (any more units consumed will decrease utility)
What is the utility maximisation theory
That individuals and organisations seek to attain the highest level of utility/ satisfaction from their economic decisions
A consumer will consume a good up until marginal utility is equal to price/ cost for the consumer.
What are the utility maximisation constraints
Limited income- consumers cannot purchase all the goods they need to maximise utility
Limited time available
Irrational behaviour - Buying goods and later regretting it
Loyalty - Loyalty to local shops rather than buying from a supermarket but for cheaper
Sense of morality / religion - not eating meat, not eating avocado
Utility and price relationship diagram
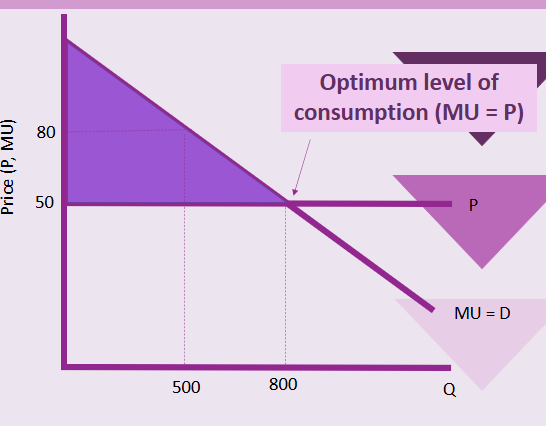
What is consumer surplus
The additional amount over the price of which the consumer would be willing to pay for the good (highlighted in purple on diagram)
Give a comparison of how the marginal utility curve operates
The marginal utility is derived from the demand curve - a rise in fashion would lead to the marginal utility curve shifting to the right
If marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost / marginal cost exceeds marginal benefit what the effect on total utility
Total utility is increased/ Total utility is decreased
What is Adam Smith’s “The Paradox of Value”
Though water is more useful than diamonds in terms of survival but diamonds commands a higher price in the market
What is asymmetric information
A form of imperfect information
One side of the deal knows more than the other - usually the seller but it can be either
Example: Someone sells an antique but it’s actually from 1237 buyer knows this and gets it at a lower price
What is a merit good
A positive consumption externality
What is a demerit good
A negative consumption externality
What is the rule of thumb - heuristic
Consumers follow rule of thumb to make satisficing decisions