Atomic Theory, Structure, and Chemical Formulas for Chemistry Students
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Dalton's Atomic Theory
All matter consists of atoms; tiny indivisible particles of an element that cannot be created or destroyed.
The Law of Conservation of Mass
Matter cannot be created or destroyed.
The Law of Constant Composition
A specific compound is composed of the same elements in the same mass fractions.
The Law of Multiple Proportions
If elements A and B react to form two compounds, the different masses of B that combine with a fixed mass of A can be expressed as a ratio of small whole numbers.
Atomic Structure
The nucleus consists of protons and neutrons.
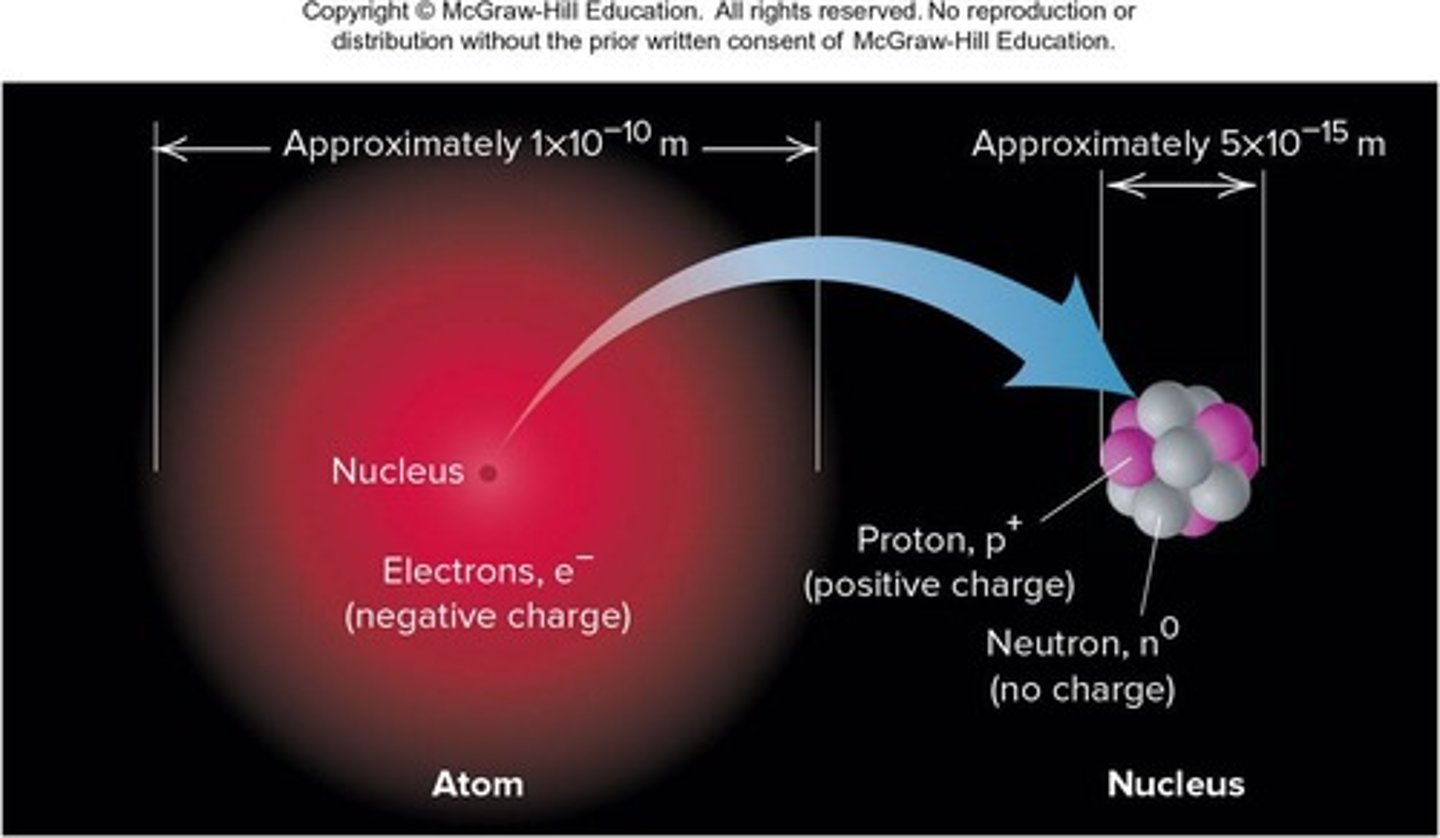
Mass Contribution of the Nucleus
The nucleus contributes 99.97% of the atom's mass but occupies only about 1 quadrillionth of its volume.
Nucleus Diameter
The nucleus diameter is about 20,000 times smaller than the diameter of the atom.
Atomic Number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is its atomic number (Z).
Defining Trait of an Element
The atomic number determines the identity of the atom.
Coulomb (C)
The SI unit of charge.
Atomic Mass Unit (amu)
The atomic mass unit equals 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
Mass Fraction
The ratio of the mass of a component to the total mass of the mixture.
Percent by Mass
The mass fraction multiplied by 100.
Neutral Atom
A neutral atom means that the total (+) charge = total (-) charge; the # of p+ = the # of e-.
Atomic Number (Z)
Indicates the # of e-.
Periodic Table
An organized, classification scheme for every known element in the universe, arranged in increasing atomic number (Z) order.
Groups
Vertical columns in the periodic table that contain a 'family' of elements; elements in groups are the most chemically similar.
Periods
Horizontal rows in the periodic table that display a predictable repeating pattern of chemical properties.
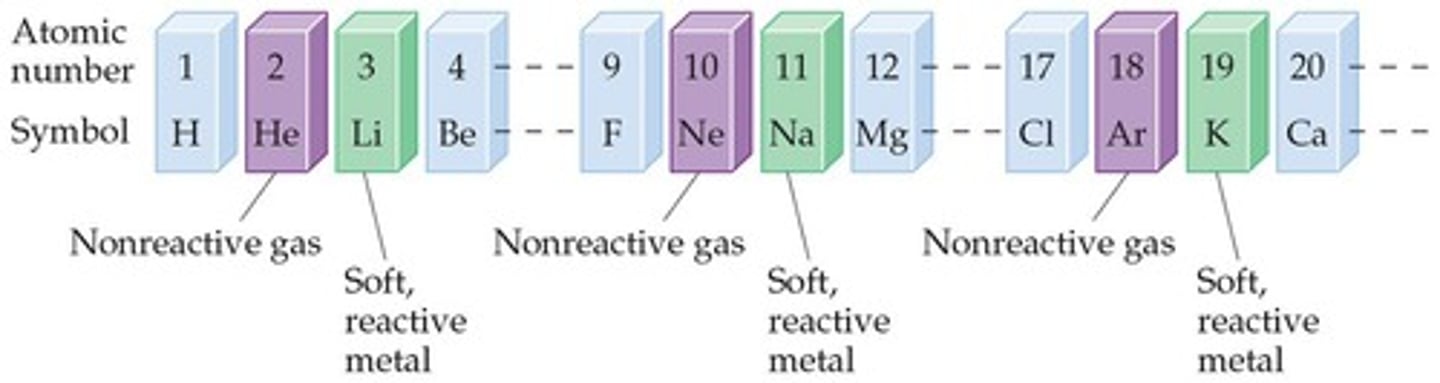
Alkali Metals
Group 1A elements (except H).
Alkaline Earth Metals
Group 2A elements.
Halogens
Group 7A elements.
Noble Gases
Group 8A elements.
Mass Number (A)
# of p+ + # of n0.
Atomic Symbol (X)
Element symbol from the periodic table.
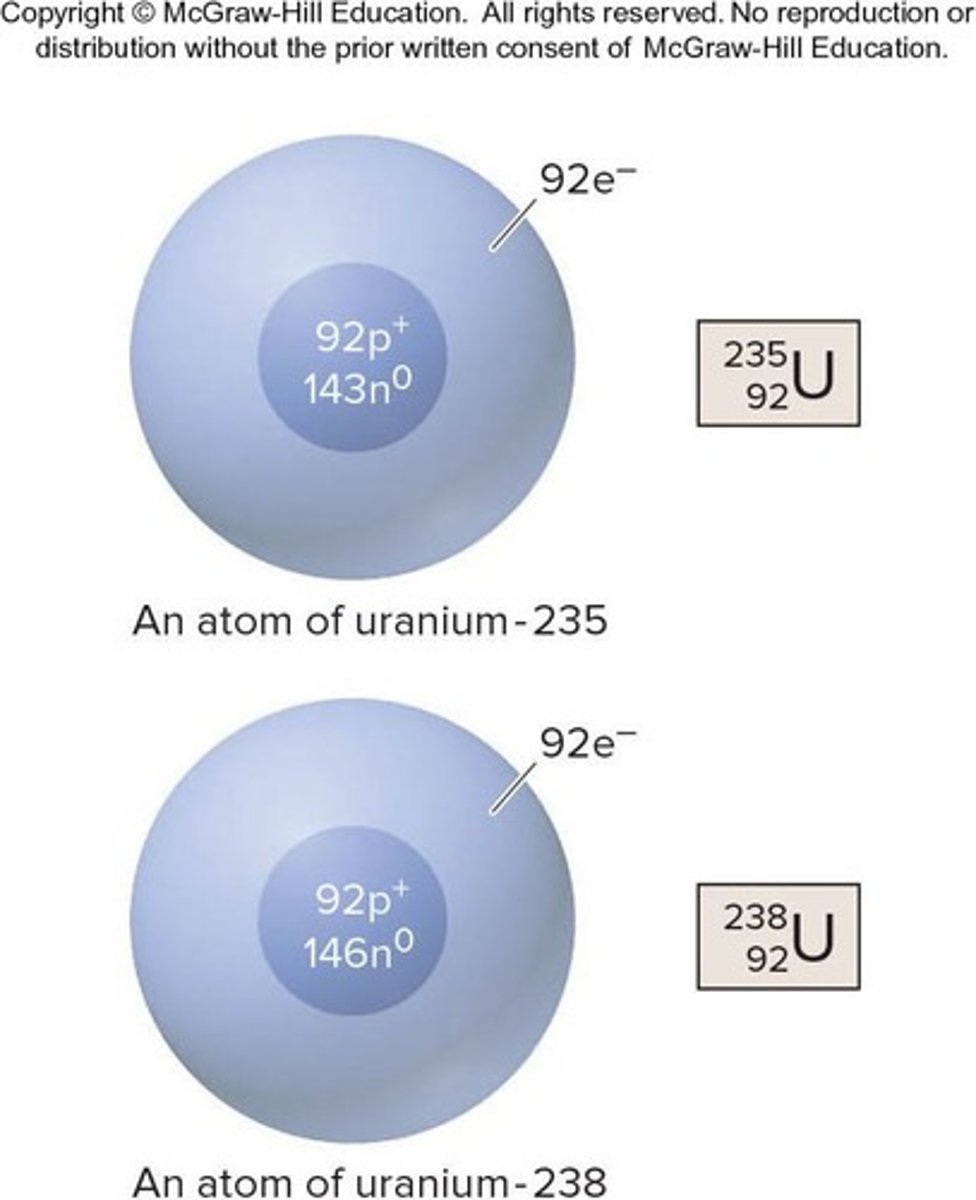
Isotopes
Atoms that have the same # of p+ but a different # of n0; they have the same atomic number (Z) but a different mass number (A).
Ion
An atom (or molecule) that has lost or gained one or more electrons.
Cation
A positively charged ion.
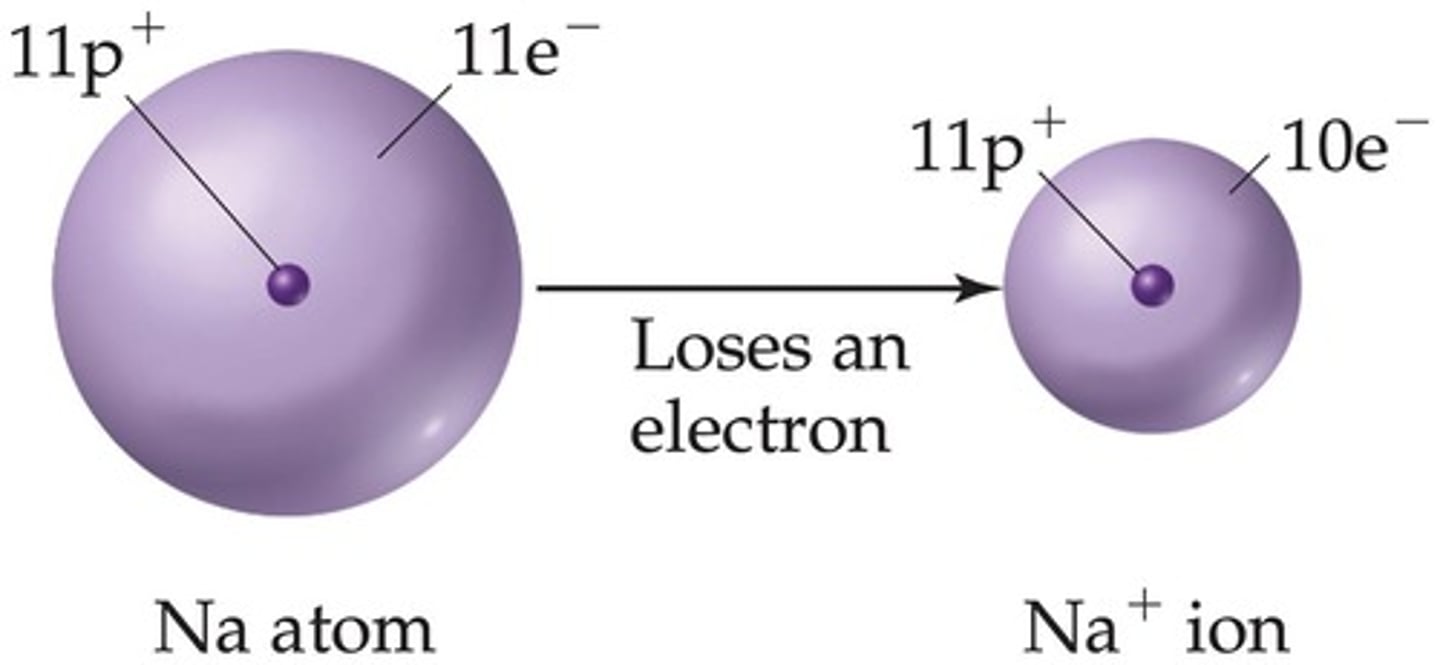
Anion
A negatively charged ion.
Atomic Mass
The atomic mass (in amu) of a single atom is approximately equal to its Mass Number (A).
Weighted Average of Atomic Mass
The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of all the masses of isotopes present in a natural sample.
Fractional Abundance
The percentage of a specific isotope present in a sample, used to calculate atomic mass.
Calculation of Atomic Mass
Average mass = (fractional abundance × isotopic mass) summed for all isotopes.
Molecular Formula
A molecular formula indicates the actual numbers of atoms of each element in a molecule of the compound.
Empirical Formula
An empirical formula indicates the smallest whole-number ratio of the number of atoms (or ions) in the compound.
Avogadro's Number
1 mol = 6.022 x 10^23 entities, which is the amount of a substance that contains the same number of entities as there are atoms in exactly 12 g of carbon-12.
Mole
The amount of a substance that contains the same number of entities as there are atoms in exactly 12 g of carbon-12.
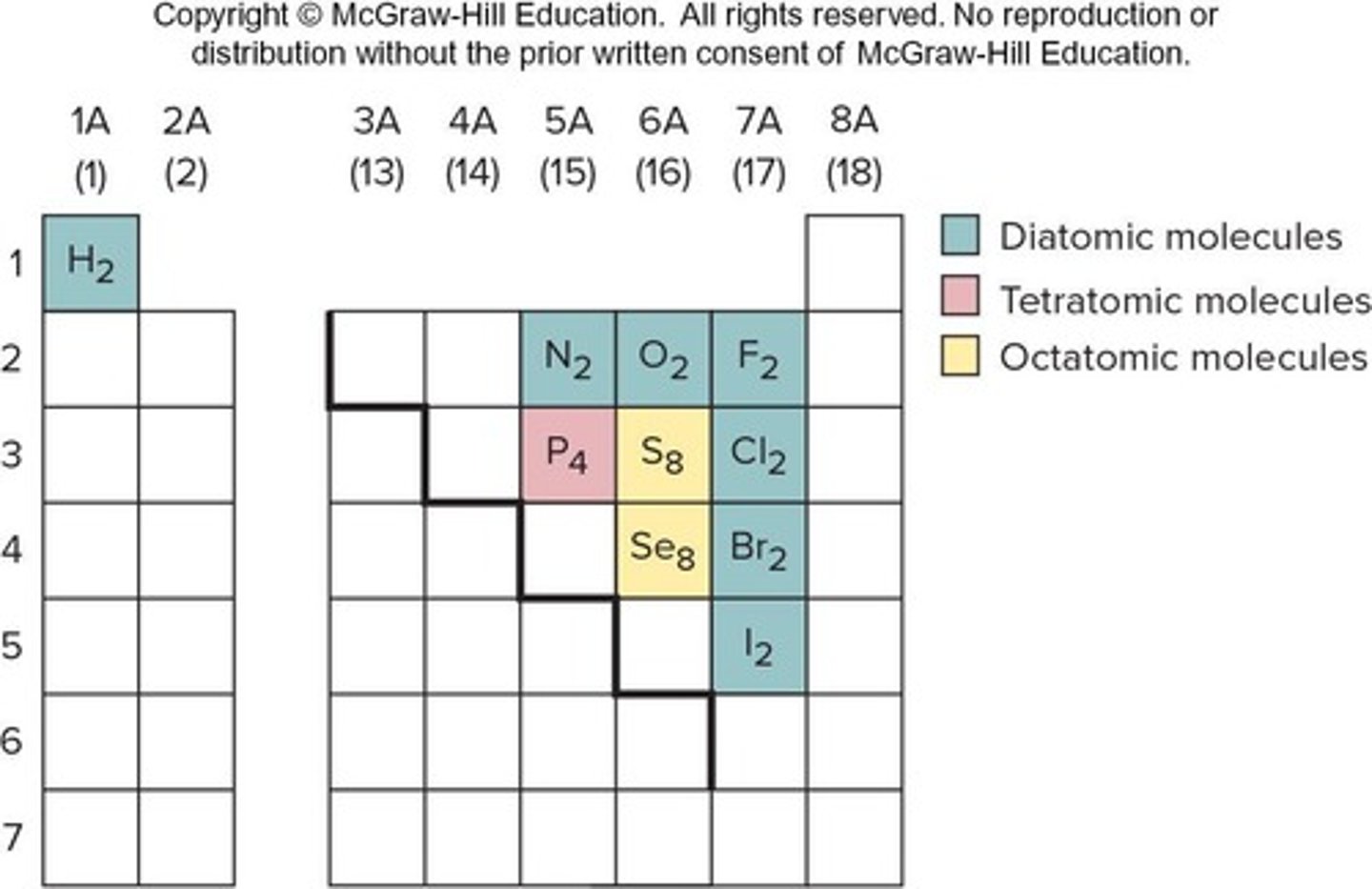
Diatomic Elements
There are seven diatomic elements: H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, & I2.