Chem exam #4
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Endothermic vs. Exothermic processes
Endothermic: absorbs heat (melting, evaporation, Boiling water)
Exothermic: releases heat (condensation, combustion, Burning wood or paper Candle burning)'
Formula for internal energy change (ΔE)
The formula for internal energy change (ΔE) is ΔE = q + W, where q represents the heat added to the system and W is the work done on the system.
When energy is entering the sytem ΔE is what
greater than zero
ΔE surroudings
heat gained by surroundings (positive)
When energy is leaving the system ΔE is what
less than zero
ΔE system
heat released by system (negative)
Equation for when Heat absorbed/released by a substance
q = m · Cs · ΔT
◦ m = mass (g), Cs = specific heat, ΔT = Tfinal – Tinitial.
Thermal equilibrium principle
q of the heat lost + q heat gained = 0
lost = higher inital temp
gained = lower inital temp
Diamagnetic vs. Paramagnetic
Diamagnetic: all electrons paired (Zn, Cd²⁺).
Paramagnetic: unpaired electrons (Fe²⁺, Cu²⁺).
How to find atomic radius
left —> right decreases
top —> bottom increases
How to find ionic radius
less protons = higher ionic radius
more protons = lower ionic radius
How to find metallic character
left —> right decreases
top —> bottom increases
Node definition
point where there is no probability of finding an electron
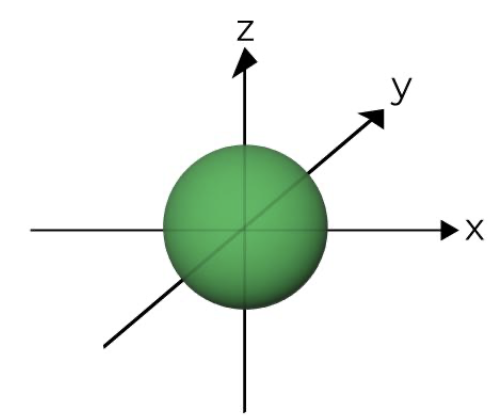
S orbital (holds 2 electrons)
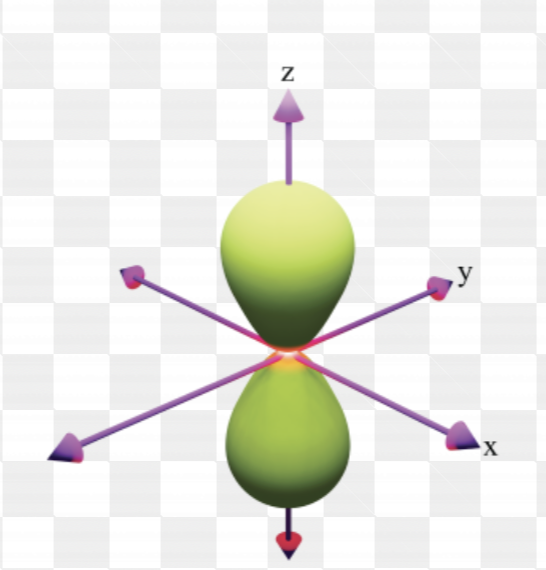
p orbital (holds 6 electrons)
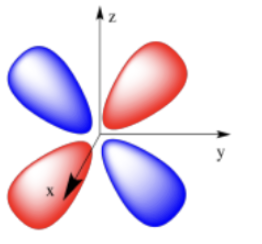
d orbital (holds 10 electrons)
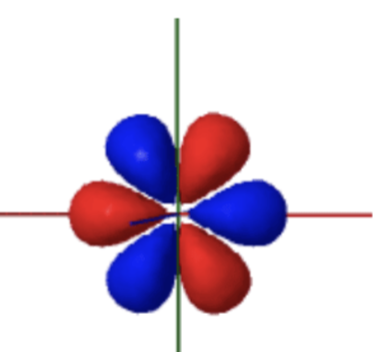
f orbital (holds 14 electrons)
Bomb calorimeter equation
qcal = Ccal · ΔT which gives you Qrxn
convert mass of compound to mol
use ΔErxn = qrxn / mol compound.
What does Hess’s Law say?
You can add or subtract known reactions to get a new one, and add/subtract their heats (ΔH) the same way.
Photon energy equation
E = (hc)/λ
◦ Use for wavelength/energy conversions.
◦ h = Planck’s constant, c = speed of light.
Energy per mole of photons
Multiply E (per photon) × Avogadro’s number (6.022 × 10²³).