THE CIRCULAR FLOW MODEL | MICRO
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
FOUR SECTORS IN THE ECONOMY
Government Sector
Business Sector
Household
Foreign Sector
Roles of the Government Sector
Provide the legal and social framework,
Maintain competition,
Provide public goods and services,
National defense,
Income and social welfare,
Correct for externalities and stabilize the economy.
Roles of the Business Sector
The blank represents the producers of goods and services in the economy. They may be proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations. To produce goods and services, they buy inputs in factor markets. Then, they sell output in the goods market to earn income.
Roles of the Household Sector
Supplying inputs to business
blank supply inputs to the business sector in factor markets. They provide labor as an input in the production process. They may work as blue-collar workers and do manual work like in a factory. Or, they work as white-collar workers to do professional, managerial, or administrative work. They receive salaries, wages, and other benefits such as insurance and pensions.
Consumers for goods and services
blank act as consumers in the product market. They buy goods and services from the business sector using their supply inputs’ money. And the money they spend flows into the business sector as income.
As consumers, households play a strategic role in driving the economy. Their money contributes significantly to aggregate demand (measured by GDP), usually exceeding spending by the business, government, and external sectors.
Roles of Foreign Sector
The blank is when a country cannot satisfy their needs effectively between the closed
economy: households, businesses, and the government. Countries then convert to an open
economy to satisfy their needs effectively. To solve the problem that the country is having they
have to trade with other countries to gain a strong economy so that they will be able to satisfy the needs of their people.
When countries trade, they do not have to rely solely on their own resources because they can sell it and gain other resources form the different countries. Some countries may not have good access to resources so they will not be able to use the foreign sector effectively.
Relationship of the Business Sector and Household Sector
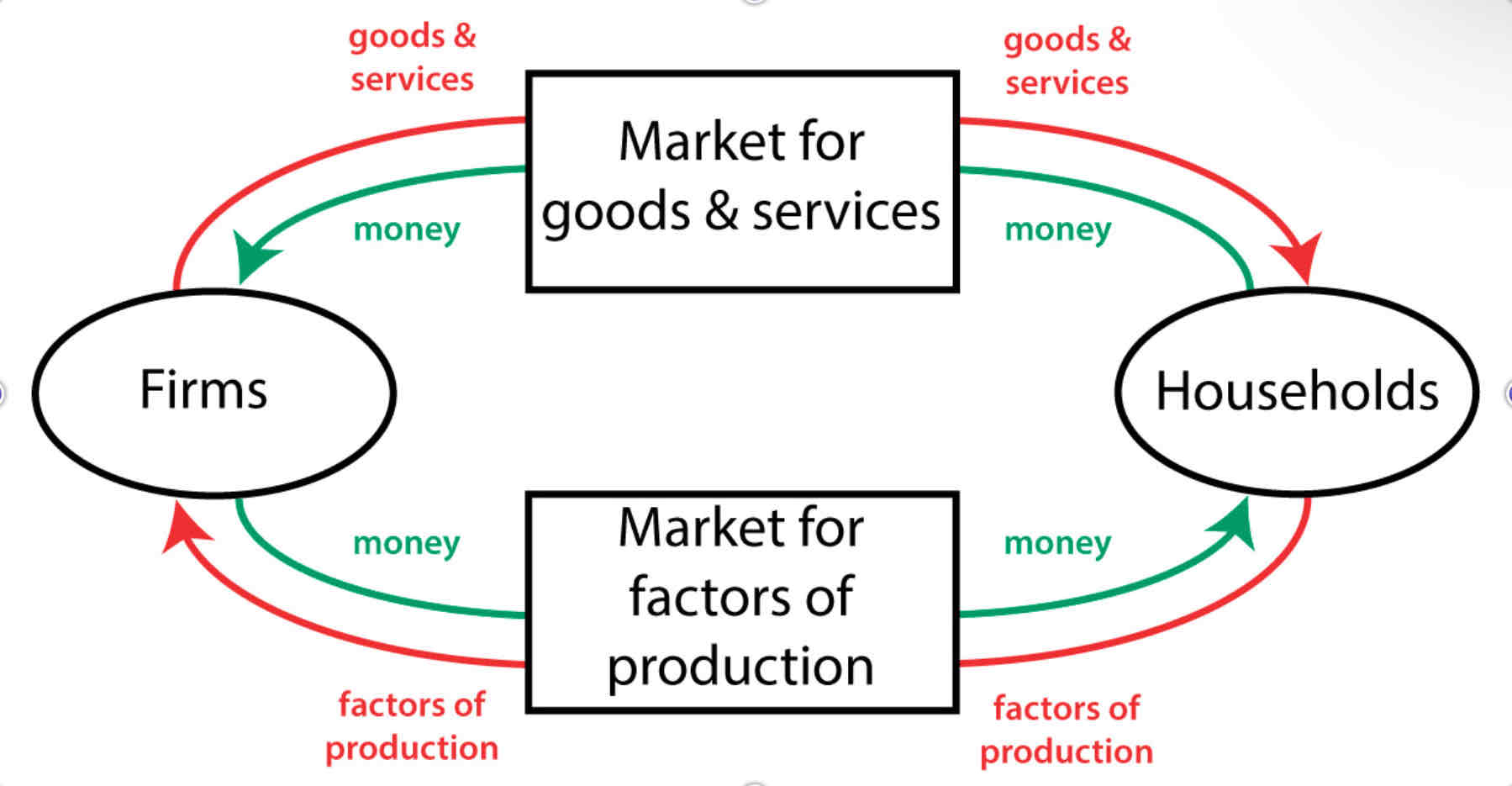
Resource Market
at the upper level of the diagram, the place where resources are bought and sold.
Product Market
the lower level of the diagram, the place where goods and services produced by businesses are bought and sold to the household.
Factors of Production
LAND
LABOR
CAPITAL
ENTREPRENEUR
Land
it includes natural resources like minerals, water, and forests, also includes air.
Labor
is the human effort and skill that goes into production.
Capital
it is the man-made equipment and machinery that helps production.
Entrepreneur
it is the risk-taker and innovator that organizes the other factors. They also possible entrants in the business sector that provide additional capital for the production of goods and services.
Factors Payment
Rent for land
Wage for Labor
Interest for Capital
Profit for Entrepreneur
Positive Economics
is an economic analysis that considers economic conditions “as they are” or “ as it is” and it answers the
question “what is?”
blank is a branch of economics that describes and explains economic happenings just the way they are
and not the way they ought to be. When explaining an economic phenomenon, positive economics focuses
on things as they are and uses obtainable facts to explain what happened or what is currently happening
in an economy.
blank entails investigating the occurrences in an economy and explaining them just the way they are.
Facts and verifiable information derived from the investigations can be used to make future projections
for an economy.
Normative Economics
an economic analysis which judges economic condition “ as it should be”
it answers the question “ what should be?”
blank aims to determine what should happen or what ought to be.
While positive economics describe economic programs, situations, and conditions as they exist,
blank aims to prescribe solutions.
blank expresses ideological judgments about what may result in economic activity if public policy
changes are made.
Behavioral economics tends to be a normative project.
blank cannot be verified or tested.
NOTE
Unlike normative economics, positive economics focuses on causes and effects, behavioral relationships, and facts involved in the evolution and development of economic theories. Positive economics is often called "what is" economics. On the other hand, normative economics is referred to as "what should be" or "what ought to be" economics.
Ceteris Paribus
means all other things are constant or all else equal
a device use to analyze the relationship between two variables while the other factors are held constant
TYPES OF ECONOMIC SYSTEM
Traditional Economy
Command Economy
Market Economy/Capitalism
Socialism
Mixed Economy
Traditional Economy
a subsistence economy, a family produces goods only for its own consumption
Command Economy
a type of economy wherein the manner of production is dictated by the government. The government decides in what, how, how much, and for whom to produce.
Market Economy/capitalism
the resources are privately owned and the people themselves make the decisions
Socialism
is an economic system wherein the key enterprises are owned by the state
Mixed Economy
a mixture of market and command systems