BMB 428 final exam
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Open system
Mass, heat and work can be exchanged with the surroundings
Closed System
matter not exchanged
Adiabatic system
Only work and energy can be exchanged with the surroundings (Δq = 0)
Isolated system
Nothing is exchanged with the surroundings (no heat, work, energy or matter)
Which of the following is an extensive property?
specific heat capacity
pressure
temperature
energy
energy
Isothermal
ΔT = 0
Reversible rxn
A system is at or near equilibrium (Pext = Pint)
Irreversible Rxn
System is not at equilibrium, occurs spontaneously (Pint does not equal Pext)
Extensive property and examples
depends on the amount of matter (ex: volume, heat capacity, gibbs free energy, enthalpy (H), mass, entropy (S)
Intensive Property and examples
does not depend on the amount of matter (ex: temperature, pressure, specific heat capacity, density)
Ideal gas law
PV = nRT
1st law of thermodynamics and accompanying equations
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted
du = dq + dw
Euniverse = Esystem + Esurroundings = 0
2nd law of thermodynamics. and accompanying equations
Entropy of an irreversible process increases and the entropy of a reversible process remains unchanged
ΔSuniverse > 0 (irreversible rxn)
ΔSuniverse = 0 (reversible rxn)
ΔSuniverse = ΔSsystem + ΔSsurroundings >/= 0
Heat is a property (T/F)
False
Which is FALSE?
A diatomic ideal gas has three degrees of translational freedom
A diatomic ideal gas has three degrees of rotational freedom
A diatomic ideal gas has two degrees of vibrational freedom
None of the above
A diatomic ideal gas has three degrees of rotational freedom.
it has 2 degrees of rotational freedom
3 of translational
2 of vibrational
overall 7
Units of heat capacity
J/K
ΔH = Δq at…
constant pressure
A gas in a piston (the system) is expanded reversibly in an isothermal process. Which of the following is true?
heat is absorbed by the gas from the surroundings
heat is neither absorbed nor given off by the gas to the surroundings
heat is given off by the gas to the surroundings
cannot tell
Heat is absorbed by the gas from the surroundings
3rd law of thermodynamics and accompanying equations
Every substance has a finite positive entropy, but at the absolute zero of temperature, the entropy may be zero, and it does in the case of a pure, crystalline substance
LimS = 0 (as T—> 0K)
From the perspective of the universe, what is the criteria for a spontaneous process?
ΔSuniverse > 0 (spontaneous = irreversible)
A state function is…
a property
When ice melts (a phase transition)…
heat is absorbed and the temp of the water vapor stays the same
For the irreversible expansion of a diatomic ideal gas at constant temperature…
the enthalpy decreases
the enthalpy is unchanged
the enthalpy increases
the entropy is unchanged
enthalpy is unchanged
What is the sign for heat being absorbed?
Δq (system) = +
The heat capacity of a diatomic ideal gas at constant pressure is:
9/2 nR
Cp = Cv + nR
Cv = 7/2 nR + nR = 9/2 nR
Boyle’s Law
P = 1/V
PV = constant
P1V1 = P2V2 at constant Temp
Charle’s Law
P = T at constant n and V so, P1/T1 = P2/T2
Dalton’s Law
Ptotal = sum of Pis
What is Euler’s criteria and what does it do?
Proves if something is a property
Equation for Enthalpy (H)
H = U + PV
Equation for du
du = dq + dw
du = TdS-PdV
Equation for G
G = H-TS
Equationn for A (Helmholtz free energy)
A = U = -TS
What is heat (q)
Thermal energy transferred between systems due to a temperature difference
What are the state functions?
Internal energy (E)
Entropy (S)
Enthalpy (H)
Pressure (P)
Volume (V)
Temperature (T)
What are not state functions?
heat (q) and work (w)
Equation for heat with specific heat in it
q = msΔT
s= specific heat
Heat capacity
specific heat capacity
molar heat capacity
Amount of heat that can be held
specific heat = one gram, Cs
molar heat = one mole, Cm
Equation for Cs (specific heat capacity)
Cs = q / mΔT
Equations for heat capacity (for monoatomic ideal gas) at:
constant volume (Cv)
constant pressure (Cp)
Cv = dU/dT = 3/2 nR
Cp = dH/dT = 5/2 nR
Equations for heat capacity (for diatomic ideal gas) at:
constant volume (Cv)
constant pressure (Cp)
Cv = 7/2*nR
Cp = 9/2*nR
Why is du = dq at constant volume
because dw = 0
dw = -Pext * dV
V = volume
dV = 0 so dW = 0
dw equation
dw = -Pext*dV
V = volume
Pext = external pressure
w = work
d= change
What is the SI unit for pressure?
atm
Pint equation (pressure internal)
P = nRT/V
SI unit for temperature
Kelvin (K)
Internal energy sign
U
Internal energy equation for monoatomic ideal gas and diatomic ideal gas
monoatomic: U = 3/2nRT
diatomic: 7/2nRT
For a reaction that is reversible or irreversible the value for U is ____
the same
What is entropy
disorder (S)
Equation for entropy (ΔS)
ΔS = dqrev/T
qrev = reversible heat
ΔS equation with Boltzmann constant in it
ΔS = Kb*ln*Ω
Kb = boltzmann constant (R/Na)
Ω = # of microstates
Definition of heat capacity at constant volume
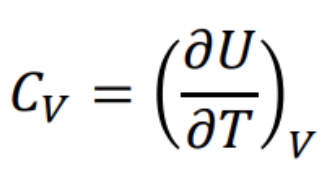
T/F : the solute is the solid component of a solution
False
T/F: the molarity of a 0.0012 molal aqueous solution is about 1.2mM
True
T/F: The total concentration of reactants and products is constant for a chemical reaction
False
T/F: The more stable species in a mixture has a greater chemical potential
False
T/F: The rise of a protein α-helix is 3.6 angstrom
False
What is the pitch of the alpha helix of DNA
5.4 angstroms
What is the Rise of an alpha helix in DNA
1.5 angstroms
What is the # of residues per turn in DNA alpha helix
3.6 residues
how do you calculate pitch?
(# residues per turn)x Rise
Molality
moles solute / kg solvent
What is the equation describing Raoult’s Law for the solution containing solute A and solvent B
Pa = Xa*Pa*
Pa = Xb*Pa*
Pa = Xa*Pb*
Pa = Xa*Ka
Pa = Xa*Pa*
Equation for Henry’s Law for the solution containing solute A and solvent B is:
Pa = XaPa*
Pa = XaPb*
Pa = XaKa
Pa=XaKb
Pa = XaKa
Raoult’s Law applies to:
ideal solutions
non-ideal solutions
dilute non ideal solutions
none of the above
ideal solutions
Henry’s Law applies to:
ideal solutions
non-ideal solutions
dilute non-ideal solutions
none
dilute non-ideal solutions
What is the entropic contribution to the Gibbs free energy of a process?
-TΔS
The entropy of mixing two liquids is:
always +
always -
is ± depending on the nature of the liquids
is ± depending on the temperature when mixed
always +
The chemical potential of an aqueous dilution of ethanol is:
less than pure ethanol
the same as pure ethanol
greater than pure ethanol
less or greater than pure ethanol depending on temperature
less than pure ethanol
The equilibrium constant for a gas chemical reaction calculated using molarity units and the equilibrium constant for the same reaction calculated using pressure units is…
same or different depending on the stoichiometry of the reaction
Liquid N boils at a very low temp because…
the dispersion interactions between nitrogen molecules are weak
What is G at equilibrium?
ΔG = 0
At equilibrium
Keq < 1
Keq = 1
Keq > 1
insufficient info to tell
insufficient info to tell
Which is not a van der Waals interaction:
dipole-dipole
ion-induced dipole
dipole-induced dipole
london interactions
ion-induced dipole
How do you find what the annealing temperature should be for PCR?
Tm - 5°C
What is the dielectric constant of water?
80
The boiling point of a solution will be…
lower than BP of pure solvent
equal to BP of pure solvent
higher than BP of pure solvent
lower or higher depending on nature of solute and solvent
higher than BP of pure solvent (bc of boiling point elevation)
Alaskan wood frogs can survive -40°C temps because of the following colligative property
freezing point depression
Hydrophobic interactions are the consequence of which law of thermodynamics
2nd