Test #1 (Unit 1)
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
What is the principle of Piezoelectricity?
“Some materials, when deformed by an applied pressure, produce a voltage”
What principle do ultrasound transducers operate according to?
Principle of Piezoelectricity
How do transducers create a voltage using the principle of Piezoelectricity?
Convert electric voltages into ultrasound pulses
Convert returning echoes into voltages
What are other names for Piezoelectric elements?
Crystal
Active element
Transducer element
What are some examples of natural Piezoelectric elements?
Quartz
Tourmaline
Rochelle salt
What are some examples of synthetic Piezoelectric elements?
Lead zirconate titanate (PZT)
What happens when a voltage is applied to a Piezoelectric element? What does this depend on?
Thickness of element increases or decreases
Depends on polarity of voltage
If a Piezoelectric element is not natural, how do they become Piezoelectric?
Heat material to Curie point
Material loses magnetic properties
Polarize dipoles with a strong electric current
Alignment circuit
Cool crystal below Curie point
Remove from alignment circuit
Aligned dipoles are fixed parallel to each other
Material can
Exhibit piezoelectric properties
Generate sound waves
What temperature is Curie point?
365° C
What would happen if a synthetic Piezoelectric element was created and reheated to the Curie point?
Destroys all Piezoelectric properties
What is Piezoelectricity?
When applied pressure produces a voltage
What does fo mean?
Operating frequency
What is the fo of a crystal determined by?
Crystal
Propogation speed
Thickness
Propogation Speed of Crystal (cPZT) Formula
cPZT
Crystal Thickness (cth) Formula
Wavelength / 2
Operating Frequency (fo) Formula
fo = cPZT / 2 * cth
How are thickness and operating frequency related?
Indirectly
Thin elements = high freq
Thick elements = low freq
What principle do ultrasound waves follow?
Huygens’ Principle
What is Huygens’ Principle?
Any point on a spherical wave can become origin for a new spherical wave
What is the sound beam a combination of?
All sound arising from different point-like sources (wavelets) on transducer crystal face
What is the beam profile formed by?
Constructive and destructive interference as wavelets collide within beam
What occurs due to the superposition of all sound waves in the beam?
Natural focusing (narrowing)
What shape is the sound beam?
Three-dimensional
How is the shape of the sound beam determined?
Crystals
Axial Plane
Along direction of sound travel
Parallel
Lateral Plane
Perpendicular to direction of sound travel
Elevational Plane
Thickness of sound beam
What occurs when additional beams travel out in directions not included in the main beam path?
Side lobes
When do side lobes occur?
ONLY in single element transducers
What produces the width of a sound beam? How is the width determined?
Transducer
The distance from the transducers face
Is intensity uniform throughout a beam? Why?
No
Area varies (intensity = power/area)
How are beam diameter and resolution related?
Inversely
Small beam = good resolution
Large beam = bad resolution
Near Zone
AKA Fresnel zone, near field
Region extending from transducer to minimum
beam width
How are beam width and distance related in the near zone?
Inversely
Beam width decreases = increasing distance
Beam width increases = decreasing distance
Far Zone
AKA far field, Fraunhofer zone
Region that lies beyond min beam width
How are beam width and distance related in the far zone?
Directly
Beam width increases = increasing distance
Beam width decreases = decreasing distance
Focal Point
Smallest beam
Maximum intensity
When does a beam have the best resolution?
At the focal point
Focal Zone
Where beam is focused on each side of focal point
Maximum
Sensitivity
Intensity
When does a beam have the best lateral resolution?
At the focal zone
How are diameter and intensity related in the focal zone?
Inversely
Diameter decreases = intensity increases
Diameter increases = intensity decreases
Near Zone Length (NZL)
Distance from transducer face to where the beam has the smallest diameter
Additional focusing can be added
What is the formula for the beam width at natural focus?
Crystal D / 2
How are diameter and NZL related?
Directly
Increase diameter = increase NZL
Decrease diameter = decrease NZL
How are frequency and NZL related?
Directly
Increase diameter = increase NZL
Decrease diameter = decrease NZL
Far Field Divergence
When the beam diameter increases after natural focus
How are diameter and far field divergence related?
Indirectly
Increased diameter = Low divergence
Decreased diameter = High divergence
How are frequency and far field divergence related?
Indirectly
Increased frequency = Low divergence
Decreased frequency = High divergence
At a distance of one near zone length the diameter of the beam is…?
½ the crystal diameter
At a distance of 2 near zone lengths the diameter of the beam is…?
The crystal diameter
What two things does focusing contribute to?
Better resolution (narrow beam)
Stronger beam (decreased area)
Where can focusing be achieved?
ONLY in the near zone
What transducers can only be focused mechanically?
Single element
Curved crystal
Acoustic lens
Mirrors
A-mode (Amplitude Mode)
Displayed on graph
X-axis = depth
Y-axis = strength
B-mode (Brightness Mode)
2D images, B-scans, displayed on a matrix
Displayed dots with brightness
What does brightness on B-mode show?
Strength
Location
M-mode (Motion Mode)
Displayed on a graph
X-axis = time
Y-axis = depth
What imaging mode is used most used today?
B-mode
What imaging mode is used for cardiac and fetal cardiac?
M-mode
Transducer (Probe)
Device that converts one form of energy to another
Bandwidth (BW)
Range of frequencies produced by the transducer
How are pulse length and bandwidth diameter related?
Inversely
Short pulses = broad bandwidth
Long pulses = narrow bandwidth
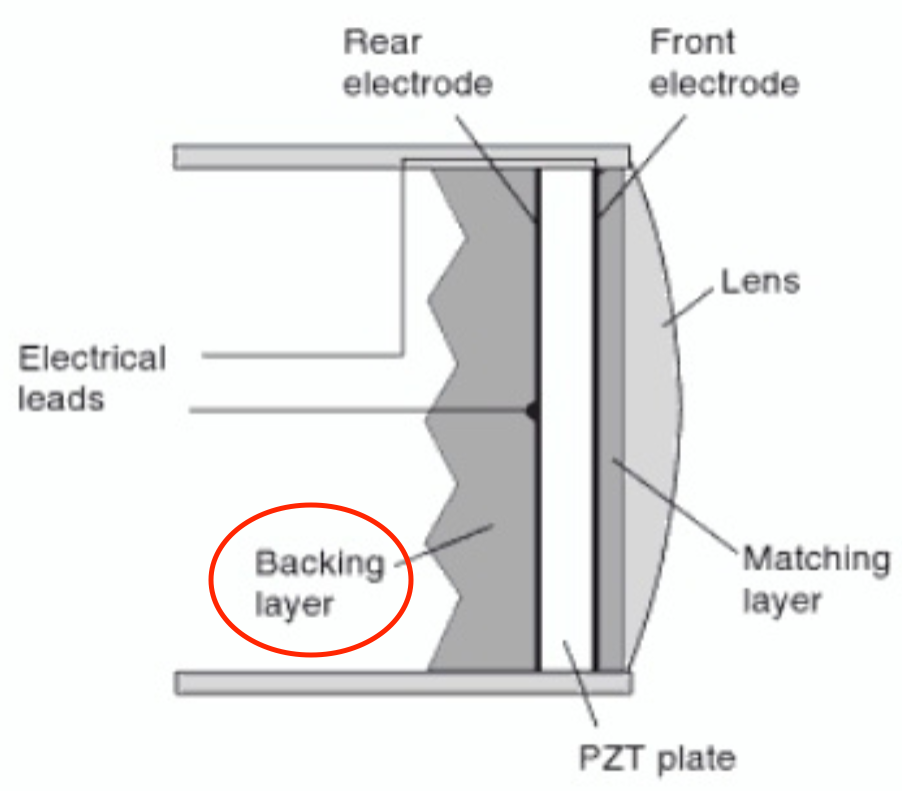
Damping (Backing) Material
Epoxy resin attached to back of element
What does damping material do?
Absorbs vibrations
Reduces #cycles/pulse
How are pulse duration (PD) and spatial pulse length (SPL) related to resolution?
Low PD and SPL = Improved resolution
High PD and SPL = Reduced resolution
How is bandwidth with damping related to quality factor, efficiency, and sensitivity?
Inversely
Increased bandwidth and damping = Decreased QF, efficiency and sensitivity
Decreased bandwidth and damping = Increased QF, efficiency and sensitivity
How are diagnostic imaging transducers damped? How many cycles per pulse does this produce?
Highly damped
2-3 cycles per pulse
How are pulsed-wave Doppler transducers damped? How many cycles per pulse does this produce?
Less damped
5-30 cycles per pulse
How are continuous wave Doppler transducers damped? Why?
Not damped
Reflects all energy into patient
What are the pros of damping?
Improves resolution
Broadens bandwidth
What are the cons of damping?
Reduces ultrasound amplitude
Decreases sensitivity of system
What does quality factor determine?
Sensitivity
What does quality factor detect?
Weak echoes
Quality Factor (QF) Formula
fo / BW
Matching Layer
Located on the transducer face
Has impedance value between crystal and tissue
What does the matching layer do?
Improves sound transmission into body
Reduces reflection
Matching Layer Thickness Formula
Wavelength / 4
What does coupling gel do?
Eliminates air between transducer and skin
Eliminate strong reflection caused by air
Improves transmission of sound into and out of body
What is the DMU frequency range?
1-20 MHz
Which frequencies provide inadequate axial resolution?
Lower than 1 MHz
Which frequencies cannot penetrate deep enough for ultrasound?
Above 20 MHz
What frequency transducer should be used for abdomen, pelvis, and OB?
1-5 MHz
What frequency transducer should be used for adult echo, abdomen, and abdominal Doppler?
1-5 MHz
What frequency transducer should be used for vascular, thyroid, scrotum, and MSK?
5-12 MHz
What frequency transducer should be used for breast?
10-20 MHz
How are frequency and penetration related?
Low frequency = Improved penetration
High frequency = Reduced penetration
How are penetration and resolution related?
Improved penetration = Reduced resolution
Reduced penetration = Improved resolution
What is a complete scan of the ultrasound beam called?
Frame
What is required for real-time scanning?
Transducer arrays
What means are used for sweeping, steering, and focusing the beam? What is this accomplished by?
Electronic means involving constructive interference
Accomplished by
Sequencing
Phasing
Sequencing
Pulses are applied to small groups of elements in rapid succession
What is the time delay between pulses determined by?
Depth (time it takes for all echoes to return)
What does sequencing allow to happen?
Fast acquisition of images and frame rates
Real-time scanning
Phasing
Pulses are applied to elements in rapid succession
What does phasing allow to happen?
Sweeping
Real-time scanning
Steering direction
Focusing scanning plane and perpendicular to scanning plane
Beam Steering
Sweeping the beam
Accomplished with phasing
What does beam steering produce?
Automatic scanning
How are time and beam steering related?
Directly
Increased delay = Increased steering
Decreased delay = Decreased steering
How do you know what direction a beam is going during beam steering?
Beam goes toward side activated last
Right to left = steered left
Left to right = steered right
What planes does focusing occur in?
All 3 planes