6: Review of Exercise Physiology - Cardiovascular System
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Veins
receives deoxygenated blood
Right Atrium
receives DEOXYGENATED blood
Tricuspid Valve
right AV valve
Right Ventricle
sends DEOXYGENATED blood to lungs
Pulmonic valve
semilunar valve
Pulmonary ____→ _____ → Pulmonary _____
Pulmonary artery → Lung → Pulmonary vein
Left Atrium
receives oxygenated blood from lung
Bicuspid Valve
Left AV valve
Left Ventricle
send oxygenated blood to the aorta/body
Aortic valve
semilunar valve
aorta
Main artery that carries oxygenated blood from the Left Ventricle to the body
diastole
relaxation phase: ventricles FILL with blood
atrioventricular valves are open
aortic and pulmonic valves closed
systole
contraction phase during which ventricles EXPEL blood
atrioventricular valves are closed
aortic and pulmonic valves open
intrinsic control *4
autorhythmaticity
sinoatrial node
atrioventricular node
purkinje fibers
autorhythmaticity
ability to initiate impulse for contraction at regular intervals
controlled by the SA node (pacemaker
sinoatrial node
pacemaker of cardiac contraction
atrioventricular node
delays impulse by 1/10 of second, allowing atria to contract before ventricles
purkinje fibers
rapidly spreads impulse to contract throughout ventricles
electrocardiogram (ECG)
records the electrical activity of the heart
P wave
atrial depolarization
QRS complex
ventricular depolarizations
atrial repolarization
T wave
ventricular repolarization
ECG abnormalities may indicate what?
Coronary heart disease
What 2 things can ST elevation indicate?
sign of myocardial ischemia ← blockage of coronary artery
myocardial infarction
What 3 things can ST depression indicate?
sign of myocardial ischemia
non-ischemic: ventricular hypertrophy, hypothermia, digoxin
normal variant: hyperventilation
Diastole: Pressure in ventricles is ____
low
Diastole: Ventricles are _____
filling with blood from atria
Diastole: AV valves open when ___
ventricular pressure is less than atrial pressure
systole: pressure in ventricles ____
rises
systole: blood is ejected in _____
pulmonary and systemic circulation
systole: semilunar valves open when _____
ventricular pressure is greater than aortic pressure
first heart sound (lub)
closing of AV valves
second heart sound (dub)
closing of aortic and pulmonary valves
what is the equation for cardiac output?
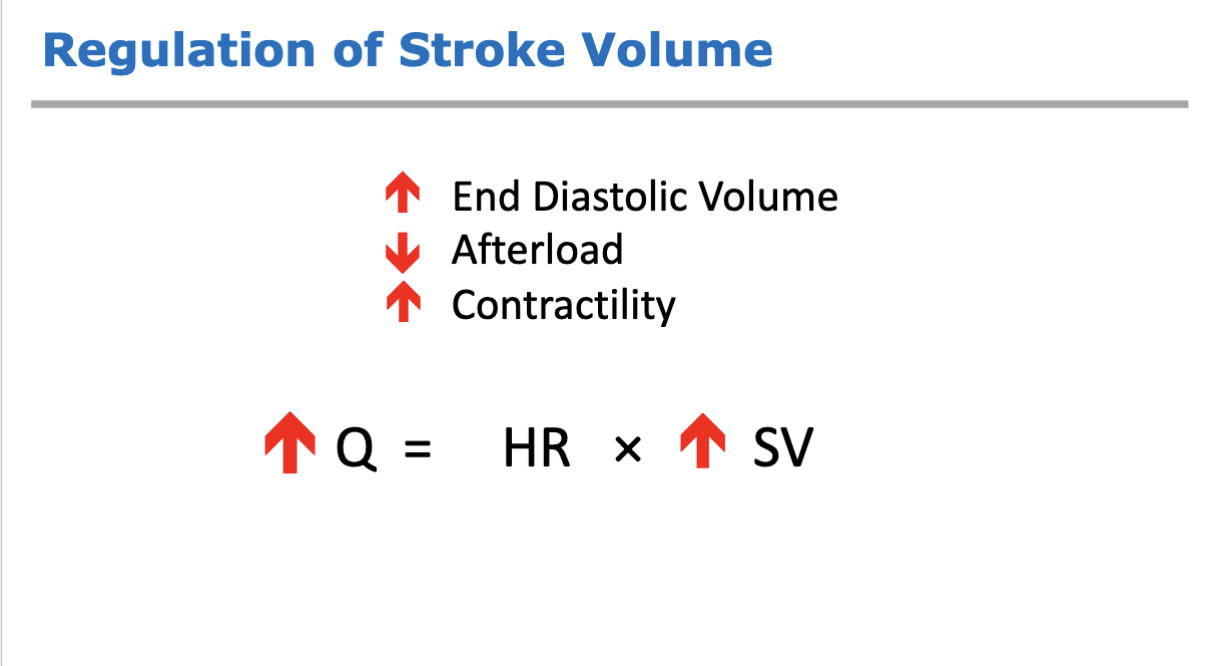
Q = heart rate (HR) x stroke volume (SV)
What are the 2 types of control that regulate heart rate?
intrinsic
extrinsic
What are the 3 types of control that regulate stroke volume?
end diastolic volume
afterload
contractility
What is an example of intrinsic control of heart rate?
Autorhythmaticity
What two systems regulate heart rate?
parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system
how does the PNS affect heart rate?
by the vagus nerve
slows HR by inhibiting SA and AV node
how does the SNS affect heart rate?
by the cardiac accelerator nerves
increases HR by stimulating SA and AV node
what is parasympathetic tone?
baseline level of activity of the PNS → low resting HR
what causes an increase in HR at onset of exercise
parasympathetic withdrawal
What causes the later increase in heart rate during exercise (after ~100 beats/min)?
increased SNS stimulation
Name two types of sensory receptors involved in the extrinsic neural control of blood pressure and heart rate
Baroreceptors
Mechanoreceptors
Baroreceptors (sensory/afferent)
located in the carotid artery and aortic arch
Mechanoreceptors
detect beat to beat blood pressure
what do baroreceptors do if BP is high?
send signals to medulla oblongata
to increase parasympathetic nervous activity (PNA)
to decrease sympathetic nervous activity (SNA)
decrease HR → reduced BP
end-diastolic volume (EDV)
volume of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole (preload)
aortic blood pressure
pressure the heart must pump against to eject blood (afterload)
strength of ventricular contraction (contractility)
enhanced by:
circulating EPI and NE
direct sympathetic stimulation of heart
frank-starling mechanism
greater EDV → more forceful contraction
due to stretch of ventricles
what is EDV dependent on
venous return
what 3 factors increase venous return?
venoconstriction (by SNS)
skeletal muscle pump
respiratory pump
skeletal muscle pump
rhythmic skeletal muscle contractions force blood in the extremities toward the heart
one-way valves in veins prevent backflow of blood
respiratory pump
changes in thoracic pressures pull blood toward heart
afterload
tension developed in the wall of the left ventricle during ejection
high afterload results in ____
decrease in stroke volume
requires greater force generation by the myocardium to eject blood into the aorta
how does increased ventricular contractility affect stroke volume
results in higher stroke volume
what 2 factors enhance ventricular contractility?
circulating EPI and NE
direct sympathetic stimulation of heart
regulation of stroke volume equation
what 3 factors influence arterial BP?
determinants of mean arterial pressure (MAP)
short-term regulation
long-term regulation
determinants of mean arterial pressure
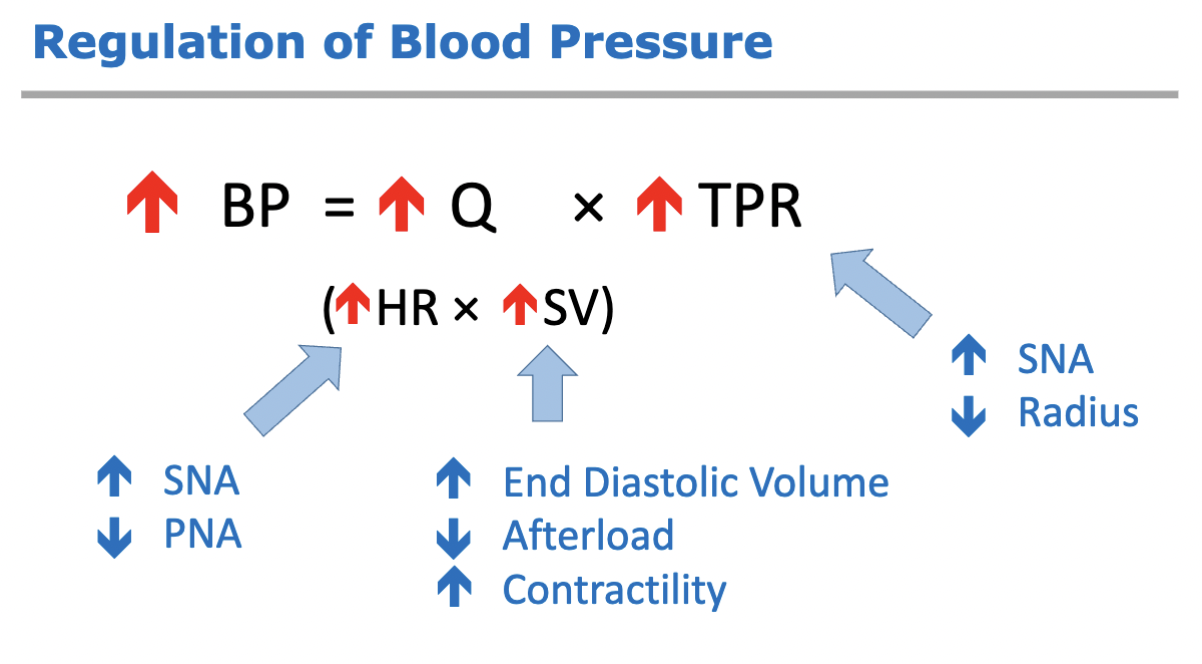
cardiac output
total vascular resistance
ABP = CO x TPR
short-term regulation
sympathetic nervous system to heart and vasculature
baroreceptors in aorta and carotid arteries
increase in BP → decreased SNS activity → normalizes BP
decrease in BP → increased SNS activity → normalizes BP
long-term regulation
kidneys by controlling blood volume
vasodilation’s relationship to resistance and BP
decreases both resistance and BP
vasoconstriction’s relationship to resistance and BP
increases both resistance and BP
regulation of blood pressure chart