Unsupervised learning
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Association Rules
Quantify: support and confidence
Support
the proportion of transactions where both the antecedent and consequent appear together
Confidence
the likelihood of finding the consequent in a transaction given the presence of the antecedent
Anomaly Detection
Point (Global) Anomalies
Individual data points that differ significantly from the majority of the dataset. These are the most common type of anomaly and are typically far from the mean or median. Example: A single fraudulent transaction in a bank account
Contextual (Conditional) Anomalies
Data points that are normal in one context but anomalous in another. Their deviation is significant within a specific context or condition. Example: A temperature of 25°C might be normal in summer but anomalous in winter, making it an outlier only in the context of the season.
Collective Anomalies
A group of data points that together represent abnormal behaviour, even if individual points may not be outliers. For example, a sudden surge in server traffic could indicate an attack.
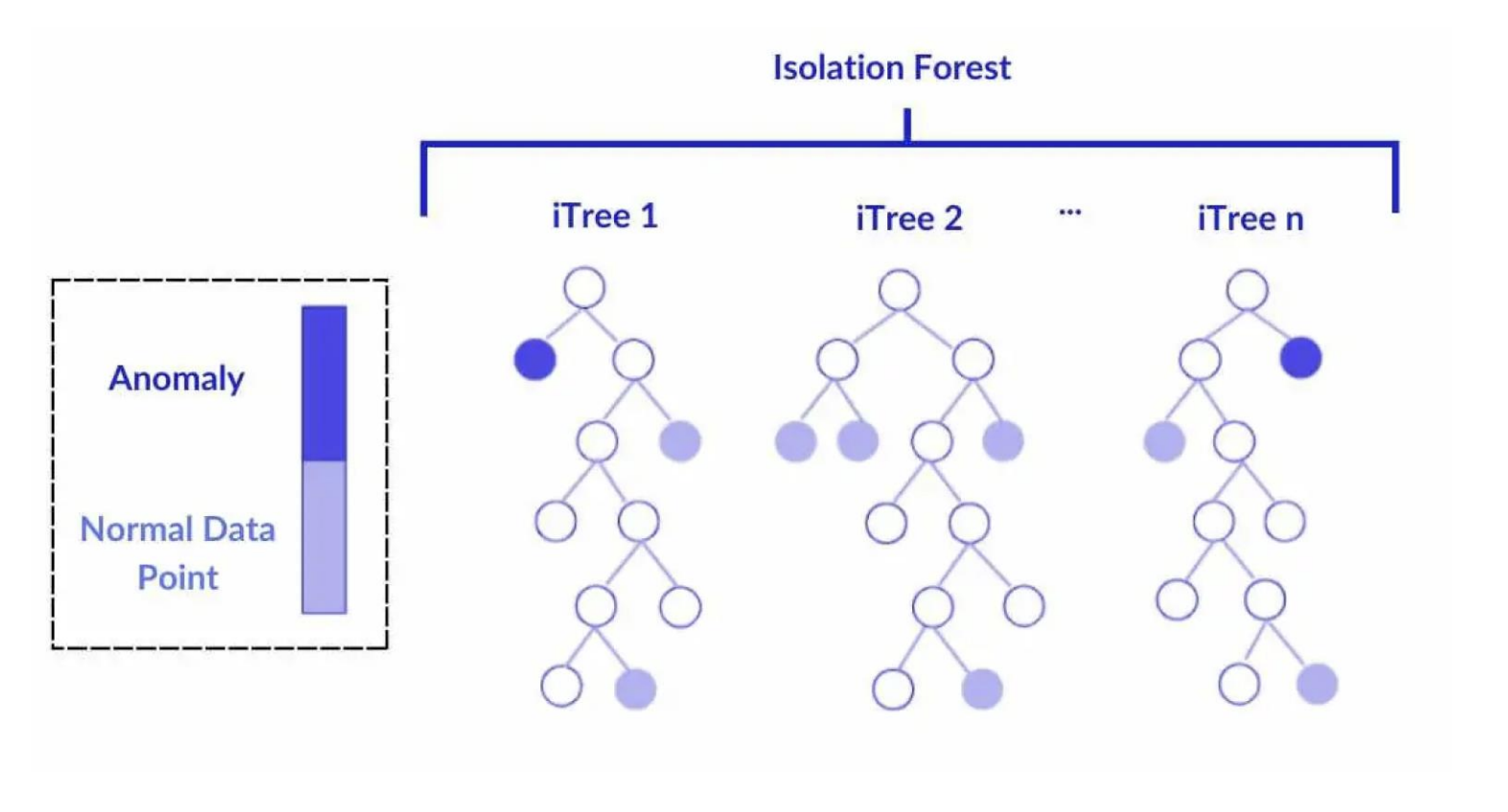
Isolation Forest
Uses decision trees to separate data points, aiming to isolate anomalies, which are “few and distinct.”
Anomalies appear on shorter branches (easier to isolate), while regular points go deeper in the tree (harder to separate).