The Nervous System: Neuron and Synapse !!!
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
What is a neuron?
specialized cells that conduct nerve impulses
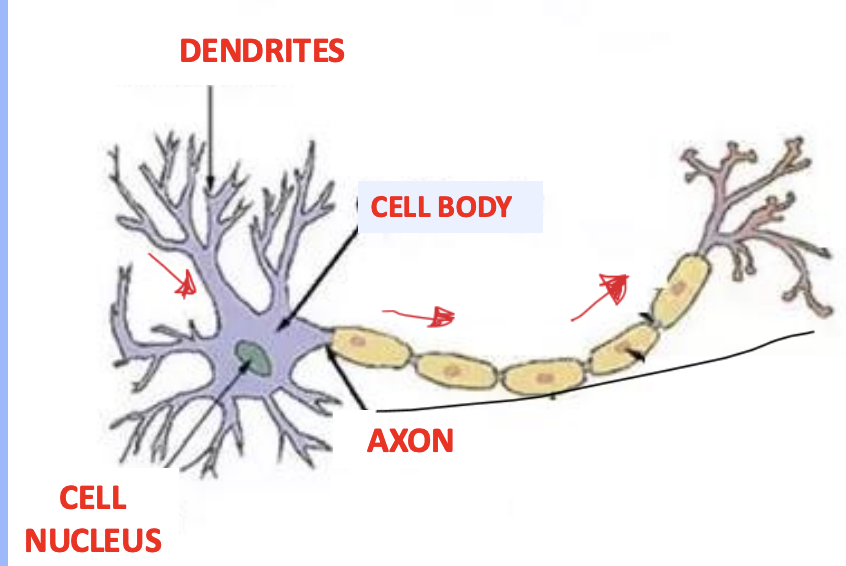
What 3 main parts is The neuron is composed of?
1.DENDRITES
Cell Body
Axon
What are dendrites?
Short, usually branched processes that carry impulses toward the cell body
What is the function of the cell body?
Contains the nucleus and maintains the cell
What is an axon?
A long process that carries impulses away from the cell body
How does information flow within a neuron?
It flows in one direction — from the dendrites → cell body → axon
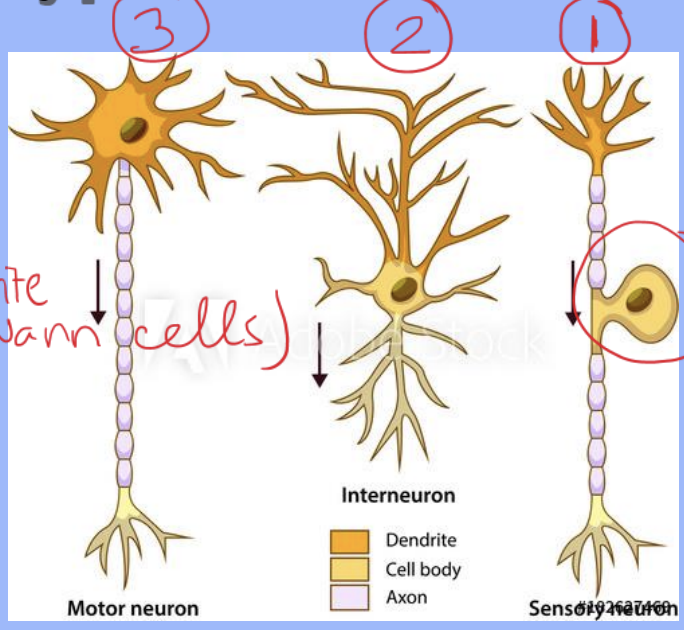
What are the 3 types of Neurons?
1.Sensory Neurons
2.Interneurons
3.Motor Neurons
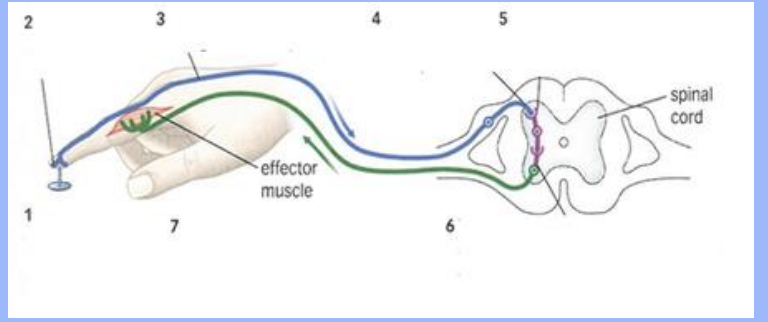
What is a reflex arch? Automatic respose that skips the brain
Automatic respose that skips the brain
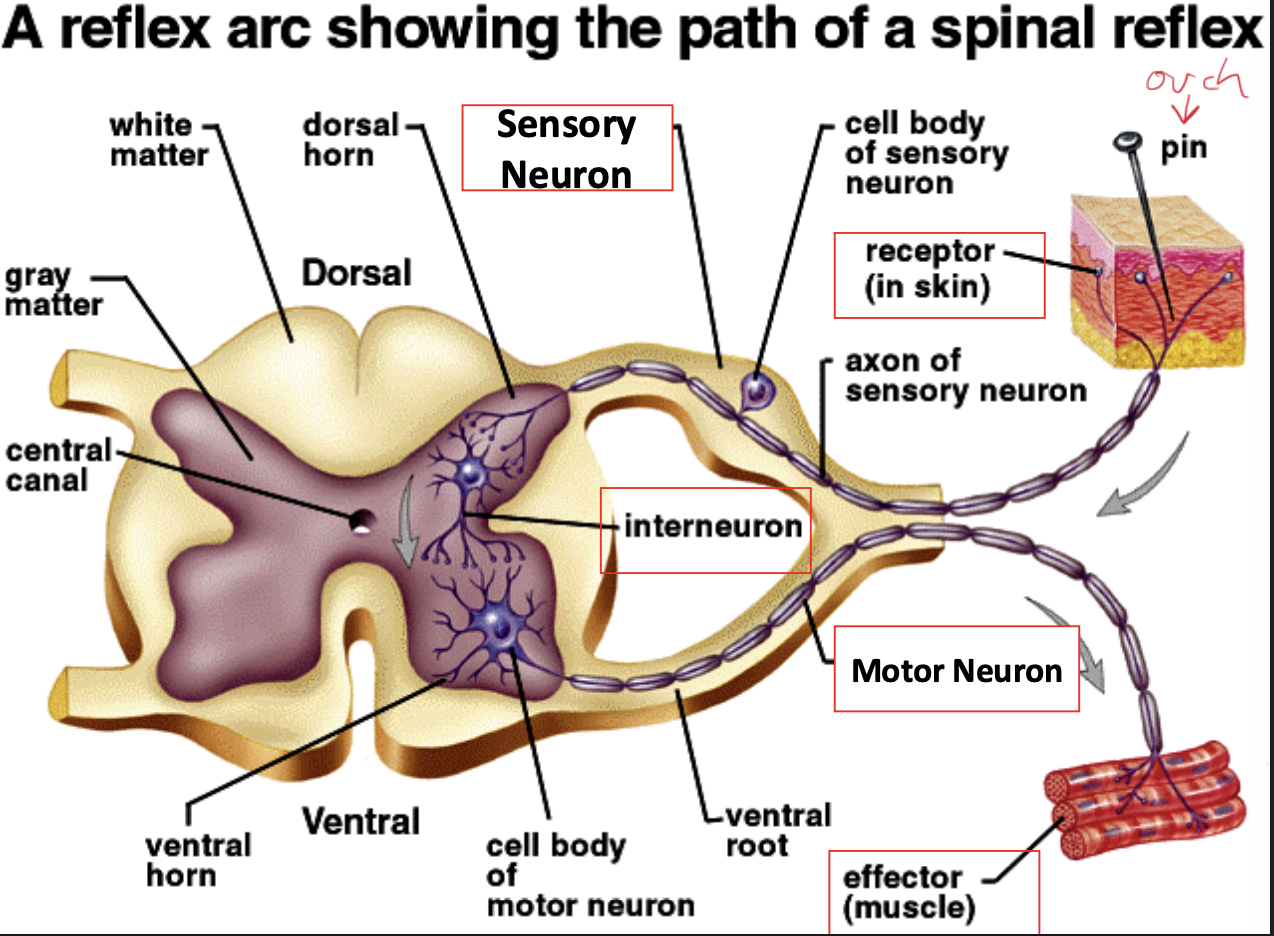
What is a receptor in a reflex arc?
A structure that detects a stimulus and starts a nerve impulse
What must happen for a receptor to activate?
The stimulus must surpass a threshold
Give examples of receptors.
Stretch receptors (lungs)
pain receptors (skin)
photoreceptors (eyes)
chemoreceptors (heart & brain)
What is the role of a sensory neuron in a reflex arc?
Carries sensory information from the receptor to the interneuron
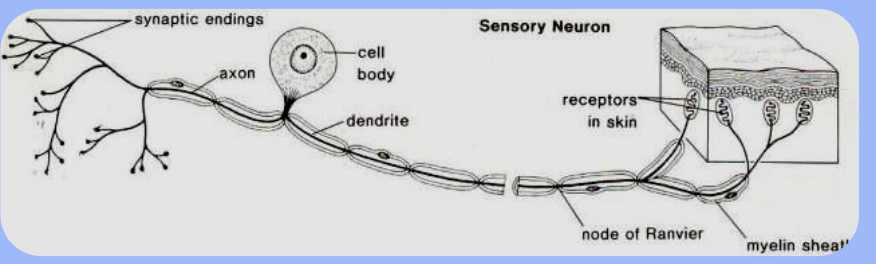
What structural feature does a sensory neuron have?
A long dendrite
Where is the nucleus (cell body) of a sensory neuron located?
In the dorsal root ganglion, off to the side
What is the function of an interneuron in a reflex arc?
Connects the sensory neuron to the correct motor neuron to produce the proper response
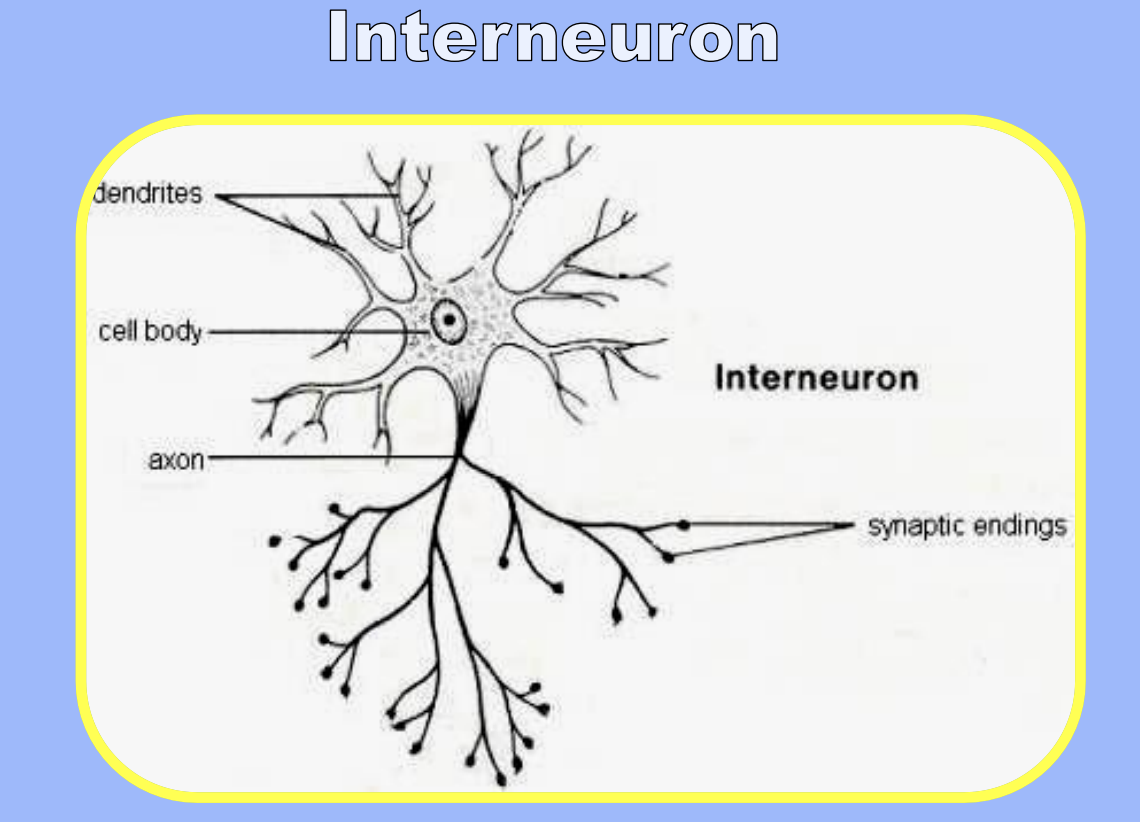
What are the structural features of an interneuron?
Short dendrite and short axon
Where are interneurons located?
Entirely within the spinal cord / CNS
What is the function of a motor neuron in a reflex arc?
Carries the impulse from the CNS to an effector
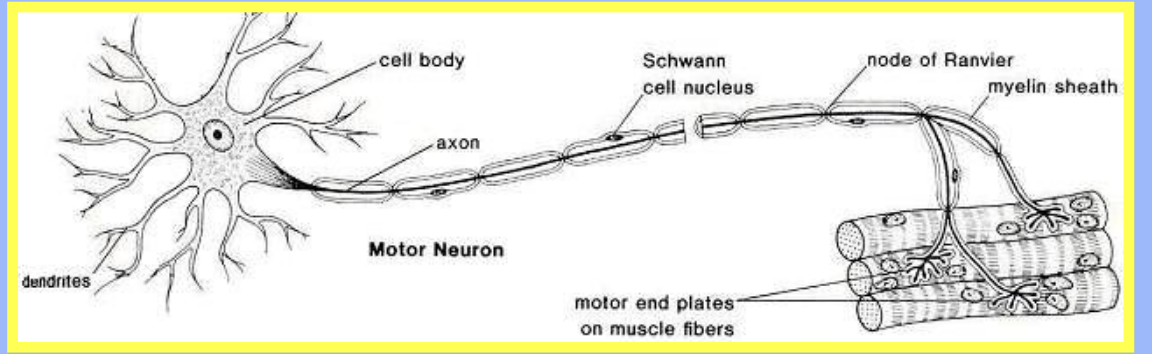
What are the structural features of a motor neuron?
Short dendrites and a very long axon (up to 3 m)
Where are the dendrites and axon of a motor neuron located?
Dendrites are in the CNS; the axon extends outside the spinal cord
What is an effector in a reflex arc?
A muscle or gland that responds to a nerve impulse
What happens when a muscle effector is stimulated?
The muscle contracts
What happens when a gland effector is stimulated?
The gland releases a hormone
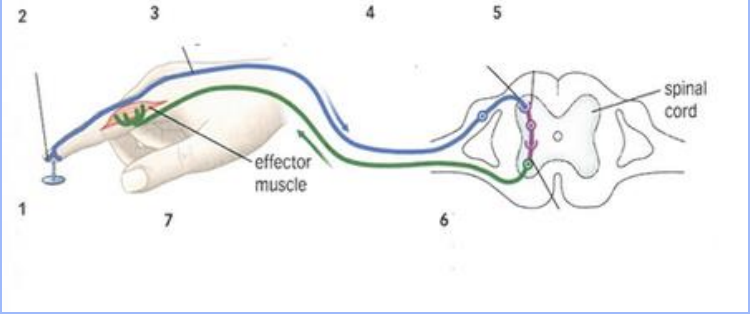
What are mixed nerves?
Nerves that contain both sensory dendrites and motor axons
What do nerve bundles contain?
Hundreds of long fibres from different neurons
How do impulses travel in mixed nerves?
In both directions to different places
What is a nerve?
A bundle of long fibres from neurons
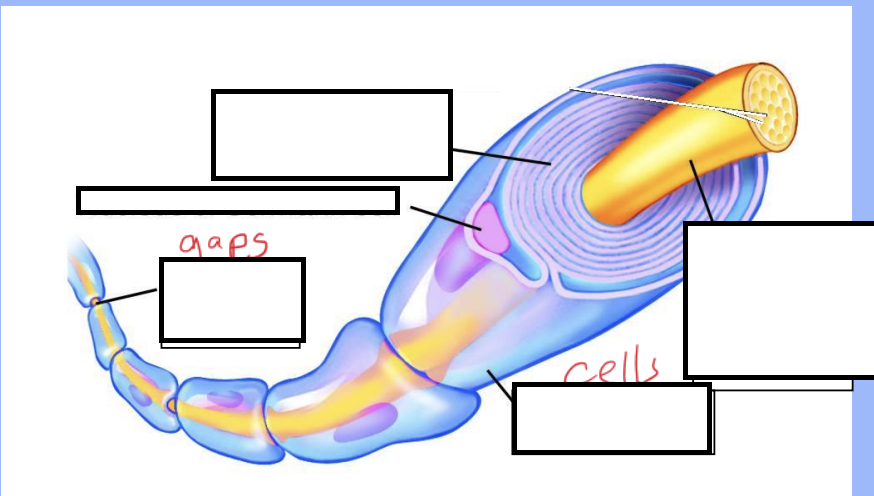
What covers the long fibres of neurons?
The myelin sheath, a fatty covering
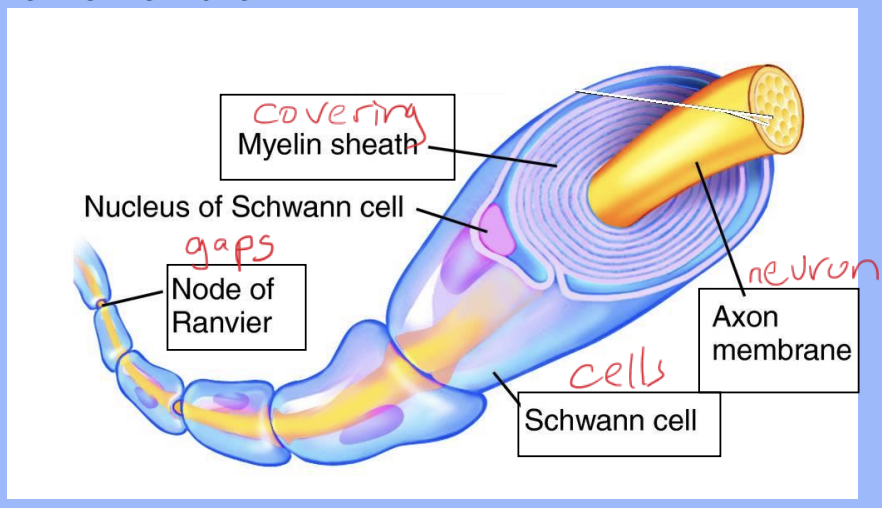
What cells make up the myelin sheath?
Schwann cells that wrap around the nerve fibre
What are the two functions of the myelin sheath?
1) Insulates neurons from each other
2) Speeds up nerve impulses
What are the nodes of Ranvier and their function?
Gaps between Schwann cells where the impulse jumps from node to node, speeding up transmission
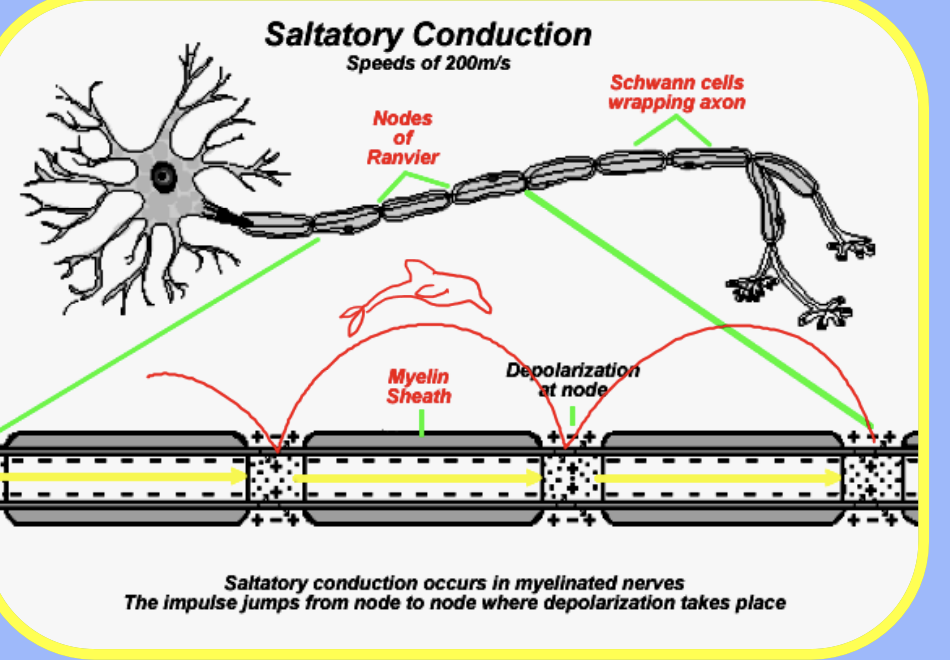
What is the resting state of a neuron?
-70 mV
Where are sodium ions (Na⁺) concentrated at rest?
Outside the axon
Where are potassium ions (K⁺) and negative organic ions concentrated at rest?
Inside the axon (in the axoplasm)
What (3 things) control the movement of ions in and out of a neuron?
Sodium channels, potassium channels, and the sodium-potassium pump
Why is the outside of a neuron slightly positive at rest?
Because of the distribution of ions (more Na⁺ outside than K⁺ inside)
Are ions able to move in or out of the neuron at rest?
No, the membrane is not permeable to them
What is the state of sodium and potassium gates at rest?
The gates are closed
What triggers depolarization in a neuron?
A stimulus strong enough to surpass threshold (-55 mV)
What happens to the membrane during depolarization?
It becomes permeable to sodium
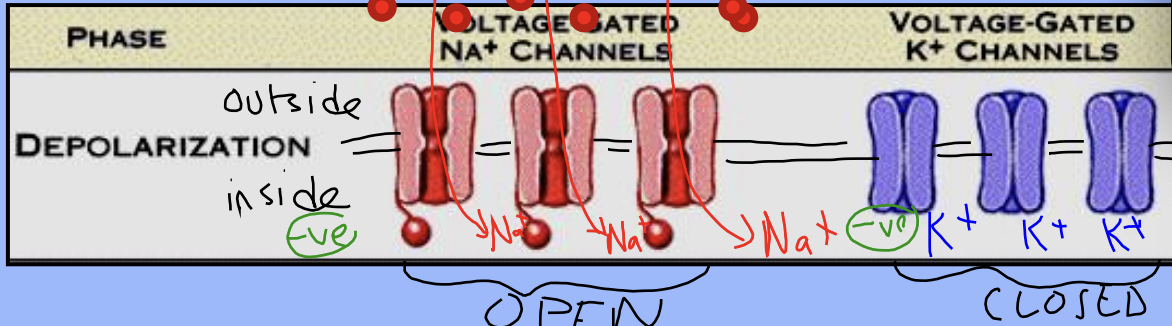
What happens to sodium ions during depolarization?
Sodium floods into the axon, making the inside positive (+30 mV)
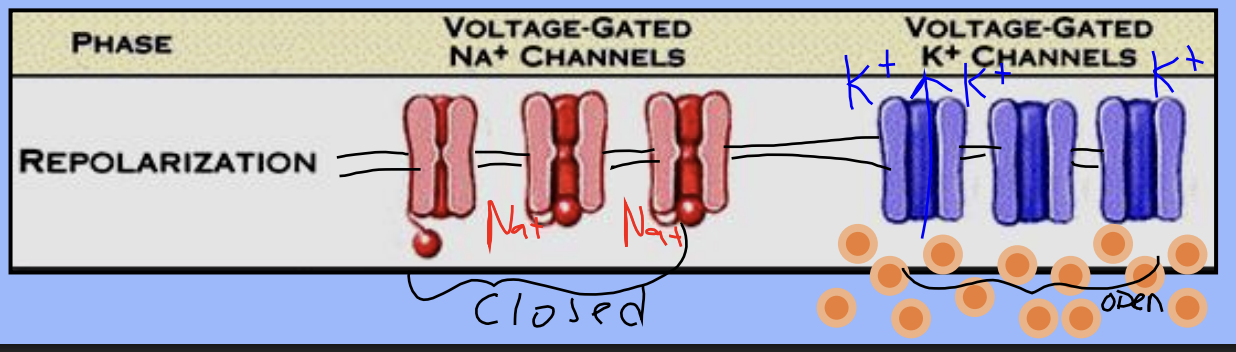
What triggers repolarization in a neuron?
The voltage reaching +30 mV causes potassium gates to open
What happens to potassium ions during repolarization?
Potassium floods out of the axon, restoring the original polarity (-70 mV)
What happens to sodium gates during repolarization?
A: Sodium gates close
What happens to the sodium and potassium gates during the recovery phase?
They are all closed
How are sodium and potassium ions returned to their original positions?
By the sodium-potassium pump using ATP
Why can the neuron not fire during the refractory period?
Because the ions have not been reset to resting conditions yet
What is the “all-or-none” response in neurons?
If the threshold (-55 mV) is reached, an impulse will fire, and each impulse is the same strength
Can a neuron fire a weaker or stronger impulse than normal?
No, all impulses are equal once threshold is reached
True or False: A stronger stimulus produces a bigger impulse.
It produces more impulses (more nerves or a faster series), not a bigger single impulse
What is an action potential?
The ionic changes in a neuron fiber that occur during the movement of a nerve impulse (opposite of resting potential)
What is the small space between neurons called?
The synaptic gap
Does the axon of one neuron directly touch the next cell?
No, the axon does not make direct contact with the receiving cell
How does the impulse cross the synaptic gap?
The electrical signal cannot cross directly; it must activate the target neuron, muscle, or gland through chemical means
Which neuron sends the message at a synapse?
The presynaptic neuron
Which cell receives the message at a synapse?
The postsynaptic neuron or effector
What does the presynaptic membrane do?
Encloses synaptic vesicles filled with neurotransmitters made by the axon
What does the postsynaptic membrane do?
Contains protein receptor sites that recognize specific neurotransmitters
How do the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes work together?
The presynaptic neuron releases neurotransmitters, which are detected by receptors on the postsynaptic membrane to pass the message
What is the synaptic cleft and what is it filled with?
The small gap between neurons, filled with extracellular fluid and enzymes
What happens when a nerve impulse reaches the axon terminal?
Calcium gates open, and Ca²⁺ ions enter the axon terminal
What happens after calcium enters the axon terminal (Step 2)?
Calcium binds to contractile proteins on vesicles, causing them to move toward the presynaptic membrane
What happens in Step 3 of synaptic transmission?
Exocytosis releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic gap, where they diffuse across to the next cell
What happens in Step 4 of synaptic transmission?
Neurotransmitters bind to receptor sites on the postsynaptic membrane
What happens in Step 5 of synaptic transmission?
Neurotransmitter binding changes the postsynaptic membrane voltage, opens sodium gates, and depolarizes the membrane
What happens in Step 7 of synaptic transmission?
Enzymes in the synaptic gap break down neurotransmitters, resetting the synapse to its original state
Where does the energy for synaptic transmission come from?
Mitochondria in the axon bulb, which supply energy for the entire process
What is acetylcholine responsible for?
Promotes responses in a relaxed state and controls skeletal muscles
How is acetylcholine removed after it acts?
Destroyed by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase
What is noradrenaline (norepinephrine)?
An excitatory neurotransmitter that usually increases activity of the receiving cell
What situations is noradrenaline involved in? How is noradrenaline removed after it acts?
Fight or flight’ responses (stress). Destroyed by the enzyme monoamine oxidase (MAO)
Which neurotransmitter is mainly active in a relaxed state?
Acetylcholine
Which neurotransmitter is mainly active during stress?
Noradrenaline / norepinephrine
Which neurotransmitter helps control skeletal muscles?
Acetylcholine
How can drugs affect synaptic transmission?
They can change how neurotransmitters or receptors work in the synapse
How does alcohol affect the synapse?
It makes GABA neurotransmitters last longer, which quiets brain activity more than normal
How do some drugs affect neurotransmitters in the synapse?
They block enzymes or reuptake, preventing neurotransmitters from being destroyed or removed
How does Prozac affect serotonin?
It prevents serotonin from being reabsorbed, allowing it to work longer
How does cocaine affect the synapse?
It increases dopamine release and blocks reuptake, causing pleasure sensations
How does ecstasy affect the synapse?
It increases serotonin release and blocks reuptake, producing feelings of intimacy and reduced inhibition
How does morphine affect the synapse?
It binds to endorphin receptors, causing a sense of well-being (like after exercise)
How does nicotine affect the synapse?
It binds to acetylcholine receptors, causing arousal and reward sensations
How do some drugs block neurotransmitter action?
They occupy receptor sites, preventing neurotransmitters from binding
What does the hypothalamus do?
Regulates homeostasis (thirst, hunger, body temperature, water balance, blood pressure) and links the nervous system to the endocrine system
What is the pituitary gland and why is it called the “master gland”?
A small gland that produces many hormones, controlling other glands in the body