AP Macroeconomics Ultimate Guide
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Labor Participation Rate
number of people in labor force/working age population x 100
Unemployment rate
number of people unemployed/number of people in labor force x 100
% Change in GDP
(New GDP - Old GDP)/Old GDP x 100
Consumer Price Index
Value of market basket/Value in base year x 100
GDP deflator
Nominal GDP/Real GDP x 100
GDP (Expenditure Approach)
C + I + G + (X - M)
GDP (Income Approach)
Wages + Rent + Interest + Profit
MPS =
1 - MPC
Spending Multiplier
1/MPS
Tax Multiplier
MPC/MPS or (1/MPS) - 1
Money Multiplier
1/Reserve Requirement
Real Interest Rate
Nominal Interest Rate - Expected Inflation
Quantity Theory of Money
M x V = P x Y
Increase in Human Capital
Increase in Economic Growth
Increase in Demand
Equilibrium Price Up
Increase in Supply
Decrease in Equilibrium Price
Increase in Consumer Spending
Increase in Real GDP
Increase Interest Rates
Decrease in Investment
Increase in Inflation
Decrease in Real Wages
Increase in Discouraged workers
Decrease in Unemployment rate
Increase in Aggregate Demand
Increase in Price Level
Increase in SR Aggregate Supply
Decrease in Pirice Level
Increase in Government
Increase in Real GDP
Increase in Taxes
Decrease in Disposable Income
Increase in MPC
Increase in Spending Multiplier
Increase Interest Rates
Decrease in Bond Prices
Increase in Money Supply
Decrease in Nominal Interest Rates
Increase in Reserve Requirement
Decrease in Money Supply
Increase in Discount Rate
Decrease in Money Supply
Increase in Central Bank buys bonds
Increase in Money Supply
Increase in Interest on Reserves
Decrease in Aggregate Demand
Increase in Inflation
Decrease in Real Interest Rate
Increase in Deficit Spending
Increase in Real Interest Rates
Increase in Capital Stock
Increase in Economic Growth
Increase in Appreciation
Decrease in Net exports
Increase in Interest Rates
Increase in Net Capital inflow
Comparative Advantage
A country makes a good at a lower opportunity cost than another country
Investment
Business spending on physical capital, never personal investing
Full Employment
When there is only frictional and structural unemployment
Long-run self-adjustment
When there’s a positive or negative output gap, SRAS will eventually shift.
Fiscal policy
Government changes spending and/or taxes. This shifts AD.
Monetary policy
When there are limited reserves, Central banks can influence interest rates by changing the reserve requirement, discount rate, or by doing open market operations. This shifts AD.
Open Market Operations
When Central banks buys or sell bonds.
Crowding Out
Deficit spending leads to higher real interest rate and less investment
Capital Inflow
High interest rates decrease investment but attract more foreign financial capital.
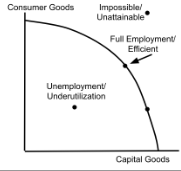
Production Possibilites Curve
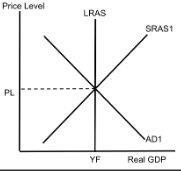
AD/AS (Full Employment)
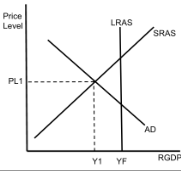
AD/AS (Negative Output Gap)
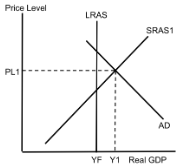
AD/AS (Positive Output Gap)
AD/AS (Recession Self-Adjust)
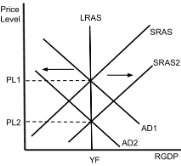
AD/AS (Inflation Self-Adjust)
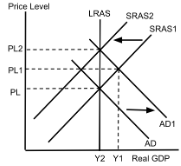
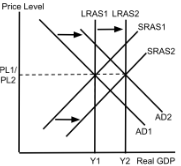
AD/AS (Economic Growth)
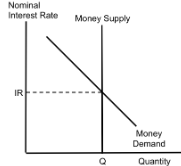
Money Market
Reserve Market
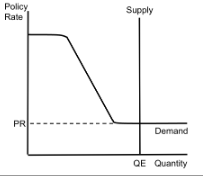
Loanable Funds
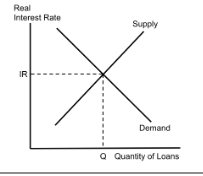
Phillips Curve
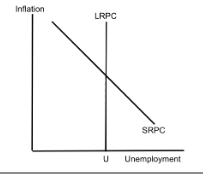
Foreign Exchange
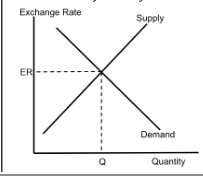
Discount Rate
The interest rate the Federal Reserve charges banks to borrow money. Lowering it encourages banks to lend more, stimulating the economy.
Policy Rate
A general term for key interest rates set by central banks (like the discount rate or federal funds rate) to influence economic activity.
Ample Reserves
When banks hold more reserves than required, giving them flexibility to lend more, which can support economic growth.
Limited Reserves
When banks less reserves than required, giving them less flexibility to lend more.
Cyclical Unemployment
Job loss due to economic downturns; occurs when demand for goods and services decreases.
Frictional Unemployment
Short-term unemployment during transitions between jobs or entering the workforce.
Structural Unemployment
Long-term unemployment from a mismatch between workers' skills and job requirements, often due to technological changes.
Seasonal Unemployment
Job loss related to seasonal work patterns, such as holiday retail or agricultural harvesting.
Human Capital
The skills, knowledge, and experience possessed by individuals, enhancing their productivity.
Capital Investment
Spending on physical assets like machinery or buildings to increase production capacity.
Capital Outflow
When money leaves a country to invest in foreign assets, often due to better returns or economic instability at home.
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
The fraction of additional income that a household spends on consumption.
Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS)
The fraction of additional income that a household saves rather than spends.
Remittance
Money sent by individuals working abroad to family or others in their home country.
Tax Credit
A direct reduction in the amount of taxes owed, often used to encourage specific behaviors like education or investment.
M1 Money
The most liquid forms of money—immediately available for spending.
M2 Money
A broader measure of money that includes M1 plus assets that are slightly less liquid.