Materials Part C - Powder metallurgy
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
How is friction stir welding done?
Rotating tool with flat face is pressed ontop of mating edge and draw across seam while spinning so soften and join the metals.
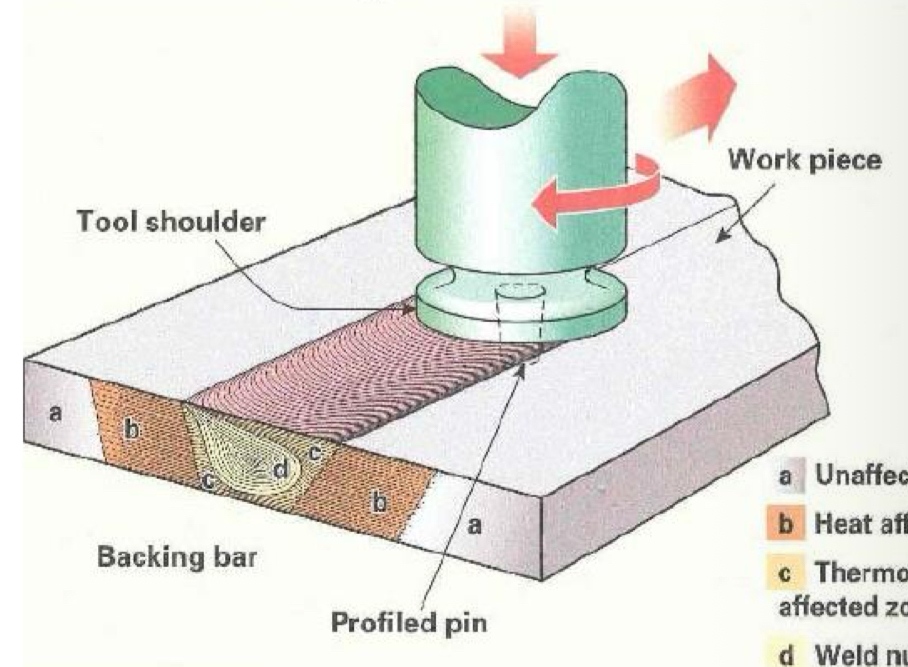
What are the advantages behind friction stir welding?
Excellent mechanical properties
No porosity or distortion
Non consumable tool can be used for many operations
Can be used for on the spot repair work
What are the disadvantages behind friction stir welding?
Expensive equipment
Very difficult to apply to some materials.
What are some applications for friction stir welding?
Shipbuilding and marine structures
Wings, fuel tanks
train bodies, railway tankers, container bodies
What are the main manufacturing processes in powder metallurgy?
Additive layer manufacturing
Metal Injection moulding
Hot isostatic pressing
How is the metal powder created?
Through a repaid solidification process where a liquid stream of metal is blasted with an inert gas or water.
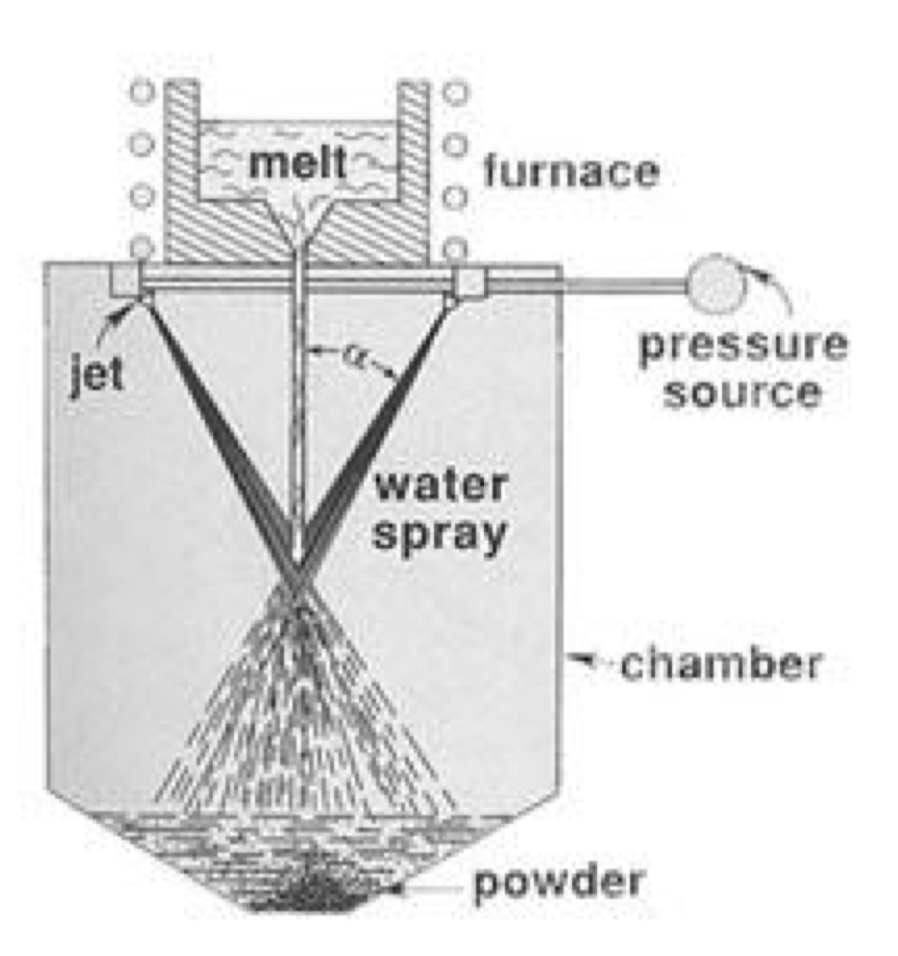
What are the 2 types of powder additive layer manufacture?
Blown powder
C02 laser is used to melt layers of powder in place are they blown in by several nozzles
Powder bed
Powder is inserted layer by layer and a laser passes over each layer solidifying the powder in area where it is needed.
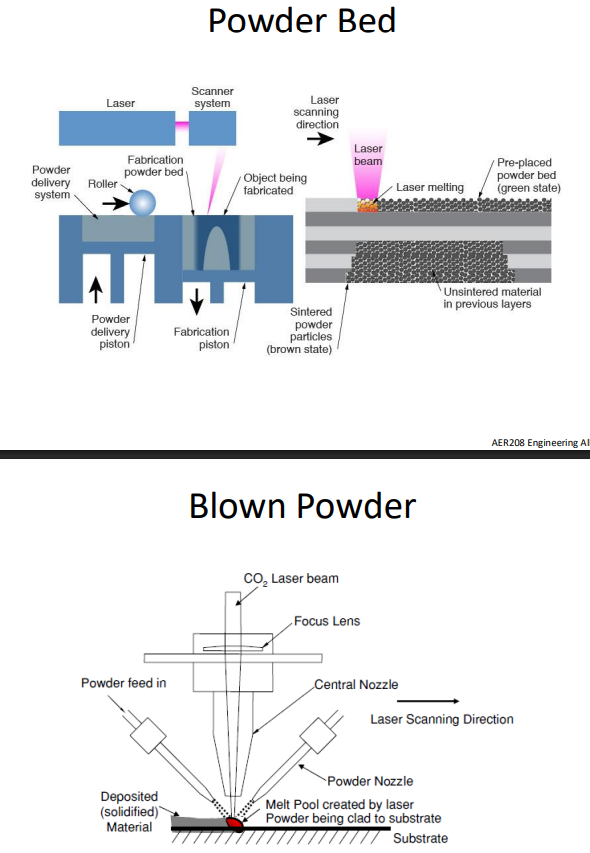
What are some drawbacks behind this method of manufacturing (laser systems specifically)?
Since heating is very localised, surrounding powder is cold leading to residual stress in the part
Thin walls are almost impossible
What are other limitation with additive style manufacture?
Creation of overhangs is difficult leading to wasted support material.
Cant have enclosed space for powder bed manufacture since void will be full of loose powder.
What are the advantages of using electron beam instead?
Preheating occurs on every layer
This leaves the part annealed with no residual stress
Fatigue properties are therefore much better than cast parts and comparable to forged
What are the overall advantages to additive manufacture processes?
Shorter lead time therefore designs can be iterated faster
Less wasted material
Allows for more creative freedom when making parts
Can use difficult to machine alloys
What are 2 other powder metal processing routes?
Metal injection moulding
Hot Isostatic Pressing
What are the main stages involved in metal injection moulding?
Metal powder and binder is mixed
Binder metal mix is heated and forced into mould
Part is then placed in oven and heated further to remove binder
Part is placed in even hotter oven and fed with highly pressurised noble gas to compress and sinter final part
This is done to remove porosity left from the binder.
What are some considerations when looking at metal injection moulding of a part?
Powder need to be of high quality (spherical and fine)
Binder - Secret formula
Careful handling of debinded part (high porosity)
Sintering - Correct atmosphere and temperature are required
Part shrinkage
What are advantages to metal injection moulding?
Offers high flexibility for chemistry and geometry
Much lower energy footprint per part than casting
What are some limitations for metal injection moulding?
Carbon pickup
Powders for specialty alloys are very expensive
What are key advantages of hot isostatic pressing?
Consolidation of materials in solid state
Minimises segregation of heavy atoms (happens in melt routes)
Smaller grain size than sintering
Heals porosity of castings
What are some key considerations of hot isostatic pressing?
Capsule needs to be manufactured
Efficient at transferring pressure
Joinable
Low cost
Design of part needs to be carefully considered and process needs to be simulated
Removal of mould requires strong acids and is a lengthy process
Give key conclusions to HIP?
Costly
Complex
Low volume
Shape and surface quality is excellent